Global Battery Energy Storage Systems for Smart Grid Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Battery Type (Lithium-ion, Lead-acid, Flow Batteries, Others), By Connectivity (On-Grid, Off-Grid), By End-Use (Utilities, Commercial And Industrial, Residential) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Nov 2025
- Report ID: 164921
- Number of Pages: 254
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
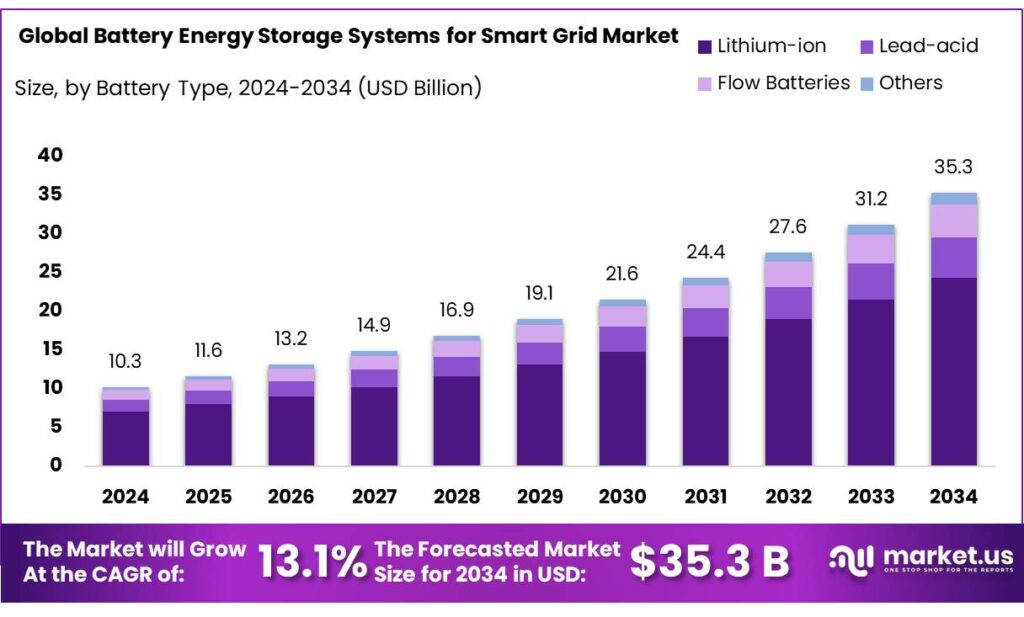
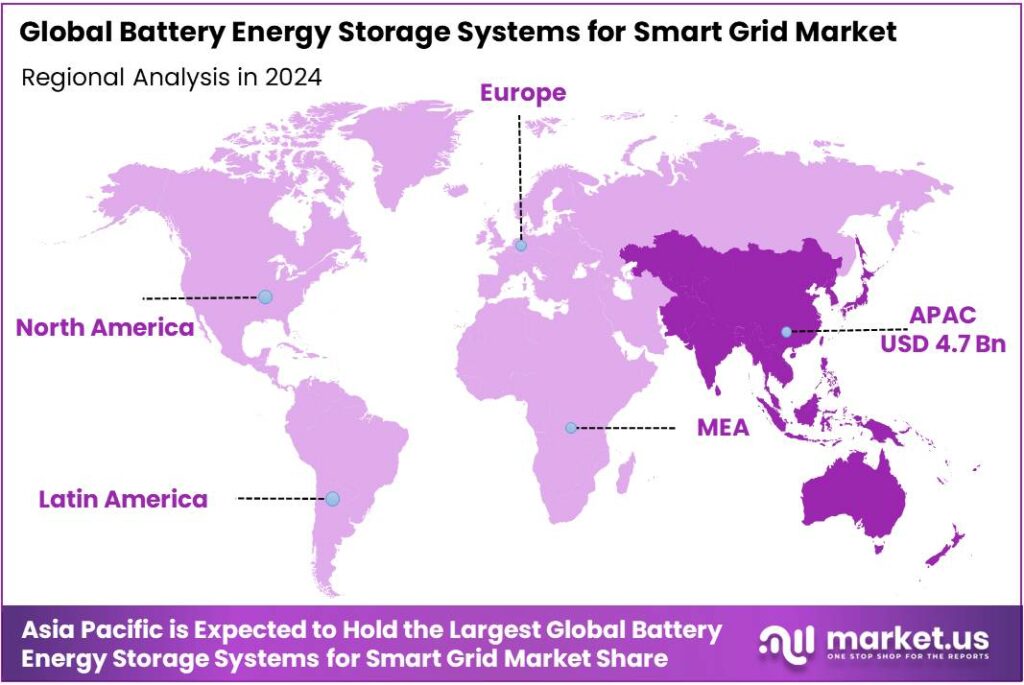
The Global Battery Energy Storage Systems for Smart Grid Market size is expected to be worth around USD 35.3 Billion by 2034, from USD 10.3 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 13.1% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024 Asia-Pacific (APAC) held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 45.9% share, holding USD 4.7 Billion in revenue.
