Waste to Energy Market Size, Share, And Business Benefits By Technology (Thermochemical, Biochemical), By Waste Type(Municipal Solid Waste, Process Waste, Agriculture Waste, Others), By Application (Electricity, Heat, Others), By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends, and Forecast 2024-2033
- Published date: December 2024
- Report ID: 135781
- Number of Pages: 281
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
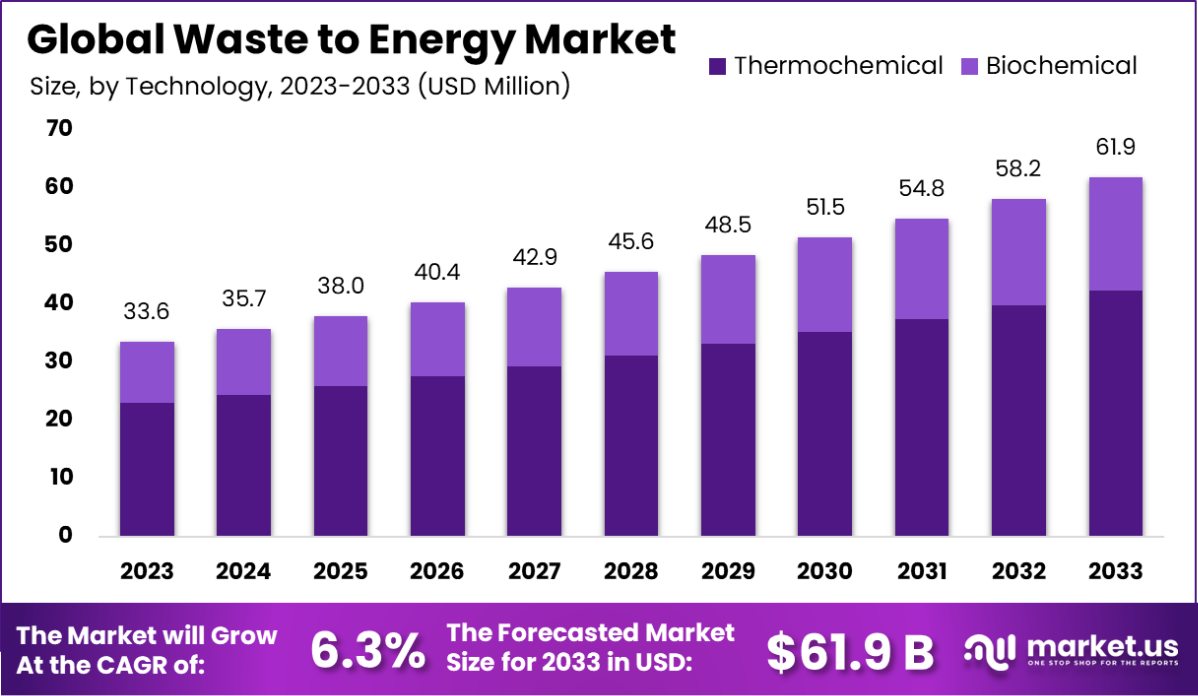
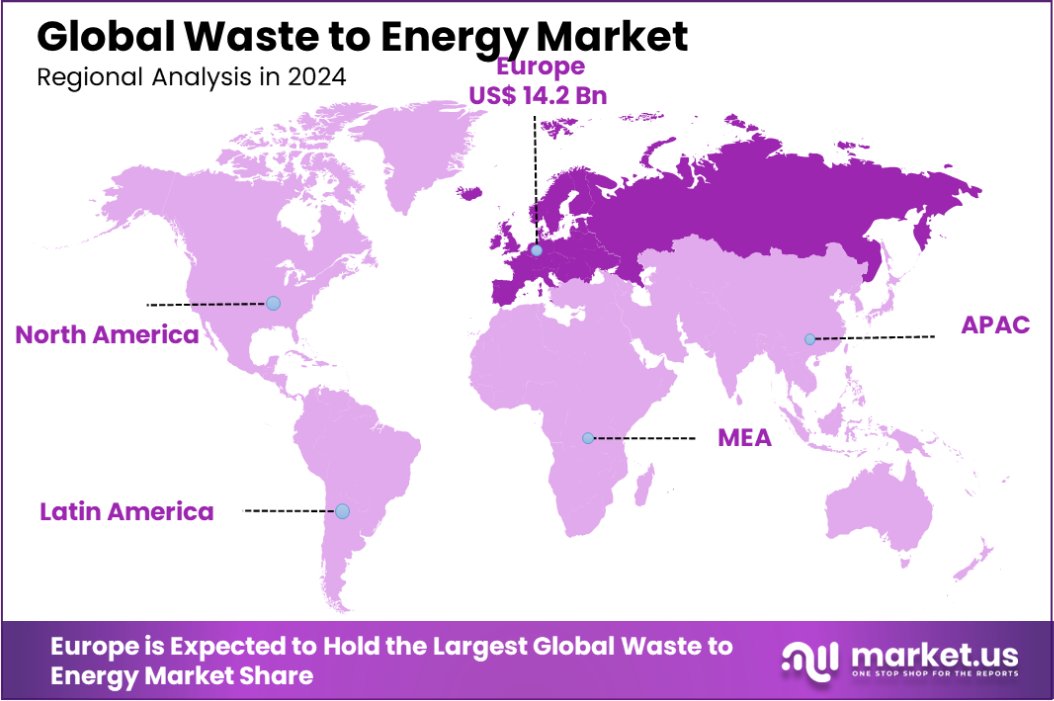
The Global Waste to Energy Market is expected to be worth around USD 61.9 Billion by 2033, up from USD 33.6 Billion in 2023, and grow at a CAGR of 6.3% from 2024 to 2033. The European waste-to-energy market holds 42.3%, valued at USD 14.2 billion.
Waste to Energy (WtE) is a process that converts non-recyclable waste materials into usable heat, electricity, or fuel through various processes such as combustion, gasification, pyrolysis, anaerobic digestion, and landfill gas recovery. This transformation helps in reducing the volume of waste sent to landfills and generates energy from materials that would otherwise remain untapped.
The Waste to Energy Market is expanding due to several factors. One significant growth factor is the increasing global urbanization leading to larger amounts of municipal solid waste. This, coupled with rising awareness about sustainable waste management practices, drives the demand for WtE solutions.
Additionally, government initiatives supporting renewable energy sources and stricter waste disposal regulations present substantial opportunities for market expansion. These policies encourage the development of WtE facilities to manage waste effectively while contributing to energy generation, aligning with global sustainability goals.
The Waste to Energy (WTE) market in the United States showcases a robust sector dedicated to sustainability and energy production through the management of municipal solid waste (MSW). As of 2022, the nation hosts 60 operational WTE plants, embodying a cumulative generating capacity of 2,051 megawatts (MW).
