Global Small Wind Power Market Size, Share, Growth Analysis By Axis Type (Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines (HAWT), Vertical Axis Wind Turbines (VAWT)), By Grid Type (On-Grid, Off-Grid), By Capacity (Up To 1 KW, 1 KW – 10 KW, 10 KW to 100 KW), By Application (Residential, Commercial, Utility), By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends, and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: March 2025
- Report ID: 140795
- Number of Pages: 257
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
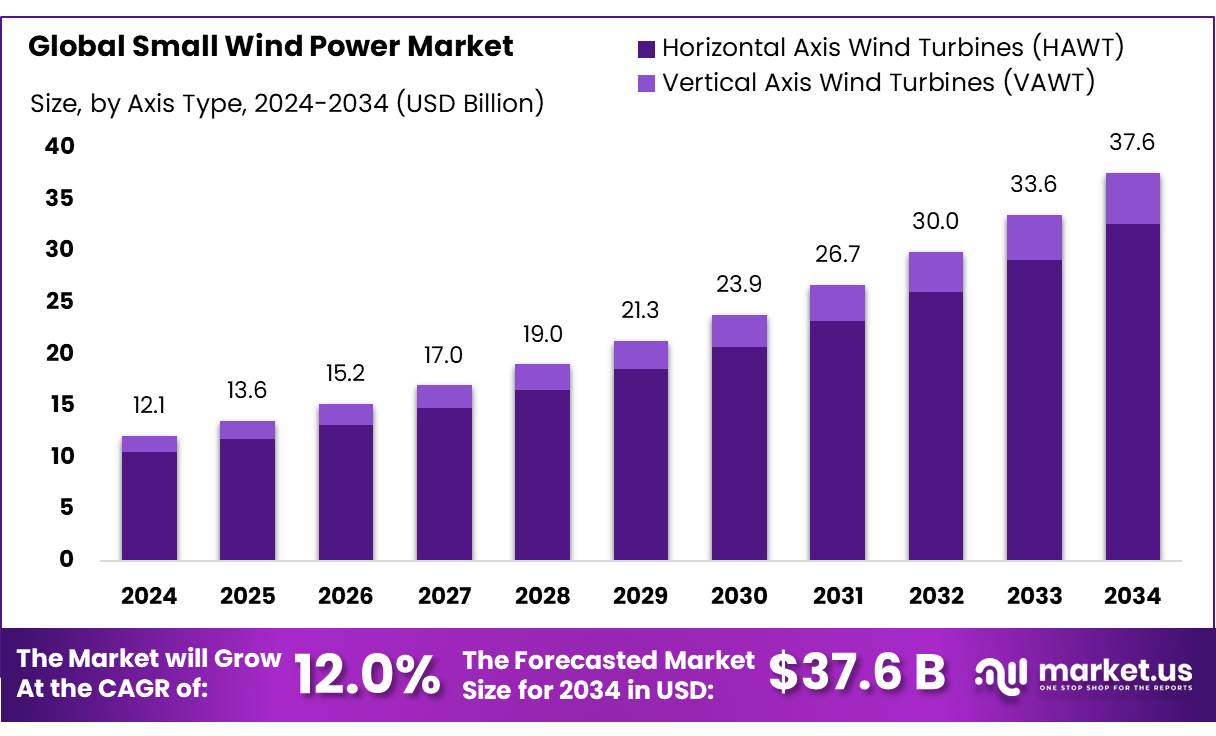
The Global Small Wind Power Market size is expected to be worth around USD 37.6 Bn by 2034, from USD 12.1 Bn in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 12.0% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
Small wind power are renewable energy systems designed to generate electricity by harnessing wind energy in locations with a suitable wind resource but where large wind farms may not be feasible due to terrain or logistical challenges. These turbines are typically used for residential, agricultural, and remote applications, such as powering homes, farms, telecommunication towers, offshore platforms, and yachts. They offer a cost-effective, environmentally friendly, and low-noise alternative to traditional energy sources, making them ideal for areas with a lower power demand or locations where large infrastructure projects are not possible.
