Global Fuel Cell Market Size, Share, Upcoming Investments Report By Type (Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell, Solid Oxide Fuel Cell, Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cell, Alkaline Fuel Cell, Microbial Fuel Cell), By Components (Stack, Balance of plant (BOP)), By Fuel (Hydrogen, Ammonia, Methanol, Ethanol, Hydrocarbon), By Size (Small Scale, Large Scale), By Power Outage (Less Tahn 100KW, 100-200K, Greater Than 200KW), By Application (Portable, Stationary, Fuel Cell Vehicles), By End-use (Residential, Commercial and Industrial, Transportation, Data Centers, Military and Defense, Utilities and Government/Municipal Institutes), By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2024-2033
- Published date: Dec 2024
- Report ID: 135776
- Number of Pages: 259
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
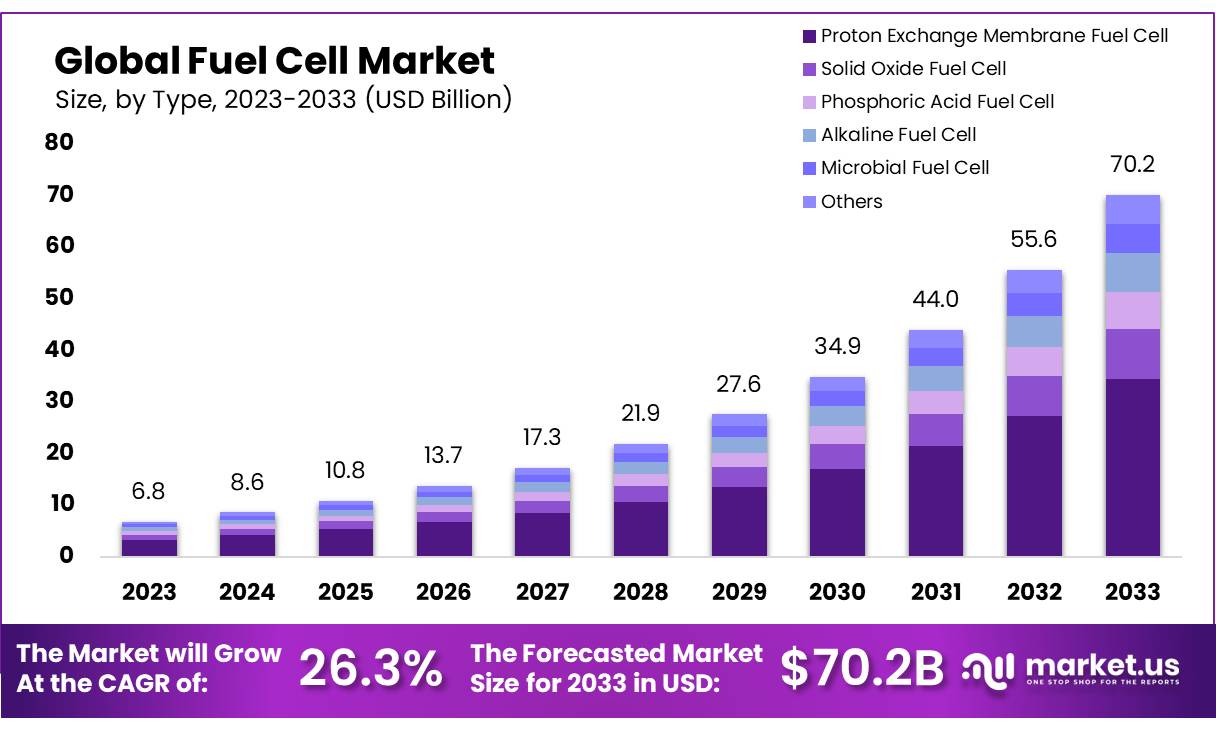
The Global Fuel Cell Market size is expected to be worth around USD 70.2 Bn by 2033, from USD 6.8 Bn in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 26.3% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
A fuel cell is a device that converts chemical energy from a fuel, such as hydrogen or methanol, into electrical energy through an electrochemical reaction with oxygen or another oxidizing agent. Unlike traditional combustion engines, which burn fuel to create power, fuel cells generate electricity without combustion, making them cleaner and more efficient.