Battery energy storage systems (BESS) have moved from pilots to core grid assets, enabling utilities to integrate more variable wind and solar, defer wires upgrades, and improve system reliability. Globally, grid-scale batteries have expanded rapidly: the International Energy Agency (IEA) notes installed grid-scale battery capacity stood near 28 GW at end-2022 and is now the dominant source of new storage growth alongside pumped hydro.
- IRENA reports fully-installed BESS costs dropped 93% between 2010 and 2024—from about USD 2,571/kWh to USD 192/kWh—with 2024 alone seeing a 38% decline for typical 2-hour systems versus 2023, strengthening project economics across markets.
The industrial landscape features two reinforcing demand drivers: surging renewables build-out and power-market needs for flexibility. IEA projects global renewable capacity will grow 2.7× by 2030 versus 2022, tightening the requirement for short-duration balancing and ramping services that batteries provide. In the United States, utility-scale battery capacity exceeded 26 GW in 2024 after adding 10.4 GW that year—the second-largest capacity addition after solar—illustrating how storage has become a mainstream grid resource.
EIA expects another record year in 2025 with 18.2 GW of battery additions planned. Europe is following a similar trajectory: 21.9 GWh of BESS was installed in 2024, lifting the continent’s total to 61.1 GWh, even as growth moderated from previous years.
- Policy is a decisive catalyst. The European Commission estimates total EU electricity storage capacity at roughly 89 GW in 2024 (mainly pumped hydro) and points to needs above 200 GW by 2030 and 600 GW by 2050 to support decarbonisation—targets that implicitly open space for vast BESS deployment.
India has launched a dedicated viability-gap-funding (VGF) program for grid-connected BESS; official guidelines were issued in March 2024, and subsequent updates reduced the support benchmark as costs fell—from an earlier ₹96 lakh/MWh estimate to ₹46 lakh/MWh or 30% of capex, whichever is lower—improving affordability for state tenders. Recent allocations include central assistance of ₹18 lakh/MWh for a multi-state 30 GWh tranche, with Rajasthan publicly indicating support for a 4,000 MWh portfolio under this scheme.
Operationally, BESS is already shaping market behavior. U.S. operators increasingly use batteries for energy arbitrage—charging off-peak and discharging at peaks—designating this as the primary use for over 10,000 MW of capacity while simultaneously providing contingency reserves and renewable smoothing.
Key Takeaways
- Battery Energy Storage Systems for Smart Grid Market size is expected to be worth around USD 35.3 Billion by 2034, from USD 10.3 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 13.1%.
