Global Biochar Market Size, Share, Growth Analysis By Feedstock (Forestry Residues, Agricultural Residues, Municipal Waste, Animal Manure, Biomass Crops, Others) By Technology (Pyrolysis, Gasification, Others), By Application (Agriculture, Livestock Farming, Water And Wastewater Treatment, Construction Materials, Others), By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends, and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Nov 2025
- Report ID: 167760
- Number of Pages: 280
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
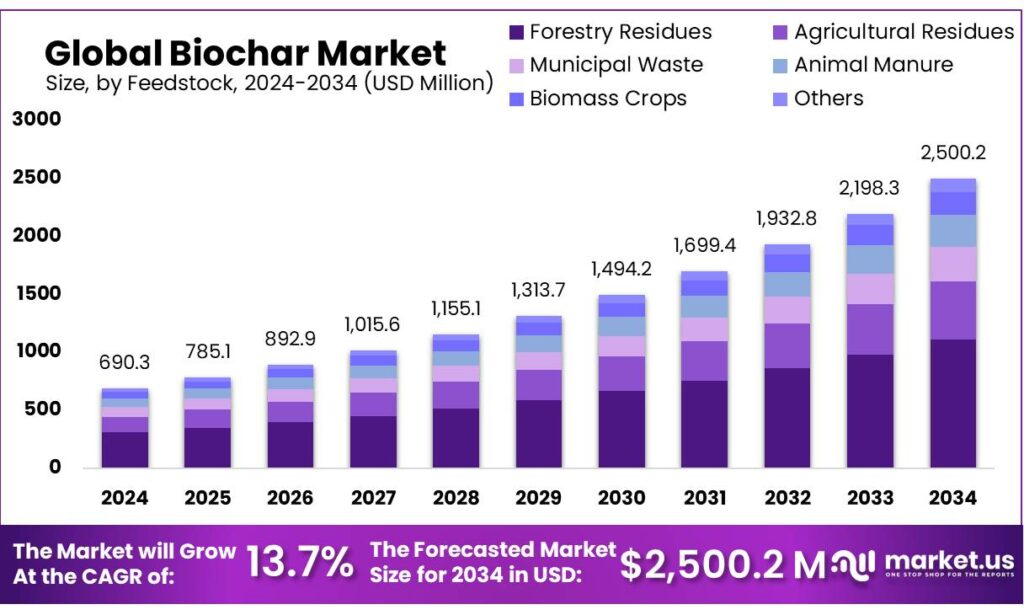
The Global Biochar Market size is expected to be worth around USD 2500.2 Million by 2034, from USD 690.3 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 13.7% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. North America held in around 44.6% market in 2024. In 2024, the biochar market in the US was valued at USD 274.3 million is expected to grow significantly in the forecast period.
The global biochar industry is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing environmental awareness and supportive government policies promoting sustainable agricultural practices and carbon management solutions. Biochar, a form of black carbon produced through the thermal decomposition of biomass—such as forestry residues, agricultural residues, municipal waste, animal manure, and biomass crops—has emerged as a valuable product across multiple sectors. Its primary use remains in agriculture, where it serves as an effective soil amendment that enhances soil carbon content, improves nutrient availability, reduces nutrient leaching, and increases water retention, aeration, and overall soil structure to boost crop productivity.
Beyond its agricultural applications, biochar is gaining attention as a strategic tool for climate change mitigation. Its ability to sequester carbon and enhance soil fertility positions it as a dual-benefit solution for environmental sustainability and agricultural efficiency. Following the Paris Agreement in 2016, biochar, alongside bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS), has been recognized as a promising approach for reducing global greenhouse gas emissions.
Since 2019, the commercial adoption of biochar has accelerated rapidly, fueled by the growth of the voluntary carbon market. As of June 2025, corporate buyers and nonprofit organizations have collectively purchased more than 2.7 million tonnes of CO₂ equivalent (tCO₂e) in voluntary carbon credits from over 80 biochar producers worldwide. Furthermore, established and emerging carbon dioxide removal (CDR) registries have introduced certification protocols to validate biochar carbon credits, reinforcing market transparency and investor confidence.