Small wind power can either be grid-connected or operate independently as stand-alone units, and they are often used in hybrid systems combined with solar photovoltaics to optimize energy production based on seasonal or diurnal variations in wind and solar availability. The market for small wind power has been growing steadily as global energy sectors shift toward more sustainable and decentralized power generation options.
The increasing adoption of renewable energy and the push for reduced greenhouse gas emissions have significantly contributed to the rise of small wind power. They play an important role in meeting national and state renewable energy targets and reducing the ecological footprint, especially in rural or off-grid areas. Their applications not only support energy independence but also help to improve energy security and resilience, especially in areas with limited access to conventional energy sources.
As governments and industries promote decentralized renewable energy solutions, the small wind turbine market is expected to continue expanding, with significant contributions to mitigating climate change and enhancing sustainable energy development.
Key Takeaways
- The global small wind power market was valued at US$ 12.1 billion in 2024.
- The global small wind power market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 12.0% and is estimated to reach US$ 37.6 billion by 2034.
- Among axis types, Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines (HAWT) accounted for the largest market share of 87.4%.
- Among grid types, on-grid accounted for the majority of the market share at 81.2%.
- By capacity, 10 KW To 100 KW accounted for the largest market share of 48.5%.
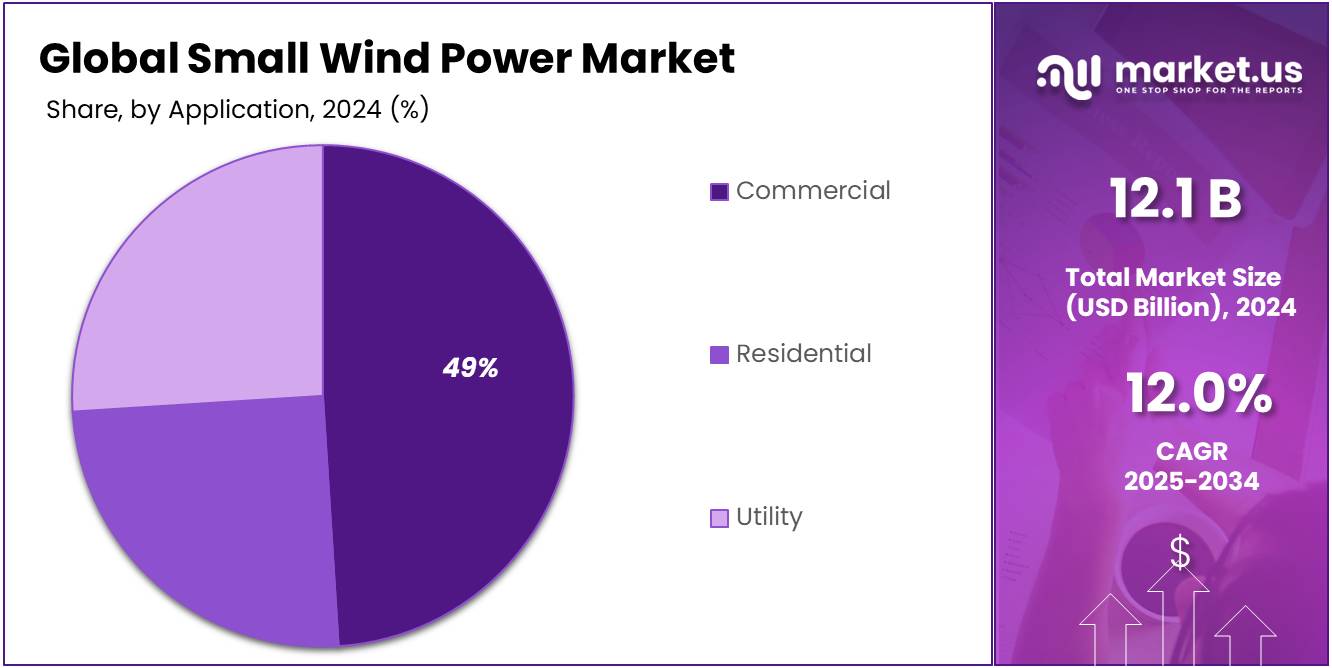
- By application, commercial accounted for the majority of the market share at 49.3%.