- Lithium-ion held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 68.9% share in the Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) market
- On-Grid held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 72.3% share in the Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) market
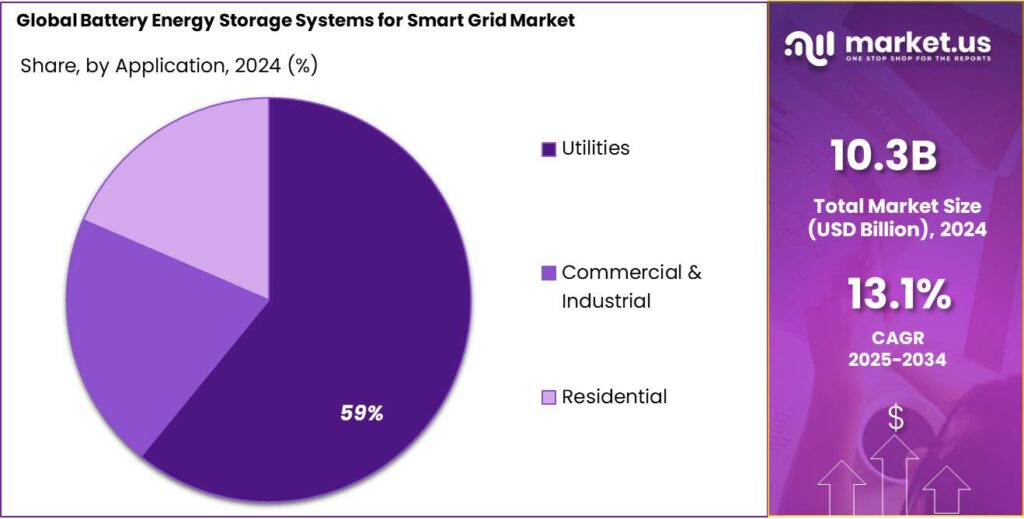
- Utilities held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 59.2% share in the Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) market for smart grids.
- Asia-Pacific (APAC) region, the market for battery energy storage systems (BESS) in smart grid applications stood out with a dominant position in 2024, capturing approximately 45.90% of the global regional market and reaching a value of about USD 4.7 billion.
By Battery Type Analysis
Lithium-ion dominates with 68.9% share driven by efficiency and long cycle life
In 2024, Lithium-ion held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 68.9% share in the Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) market for smart grids. This technology has become the preferred choice due to its high energy density, superior efficiency, and declining cost per kilowatt-hour, which have strengthened its adoption across utility and commercial sectors. The widespread integration of renewable energy resources such as solar and wind has further enhanced the demand for Lithium-ion systems, as they offer rapid response times and scalability that align well with grid stability requirements.
Extensive deployment of large-scale grid storage projects using Lithium-ion batteries was observed across North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific. Utilities and energy developers prioritized these systems for peak load management and renewable integration, as they deliver cycle lives exceeding 6,000–8,000 cycles and round-trip efficiencies above 90%. In 2025, the market is expected to continue expanding steadily, supported by ongoing investments in renewable infrastructure and advancements in battery chemistry that are improving performance and safety standards. The reduction in cell costs and innovations in recycling processes are also expected to reinforce the technology’s sustainability outlook.
By Connectivity Analysis
On-Grid systems dominate with 72.3% share owing to large-scale grid integration and reliability needs
In 2024, On-Grid held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 72.3% share in the Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) market for smart grids. The segment’s leadership was driven by the rapid expansion of grid-connected renewable energy installations, increasing power demand, and the growing need for frequency regulation and grid balancing services. On-grid systems have been widely adopted by utilities and transmission operators to stabilize fluctuating power flows from solar and wind energy sources, ensuring consistent electricity supply and grid reliability.
These systems enable utilities to store excess generation during off-peak hours and discharge it during demand peaks, reducing curtailment and improving overall energy efficiency. In 2025, the on-grid segment is expected to maintain steady growth as grid modernization programs and smart grid investments expand globally. The adoption of advanced energy management systems and automated grid control technologies will further enhance operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
By End-Use Analysis
Utilities dominate with 59.2% share driven by large-scale energy storage deployment and grid stability goals
In 2024, Utilities held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 59.2% share in the Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) market for smart grids. This dominance was primarily supported by the increasing adoption of large-scale energy storage projects aimed at enhancing grid stability, integrating renewable energy, and ensuring reliable power supply during peak demand periods. Utilities across developed and emerging economies have been investing heavily in advanced storage infrastructure to manage fluctuating generation from solar and wind sources and to improve the efficiency of transmission and distribution networks.