Key Takeaways
- The global biochar market was valued at USD 690.3 million in 2024.
- The worldwide biochar demand is projected to grow significantly at a CAGR of 13.7% and is estimated to reach USD 2,500.2 million by 2034.
- By feedstock, forestry residues held 44.5% market share in 2024.
- Among technology, pyrolysis accounted for the largest market revenue share of 75.6%.
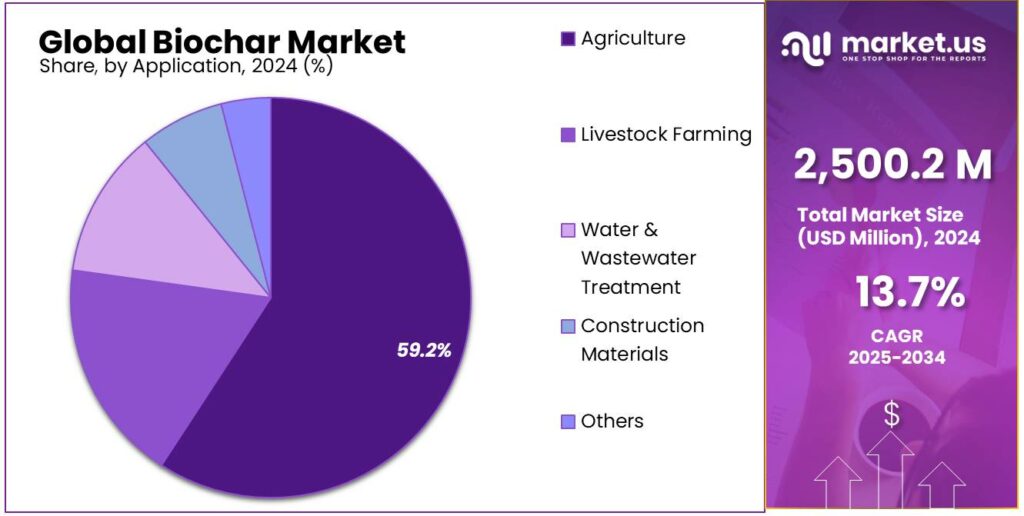
- By application, the market was dominated by agriculture sector with significant market share of 59.2%.
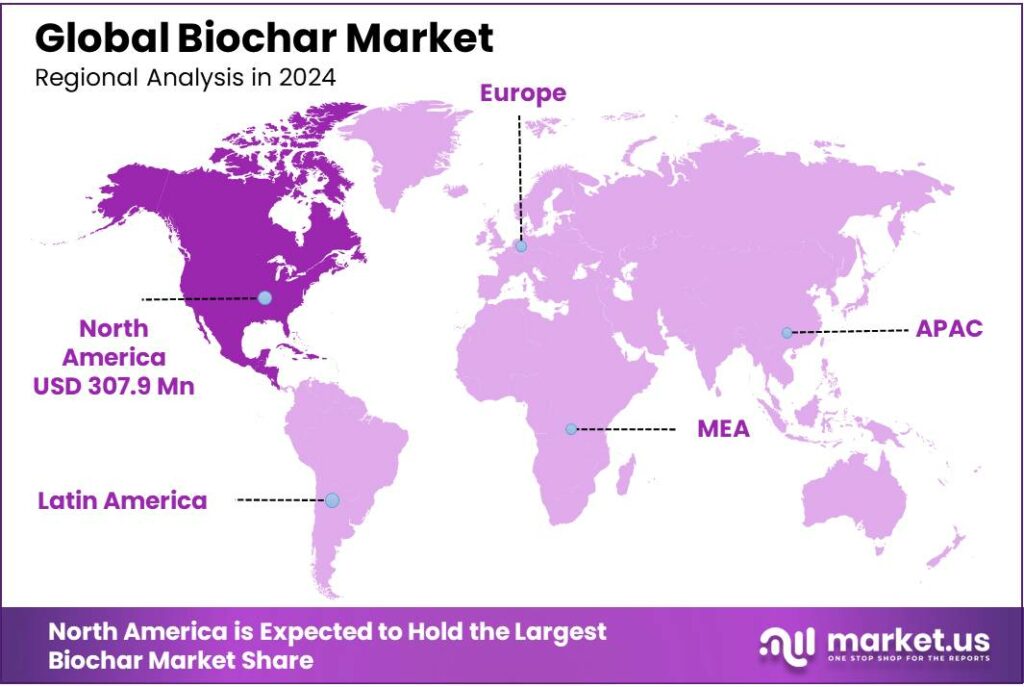
- North America biochar market was accounted for 44.6% market share in 2024 and estimated to reach US$ 1,005.1 Mn by 2034.