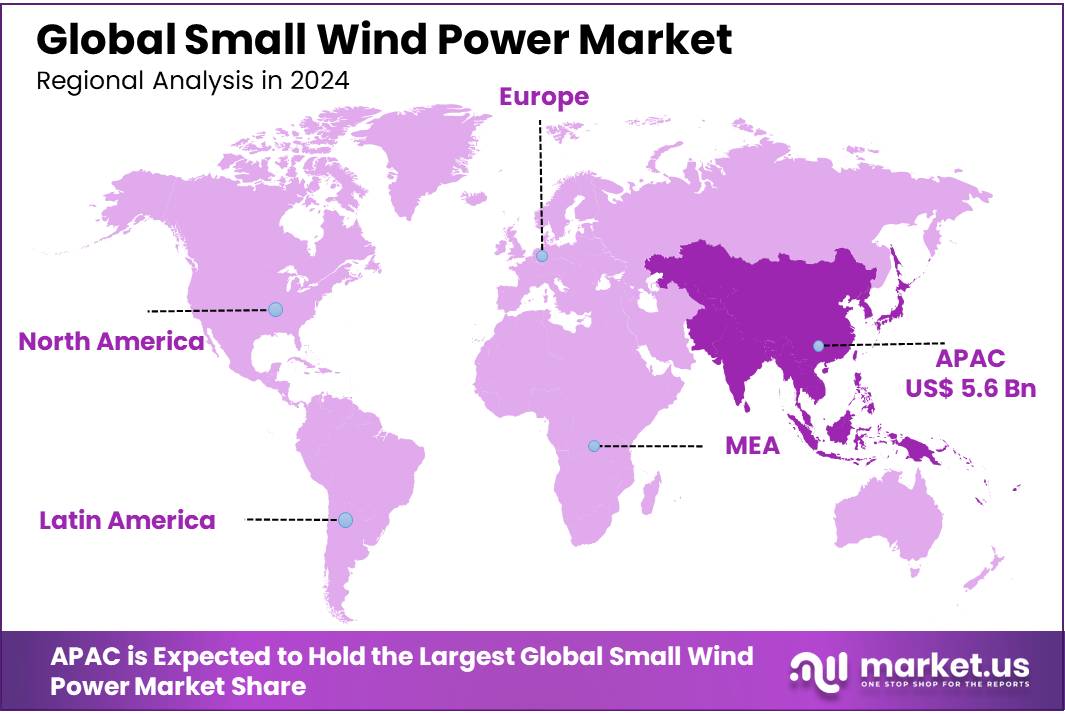
- Asia Pacific is estimated as the largest market for small wind power with a share of 46.3% of the market share.
By Axis Type Analysis
The small wind power market is segmented based on axis type into Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines (HAWT) and Vertical Axis Wind Turbines (VAWT). In 2024, the Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines (HAWT) segment held a significant revenue share of 87.4%. Due to their well-established technology, high efficiency, and ability to generate more power at larger scales compared to Vertical Axis Wind Turbines (VAWTs). HAWTs are widely used in both onshore and offshore wind farms, making them the dominant choice for utility-scale power generation.
Their proven performance, high capacity factor, and scalability have made them the preferred option for large wind energy projects, driving their significant share of the market. Additionally, advancements in turbine design and material technology have further enhanced their performance, contributing to their strong position in the market.
By Grid Type Analysis
Based on grid type, the market is further divided into on-grid and off-grid. The predominance of the on-grid, commanding a substantial 67.4% market share in 2024. Due to its ability to integrate seamlessly with existing electrical infrastructure, allowing excess energy to be fed back into the grid. This not only provides a reliable power supply but also offers financial incentives such as feed-in tariffs or net metering.
Additionally, On-Grid systems benefit from economies of scale and the growing adoption of renewable energy policies, making them a more cost-effective and scalable solution for both residential and commercial users. The increasing demand for renewable energy sources, coupled with government regulations promoting grid-connected systems, has further accelerated the growth of the On-Grid segment.
