Global Sustainable Food Market Size, Share, And Business Benefits By Product Type (Fruits and Vegetables, Seafood and Seaweed, Cereals and grains, Mussels, Mushrooms), By Distribution Channel (Hypermarkets/Supermarkets, E-Commerce, Convenience Stores), By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends, and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: October 2025
- Report ID: 163396
- Number of Pages: 325
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
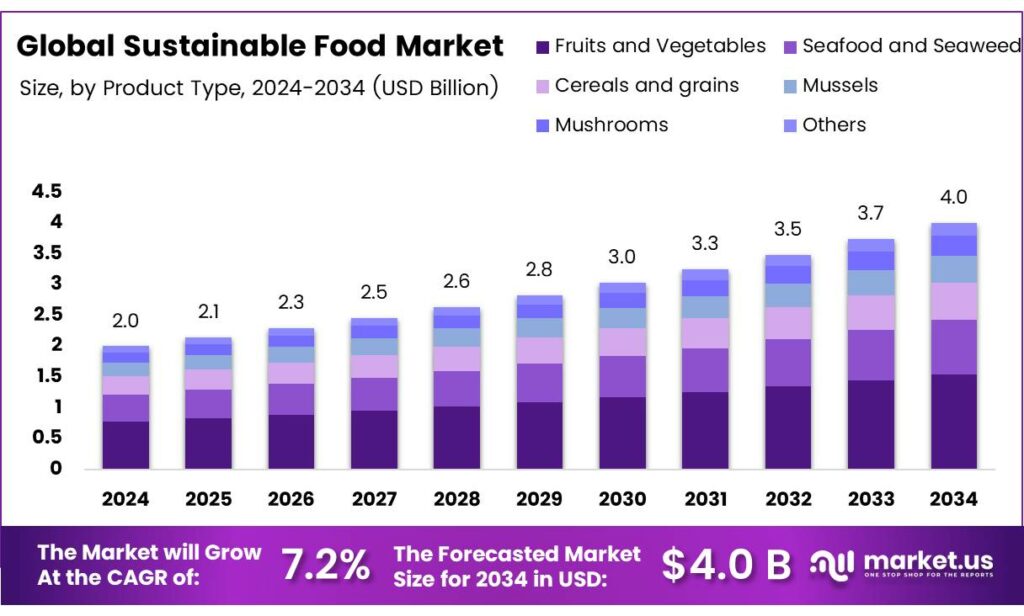
The Global Sustainable Food Market size is expected to be worth around USD 4.0 billion by 2034, from USD 2.0 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 7.2% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
Food systems include all actors and activities involved in producing, aggregating, processing, distributing, consuming, and disposing of food from agriculture, forestry, or fisheries. They operate within wider economic, societal, and natural contexts, comprising sub-systems like farming, waste management, and input supply. These systems interact with energy, trade, and health sectors, meaning changes in one area, such as energy policies promoting biofuels, can significantly impact food production and availability.
Food production generates about 30% of global greenhouse gas emissions, with livestock responsible for nearly half, 14.5%. It uses 40% of the world’s land, 70% of freshwater, and drives most species to extinction. Nutrient runoff causes eutrophication and dead zones in waters. Meanwhile, 60% of fish stocks are fully fished, 33% overfished, and only 7% underfished.
These pressures contribute to global environmental changes that increase mortality, conflict, and food insecurity. Agriculture both causes and suffers from these crises. Without urgent reform, the world risks failing the Sustainable Development Goals and the Paris Agreement. Global food systems are fundamentally unsustainable, requiring a rethink of both production methods and consumption patterns.
A sustainable food system ensures food security and nutrition for all without compromising future generations’ economic, social, or environmental foundations. It requires profitability (economic sustainability), broad societal benefits (social sustainability), and neutral or positive environmental impacts (environmental sustainability). Central to the UN Sustainable Development Goals, sustainable food systems are vital for ending hunger and improving nutrition.
Key Takeaways
- The Global Sustainable Food Market is projected to reach USD 4.0 billion by 2034 from USD 2.0 billion in 2024, with a CAGR of 7.2% from 2025 to 2034.
- The Fruits and Vegetables segment dominates with 38.6% market share, driven by health awareness and organic produce demand.
