Global Wind Turbine Scrap Market Size, Share, And Business Benefits By Service (Collection and Segregation, Recycling, Disposal), By Product (Iron and Steel, Plastic, Precious Metals, Fiber Glass Composites, Others), By Source (Decommissioned Turbines, Dismantled Turbine Components, Manufacturing Waste, Transportation Damage), By Turbine Size (Small Scale, Medium Scale, Large Scale), By End-Use (Recycling, Resale, Energy Recovery, Others), By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends, and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: February 2025
- Report ID: 140802
- Number of Pages: 327
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
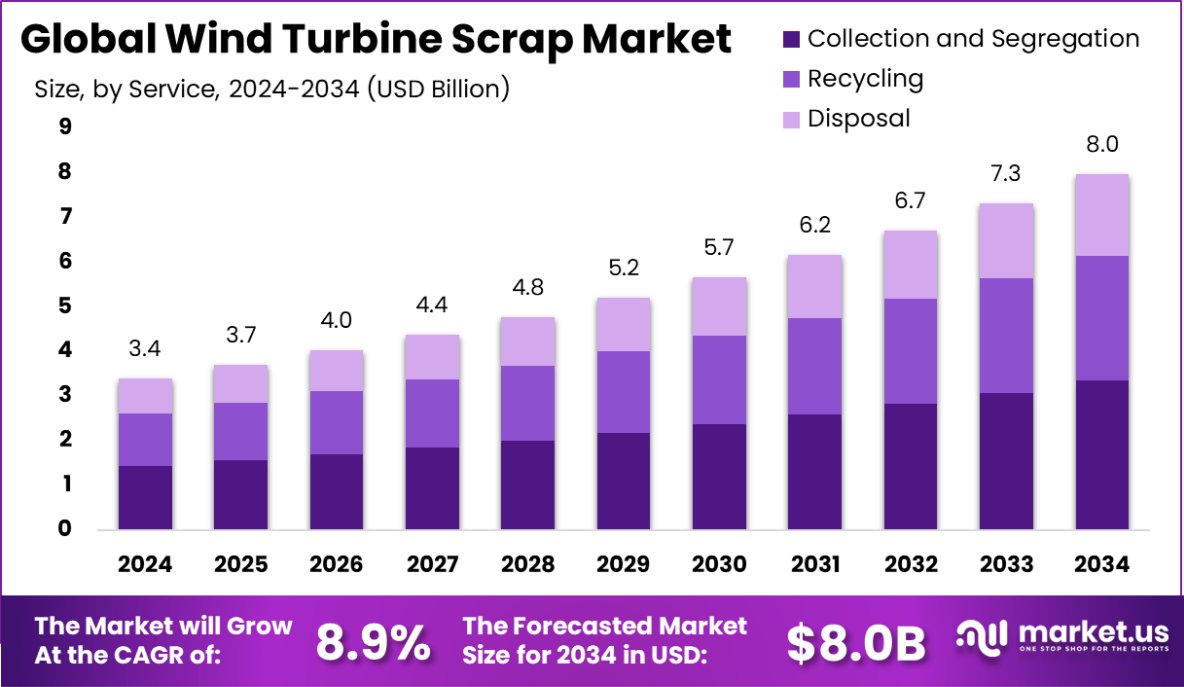
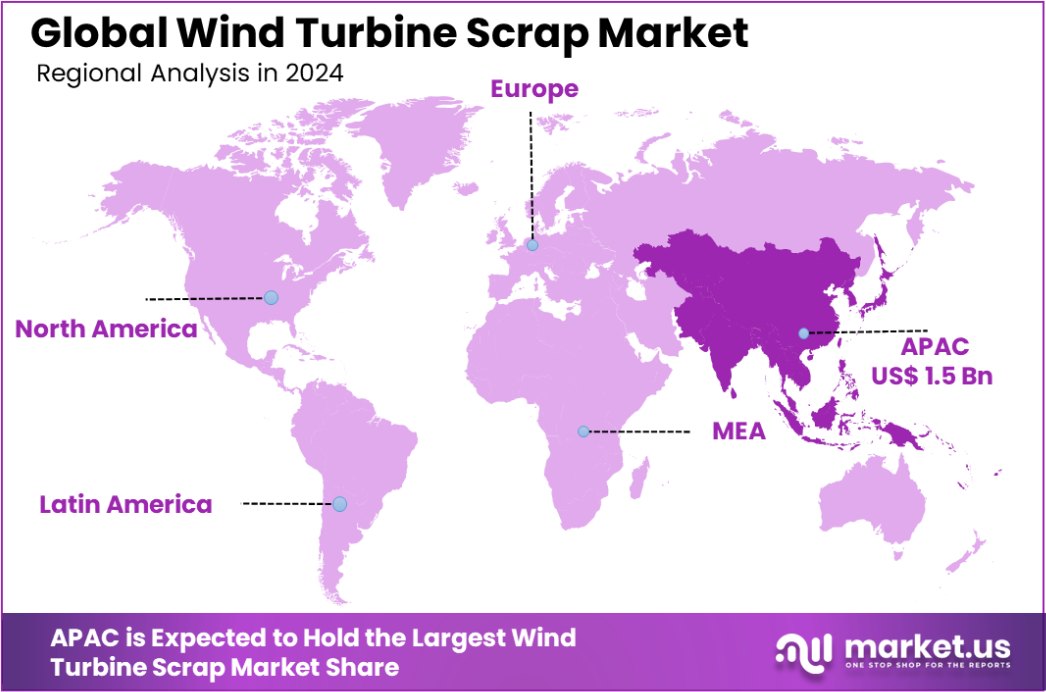
Global Wind Turbine Scrap Market is expected to be worth around USD 8.0 Billion by 2034, up from USD 3.4 Billion in 2024, and grow at a CAGR of 8.9% from 2025 to 2034. Asia-Pacific leads the Wind Turbine Scrap Market with a 44.5% share, USD 1.5 billion.
Wind turbine scrap refers to the materials and components that remain after a wind turbine has reached the end of its operational life. These materials include metals like steel and copper, as well as composite materials used in the blades and other components. The recycling or disposal of these materials is crucial due to their volume and the environmental implications of their decomposition.
The wind turbine scrap market deals with the processes and services related to the recycling, repurposing, and disposal of decommissioned wind turbines. This market is growing as more turbines installed during the early days of wind energy are now reaching the end of their life cycles. It’s driven by the need for sustainable disposal methods that align with global environmental goals.