Utility operators worldwide expanded deployment of grid-connected battery systems to reduce dependence on fossil fuel-based peaker plants and to enable a smoother transition to clean energy. The adoption of smart grid technologies allowed utilities to optimize energy dispatch, improve response times, and maintain system frequency more effectively. By 2025, the utility segment is expected to sustain steady growth, supported by supportive policy frameworks, capacity expansion projects, and technological advancements that are lowering installation and operation costs.
Key Market Segments
By Battery Type
- Lithium-ion
- Lead-acid
- Flow Batteries
- Others
By Connectivity
- On-Grid
- Off-Grid
By End-Use
- Utilities
- Commercial & Industrial
- Residential
Emerging Trends
Aggregating Cold-Chain Batteries into Virtual Power Plants (VPPs)
Cooling gaps quantify the upside for BESS-VPPs. UNEP reports that lack of effective refrigeration directly causes roughly 500–526 million tonnes of food loss each year—about 12% of global production. If developing countries expand cold-chain density to match advanced economies, an additional 144 million tonnes of food could be saved annually—savings that depend on dependable, local power at every node. BESS makes that reliability possible and, when aggregated, unlocks grid-service revenue that improves payback.
- The International Institute of Refrigeration adds that about 12% of global production is lost to insufficient cold chains and that up to 475 million tonnes could be saved with adequate refrigeration—enough to feed ~950 million people; this scale supports the emergence of “anchor-tenant” VPPs built around cold storage clusters.
Policy is catching up to this operational reality. India—a fast-growing cold-chain market—has made VPP-style aggregation bankable by lowering the cost of capital for grid-tied storage. On June 9, 2025, the Ministry of Power set Viability Gap Funding (VGF) at ₹18 lakh per MWh, targeting 30 GWh of BESS, creating a national pathway for distribution-level batteries to provide evening firmness and ancillary services.
The central government’s annual and parliamentary filings also show momentum at scale, with 15,829 MW / 51,106 MWh of BESS in construction or bidding as of mid-2025—ample headroom for aggregator portfolios that enroll cold-chain loads. Earlier guidance similarly earmarked 4,000 MWh of BESS by 2027–28 with ₹3,760 crore support, signaling continuity in storage policy even as tenders grow.
Drivers
Safeguarding food Cold Chains and Processing with Grid-Connected Storage
A powerful, often overlooked driver for Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) on smart grids is the need to protect the food cold chain and 24×7 food processing from rising grid disruptions and heat stress. The FAO estimates that about 13–14% of food is lost between harvest and retail; preventing temperature excursions during storage and transport is a critical gap BESS can help close by riding through outages and smoothing voltage and frequency at facilities and logistics hubs.
Cooling access is no longer just a development target—it’s a grid resiliency issue. UNEP reports that the lack of effective refrigeration directly causes the loss of roughly 526 million tonnes of food each year—around 12% of global production. Where developing countries reach the same cold-chain density as advanced economies, an additional 144 million tonnes of food could be saved annually—a volume only achievable if power is reliable at every node of the chain. BESS provides the fast, local backup and power-quality support that diesel sets alone cannot, while allowing demand-shifting to avoid tariff peaks.
Industry specialists now quantify refrigeration’s macro role. The International Institute of Refrigeration’s latest brief notes about 12% of global food production is lost due to insufficient cold chains, and says expanding cold-chain infrastructure could save ~475 million tonnes of food per year. Such scale implies a structural, multi-year demand for distribution-level storage—particularly 1–4-hour BESS—at packhouses, reefer corridors, and wholesale markets to keep compressors and controls energized during grid events.