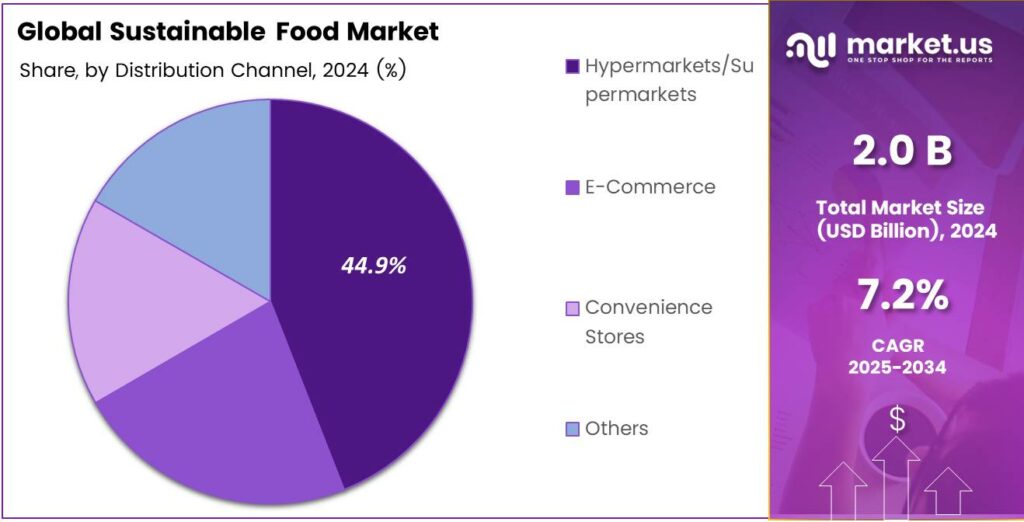
- Hypermarkets and Supermarkets lead distribution with a 44.9% share, owing to one-stop shopping convenience and product variety.
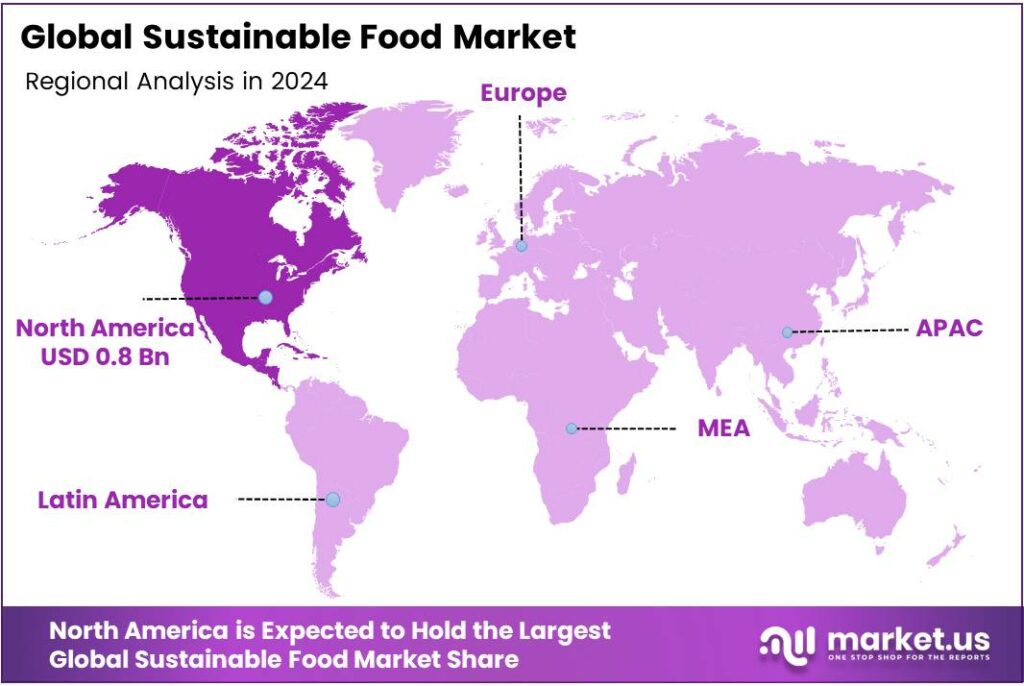
- North America holds a 41.5% dominant share in 2024, valued at USD 0.8 billion in the global market.