These facilities play a crucial role in the energy ecosystem by producing approximately 14,000 gigawatt-hours (GWh) annually over the past decade, reflecting a stable and significant contribution to the renewable energy landscape.
The environmental impact and utility of these plants are substantial. In 2018, the U.S. combusted nearly 35 million tons of MSW—equating to 11.8% of the total MSW generated—that year, harnessing it for energy recovery. This process not only helps reduce landfill usage but also contributes to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
The scale of these operations varies, with the average WTE plant possessing a capacity of 34 MW. Notably, none of the existing plants exceeds 100 MW, indicating a market dominated by mid-sized facilities that collectively manage significant volumes of waste.
In 2022 alone, WTE facilities processed 16.0 million tons of biogenic waste material alongside 10.3 million tons of non-biogenic waste, underscoring their pivotal role in waste management and energy production. This capacity for handling a diverse range of waste materials further emphasizes the WTE sector’s adaptability and alignment with national sustainability goals.
Moving forward, the market is poised for growth, driven by increased waste output, the push for renewable energy sources, and evolving technologies that enhance efficiency and environmental compliance in WTE operations.
Key Takeaways
- The Global Waste to Energy Market is expected to be worth around USD 61.9 Billion by 2033, up from USD 33.6 Billion in 2023, and grow at a CAGR of 6.3% from 2024 to 2033.
- The Waste to Energy market majorly employs thermochemical technologies, capturing a significant 68.4% share.
- Municipal Solid Waste is predominantly processed in this sector, accounting for 56.6% of the waste type.