Feedstock Analysis
Forestry residues maintained a leading position in the global biochar market in 2024, accounting for approximately 44.5% of total feedstock utilization. This segment includes logging residues, sawdust, wood chips, bark, and thinning materials generated from forest management activities and wood-processing operations. The steady and reliable availability of these residues, along with their favorable physicochemical properties, makes them a preferred choice for large-scale and commercial biochar production.
Woody biomass derived from forestry operations is characterized by high lignin and fixed carbon content, low ash levels, and moderate volatile matter, resulting in high energy density and efficient carbon conversion during pyrolysis. These attributes support the production of stable, carbon-rich biochar with superior structural integrity, making forestry residues one of the most effective feedstocks for both agricultural applications and long-term carbon sequestration projects.
The increasing global focus on sustainable forest management further enhances the growth potential of this segment. Many regions are expanding forest thinning operations and residue recovery efforts to reduce wildfire risks, improve forest ecosystem health, and prevent the accumulation of unmanaged biomass. Utilizing this material for biochar production transforms a historically underused or discarded resource into a high-value product, reducing emissions from decomposition or open burning and contributing to circular economy objectives.
Technology Analysis
In 2024, pyrolysis remained the leading technology in the global biochar market, accounting for approximately 75.6% of total market share. Pyrolysis is the most widely adopted method for biochar production due to its efficiency, scalability, and ability to process diverse biomass feedstocks. The process involves the thermochemical decomposition of biomass at temperatures ranging from 200°C to 1300°C under low-oxygen or inert atmospheric conditions, resulting in the formation of biochar along with syngas and bio-oil as co-products.
Pyrolysis technologies are categorized based on heating rate and residence time into slow pyrolysis, fast pyrolysis, flash pyrolysis, and intermediate pyrolysis. Among these, slow pyrolysis is the preferred method for commercial biochar production. Its slower heating rates, combined with lower temperatures and extended residence times, favor the formation of stable, carbon-rich solid material that is suitable for long-term soil amendment and carbon sequestration applications.
Application Analysis
In 2024, the agriculture sector remained the leading application segment in the global biochar market, accounting for approximately 59.2% of total demand. Biochar’s strong dominance in agriculture is attributed to its proven ability to enhance soil health, improve nutrient efficiency, and support sustainable farming practices. Numerous studies have demonstrated that biochar application improves key soil physical properties—including porosity, bulk density, and moisture retention—while also strengthening hydrological characteristics and overall soil fertility.
When incorporated as a soil amendment, biochar enhances water use efficiency and increases crop productivity across a wide range of soil types. Research indicates that, depending on soil characteristics and application rates, biochar can increase soil porosity by 14–64% and reduce bulk density by 3–31%. In sandy soils, the addition of 20% biochar can nearly double water retention capacity and significantly reduce erosion and soil loss. These improvements foster greater nutrient availability, support the growth of beneficial soil microorganisms, and enhance long-term soil management outcomes.