By Product Type
Fruits and Vegetables dominate with 38.6% due to rising health awareness and demand for organic produce.
In 2024, Fruits and Vegetables held a dominant market position in the By Product Type Analysis segment of the Sustainable Food Market, with a 38.6% share. Consumers increasingly prefer fresh, pesticide-free options. This sub-segment thrives on seasonal availability and local farming. Moreover, certifications boost trust.
Shifting to Seafood and Seaweed, this sub-segment gains traction from omega-3 benefits and marine sustainability. Eco-labeled products appeal to health-conscious buyers. Additionally, aquaculture innovations reduce overfishing concerns. Demand rises in coastal regions. However, supply chain traceability remains key for expansion.
Moving onward to Cereals and Grains, ancient varieties like quinoa and millet lead preferences. Organic farming practices enhance soil health. Furthermore, gluten-free trends drive growth. Packaging emphasizes carbon footprints. Consumers seek whole-grain nutrition, supporting steady market penetration.
By Distribution Channel
Hypermarkets and Supermarkets dominate with 44.9% due to one-stop shopping convenience and wide product variety.
In 2024, Hypermarkets and Supermarkets held a dominant market position in the By Distribution Channel Analysis segment of the Sustainable Food Market, with a 44.9% share. These outlets offer bulk buys and promotions. Shoppers value in-store eco-displays. Additionally, loyalty programs encourage repeat visits. Accessibility in urban areas fuels dominance.
Transitioning to E-Commerce, online platforms expand rapidly with home delivery. Sustainability filters help selections. Moreover, subscription models ensure regular supplies. Virtual reality tours showcase farms. This channel attracts tech-savvy millennials seeking convenience without compromise.
Finally, Convenience Stores cater to on-the-go consumers. Grab-and-go sustainable snacks rise in popularity. Compact packaging suits urban lifestyles. Furthermore, partnerships with local producers add freshness. Though smaller in scale, they bridge quick needs effectively.
Key Market Segments
By Product Type
- Fruits and Vegetables
- Seafood and Seaweed
- Cereals and grains
- Mussels
- Mushrooms
- Others
By Distribution Channel
- Hypermarkets/Supermarkets
- E-Commerce
- Convenience Stores
- Others
Emerging Trends
Cutting food loss and waste across the chain
- Governments, retailers, restaurants, and households are treating food loss and waste reduction as a climate, cost, and hunger solution, not an afterthought. The latest UN data shows 1.05 billion tonnes of food were wasted, about 19% of food available to consumers, equal to 132 kg per person; households caused 60%, food service 28%, and retail 12%.
At the other end of the chain, about 13.2% of food is lost after harvest and before retail, pointing to cold-chain, storage, and handling fixes that pay back quickly. Policy is catching up fast. The United States aims to halve food loss and waste, with the FDA, USDA, and EPA releasing a national strategy and ramping interagency collaboration with states, cities, and businesses. That unlocks funding, public procurement pilots.
In Europe, lawmakers agreed on 2030 targets: cut waste 10% in processing/manufacturing and 30% per capita across retail, restaurants, food services, and households, anchoring reduction into law and requiring more donation and measurement. UN estimates attribute 8–10% of global greenhouse gases to food that is never eaten, bigger than aviation plus shipping combined, and that’s before counting the land and water squandered.
Drivers
Climate change and resource pressures on food systems
One of the strongest drivers behind the urgent move towards sustainable food systems is the rapidly growing impact of climate change and natural-resource strain on agriculture. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), our current food and agriculture systems must shift because food and agriculture production systems worldwide are facing unprecedented challenges from an increasing demand.
FAO estimates that to feed a projected global population of around 9.6 billion by 2050, food production must increase by at least 60% a scale of growth that simply cannot be met without simultaneously tackling resource depletion, land-use change, and climate impacts.
- In 2024, over 295 million people across 53 countries faced acute hunger amid severe food-security breakdowns, an increase of nearly 14 million from the year before. These statistics underline that food systems are already strained, especially where extreme weather, droughts, floods, or other climate shocks intersect with fragile supply chains.