By Capacity Analysis
Based on capacity, the market is further divided into Up To 1 KW, 1 KW – 10 KW, and 10 KW to 100 KW. The predominance of the 10 KW To 100 KW, commanding a substantial 48.5 % market share in 2024. due to its versatility and suitability for a wide range of applications, including residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. This capacity range provides a balanced solution for users who require more energy generation than smaller systems can offer, while still being scalable and cost-effective compared to larger utility-scale wind turbines.
Additionally, advancements in turbine efficiency, improved technology, and government incentives for renewable energy adoption have made 10 KW to 100 KW wind turbines more attractive to both businesses and homeowners looking for reliable, sustainable, and cost-efficient energy sources.
By Application Analysis
Based on Application, the market is further divided into Residential, Commercial, and Utility. The predominance of the commercial sector commanded a substantial 49.3 % market share in 2024. due to the increasing adoption of small wind turbines in businesses and industries seeking ways to reduce energy costs and improve sustainability. Commercial establishments, such as offices, warehouses, and factories, often have higher energy demands and are more inclined to invest in renewable energy solutions that can help mitigate rising electricity costs.
Additionally, the growing focus on corporate social responsibility (CSR), government incentives for renewable energy adoption, and the potential for long-term cost savings make small wind turbines an appealing option for the commercial sector. These factors, combined with the ability to generate clean energy and achieve energy independence, have led to the segment’s strong market dominance.
Key Market Segments
By Axis Type
- Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines (HAWT)
- Vertical Axis Wind Turbines (VAWT)
By Grid Type
- On-Grid
- Off-Grid
By Capacity
- Up To 1 KW
- 1 KW – 10 KW
- 10 KW To 100 KW
By Application
- Residential
- Commercial
- Utility
Drivers
Expanding Adoption in Residential and Commercial Sector
The expanding adoption of small wind turbines in the residential and commercial sectors is significantly driving the growth of the global small wind turbine market. As energy costs rise and concerns over environmental sustainability intensify, both homeowners and businesses are increasingly turning to small wind turbines as a viable solution for decentralized energy generation. In residential applications, small wind turbines offer a cost-effective way for homeowners to reduce their electricity bills while promoting energy independence. In commercial settings, businesses are leveraging these turbines to lower operational costs, enhance energy resilience, and meet sustainability targets.
- According to reports published by Pacific Northwest National Laboratory states that in 2023 Commercial customers accounted for 42 percent of distributed wind projects in 2023, while agricultural customers made up 34 percent of projects.
The growth is further fueled by government incentives, subsidies, and supportive policies designed to encourage renewable energy adoption. As energy efficiency becomes a priority, small wind turbines are viewed as a practical investment, with scalable solutions that meet the varying needs of different sectors. This trend is particularly strong in regions with favorable wind resources, where small wind turbines are seen as an effective and reliable alternative to traditional power sources. These efforts align with global climate goals, such as achieving net-zero emissions by 2050. As part of the COP28 climate agreements, nations across the globe have committed to tripling global renewable energy capacity by 2030, further fueling demand for small wind turbine systems. As the market continues to expand, small wind turbines are becoming a key component of both residential and commercial energy portfolios, accelerating the transition to clean, renewable energy worldwide.
- For instance, according to a 2023 report by the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, distributed wind projects across ten states in the United States received a total of $12.4 million in state-level incentives, state-level production tax credits (PTCs), and USDA REAP grants.
Restraints
Availability of Alternative Energy Sources
The availability of alternative energy sources significantly restrains the growth of the global small wind power market. While wind power has gained traction as a renewable energy solution, other sources such as solar, hydropower, geothermal energy, and biofuels offer more convenient, cost-effective, and sustainable power options for commercial, agricultural, and residential sectors. These alternatives are often easier to implement and maintain compared to wind power, making them more attractive to consumers and businesses.
In contrast, the installation of small wind turbines can be a complex and time-consuming process. Issues such as logistical challenges in transporting large turbine components, including blades and towers, can delay projects. Additionally, the size and dimensions of these components pose significant obstacles when navigating roads, requiring special handling and elongated routes to avoid urban roadblocks or infrastructure limitations like low overpasses.