- Public policy is reinforcing this shift from diesel-only backup to grid-integrated storage. India, a fast-growing cold-chain market, has launched a national Viability Gap Funding program for BESS to firm renewable power and improve service quality. Operational guidelines were issued on March 15, 2024, and in June 2025 the Ministry of Power set VGF at ₹18 lakh per MWh, targeting 30 GWh of BESS with allocations to multiple states—explicitly supporting projects that stabilize evening supply when refrigeration loads spike. Rajasthan alone was allocated 4,000 MWh with ₹720 crore central assistance, signalling state-level adoption for agri-logistics belts.
Restraints
Upfront Affordability and Financing Gaps at Food-Cold-Chain Nodes
Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) promise steadier power for smart grids, but the food sector—the very places where storage would prevent spoilage—often cannot shoulder the upfront cost or secure financing on workable terms. Cold storage and packhouses already run on thin margins and high electricity intensity. A multi-country technical study finds cold rooms account for 60–80% of a packhouse’s total energy use, so any new capex that doesn’t cut bills immediately is hard to justify without concessional finance or incentives.
Paradoxically, the food system’s losses underscore why BESS is needed, but they also expose the affordability bind. FAO reports about 13–14% of all food is lost from harvest to retail; the cash lost in that leakage narrows the ability of processors and storage owners to finance new grid-connected batteries without support. The International Institute of Refrigeration highlights the scale of potential benefit—~12% of global food production is lost to insufficient cold chains; up to 475 million tonnes could be saved with adequate refrigeration—but without affordable financing, many facilities cannot move first on batteries or integrated solar-plus-storage.
Policy is beginning to help, but support remains uneven and can be lower than what food-sector operators need. The World Bank’s battery program notes it launched USD 1 billion to mobilize an extra USD 4 billion for storage in emerging markets—an essential path to reduce cost of capital—but projects still must clear site-level cash-flow hurdles and grid interconnection timelines that small and mid-size cold chains struggle with.
- India’s national scheme shows how design matters: the government issued operational guidelines for BESS viability-gap funding in March 2024, then in June 2025 set ₹18 lakh per MWh support targeting 30 GWh and allocated 4,000 MWh to Rajasthan—serious help, yet developers still need long-term offtake and tariff certainty to make food-hub projects bankable.
Opportunity
Cold-Chain–Anchored BESS as a Grid Flexibility Backbone
Technical briefs from the International Institute of Refrigeration (IIR) translate those losses into a concrete mitigation frontier: around 12% of global food production is lost due to insufficient cold chains, and up to 475 million tonnes could be saved with adequate refrigeration—enough to feed ~950 million people. Embedding 1–4-hour BESS at cold rooms and distribution hubs can keep compressors, controls, and safety systems running through grid disturbances, while enabling demand-shifting and frequency support to the wider system.
Grid stress itself is rising, which strengthens the case for distributed storage at these nodes. U.S. federal sources highlight a pronounced uptick in weather-related outages: the Department of Energy reported that the average annual number of weather-related outages increased by almost 80% since 2011, with cumulative 2000–2021 events exceeding 1,500; that volatility directly threatens temperature-controlled inventories and creates premium value for fast-responding storage.
Climate Central’s national analysis—cited by the U.S. Energy Codes program—similarly shows a ~67% increase in major weather-related outages since 2000, underscoring why utilities will pay for behind-the-meter flexibility that improves local reliability.
Policy momentum is beginning to translate the food-security case into bankable BESS offtake. In India—one of the world’s fastest-growing cold-chain markets—the Union Ministry of Power issued operational VGF rules for grid-connected storage and, on June 9, 2025, set Viability Gap Funding at ₹18 lakh per MWh targeting 30 GWh of BESS, explicitly to stabilize evening supply and integrate renewables.
Regional Insights
APAC leads regionally with 45.90% share and a USD 4.7 billion market size
In the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region, the market for battery energy storage systems (BESS) in smart grid applications stood out with a dominant position in 2024, capturing approximately 45.90% of the global regional market and reaching a value of about USD 4.7 billion. This strong performance is primarily attributed to aggressive deployment of grid-scale storage in countries such as China, Australia, India, Japan and South Korea, supported by ambitious renewable energy targets and modernization of ageing transmission and distribution networks.