One significant growth factor for the wind turbine scrap market is the increasing focus on sustainable practices within the renewable energy sector. As governments and organizations push for greener policies, the need to efficiently recycle or repurpose old turbines is becoming more critical. This factor ensures a steady flow of materials through the scrap market, promoting continuous growth.
Demand for wind turbine scrap services is primarily driven by the expanding installations of wind turbines worldwide. As these turbines age, the demand for decommissioning services rises, boosting the market. The finite lifespan of wind turbines, typically 20-25 years, creates a cyclical demand for scrap services, ensuring long-term viability for market players.
Opportunities within the wind turbine scrap market include technological innovations in recycling methods, particularly for composite materials used in turbine blades. Developing more efficient recycling technologies could significantly reduce landfill waste and support the creation of secondary markets for recycled materials.
In 2024, the Wind Turbine Scrap Market is gaining momentum with increased decommissioning activities and material recovery. Mingyang Smart Energy announced a 100,000 kW wind farm project in Yumen, China, set to begin construction in H2 2024, signaling future turbine replacements. Meanwhile, Belson Steel acquired 4,950 tons of wind tower scrap from Pyron Wind Farm, Texas (Aug-Nov 2024), highlighting rising scrap recovery efforts.
Key Takeaways
- Global Wind Turbine Scrap Market is expected to be worth around USD 8.0 Billion by 2034, up from USD 3.4 Billion in 2024, and grow at a CAGR of 8.9% from 2025 to 2034.
- Collection and segregation services dominate the market, holding a 42.2% share in the wind turbine scrap sector.
- Iron and steel materials lead product recycling with a 45.3% share in the wind turbine scrap market.
- Decommissioned turbines are the primary source of scrap, contributing 52.1% to the wind turbine scrap market.
- Medium-scale turbines represent a significant portion, accounting for 42.3% of the scrap in the market.