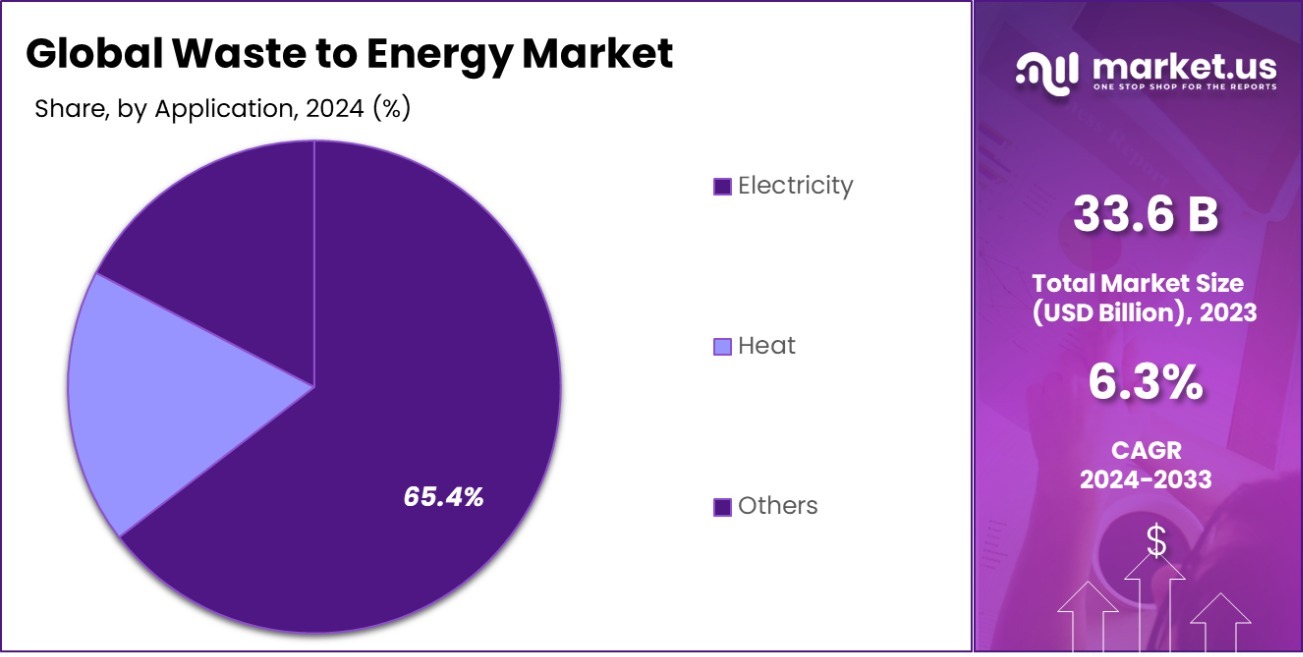
- Electricity generation is a primary application within this market, comprising 65.4% of its usage.
- The waste-to-energy market in Europe holds a 42.3% share, valued at USD 14.2 billion.
Waste to Energy Business Benefits
Investing in waste-to-energy (WtE) businesses offers significant environmental and economic benefits. WtE plants can reduce waste volume by approximately 87%, substantially decreasing landfill usage and mitigating associated environmental hazards.
Environmentally, WtE facilities contribute to lower greenhouse gas emissions. For instance, ecomaine’s WtE plant processes over 175,000 tons of waste annually, generating about 100,000 megawatt-hours of electricity—sufficient to power approximately 15,000 homes each year. This process reduces waste volume by 90%, resulting in smart greenhouse gas emissions that are between 53% and 267% lower than those from landfills.
Economically, WtE facilities can generate revenue through tipping fees and energy sales. The U.S. Department of Energy notes that the United States has the potential to use 77 million dry tons of wet waste per year, generating about 1.079 quadrillion British thermal units (Btu) of energy.
By Technology Analysis
In the Waste to Energy market, thermochemical processes dominate with a substantial 68.4% share.
In 2023, Thermochemical held a dominant market position in the “By Technology” segment of the Waste to Energy Market, securing a 68.4% share. This technology, which includes processes like gasification, pyrolysis, and combustion, has become increasingly popular due to its efficiency in converting high volumes of waste into energy.
Thermochemical methods are particularly valued for their ability to process a wide range of waste types, including non-recyclable plastics and other municipal solid waste, into usable forms of energy like electricity and heat.
On the other hand, the Biochemical category, which primarily involves anaerobic digestion and fermentation techniques, accounted for a smaller portion of the market. Although it represents a lesser share, biochemical processes are crucial for converting organic waste materials into biogas and other biofuels.
These methods are celebrated for their environmental benefits, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable waste management practices.
Together, these technologies underscore the growing emphasis on sustainability and the shift towards more renewable energy sources in waste management strategies. As the global population continues to grow and urbanize, the reliance on advanced waste-to-energy technologies is expected to rise, potentially reshaping how cities around the world manage their waste challenges.