Major national programmes in APAC have accelerated storage adoption: China, for example, added 10.37 GW (≈ 24.18 GWh) of electrochemical energy storage capacity in the first half of 2024, marking year-on-year growth of around 40 % and 64.3 % respectively. Meanwhile, in 2024 the APAC region’s stationary battery storage market was underpinned by China’s 35.3 % share and Australia’s 15.3 % share of their regional segment.
The value-proposition is reinforced by supportive industrial policies: local manufacturing of battery cells in China and South Korea is driving cost reductions and competitive advantages for APAC-based deployment. Further, the integration of large volumes of solar and wind generation within the region creates mounting demand for storage solutions to stabilise the grid, mitigate curtailed renewable output and provide frequency-regulation services. Data suggests that APAC accounted for over 60 % of global renewable energy additions in 2023, an indicator of the scale of underlying support.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
ABB Ltd., headquartered in Switzerland, is a major global provider of smart grid and energy automation technologies. The company integrates Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) with digital control platforms like ABB Ability™ to enhance grid stability, peak shaving, and renewable integration. In 2024, ABB expanded its microgrid solutions in Europe and Asia to support utility-scale hybrid renewable plants. With revenues surpassing US$32 billion in 2024, ABB continues to focus on modular, scalable, and AI-driven energy management systems for smart grids.
Siemens AG, based in Germany, develops advanced grid-scale energy storage solutions combining battery technology, power electronics, and smart automation. In 2024, Siemens launched grid-connected BESS projects in Germany and the U.S., strengthening renewable integration and grid balancing. The company’s Smart Infrastructure division reported €77 billion in 2024 revenue, reflecting strong demand for digital grid services. Siemens’ storage offerings, built around its SICAM and Spectrum Power platforms, help utilities manage load fluctuations and maintain grid reliability with renewable power sources.
Samsung SDI, a South Korean energy and battery manufacturer, delivers lithium-ion and solid-state battery systems for both stationary and mobility applications. In 2024, Samsung SDI achieved ₩23.3 trillion (US$17 billion) in sales, driven by grid-scale and EV battery demand. The company’s ESS division focuses on high-energy, long-life cells used in utility-scale renewable integration and industrial backup systems. Samsung SDI’s energy storage platforms are integrated with smart grid software to optimize demand response, frequency regulation, and peak-load management.
Top Key Players Outlook
- ABB Ltd.
- Siemens AG
- Samsung SDI Co., Ltd.
- LG Chem Ltd.
- Tesla, Inc.
- Panasonic Corporation
- Hitachi, Ltd.
- NEC Corporation
- Toshiba Corporation
- BYD Company Limited
- Eaton Corporation plc
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024, Tesla deployed 31.4 GWh of energy storage products (up from 14.7 GWh in 2023) and its Energy Generation & Storage segment pulled in US$10.1 billion in revenue (+67% y/y).
In 2024, ABB reported US$ 32.9 billion in revenues (+2 % year-on-year) and an operational EBITA of US$ 5.968 billion with a margin of 18.1%—strong signs of profitability and scale.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 10.3 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 35.3 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 13.1% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Battery Type (Lithium-ion, Lead-acid, Flow Batteries, Others), By Connectivity (On-Grid, Off-Grid), By End-Use (Utilities, Commercial And Industrial, Residential) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape ABB Ltd., Siemens AG, Samsung SDI Co., Ltd., LG Chem Ltd., Tesla, Inc., Panasonic Corporation, Hitachi, Ltd., NEC Corporation, Toshiba Corporation, BYD Company Limited, Eaton Corporation plc Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Battery Energy Storage Systems for Smart Grid MarketPublished date: Nov 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Battery Energy Storage Systems for Smart Grid MarketPublished date: Nov 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- ABB Ltd.
- Siemens AG
- Samsung SDI Co., Ltd.
- LG Chem Ltd.
- Tesla, Inc.
- Panasonic Corporation
- Hitachi, Ltd.
- NEC Corporation
- Toshiba Corporation
- BYD Company Limited
- Eaton Corporation plc