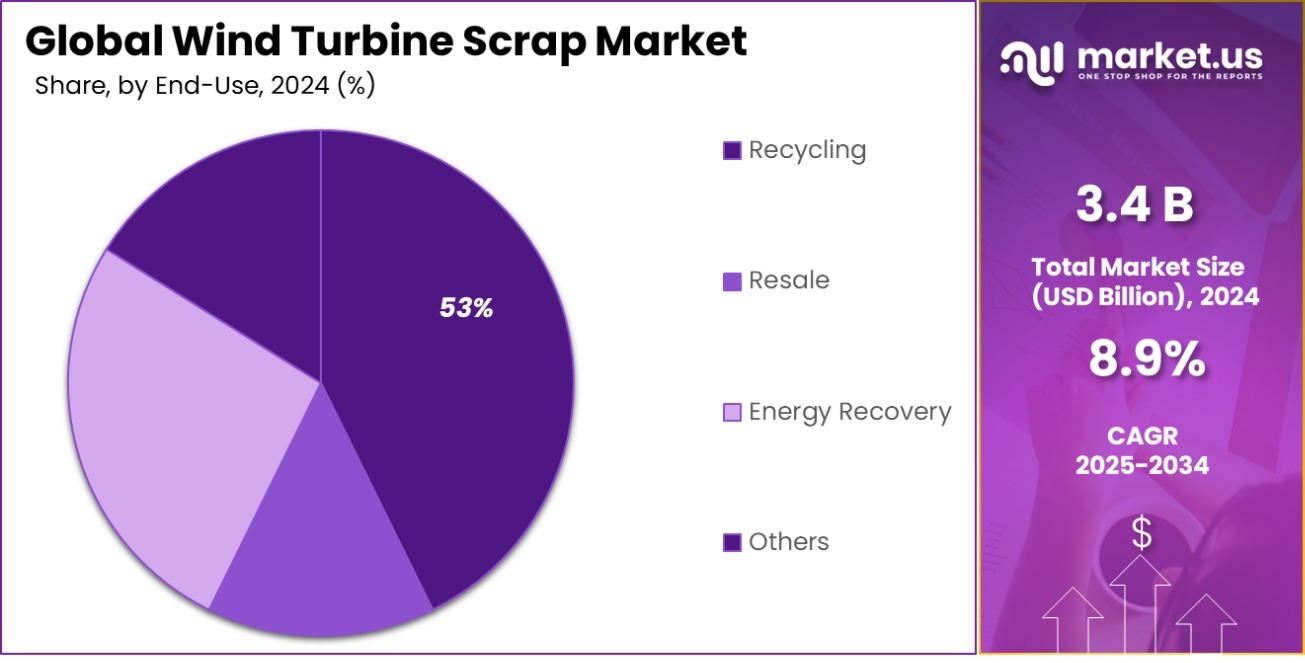
- Recycling processes are the main end-use of scrapped materials, making up 53.3% of the market’s focus.
- In 2024, Asia-Pacific led the Wind Turbine Scrap Market with a 44.5% share, valued at USD 1.5 billion.
By Service Analysis
Collection and segregation dominate services at 42.2% in the wind turbine scrap market.
In 2024, Collection and Segregation held a dominant market position in the By Service segment of the Wind Turbine Scrap Market, with a 42.2% share. This segment’s leadership is primarily driven by the increasing number of decommissioned wind turbines and the necessity for systematic dismantling and sorting of materials.
With wind energy capacity expanding globally, older turbines reaching the end of their lifecycle have fueled demand for organized collection processes. Efficient segregation of metals, composites, and electronic components plays a crucial role in ensuring maximum material recovery and reducing environmental impact.
The Recycling and Repurposing segment is also experiencing notable growth, supported by rising regulatory pressures and the development of advanced recycling technologies. As governments enforce stricter waste management policies, market players are investing in innovative methods to recycle composite materials, particularly turbine blades, which are historically difficult to process.
Additionally, the Disposal and Landfilling segment, while still relevant, is facing a decline due to sustainability initiatives discouraging landfill waste. Companies are focusing on minimizing landfill contributions by improving material recovery rates. Overall, the market is shifting towards a circular economy model, emphasizing resource efficiency and sustainability in wind turbine end-of-life management, with collection and segregation remaining a key component of this evolving landscape.
By Product Analysis
Iron and steel lead products account for 45.3% of the market.
In 2024, Iron and Steel held a dominant market position in the by-product segment of the Wind Turbine Scrap Market, with a 45.3% share. This dominance is attributed to the high volume of steel used in wind turbine structures, including towers, nacelles, and other supporting components.