By Waste Type Analysis
Municipal Solid Waste is the most commonly treated waste type, representing 56.6% of the market.
In 2023, Municipal Solid Waste held a dominant market position in the “By Waste Type” segment of the Waste to Energy Market, boasting a 56.6% share. This significant figure highlights the growing reliance on urban waste management solutions to generate energy, reflecting broader sustainability trends.
Process Waste and Agricultural Waste also contributed to the market, though to a lesser extent. These segments underscore the diverse sources of waste that can be harnessed to meet energy demands, showcasing innovative approaches to waste management.
The prominence of Municipal Solid Waste is indicative of the scale at which urban areas are engaging with waste-to-energy technologies. This trend is driven by the dual challenges of managing increasing waste volumes and meeting energy needs sustainably.
As cities continue to grow, the integration of effective waste-to-energy solutions becomes crucial. The market’s dynamics suggest a robust interest in transforming everyday waste into a valuable resource, thus supporting both environmental goals and energy security.
These insights are essential for stakeholders looking to invest in or expand their capabilities within this promising sector.
By Application Analysis
The primary application of Waste to Energy technology is electricity generation, accounting for 65.4%.
In 2023, Electricity held a dominant market position in the “By Application” segment of the Waste to Energy Market, capturing a substantial 65.4% share. This prominence underscores its crucial role in transforming waste materials into usable energy. Alongside Electricity, Heat also plays a significant part in this segment, though it occupies a smaller portion of the market.
This trend towards Electricity is driven by increasing investments in sustainable and renewable energy sources, as governments and corporations alike seek to reduce carbon footprints and promote environmental sustainability. The integration of advanced technological solutions has further enhanced the efficiency of converting waste to electricity, thereby bolstering its market share.
Meanwhile, the Heat segment benefits from its application in district heating systems and industrial processes, where the recovery of heat from waste conversion processes can significantly reduce energy costs and dependency on conventional fossil fuels.
As the waste to energy sector evolves, the continued growth and adaptation of these technologies are likely to reshape market dynamics. This ongoing development not only supports global sustainability efforts but also presents new opportunities for innovation and investment in the energy sector.
Key Market Segments
By Technology
- Thermochemical
- Biochemical
By Waste Type
- Municipal Solid Waste
- Process Waste
- Agriculture Waste
- Others
By Application
- Electricity
- Heat
- Others
Driving Factors
Rising Demand for Renewable Energy Sources
The increasing demand for renewable energy solutions globally is a major driver for the waste to energy market. As fossil fuel reserves deplete and the world seeks more sustainable energy sources, converting waste into energy offers a dual benefit—reducing landfill mass and generating energy.
Technologies such as incineration, gasification, and anaerobic digestion are gaining traction because they convert waste products into electricity, heat, or fuel, thus providing a cleaner alternative to conventional energy sources.
Government Policies Favoring Sustainable Waste Management
Governments worldwide are implementing stricter regulations on waste management to combat pollution and reduce reliance on landfilling. These policies often include incentives for waste to energy projects, such as subsidies, tax benefits, and financial support for research and development.
Such regulatory support encourages municipal and private investments in waste to energy facilities, making it an attractive option for cities dealing with large volumes of waste and aiming for sustainability goals.
Technological Advancements in Waste to Energy Conversion
The waste to energy market is propelled by continuous advancements in technology that increase the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of converting waste into energy. Innovations in thermal and biological treatment processes have enhanced the energy output while minimizing environmental impacts.
Improved sorting and preprocessing technologies also maximize the capture of usable waste materials. These technological enhancements make waste to energy conversion more appealing and feasible for broader adoption.
Restraining Factors
High Initial Investment and Operating Costs
The Waste to Energy (WtE) market faces significant financial barriers due to the high initial costs required to establish facilities. These plants demand advanced technology and infrastructure, making them capital-intensive. Moreover, the operating costs linked to maintenance, labor, and compliance with environmental regulations further strain financial resources.
This high expenditure limits market entry to entities capable of making substantial investments, thereby restricting the growth and widespread adoption of WtE solutions, especially in regions with limited financial support for renewable energy projects.
Stringent Environmental Regulations
WtE facilities are subject to rigorous environmental regulations aimed at controlling emissions and ensuring safe waste processing. These regulations are often strict and vary significantly by region, creating a complex legal landscape for operators. Compliance requires advanced technology and can lead to increased operational costs.