The process involves two electrodes – the anode and cathode – and an electrolyte that allows ions to move between the electrodes. At the anode, the fuel (often hydrogen) splits into electrons and protons; the electrons flow through an external circuit, generating electricity, while the protons move through the electrolyte to the cathode. At the cathode, the protons, electrons, and oxygen combine to form water, the main byproduct of the reaction, making fuel cells an environmentally friendly energy source.
The fuel cell market is witnessing strong adoption in end-use industries such as transportation, stationary power generation, and industrial applications. In the transportation sector, global sales of hydrogen-powered vehicles, including fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs), are expected to reach 5.4 million units by 2030, driven by increasing demand for zero-emission vehicles.
- According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), over 10,000 fuel cell vehicles were sold globally in 2022, and this number is anticipated to grow at a compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 40% over the next decade (IEA, 2023).
Governments worldwide are supporting fuel cell development through regulations and incentives. The European Union has committed to a target of 10 million tons of renewable hydrogen production by 2030 as part of its hydrogen strategy.
The EU’s Hydrogen Backbone project, a €43 billion initiative, aims to establish a cross-border hydrogen infrastructure network of 23,700 km by 2040 (European Commission, 2020). In the U.S., the Biden administration’s infrastructure plan includes an $8 billion investment in creating regional hydrogen hubs, which will support the deployment of fuel cell vehicles and stationary power generation systems.
Private and public investments in fuel cell technology are rising sharply. In 2022 alone, global investments in hydrogen projects exceeded $1 billion, with a large portion allocated to fuel cell research and infrastructure development.
Leading energy companies like Shell and Toyota have partnered to invest in hydrogen fuel cell trucks, with Toyota’s collaboration with Hino Motors planning to deploy 1,000 hydrogen-powered trucks by 2030 (Toyota, 2021). Similarly, Hyundai and SK Group in South Korea have partnered to develop a green hydrogen value chain, investing over $5 billion by 2030.
The global hydrogen trade is also gaining momentum, with key exporters like Australia and the Middle East increasing hydrogen production to meet growing global demand. Australia plans to become a major exporter of green hydrogen, with the Australian government predicting hydrogen export revenues could reach $1.7 billion annually by 2040.
The EU and Japan are expected to become significant importers of hydrogen, with Japan targeting the import of 3 million tons of hydrogen annually by 2030 (Japan Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry, 2021).
The fuel cell sector is also seeing significant innovation, particularly in fuel cell efficiency and cost reduction. In 2022, Ballard Power Systems announced a breakthrough in reducing the cost of fuel cell production by 30%, thanks to new membrane technology.
Key Takeaways
- Fuel Cell Market size is expected to be worth around USD 70.2 Bn by 2033, from USD 6.8 Bn in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 26.3%.
- Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC) held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 49.4%.
- Stack held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 59.5% share of the fuel cell market.
- Hydrogen held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 75.4% share of the fuel cell market.
- Small Scale held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 67.5% share of the fuel cell market.
- <100KW held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 47.8% share of the fuel cell market.
- Stationary held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 58.5% share of the fuel cell market.
- Commercial & Industrial held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 39.2% share.