As older wind turbines are decommissioned, the recovery and recycling of iron and steel have become a crucial part of the industry, driven by their high market value and ease of recyclability. The growing demand for scrap steel in the construction and manufacturing industries further strengthens this segment’s leadership.
The Composite Materials segment is also gaining traction, particularly due to the challenges associated with recycling turbine blades made of fiberglass and carbon fiber. As industry players invest in innovative recycling technologies, such as pyrolysis and chemical treatment, the segment is expected to witness gradual growth.
Meanwhile, the Copper and Other Metals segment remains a significant contributor, with copper being extensively used in wind turbine generators and electrical wiring. The rising adoption of electric vehicles and renewable energy infrastructure is further fueling demand for recycled copper. Overall, the wind turbine scrap market is shifting towards a circular economy, with iron and steel maintaining a dominant role in material recovery.
By Source Analysis
Decommissioned turbines form the largest source segment, holding 52.1% market share.
In 2024, Decommissioned Turbines held a dominant market position in the By Source segment of the Wind Turbine Scrap Market, with a 52.1% share. The segment’s dominance is driven by the increasing number of aging wind farms reaching the end of their operational life. With wind turbines typically having a lifespan of 20–25 years, a significant wave of decommissioning has begun, particularly in regions that were early adopters of wind energy. The disposal and recycling of these decommissioned turbines have become a key focus, with market players emphasizing efficient material recovery to minimize waste and maximize recyclability.
The Manufacturing Scrap segment is another notable contributor, consisting of leftover materials from turbine production. As turbine manufacturers increase production capacity to meet rising global demand for renewable energy, the volume of manufacturing scrap is also growing. However, this segment remains secondary to decommissioned turbines due to its lower material output.
The Maintenance and Repair Waste segment holds a smaller share, generated from routine upkeep and component replacements. While this segment does not contribute large volumes of scrap, it remains essential in sustaining the circular economy for wind turbine components. Overall, the market is experiencing a shift toward sustainable decommissioning processes, reinforcing the dominance of decommissioned turbines as the primary scrap source.
By Turbine Size Analysis
Medium-scale turbines have a 42.3% share of the turbine size category.
In 2024, Medium Scale held a dominant market position in the By Turbine Size segment of the Wind Turbine Scrap Market, with a 42.3% share. This dominance is largely driven by the widespread deployment of medium-scale turbines in onshore wind farms, which are now reaching the end of their operational life.
These turbines, typically ranging from 100 kW to 1 MW, have been extensively used in commercial and industrial applications, leading to a substantial volume of decommissioned units contributing to the scrap market. The manageable size of these turbines also facilitates easier dismantling, transportation, and material recovery, making them a preferred segment for recycling companies.
The Large Scale segment is also witnessing growth as offshore wind projects and utility-scale installations increasingly approach decommissioning timelines. With turbines in the 2 MW and above category becoming more common, the volume of scrap from this segment is expected to rise steadily in the coming years. However, logistical challenges and higher decommissioning costs have kept its market share lower than medium-scale turbines.
The Small Scale segment, primarily consisting of turbines under 100 kW used in residential and small commercial settings, holds a relatively minor share. While decommissioning activity in this category remains limited, advancements in distributed wind energy may drive future scrap volumes.
By End-Use Analysis
Recycling is the primary end-use, comprising 53.3% of the market.
In 2024, Recycling held a dominant market position in the By End-Use segment of the Wind Turbine Scrap Market, with a 53.3% share. The dominance of this segment is driven by the increasing focus on sustainability and regulatory mandates promoting circular economy practices. With a growing number of wind turbines reaching the end of their operational lifespan, the demand for efficient recycling solutions has surged.
Key materials such as steel, copper, and aluminum from decommissioned turbines are being recovered and repurposed, fueling the expansion of the recycling market. Additionally, advancements in recycling technologies, particularly for composite turbine blades, are enhancing material recovery rates and minimizing landfill waste.
The Repurposing segment is also gaining traction as companies explore innovative ways to reuse wind turbine components. Applications such as converting old blades into infrastructure elements, including bridges and noise barriers, are emerging as viable alternatives to disposal. This segment, however, remains secondary due to the technical challenges involved in repurposing turbine materials.
The landfill segment continues to decline as sustainability goals and environmental regulations increasingly restrict landfill use. With policies pushing for greener alternatives, market players are focusing on enhancing recycling and repurposing capabilities, reinforcing recycling’s dominance in the wind turbine scrap market.