Moreover, wind power faces environmental concerns that impact its growth. Although the risk of fires or leaks from small wind turbines is low, such incidents still occur, raising safety and maintenance concerns.
The noise generated by turning turbine blades and potential harm to wildlife, particularly birds and bats, can also contribute to local resistance against wind power installations. Unlike other renewable energy sources that are generally seen as more consistent and predictable, wind power is highly dependent on wind availability, which can fluctuate. Wind farms also face visual and noise-related concerns, impacting local communities’ acceptance of wind power projects. These factors, coupled with the advantages of alternative energy sources, hinder the widespread adoption of small wind power systems, limiting their market growth.
Opportunity
Growth in Agriculture Electrification Projects
The growth in agricultural electrification projects presents a significant opportunity for the small wind power market. As agriculture continues to embrace renewable energy sources, small wind turbines are becoming an attractive solution to reduce dependency on conventional energy and lower operational costs. Farms and agricultural businesses, particularly in rural areas, are seeking sustainable ways to meet their energy needs while also benefiting from additional revenue streams. Small wind turbines offer a viable solution by providing a consistent and reliable energy source, which reduces reliance on fossil fuels, decreases energy expenses and helps farms operate more sustainably. As demand for renewable energy grows, small wind turbines are seen as an essential part of agricultural electrification, contributing to more energy-efficient farming operations.
- The RAISE initiative includes an additional $4 million investment from DOE to test and commercialize distributed wind technologies and develop business models that allow farmers to earn revenue from deploying these technologies.
Furthermore, the increasing adoption of small wind power in agriculture is supported by government policies and financial incentives that encourage the use of renewable energy in rural areas. Many governments, particularly in regions like France, China, and the United States have introduced favorable measures, including tax benefits and subsidies for farmers who host wind turbines on their land. These incentives, combined with technological advancements and the growing need for sustainable farming practices, are driving the adoption of small wind turbines. As more agricultural businesses explore renewable energy solutions, the small wind power market is expected to expand rapidly, presenting new opportunities for farmers, energy producers, and local communities alike.
- The IRA allocated $144 million in grant funding for underutilized technologies through USDA REAP (USDA 2024). A joint initiative between USDA and DOE was launched in February 2024 to help farmers cut costs and increase income through REAP-supported distributed wind projects.
Trends
Use Of AI And IOT In Turbine Management
The integration of AI and IoT trends in small wind power management is driving significant advancements in the wind turbine market, enhancing efficiency, reducing operational costs, and contributing to the growth of renewable energy adoption. IoT sensors and AI-powered analytics are being incorporated into turbines to optimize performance, monitor real-time data, and predict maintenance needs.
IoT sensors can track various metrics such as wind speed, turbine efficiency, and system health, providing crucial insights that help operators improve performance and extend the life of the turbines. AI algorithms can analyze this data to predict when maintenance is needed, reducing downtime and minimizing the costs associated with unexpected failures. This integration allows for more proactive and efficient turbine management, increasing the overall reliability and profitability of small wind power systems.
Additionally, the growing demand for sustainable and low-power energy sources, particularly in applications such as IoT networks, is creating new opportunities for small wind power. As the IoT ecosystem continues to expand, according to International Data Corporation, the number of connected IoT devices is projected to reach 55.7 billion by 2025, thus raising the need for reliable, decentralized, and renewable energy sources.
Adoption of 3d printing in turbine manufacturing
The adoption of 3D printing in small wind turbine (SWT) manufacturing is revolutionizing the industry by enabling the production of customized, lightweight, and high-performance components. Traditional manufacturing methods often struggle to produce complex geometries, especially for turbine blades with specific aerodynamic features. 3D printing allows for intricate blade designs that optimize performance and increase energy output, making small wind turbines more efficient and cost-effective. This flexibility in design is critical for adapting turbines to diverse wind conditions, which boosts energy production and enhances the overall effectiveness of small wind systems.
In addition to performance benefits, 3D printing is driving advancements in material science for small wind turbines. Manufacturers can now use advanced, durable materials tailored for extreme conditions, ensuring turbine longevity and reliability. The ability to create stronger, lighter components reduces production costs, which makes small wind turbines more affordable for both residential and commercial markets. With reduced material waste and faster production times, 3D printing is streamlining the supply chain and contributing to the broader adoption of small wind turbines, helping to accelerate the growth of the renewable energy sector.