Biochar’s effectiveness is further elevated when combined with organic inputs such as compost, decomposed manures, and crop residues. Such mixtures improve nutrient use efficiency and contribute to sustained soil enrichment. Recent research highlights these synergies: formulations such as wheat biochar plus pig manure (WBSC) and maize biochar plus pig manure (MBSC) were shown to improve oil quality by increasing oleic acid by 45% and reducing linoleic acid by 79%, whereas raw biochar alone produced no comparable effect.
Key Market Segments
By Feedstock
- Forestry Residues
- Agricultural Residues
- Municipal Waste
- Animal Manure
- Biomass Crops
- Others
By Technology
- Pyrolysis
- Gasification
- Others
By Application
- Agriculture
- Livestock Farming
- Water & Wastewater Treatment
- Construction Materials
- Others
Drivers
Rising Focus on Sustainable Agricultural Solutions
The growing emphasis on sustainable agricultural practices is a major driver of the global biochar market. As the world faces escalating challenges such as climate change, soil degradation, and food insecurity, biochar has emerged as a promising solution that aligns with global sustainability goals. Its ability to improve soil health, enhance crop productivity, and strengthen climate resilience has positioned it at the forefront of modern sustainable farming practices. Farmers, researchers, and environmental organizations worldwide are increasingly recognizing biochar’s potential to support long-term soil fertility and carbon sequestration while contributing to ecosystem restoration.
The expanding global commitment to organic and sustainable farming further reinforces this trend. In 2023, the worldwide organic farming area increased by 2.6%, reaching 98.9 million hectares managed by 4.3 million producers. Retail sales of organic food surpassed €136 billion, led by the United States (€59.0 billion), Germany (€16.1 billion), and China (€12.6 billion). Switzerland reported the highest per capita spending (€468), while Denmark achieved the largest organic market share (11.8% of total food sales). This steady global shift toward environmentally responsible agriculture underscores the rising demand for biochar as a sustainable and economically viable soil amendment.
Restraints
High Initial Capital Investment
One of the major restraints in the global biochar market is the high initial capital investment required to establish production facilities. The cost of setting up biochar plants varies significantly depending on the scale of operation, technology adoption, and production capacity. These financial barriers can limit market entry for new participants and slow the expansion of existing producers, particularly in developing regions.
For small-scale operations, producing approximately 1–2 tons of biochar per day typically requires an investment of $150,000 to $400,000, with the pyrolysis unit alone accounting for 40–50% of total costs. Such facilities often serve as pilot projects or niche market ventures, providing limited commercial scalability. Medium-scale facilities, with production capacities ranging from 5–10 tons per day, demand investments between $800,000 and $2 million, primarily due to the inclusion of advanced continuous pyrolysis systems and automated handling technologies essential for maintaining profitability.
At the industrial level, large-scale plants capable of producing over 20 tons per day can exceed $5 million in capital expenditure. These high costs are attributed to state-of-the-art processing equipment, co-product refining systems, and complex infrastructure requirements. Consequently, while large facilities offer greater output and efficiency, the substantial upfront investment acts as a deterrent for many investors and small enterprises. This capital intensity continues to be a key challenge constraining the widespread commercialization and scalability of biochar production globally.
Opportunity
Increasing Adoption of Biochar in Construction Materials
The use of biochar in construction materials is emerging as a significant opportunity for the global biochar market, supported by stronger sustainability requirements, efforts to decarbonize the built environment, and advancements in engineered material applications. With construction activities contributing nearly 40% of global CO₂ emissions, builders and material manufacturers are increasingly seeking low-carbon inputs that align with climate targets and circular economy principles. Biochar offers a viable pathway toward reducing embodied carbon while enhancing the performance profile of widely used building materials.
Biochar’s structural and chemical characteristics give it distinct advantages in construction. Its porous matrix, moisture-regulating capabilities, and high stability improve both the mechanical and durability properties of materials such as concrete, mortar, bricks, and insulation products. Efforts to reduce the carbon footprint of concrete—one of the most emissions-intensive materials, responsible for around 8% of global CO₂ emissions—have highlighted biochar as a highly effective additive. When incorporated at typical levels of 3–10%, biochar supports improved hydration, refines the microstructure of cement paste, and enhances internal curing. Research has shown that a 10% blend can raise compressive strength by approximately 24.2%, offering a notable reduction in cracking and longer structural lifespan.