Key Market Segments
By Service
- Collection and Segregation
- Recycling
- Disposal
By Product
- Iron and Steel
- Plastic
- Precious Metals
- Fiber Glass Composites
- Others
By Source
- Decommissioned Turbines
- Dismantled Turbine Components
- Manufacturing Waste
- Transportation Damage
By Turbine Size
- Small Scale
- Medium Scale
- Large Scale
By End-Use
- Recycling
- Resale
- Energy Recovery
- Others
Driving Factors
Rising Decommissioning of Aging Wind Turbines
The wind turbine scrap market is primarily driven by the increasing number of aging wind turbines reaching the end of their operational lifespan. Most wind turbines have a lifespan of 20 to 25 years, and many installed in the early 2000s are now due for decommissioning. As governments and energy companies transition towards more efficient and larger turbines, older models are being phased out, leading to a surge in scrap materials.
This rising decommissioning trend is generating significant demand for recycling and repurposing services, as companies seek sustainable disposal solutions. Additionally, stricter regulations on waste management are encouraging the industry to adopt environmentally friendly recycling methods, further boosting market growth for wind turbine scrap processing and material recovery.
Restraining Factors
Challenges in Recycling Wind Turbine Blades
One of the biggest challenges in the wind turbine scrap market is the difficulty in recycling turbine blades. Unlike steel and copper, which can be easily recycled, turbine blades are made from fiberglass and composite materials that are not biodegradable and require complex processing. Traditional recycling methods are inefficient, leading many decommissioned blades to end up in landfills, which is against sustainability goals.
The high cost and technical difficulties in breaking down and repurposing these materials slow down market growth. However, ongoing research into innovative recycling techniques, such as chemical treatments and repurposing blades into infrastructure, could help address this issue. Until scalable solutions emerge, the challenge of blade disposal remains a major restraint for the wind turbine scrap industry.
Growth Opportunity
Advancements in Blade Recycling Technologies
A major growth opportunity in the wind turbine scrap market lies in new recycling technologies for turbine blades. Traditionally, fiberglass and composite materials in blades have been difficult to recycle, leading to disposal challenges. However, recent advancements in chemical recycling, mechanical processing, and repurposing methods are creating new possibilities. Companies are developing techniques like pyrolysis, solvolysis, and cement co-processing, which break down composite materials into reusable components.
Additionally, repurposing old blades for infrastructure projects, such as pedestrian bridges, noise barriers, and construction materials, is gaining interest. As research and investments in sustainable blade disposal increase, businesses that offer cost-effective recycling solutions will benefit the most, making this a key opportunity for market expansion and innovation.
Latest Trends
Growing Adoption of Circular Economy Practices
A key trend shaping the wind turbine scrap market is the shift towards a circular economy. With increasing concerns about waste and sustainability, companies and governments are focusing on maximizing material reuse rather than relying on landfilling. This trend is encouraging the development of closed-loop recycling systems, where materials from decommissioned turbines are repurposed into new products.
Wind energy firms are collaborating with recycling technology providers to find solutions for reusing steel, copper, and even composite blade materials. Additionally, regulations are becoming stricter, pushing companies to adopt greener decommissioning processes. As circular economy principles gain momentum, businesses that invest in sustainable recycling, material innovation, and eco-friendly disposal methods will have a competitive edge in the evolving wind turbine scrap market.
Regional Analysis
In 2024, Asia-Pacific dominated the Wind Turbine Scrap Market with a 44.5% market share, reaching a valuation of USD 1.5 billion.
In 2024, Asia-Pacific dominated the Wind Turbine Scrap Market, accounting for 44.5% market share and reaching a valuation of USD 1.5 billion. The region’s dominance is driven by the large-scale wind energy projects in China, India, and Japan, where early wind turbine installations are now approaching decommissioning. China, in particular, leads the region with an extensive wind power infrastructure and rising investments in turbine recycling technologies.
North America is another key market, supported by the growing need for sustainable disposal of aging turbines, especially in the United States and Canada. The region benefits from advanced recycling technologies and stringent environmental regulations promoting circular economy practices.
Europe remains a significant player due to its early adoption of wind energy and established decommissioning policies. Countries like Germany, Denmark, and the UK are actively investing in blade recycling and repurposing projects, aligning with EU sustainability goals.