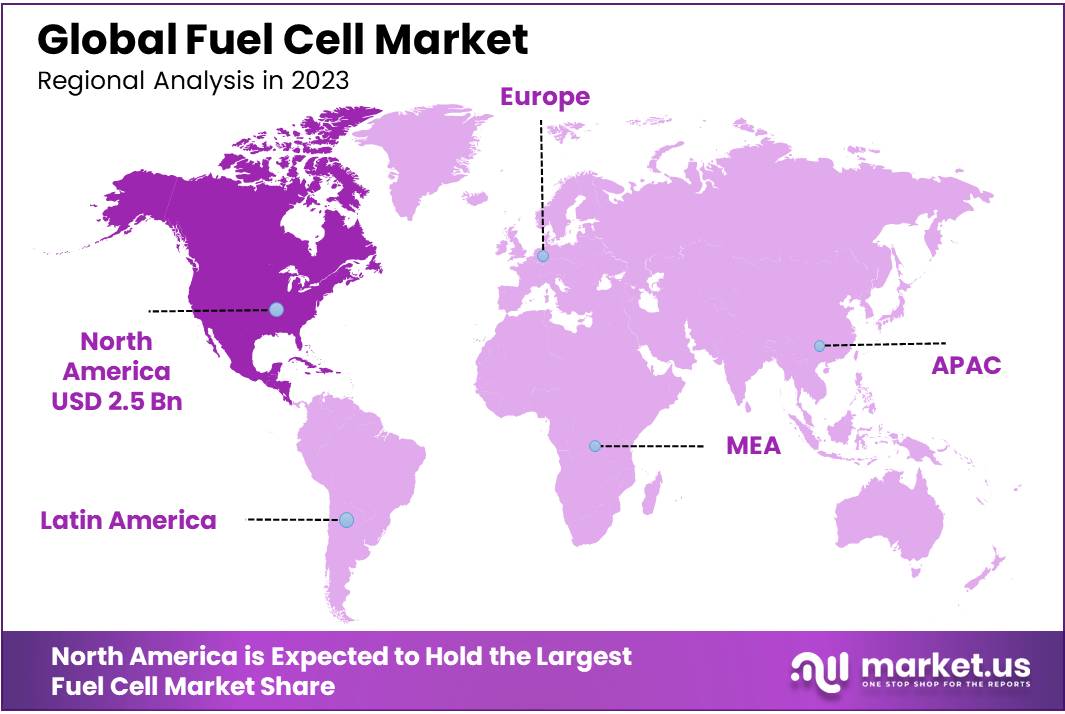
- North America dominated the fuel cell market, holding a significant share of 39.7%, valued at approximately USD 2.5 billion.
By Type
In 2023, Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC) held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 49.4% share of the fuel cell market. PEMFCs are widely used in applications such as automotive, portable electronics, and stationary power generation due to their high efficiency and low operating temperatures. The increasing demand for clean energy solutions and eco-friendly transportation options, particularly in the automotive sector, is driving the growth of this segment.
Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFCs), with their high efficiency and versatility, follow closely, holding a significant market share. SOFCs operate at higher temperatures and are primarily used in stationary power generation applications. The growing adoption of these fuel cells in industrial applications, combined with advancements in materials technology, is expected to boost their market growth.
Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cells (PAFCs) are another important segment in the fuel cell market. PAFCs are typically used in commercial and industrial applications where consistent power generation is crucial. In 2023, the segment accounted for a moderate share of the overall market, driven by their reliability and long operating life.
Alkaline Fuel Cells (AFCs) have been in the market for decades and continue to see use in specialized applications such as aerospace and military. While their share of the market is relatively smaller compared to other fuel cell types, AFCs still hold a niche position due to their low cost and simplicity in design.
Microbial Fuel Cells (MFCs) are a newer and smaller segment within the fuel cell market. MFCs use bacteria to generate electricity, offering potential for sustainable power generation, particularly in waste treatment and remote power applications. This segment is expected to grow steadily as research into MFCs advances and more applications are identified.
By Components
In 2023, Stack held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 59.5% share of the fuel cell market. The stack is the core component of a fuel cell, where the electrochemical reactions take place to generate electricity. Its performance directly influences the efficiency and power output of the fuel cell, making it a critical part of the system. With the growing demand for fuel cells in sectors like transportation and stationary power generation, the stack segment continues to lead market growth.
Balance of Plant (BOP), which includes the supporting components such as the air compressor, fuel processor, and thermal management system, accounted for a smaller but significant share of the market. While the stack is the heart of the fuel cell, the BOP ensures that the system operates smoothly and efficiently. The demand for advanced BOP solutions is growing as fuel cells are being adopted for more diverse applications, including commercial and industrial uses.
By Fuel
In 2023, Hydrogen held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 75.4% share of the fuel cell market. Hydrogen is the most widely used fuel in fuel cell systems due to its high energy density and zero-emissions output when used in electrochemical reactions. Its abundant availability and growing infrastructure for production, storage, and distribution are key drivers of its widespread adoption, particularly in sectors like transportation and industrial applications.
Ammonia, while less common, is emerging as a promising alternative fuel for fuel cells, especially for large-scale power generation. With its high energy density and easier storage compared to hydrogen, ammonia is expected to gain traction in the market. However, the infrastructure and technology for ammonia-based fuel cells are still in the early stages of development, limiting its market share in 2023.