Geopolitical Impact Analysis
Geopolitical factors shape the small wind turbine market by impacting supply chains, trade, and energy policies.The geopolitical landscape plays a significant role in shaping the small wind power market by influencing supply chains, international trade policies, and the pace of renewable energy adoption. As countries strive to meet climate goals and energy security needs, the demand for wind energy has surged, making wind power turbine technology a critical area of focus.
Geopolitical tensions, such as trade wars or sanctions, can disrupt the flow of raw materials, especially for key components like polysilicon, which is central to the production of turbine towers, nacelle, rotors (including blades and hub), generators, and foundations. For instance, trade tensions between China and the U.S. have impacted turbine prices and the availability of certain materials, leading to fluctuations in market dynamics. Furthermore, geopolitical factors influence energy policies and investments in different regions. Countries that prioritize renewable energy for energy independence or to reduce reliance on fossil fuels are increasingly adopting supportive policies, subsidies, and incentives to boost wind turbine energy capacity.
Additionally, regions with political instability may face slower adoption due to the challenges of maintaining stable infrastructure and long-term policy frameworks. The global energy transition also presents opportunities for countries to strengthen energy partnerships, such as through international collaborations on wind technologies and the development of new markets, particularly in emerging economies. Overall, geopolitical factors will continue to shape the development, expansion, and accessibility of the small wind turbine market, influencing both supply and demand for small wind power technologies.
Regional Analysis
In 2024, Asia Pacific dominated the global small wind power market, accounting for 46.3% of the total market share, Driven by increasing demand for renewable energy sources, government initiatives, and the need to address energy access in remote and rural areas. As countries in the region, including China, India, Japan, and South Korea, focus on reducing their carbon footprints and improving energy security, Small Wind Power is being recognized as a viable and cost-effective solution to meet energy demands in off-grid locations and low-wind areas.
Additionally, China, which dominates the global wind power market, is set to significantly increase wind power development in its rural regions following a new plan by the National Energy Administration. The initiative will focus on small-scale wind projects in rural areas, supported by partnerships between wind power companies and local governments.
- According to the China Wind Energy Equipment Association (2024) report a total of 86.5 MW, or 92% of the global small wind capacity deployed in 2023. China’s small wind capacity has increased each year since 2019 and the 86.5 MW installed in 2023 represents a 43% increase over small wind installations in 2022.
Furthermore, another important factor propelling the growth of the small wind power market in the Asia Pacific region is the ongoing efforts to transition toward cleaner, more sustainable energy. With countries like China and India leading the charge in renewable energy adoption, there has been a push to deploy small-scale wind power solutions, particularly in rural and agricultural sectors. These systems can be used to power homes, farms, telecommunications towers, and even remote industries that are not connected to the main electrical grid. In countries like India, the government has launched various incentives and policies aimed at promoting renewable energy, which has increased the popularity of small wind power systems.
- India is a leader in large onshore utility-scale wind installations, with a cumulative capacity of over 46 GW as of June 2024.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Key players in the Small Wind Power market focus on offering cost-effective, renewable energy to cater to high-end consumers.
Key players in the global small wind power market include Aeolos Wind Energy, Bergey Wind Power, Ennera Energy and Mobility, Gaia-Wind Ltd., and ABB Ltd, all of which are renowned for their high-efficiency turbine modules and strong global presence. City Windmills and Rise Energy focus on innovative turbine and grid technologies and extensive manufacturing capacities.
Sharp and Siemens AG offer reliable turbines and tower solutions, while ABB, Vestas Wind Systems A/S, and Ennera Energy and Mobility, S.L. are leaders in wind power and energy management systems. These companies are crucial drivers of technological advancements and the expansion of renewable energy globally.
Top Key Players
- ABB Ltd.
- Aeolos Wind Energy
- Bergey Wind Power Co
- City Windmills
- Endurance Wind Power Inc.
- Ennera Energy and Mobility, S.L.
- Eocycle Technologies Inc.