The stringent standards, while necessary for protecting the environment, act as a deterrent for new entrants and can slow down the technological advancements needed to make WtE solutions more efficient and less environmentally impactful.
Limited Waste Segregation Practices
Effective waste-to-energy conversion relies heavily on the quality of waste input, which is significantly enhanced by proper waste segregation at the source. In many regions, particularly in developing countries, waste segregation practices are inadequate or non-existent.
This leads to a mix of recyclable, organic, and inorganic waste, complicating the processing and efficiency of WtE systems. The lack of segregation not only reduces the energy recovery rates but also increases the wear and tear on facility machinery, posing a major restraint on the efficiency and expansion of the WtE market.
Growth Opportunity
Expansion into Emerging Markets for Increased Coverage
Emerging markets present a significant growth opportunity for the waste-to-energy sector, given their rapid urbanization and escalating waste generation rates. These regions often lack adequate waste management infrastructure, making them ideal candidates for the implementation of waste-to-energy solutions.
Companies can leverage local partnerships to navigate regulatory environments and cultural landscapes, enhancing their market entry strategies. By investing in these areas, businesses can not only solve local waste management challenges but also generate renewable energy, contributing to regional energy needs and sustainability goals.
Technological Innovations in Waste-to-Energy Conversion
Advancements in technology are pivotal for the growth of the waste-to-energy market. Innovations such as thermal technologies (like gasification and pyrolysis) and biological treatments (such as anaerobic digestion) can significantly enhance efficiency and energy output.
These technologies also reduce emissions and increase the types of waste that can be effectively converted into energy. Companies investing in research and development to improve these technologies can achieve lower operational costs, higher energy yields, and meet stricter environmental regulations, thus gaining a competitive edge in the market.
Integration of Circular Economy Practices
Integrating circular economy principles into waste-to-energy processes offers a substantial growth avenue. This approach emphasizes the reuse and recycling of resources to maximize value extraction from waste before energy recovery.
By adopting these practices, companies can offer more comprehensive waste management solutions that appeal to environmentally conscious stakeholders and regulators. Additionally, this integration can open new revenue streams through byproducts like biochar from pyrolysis or compost from digestion processes, further enhancing profitability and environmental sustainability.
Latest Trends
Growing Emphasis on Thermal Technologies for Energy Recovery
The Waste to Energy (WtE) market is increasingly adopting thermal technologies such as incineration and gasification. These processes are favored for their ability to reduce waste volume significantly while generating energy. Thermal WtE technologies are seeing innovations that aim to increase energy efficiency and reduce emissions.
This shift is driven by the dual need to manage escalating waste volumes in urban areas and the global push towards sustainable energy sources. Governments and private sectors are investing in advanced thermal treatment facilities, reflecting their commitment to sustainable waste management solutions.
Rise of Biogas Production from Organic Waste
Biogas production is gaining momentum as a key trend in the Waste to Energy sector. This process involves the anaerobic digestion of organic waste materials to produce methane-rich biogas, which can be used as a renewable energy source or converted into electricity and heat. The attraction to biogas technology lies in its ability to handle a variety of organic wastes, including agricultural residues, food waste, and sewage sludge.
As countries look for more circular economy solutions, biogas stands out for its potential to contribute to both waste reduction and renewable energy goals.
Integration of WtE Solutions in Smart Cities
Smart cities around the world are integrating Waste to Energy solutions into their urban infrastructure to manage waste more effectively and sustainably. This trend involves the use of technology to optimize waste collection and energy recovery processes, linking WtE systems with smart grids and renewable energy sources.
The focus is on creating energy-efficient systems that not only dispose of waste but also contribute to the energy supply of the city. This integration supports the broader vision of smart cities to enhance environmental sustainability and resource efficiency.
Regional Analysis
The waste-to-energy market in Europe holds a 42.3% share, valued at USD 14.2 billion.
The Waste to Energy (WtE) market is experiencing significant growth across various regions, driven by escalating waste volumes and a shifting focus towards renewable energy sources. In North America, advancements in thermal technologies and stringent waste management regulations propel the market forward.
Europe remains the dominating region in the WtE sector, holding a 42.3% market share and valued at USD 14.2 billion. This dominance is supported by aggressive environmental policies and high adoption rates of WtE solutions across EU member states.
Asia Pacific is witnessing rapid market expansion due to urbanization and industrialization, especially in countries like China and India, where government initiatives support infrastructure development for waste management.