Methanol is another fuel option gaining attention in the fuel cell market. It offers a liquid form that is easier to handle and store compared to hydrogen. Methanol fuel cells are primarily used in portable applications and backup power systems, where space and portability are critical. Although it holds a smaller share of the market, methanol-based fuel cells are becoming more viable due to ongoing improvements in fuel cell efficiency.
Ethanol, like methanol, is primarily used in small-scale fuel cells. It offers similar benefits in terms of easy storage and handling, making it attractive for specific applications. However, ethanol’s market share remains limited compared to hydrogen and methanol, as it is less efficient in fuel cells and lacks the extensive infrastructure of other fuels.
Hydrocarbons, such as natural gas, are also used in certain fuel cell systems, particularly in stationary power generation. While not as clean as hydrogen, hydrocarbons provide a cost-effective and widely available option for specific industrial applications. However, this segment holds a smaller share, with a trend toward cleaner alternatives like hydrogen gaining preference in the fuel cell market.
By Size
In 2023, Small Scale held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 67.5% share of the fuel cell market. Small-scale fuel cells are widely used in applications such as portable power systems, backup power, and in vehicles like forklifts and small electric cars. Their compact size, high efficiency, and ability to operate in diverse environments make them highly attractive for both commercial and residential use. The growing demand for portable energy solutions and cleaner power sources is a key driver of the small-scale fuel cell market’s growth.
Large Scale fuel cells, while holding a smaller market share, are increasingly being adopted for industrial and stationary power generation applications. They are used in large-scale energy systems such as power plants and data centers, where reliability and consistent power generation are crucial. The segment is expected to see growth, particularly as industries seek more sustainable and efficient alternatives to traditional fossil fuel-based power generation.
By Power Outage
In 2023, <100KW held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 47.8% share of the fuel cell market. This power range is most commonly used in residential, small commercial, and backup power applications. The increasing need for reliable, off-grid power solutions and clean energy alternatives is driving the growth of this segment. Smaller fuel cells are ideal for homes, small businesses, and remote areas where traditional power grids may not be accessible or reliable.
The 100-200KW range is growing steadily and is primarily used in medium-sized commercial and industrial applications. These fuel cells are used for backup power and off-grid systems, providing a balance between power capacity and cost-effectiveness. With industries and businesses looking for more sustainable energy solutions, this segment is gaining traction in regions with high energy demand and a focus on reducing carbon emissions.
The >200KW segment, while holding a smaller market share, is used in larger industrial applications, such as power plants and large commercial buildings. These fuel cells provide substantial power for facilities that require continuous, high-capacity energy generation. As large industries and municipalities seek more sustainable and cost-effective energy solutions, the demand for high-capacity fuel cells in this power range is expected to grow.
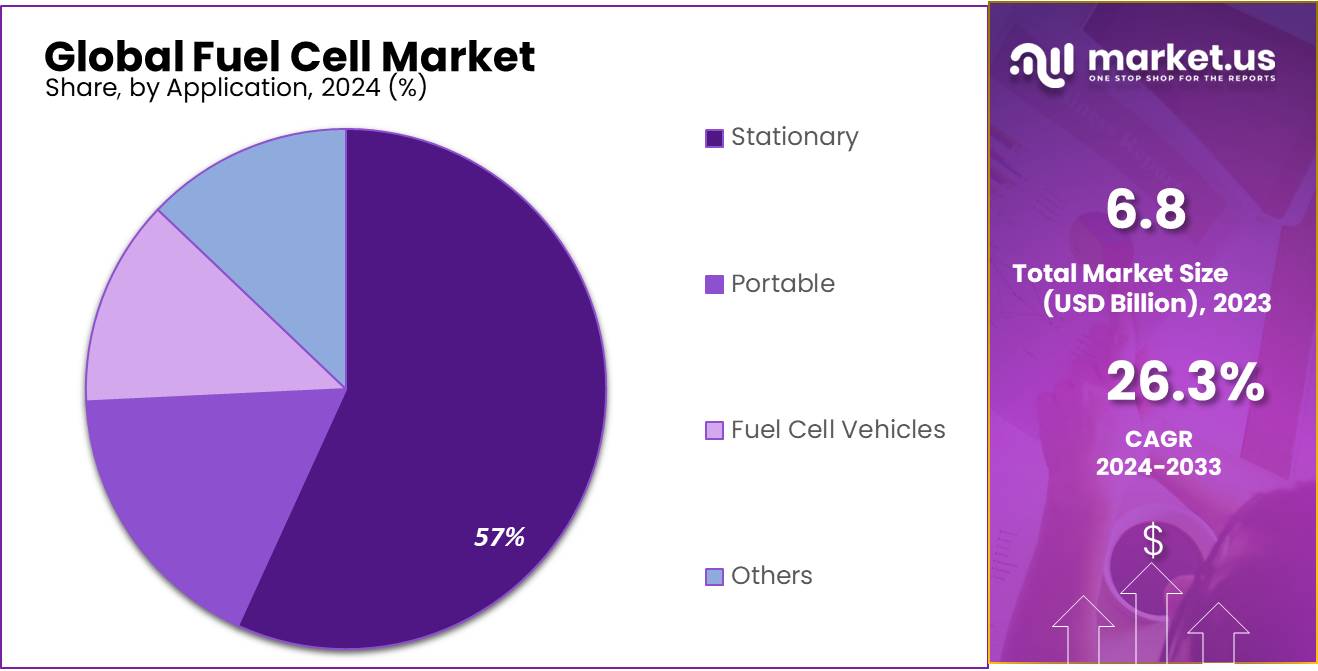
By Application