Latin America and the Middle East & Africa are emerging markets, with decommissioning activities still in their early stages. However, Brazil and South Africa show potential for future market growth as wind energy capacity expands. Overall, Asia-Pacific leads in both market share and value, shaping the global wind turbine scrap industry.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
The Wind Turbine Scrap Market in 2024 is witnessing active participation from major renewable energy firms, recycling companies, and turbine manufacturers aiming to capitalize on the growing decommissioning trend.
Asia-Pacific-based players like China Longyuan Power Group, Goldwind, and Mingyang Smart Energy are at the forefront, benefiting from the region’s 44.5% market share and USD 1.5 billion valuation. These companies are focusing on large-scale turbine replacements and advancing recycling technologies to comply with China’s evolving sustainability regulations.
European companies such as Siemens Gamesa, Nordex SE, RWE Renewables, and Vestas play a significant role in implementing circular economy strategies for turbine component reuse. Germany, Denmark, and Spain continue to lead in research and policy frameworks aimed at composite blade recycling, a critical industry challenge. RWE Renewables and EDPR are investing in sustainable decommissioning projects, integrating repurposing solutions for turbine materials.
In North America, companies like GE Renewable Energy and Veolia are driving innovations in fiberglass and metal recovery. Global Fiberglass Solutions stands out for its specialized focus on blade recycling, and developing sustainable alternatives to landfilling. Belson Steel Center Scrap Inc. is strengthening its role in metal recovery, meeting the demand for high-value scrap materials like steel and copper.
With ACCIONA Energy, Enercon, Gamesa Electric, and Suzlon Energy expanding operations globally, the market is set for technological advancements and increased investment in turbine scrap recycling, ensuring long-term sustainability for wind energy infrastructure.
Top Key Players in the Market
- ACCIONA Energy
- Acciona S.A
- Belson Steel Center Scrap Inc
- China Longyuan Power Group
- Dewind Co.
- EDP Renewables
- EDPR
- Enercon
- Gamesa Electric
- GE Renewable Energy
- Global Fiberglass Solutions
- Goldwind
- Mingyang Smart Energy
- Nordex SE
- Renewable Parts Ltd.
- RWE Renewables
- Senvion
- Senvion S.A
- Siemens Gamesa
- Suzlon Energy
- Veolia
- Vestas
Recent Developments
- In January 2025, ACCIONA announced the construction of Waste2Fiber, a wind blade recycling plant in Lumbier, Spain. The facility will use a proprietary thermal treatment technology to recycle composite materials from wind turbine blades.
- In August 2024, Enercon installed the prototype of its new E-175 EP5 wind turbine with a 6.0 MW rated output and 175-meter rotor diameter in Borchen-Etteln, Germany
- In February 2024, EDPR completed an Asset Rotation deal, selling an 80% equity stake in a 297 MW operating wind project in Alberta, Canada
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 3.4 Billion Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 8.0 Billion CAGR (2025-2034) 8.9% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Service (Collection and Segregation, Recycling, Disposal), By Product (Iron and Steel, Plastic, Precious Metals, Fiber Glass Composites, Others), By Source (Decommissioned Turbines, Dismantled Turbine Components, Manufacturing Waste, Transportation Damage), By Turbine Size (Small Scale, Medium Scale, Large Scale), By End-Use (Recycling, Resale, Energy Recovery, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape ACCIONA Energy, Acciona S.A, Belson Steel Center Scrap Inc, China Longyuan Power Group, Dewind Co., EDP Renewables, EDPR, Enercon, Gamesa Electric, GE Renewable Energy, Global Fiberglass Solutions, Goldwind, Mingyang Smart Energy, Nordex SE, Renewable Parts Ltd., RWE Renewables, Senvion, Senvion S.A, Siemens Gamesa, Suzlon Energy, Veolia, Vestas Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Wind Turbine Scrap MarketPublished date: February 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Wind Turbine Scrap MarketPublished date: February 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- ACCIONA Energy
- Acciona S.A
- Belson Steel Center Scrap Inc
- China Longyuan Power Group
- Dewind Co.
- EDP Renewables
- EDPR
- Enercon
- Gamesa Electric
- GE Renewable Energy
- Global Fiberglass Solutions
- Goldwind
- Mingyang Smart Energy
- Nordex SE
- Renewable Parts Ltd.
- RWE Renewables
- Senvion
- Senvion S.A
- Siemens Gamesa
- Suzlon Energy
- Veolia
- Vestas