Construction companies and developers are also exploring biochar to meet environmental certification criteria. Incorporating biochar into building materials contributes to reduced emissions, improved energy efficiency, and enhanced moisture control—factors recognized by leading sustainability frameworks such as LEED and BREEAM. This strengthens compliance with green-building requirements while supporting broader corporate decarbonization commitments.
Trends
Growing Integration of Biochar in Carbon Markets
The increasing integration of biochar into global carbon markets has emerged as a significant trend, driven by its strong carbon sequestration capability and added agronomic benefits. Biochar has gained considerable visibility as industries seek scalable and verifiable carbon dioxide removal (CDR) solutions. Its ability to store carbon for centuries, combined with the agricultural value it delivers, has positioned it as one of the most attractive options within voluntary carbon markets.
Since 2019, commercial adoption has risen sharply, supported by rising corporate climate commitments and heightened demand for durable carbon credits. As of June 2025, corporations and nonprofit organizations have collectively procured more than 2.7 million tonnes of CO₂ equivalent (tCO₂e) in voluntary carbon credits from over 80 biochar suppliers worldwide. This rapid expansion reflects both market confidence and the increasing recognition of biochar as a long-term carbon removal pathway.
Geopolitical Impact Analysis
Geopolitical developments and escalating tariff policies are exerting increasing pressure on the global biochar market by raising costs across the value chain and heightening supply uncertainties. Tariffs on imported pyrolysis equipment, spare parts, and essential inputs such as steel and electronic components directly elevate both capital expenditure and operating costs for biochar producers. This impact is particularly significant in regions that rely heavily on foreign-engineered machinery for establishing and scaling production facilities.
The situation intensified in June 2025, when U.S. President Donald Trump issued an order doubling tariffs on steel and aluminum imports from 25% to 50%. As steel constitutes a major component in pyrolysis reactors and related infrastructure, this policy shift is expected to raise equipment costs substantially for U.S. producers and international suppliers exporting to the country. These geopolitical and trade-related pressures collectively pose notable challenges to cost efficiency, project viability, and expansion timelines within the global biochar market.
Regional Analysis
North America emerged as the dominant region in global biochar consumption, holding approximately 44.6% of the market share in 2024. The region’s leadership is driven by rising awareness of the long-term environmental and agronomic benefits of biochar, particularly within the forestry and agriculture sectors. Growing investments, strengthened environmental regulations, and expanding climate-focused initiatives have further accelerated market development. Within the region, the United States dominated the market, accounting for about 89.1% of North America’s total biochar demand.
The U.S. has cultivated a highly supportive environment for biochar adoption, bolstered by federal and state programs aimed at promoting sustainable land management, improving soil health, and advancing carbon-smart farming practices. Initiatives under the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), including climate-smart agriculture grants and incentives for carbon sequestration activities, have contributed to increased deployment across farms, rangelands, and conservation projects.
A key regulatory milestone strengthening the market was the establishment of the Conservation Practice Standard (CPS) 336: Soil Carbon Amendment by the USDA’s Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) in 2022. CPS 336 provides both technical guidance and financial assistance to farmers seeking to enhance soil carbon levels through amendments such as biochar, compost, or hybrid mixtures. This policy has significantly improved the economic feasibility of biochar use in agricultural systems.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- The US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia & CIS
- Rest of Europe
- APAC
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- ASEAN
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
The global biochar market is characterized by a diverse and increasingly competitive landscape, with companies ranging from established industrial manufacturers to specialized biochar producers and emerging climate-tech startups. Collectively, these players are shaping a rapidly evolving industry driven by advancements in pyrolysis technologies, expanding agricultural applications, and growing demand for high-quality carbon removal solutions. As the market scales, competition is intensifying around production efficiency, feedstock optimization, regional expansion, and certification of carbon credits.