The Middle East & Africa region, although smaller in comparison, shows potential for growth through increased investments in sustainable practices and the modernization of waste management systems.
Latin America, too, is making strides with countries like Brazil leading the way in integrating WtE facilities to tackle municipal waste challenges. Collectively, these regional dynamics highlight a robust and diversifying global market landscape for Waste to Energy initiatives.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
In 2023, the global Waste to Energy (WtE) market will be significantly shaped by the activities and strategic developments of key companies. Among these, Abu Dhabi National Energy Company PJSC stands out for its investments in advanced thermal treatment facilities, aiming to support the UAE’s sustainability goals.
European players like Attero and AVR are pivotal, focusing on high-efficiency incineration technologies and the recovery of valuable materials and energy from waste, contributing to Europe’s leading position in the WtE sector.
American firms such as Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises, Inc., and Wheelabrator Technologies Inc., continue to innovate in biomass conversion and thermal technologies. These enhancements are crucial as North America looks to reduce landfill use and carbon emissions. China Everbright International Limited exemplifies growth in Asia Pacific, expanding aggressively to capitalize on China’s push towards renewable energy from waste.
Covanta Holding Corporation remains a giant, with its facilities across the U.S. demonstrating significant operational efficiencies and energy recovery rates, thus setting industry benchmarks. Meanwhile, technology providers like Hitachi Zosen Inova AG and Huawei Enterprise are advancing WtE conversion technologies, integrating digital solutions to optimize energy production and environmental compliance.
Companies like Veolia and Suez are instrumental in driving the WtE market with their global reach and comprehensive waste management solutions, aligning with circular economy principles.
Ramboll Group A/S and Viridor also contribute significantly to market dynamics through consultancy and operational excellence in European regions. Lastly, Xcel Energy Inc. highlights the integration of WtE solutions into broader renewable energy portfolios, emphasizing sustainability in energy practices.
These companies, with their diverse technological and regional approaches, play a crucial role in shaping the WtE market’s trajectory, focusing on innovation, sustainability, and regional market penetration to drive forward the industry in 2023.
Top Key Players in the Market
- Abu Dhabi National Energy Company PJSC
- Allseas
- Attero
- AVR
- Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises, Inc.
- China Everbright International Limited
- Covanta Holding Corporation
- EDF
- Hitachi Zosen Inova AG
- Huawei Enterprise
- Ramboll Group A/S
- Suez
- Veolia
- Viridor
- Wheelabrator Technologies Inc.
- Xcel Energy Inc.
Recent Developments
- In 2023, Abu Dhabi National Energy Company PJSC (TAQA) made significant strides in the waste-to-energy sector, focusing on sustainability and renewable energy integration. Notable achievements include advancing a major waste-to-energy project near the Al-Dhafra landfill, expected to process 900,000 tonnes of non-recyclable waste annually and reduce CO2 emissions by 1.1 million tonnes each year.
- In 2023, Allseas has been actively involved in various projects contributing to waste reduction and environmental sustainability, notably through its innovative “Catchy 2” system designed for collecting riverine litter. This system is positioned under Rotterdam’s Erasmus Bridge and plays a significant role in managing waste in the Maas River.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2023) USD 33.6 Billion Forecast Revenue (2033) USD 61.9 Billion CAGR (2024-2033) 6.3% Base Year for Estimation 2023 Historic Period 2019-2022 Forecast Period 2024-2033 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Technology (Thermochemical, Biochemical), By Waste Type(Municipal Solid Waste, Process Waste, Agriculture Waste, Others), By Application (Electricity, Heat, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Abu Dhabi National Energy Company PJSC, Allseas, Attero, AVR, Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises, Inc., China Everbright International Limited, Covanta Holding Corporation, EDF , Hitachi Zosen Inova AG, Huawei Enterprise, Ramboll Group A/S, Suez, Veolia, Viridor, Wheelabrator Technologies Inc., Xcel Energy Inc. Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Waste to Energy MarketPublished date: December 2024add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Waste to Energy MarketPublished date: December 2024add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Abu Dhabi National Energy Company PJSC
- Allseas
- Attero
- AVR
- Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises, Inc.
- China Everbright International Limited
- Covanta Holding Corporation
- EDF
- Hitachi Zosen Inova AG
- Huawei Enterprise
- Ramboll Group A/S
- Suez
- Veolia
- Viridor
- Wheelabrator Technologies Inc.
- Xcel Energy Inc.