In 2023, Stationary held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 58.5% share of the fuel cell market. Stationary fuel cells are primarily used for backup power and off-grid applications in commercial, industrial, and residential sectors. Their ability to provide reliable, continuous power makes them ideal for locations where grid power is unreliable or unavailable. As businesses and homeowners increasingly prioritize energy security and sustainability, the demand for stationary fuel cells is expected to continue growing.
The Portable segment, though smaller in comparison, is gaining momentum with growing demand for mobile power solutions. Portable fuel cells are used in consumer electronics, military applications, and as backup power for outdoor activities. These fuel cells offer a clean and efficient alternative to traditional batteries, especially in devices that require long-lasting, reliable power. As portable energy solutions continue to evolve, this segment is expected to see further innovation and growth.
Fuel Cell Vehicles (FCVs) represent another important application in the fuel cell market. While still in the early stages of adoption, the FCV market is growing rapidly due to advancements in hydrogen fuel cell technology and the increasing push for eco-friendly transportation. FCVs offer a clean, efficient alternative to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles, and their adoption is supported by governments and companies looking to reduce carbon emissions.
By End-use
In 2023, Commercial & Industrial held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 39.2% share of the fuel cell market. This segment includes fuel cells used for backup power, off-grid energy, and primary energy sources in businesses, factories, and large commercial buildings. Fuel cells are increasingly being adopted in these sectors due to their reliability, low emissions, and ability to reduce dependence on traditional energy sources. As industries seek more sustainable solutions, demand for fuel cells in this space is expected to grow.
The Residential segment, while smaller, is also showing strong growth. Fuel cells for homes provide clean, reliable backup power and energy for off-grid living. With rising electricity costs and increasing interest in renewable energy, more homeowners are turning to fuel cells as a way to reduce their carbon footprint and ensure uninterrupted power supply.
Transportation is another key application for fuel cells, particularly in the automotive and heavy-duty vehicle sectors. While the market is still emerging, fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) offer a clean, efficient alternative to traditional vehicles, especially in the commercial vehicle sector. Government initiatives and advancements in hydrogen infrastructure are helping to accelerate the adoption of fuel cell technology in transportation.
Data Centers are becoming a major end-use segment for fuel cells. The need for constant, reliable power in data centers has driven the adoption of fuel cells as a backup energy source. Fuel cells provide a clean, efficient alternative to diesel generators, helping data centers meet their energy needs while reducing their environmental impact.
In the Military & Defense sector, fuel cells are used for portable power systems, communication equipment, and backup power for critical operations. The demand for lightweight, reliable, and sustainable energy solutions is driving growth in this segment. Fuel cells offer high energy density and quiet operation, making them ideal for military applications.
Utilities & Government/Municipal Institutes are adopting fuel cells for large-scale power generation, especially for backup and grid stabilization purposes. With increasing pressure to reduce carbon emissions, fuel cells are becoming an important part of clean energy strategies for governments and utility providers.