- Evance Wind Turbines Ltd.
- Gaia-Wind Ltd.
- Kestrel Wind Turbines
- Kingspan Group PLC
- Northern Power Systems Corp.
- Polaris America LLC
- Qingdao Anhua New Energy Equipment Co., Ltd.
- Quietrevolution Ltd.
- Raum Energy Inc.
- Ryse Energy
- SD Wind Energy Limited
- Shanghai Ghrepower Green Energy Co., Ltd.
- Siemens AG
- Sinovel Wind Group Co., Ltd.
- Southwest Windpower Inc.
- Superwind GmbH
- TUGE Energia
- UGE International Ltd.
- Unitron Energy Systems Pvt. Ltd.
- VENSYS Energy AG
- Vestas Wind Systems A/S
- Wind Energy Solutions
- Windflow Technology Ltd.
- XZERES Corporation
- Xzeres Wind Corp.
- Zephyr Corporation
- Zkenergy Science & Technology CO., LTD.
Recent Developments
- In November 2024 – Freen OÜ, an Estonia-based manufacturer of small wind solutions, is revolutionizing wind energy with its innovative Vertical Axis Wind Turbines (VAWTs), including the Freen-20 and Freen-3. By combining efficiency, low maintenance, and versatility, these turbines are making wind energy accessible to a variety of locations, from urban rooftops to rural landscapes. Freen’s focus on compact, eco-friendly, and durable turbines is helping to shape the future of renewable energy for both residential and commercial use.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 12.1 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 37.6 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 12.0% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Axis Type (Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines (HAWT), Vertical Axis Wind Turbines (VAWT)), By Grid Type (On-Grid, Off-Grid), By Capacity (Up To 1 KW, 1 KW – 10 KW, 10 KW To 100 KW), By Application (Residential, Commercial, Utility) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape ABB Ltd., Aeolos Wind Energy, Bergey Wind Power Co, City Windmills, Endurance Wind Power Inc., Ennera Energy and Mobility, S.L., Eocycle Technologies Inc., Evance Wind Turbines Ltd., Gaia-Wind Ltd., Kestrel Wind Turbines, Kingspan Group PLC, Northern Power Systems Corp., Polaris America LLC, Qingdao Anhua New Energy Equipment Co., Ltd., Quietrevolution Ltd., Raum Energy Inc., Ryse Energy, SD Wind Energy Limited, Shanghai Ghrepower Green Energy Co., Ltd., Siemens AG, Sinovel Wind Group Co., Ltd., Southwest Windpower Inc., Superwind GmbH, TUGE Energia, UGE International Ltd., Unitron Energy Systems Pvt. Ltd., VENSYS Energy AG, Vestas Wind Systems A/S, Wind Energy Solutions, Windflow Technology Ltd., XZERES Corporation, Xzeres Wind Corp., Zephyr Corporation, Zkenergy Science & Technology CO., LTD. Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- ABB Ltd.
- Aeolos Wind Energy
- Bergey Wind Power Co
- City Windmills
- Endurance Wind Power Inc.
- Ennera Energy and Mobility, S.L.
- Eocycle Technologies Inc.
- Evance Wind Turbines Ltd.
- Gaia-Wind Ltd.
- Kestrel Wind Turbines
- Kingspan Group PLC
- Northern Power Systems Corp.
- Polaris America LLC
- Qingdao Anhua New Energy Equipment Co., Ltd.
- Quietrevolution Ltd.
- Raum Energy Inc.
- Ryse Energy
- SD Wind Energy Limited
- Shanghai Ghrepower Green Energy Co., Ltd.
- Siemens AG
- Sinovel Wind Group Co., Ltd.
- Southwest Windpower Inc.
- Superwind GmbH
- TUGE Energia
- UGE International Ltd.
- Unitron Energy Systems Pvt. Ltd.
- VENSYS Energy AG
- Vestas Wind Systems A/S
- Wind Energy Solutions
- Windflow Technology Ltd.
- XZERES Corporation
- Xzeres Wind Corp.
- Zephyr Corporation
- Zkenergy Science & Technology CO., LTD.