Leading companies such as Airex Energy, Phoenix Energy, and Carbofex Ltd. leverage advanced pyrolysis and torrefaction systems to produce consistent, high-grade biochar at commercial scale. Their strength lies in technological innovation, strong production capacity, and the ability to supply large volumes to agriculture, energy, and carbon-removal buyers. These firms often partner with utilities, forestry operators, and industrial clients to secure stable feedstock streams and improve cost efficiency. Companies like Phoenix Energy and Oregon Biochar Solutions also differentiate themselves by integrating onsite power generation or co-product valorization into their business models.
Specialized producers such as Biochar Now, LLC, Black Owl Biochar, Pacific Biochar Benefit Corporation, and CharGrow LLC focus heavily on agricultural and soil enhancement markets. Their competitive advantage stems from product diversification, proprietary biochar formulations, and direct relationships with growers seeking soil-health solutions. These firms emphasize consistent quality, certification for organic farming, and targeted agronomic performance to build customer loyalty. Many of them are also active suppliers in the voluntary carbon market, where high-durability biochar credits are gaining substantial demand from corporate carbon removal buyers.
The Major Players in The Industry
- Airex Energy
- Carbonis GmbH & Co. KG
- Carbon Gold Ltd
- Phoenix Energy
- Biochar Now, LLC
- Oregon Biochar Solutions
- CharGrow LLC
- Chardust Ltd
- ArSta eco
- BIOSORRA
- Black Owl Biochar
- Carbofex Ltd.
- Myno Carbon
- Pacific Biochar Benefit Corporation
- Swiss Biochar GmbH
- Other Key Players
Recent Development
- In September 2025: BluSky Carbon Inc., an emerging player in the carbon removal clean technology sector, announced that it entered into a preliminary strategic partnership agreement with Carbonpave USA, LLC. The collaboration is aimed at commercially deploying Carbonpave’s proprietary biochar and engineered carbon construction technologies across North America, supporting the advancement of low-carbon infrastructure solutions in the region.
- In June 2025: ICL announced the launch of BIOZ Jet, the newest addition to its BIOZ product line. Developed in collaboration with EVOIA and utilizing EVOIA’s patented FYR technology, BIOZ Jet is a liquid biochar extract formulated to stimulate early seedling development and strengthen crop resilience. The product is positioned as an effective solution for both specialty crop producers and row crop growers seeking to enhance plant performance and stress tolerance.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 690.3 Mn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 2,500.2 Mn CAGR (2025-2034) 13.7% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Feedstock (Forestry Residues, Agricultural Residues, Municipal Waste, Animal Manure, Biomass Crops, Others) By Technology (Pyrolysis, Gasification, Others), By Application (Agriculture, Livestock Farming, Water & Wastewater Treatment, Construction Materials, Others) Regional Analysis North America – The US & Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia & CIS, Rest of Europe; APAC- China, Japan, South Korea, India, ASEAN & Rest of APAC; Latin America- Brazil, Mexico & Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa- GCC, South Africa, & Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Airex Energy, Carbonis GmbH & Co. KG, Carbon Gold Ltd, Phoenix Energy, Biochar Now, LLC, Oregon Biochar Solutions, CharGrow LLC, Chardust Ltd, ArSta eco, BIOSORRA, Black Owl Biochar, Carbofex Ltd., Myno Carbon, Pacific Biochar Benefit Corporation, Swiss Biochar GmbH, Other Key Players Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Airex Energy
- Carbonis GmbH & Co. KG
- Carbon Gold Ltd
- Phoenix Energy
- Biochar Now, LLC
- Oregon Biochar Solutions
- CharGrow LLC
- Chardust Ltd
- ArSta eco
- BIOSORRA
- Black Owl Biochar
- Carbofex Ltd.
- Myno Carbon
- Pacific Biochar Benefit Corporation
- Swiss Biochar GmbH
- Other Key Players