Key Market Segments
By Type
- Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell
- Solid Oxide Fuel Cell
- Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cell
- Alkaline Fuel Cell
- Microbial Fuel Cell
- Others
By Components
- Stack
- Balance of plant (BOP)
By Fuel
- Hydrogen
- Ammonia
- Methanol
- Ethanol
- Hydrocarbon
By Size
- Small Scale
- Large Scale
By Power Outage
- <100KW
- 100-200K
- >200KW
By Application
- Portable
- Stationary
- Fuel Cell Vehicles
- Others
By End-use
- Residential
- Commercial & Industrial
- Transportation
- Data Centers
- Military & Defense
- Utilities & Government/Municipal Institutes
- Others
Drivers
Growing Focus on Clean Energy Transition
One of the major driving factors for the fuel cell industry is the increasing global push toward cleaner energy sources, supported by government initiatives and advancements in technology. Fuel cells, which convert chemical energy into electrical energy with minimal pollution, are being seen as key enablers of the clean energy transition. Governments worldwide are offering significant support to fuel cell technology as part of their commitments to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and meeting carbon neutrality targets.
For example, the European Union has set ambitious goals to reduce its carbon emissions by 55% by 2030 and become climate neutral by 2050. As part of this, the EU is actively investing in fuel cell technology, with the “Hydrogen Strategy for a Climate-Neutral Europe” launched in 2020. The strategy plans to increase hydrogen production to 10 million tons per year by 2030, with fuel cells playing a crucial role in achieving this target .
- In the United States, the Department of Energy (DOE) has invested over $100 million annually in fuel cell research and development, focusing on reducing costs and improving the performance of hydrogen fuel cells.
Moreover, Asia has also been heavily investing in fuel cell development. Japan and South Korea are leading the way, with Japan committing to hydrogen as part of its energy mix. In 2020, the Japanese government set a target of installing 200,000 fuel cell vehicles and 1,000 hydrogen stations by 2030. South Korea is also making substantial investments, with a plan to deploy over 15,000 fuel cell-powered buses by 2040.
Restraints
High Cost of Fuel Cell Technology
One of the major challenges hindering the widespread adoption of fuel cells is their high cost, particularly in terms of materials, manufacturing, and infrastructure. While fuel cell technology has advanced in recent years, it remains expensive compared to traditional energy sources, which limits its competitive edge in certain sectors.
A significant portion of the high costs comes from the materials used in fuel cells, especially platinum, which is required as a catalyst for the electrochemical reactions. Platinum costs have fluctuated, with prices reaching up to $60,000 per kilogram in 2022 (Platts Metals Daily, 2022), which significantly adds to the overall production cost of fuel cell systems.
In addition to material costs, fuel cell production and installation are expensive due to the complex manufacturing processes required.
- According to the U.S. Department of Energy, the manufacturing cost of proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cells, which are commonly used in vehicles, was about $50–70 per kilowatt in 2021, with goals to reduce this to below $30 per kilowatt by 2030.
Moreover, infrastructure for hydrogen fuel supply remains underdeveloped. The lack of refueling stations for hydrogen vehicles, for example, presents a significant barrier to the adoption of fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs). The Hydrogen Council reports that as of 2022, there were only about 500 hydrogen refueling stations globally, most of which are concentrated in a few countries like Japan, Germany, and the United States.
To achieve widespread fuel cell adoption, an expansion to over 10,000 stations globally is required by 2030, according to the same source (Hydrogen Council, 2022). This infrastructure gap further exacerbates the high costs of fuel cell deployment.
Opportunity
Expansion in Hydrogen Infrastructure Development
A significant growth opportunity for the fuel cell industry lies in the expansion of hydrogen infrastructure, which is critical to making fuel cell technology more accessible and practical for large-scale use. Hydrogen, as a clean energy source, has seen increased interest in industries such as transportation, power generation, and heavy-duty applications, but its widespread adoption is contingent on the development of a robust hydrogen infrastructure.
Governments worldwide are now prioritizing the expansion of hydrogen refueling stations and hydrogen production facilities, providing the necessary conditions for fuel cell technologies to thrive.
- In the European Union, the European Hydrogen Backbone initiative aims to create a hydrogen pipeline network spanning 23,700 km by 2040, connecting major industrial hubs and enabling the transport of hydrogen across borders.
This project is expected to support the development of a hydrogen market that could be worth up to €100 billion annually by 2050 (European Commission, 2020). In the U.S., the Biden administration has allocated $8 billion in funding to support the establishment of regional hydrogen hubs as part of its Inflation Reduction Act, targeting the development of a nationwide hydrogen infrastructure (U.S. Department of Energy, 2022).
This investment is expected to significantly boost the deployment of fuel cell vehicles, particularly in the commercial and heavy-duty transport sectors, where fuel cells are well-suited due to their high energy density and quick refueling capabilities.
Additionally, the growing interest in hydrogen as a means of decarbonizing industries like steel, cement, and chemicals presents another opportunity for fuel cells. For instance, in Japan, the National Hydrogen Strategy aims to produce 3 million tons of hydrogen annually by 2030, driving demand for fuel cells in both residential and industrial applications (Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry of Japan, 2020).
This push for green hydrogen production could open up new markets for fuel cell applications, including stationary power generation and backup power solutions for critical infrastructure.
As governments and industries invest heavily in hydrogen infrastructure, fuel cells are positioned to benefit from increased demand and a more favorable cost structure in the coming years. This opportunity to integrate fuel cell technology with expanding hydrogen infrastructure presents a clear path for growth, helping accelerate the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Trends
Increased Adoption of Fuel Cells in Heavy-Duty Transport
A significant trend emerging in the fuel cell sector is the increasing adoption of hydrogen fuel cells in heavy-duty transport, such as trucks, buses, and trains.
While fuel cells have been popular in light-duty vehicles, the potential for fuel cells in the heavy-duty sector is gaining traction due to the growing need for zero-emission solutions in commercial transportation. This trend is largely driven by the push for stricter emissions regulations and the need to decarbonize industries that are difficult to electrify.
For example, in the European Union, the Horizon 2020 program, which supports clean transport, has invested heavily in hydrogen fuel cell trucks. The EU’s “Fuel Cells and Hydrogen 2 Joint Undertaking” aims to roll out 1,000 hydrogen fuel cell trucks by 2025 as part of its strategy to reduce CO2 emissions in the logistics sector.
Meanwhile, in the United States, the California Air Resources Board (CARB) has committed to funding up to $70 million for hydrogen fuel cell truck development, contributing to California’s goal of having 200 zero-emission heavy-duty trucks on the road by 2023.
Additionally, several manufacturers are increasing their investment in hydrogen fuel cell-powered vehicles. In 2023, Hyundai Motor Company began delivering its hydrogen fuel cell-powered trucks, the Xcient Fuel Cell trucks, to Switzerland, marking the first large-scale commercial deployment of hydrogen trucks in Europe.
Hyundai plans to produce 1,600 units by 2025 (Hyundai Motor Company, 2023). Similarly, Toyota has partnered with Hino Motors to develop hydrogen-powered heavy-duty trucks, with the first deliveries expected in the U.S. by 2024.
In 2021, the U.S. government allocated $7 billion for the development of clean transportation infrastructure, including hydrogen fueling stations, as part of its infrastructure bill. This funding is expected to help address one of the biggest barriers to the widespread adoption of hydrogen fuel cell trucks: the lack of refueling infrastructure.
Regional Analysis

-
-
- Air France-KLM
- Air India Ltd
- AirAsia
- AISIN
- Alaska Airlines Inc
- AVL
- Ballard Power Systems
- Batik Air
- Bloom Energy
- Blue World Technologies
- Bosch
- Ceres Power
- China Eastern Airlines
- Convion
- EasyJet PLC
- Elcogen
- ElringKlinger
- Emirates
- Etihad
- FuelCell Energy
- Horizon Fuel Cell Technologies
- Hydrogenics
- IndiGo
- ITM Power
- Jetstar Asia Airways
- Korean Air
- Mitsubishi Hitachi Power Systems
- Nedstack Fuel Cell Technology
- Nexceris LLC
- Nuvera Fuel Cells, LLC
- Plug Power
- Pragma Industries
- Proton Motor Fuel Cell GmbH
- Roland Gumpert
- SFS Energy AG
- Singapore Airlines
- SOLIDpower Italia
- W.L. Gore & Associates