Restraints
Affordability and financing gaps block sustainable diets
The biggest brake on sustainable food is simple: people and producers can’t afford it. Even as awareness grows, the average cost of a healthy diet reached USD 4.46 (PPP) per person per day in 2024, putting balanced, diverse foods out of reach for many low-income households. Globally, about 2.6 billion people could not afford a healthy diet in 2024, a sobering signal that price, income, and access still dominate choices more than sustainability labels or intentions.
- On the supply side, millions of small farms want to adopt climate-smart, soil-building practices mulching, diversified rotations, and water-saving irrigation, but lack patient capital. Small-scale farmers receive only 0.8% of global climate finance, USD 5.5 billion/year, while their adaptation financing gap is about USD 75 billion per year. That shortfall delays basic investments in on-farm storage, solar cold rooms, and efficient pumps.
Governments are responding through school-meal standards, public procurement of local produce, fertilizer-to-soil-health reforms, and concessional funds, but today’s numbers tell us the core restraint remains economic. Until healthy diets become affordable for households, and affordable finance reaches producers at scale, sustainable food will remain a premium niche rather than the default plate.
Opportunity
Rising global agricultural production and dietary demand
- The growing global demand for food and the rising production capacities in agriculture and livestock. According to the OECD-Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) Agricultural Outlook for 2025-2034, the gross value of global agricultural production is projected to increase by 14% by 2034, reaching about USD 3.96 trillion. Agriculture sectors will lead with livestock production growing 16%, crops 14%, and fish and other aquatic foods 12% in the same period.
In simple terms, this means that more food is being produced, and more diversified food, meats, dairy, and aquaculture are going to be eaten as incomes rise and diets evolve. This increased demand and production expansion make sustainable food systems not only desirable but necessary, because meeting the extra output with old methods would strain water, land, and climate even further.
Moreover, when production scales up in regions with improving infrastructure and technology rather than simply expanding land use, this growth factor aligns with sustainability. If aquaculture grows responsibly, then fish supplies can increase without putting additional stress on wild fisheries. Together, rising global production and dietary change are pulling the food system toward new sustainable-food opportunities—better productivity, broader access, and more efficient use of resources.
Regional Analysis
North America leads with a 41.5% share and a USD 0.8 Billion market value.
In 2024, North America held a dominant share of 41.5%, valued at USD 0.8 billion in the global sustainable food market. The region’s leadership is driven by growing consumer demand for ethical, organic, and locally sourced products, alongside stringent environmental regulations that encourage sustainable farming and food processing practices.
The United States and Canada are actively adopting sustainable agriculture technologies, including precision farming, regenerative soil methods, and vertical farming systems, to reduce waste and improve food security. Federal initiatives like the USDA’s Climate Smart Commodities Program and Canada’s Agricultural Climate Solutions Fund are channeling multi-million-dollar investments toward lowering the carbon footprint of food production.
Additionally, major food companies are reorienting their portfolios toward plant-based and low-emission ingredients, responding to rising consumer awareness around climate impact and animal welfare. The widespread presence of sustainability certifications, such as Fair Trade and Non-GMO Project Verified, has further reinforced consumer trust and market expansion.
The region’s innovation ecosystem, spanning food-tech startups, universities, and corporate research centers, continues to develop new protein alternatives, biodegradable packaging, and low-impact supply chains. Collectively, these initiatives position North America as a critical hub for advancing sustainability standards and driving the global transition toward a resilient, resource-efficient, and circular food economy.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Beyond Meat is a pioneering disruptor in the plant-based protein sector, directly targeting the sustainable food market. Its core mission is to offer alternatives to animal meat, addressing environmental and ethical concerns. By focusing on innovation and strategic partnerships with major food chains, it has captured significant market share and consumer mindshare.
General Mills leverages its vast portfolio and supply chain to integrate sustainability. The company focuses on ambitious goals like regenerative agriculture, sustainable sourcing for its major brands, and reducing its environmental footprint. Its strategy involves incrementally improving existing products and acquiring emerging brands to capture eco-conscious consumers.
Tyson Foods, a global protein powerhouse, employs a dual strategy. It is investing heavily in alternative proteins through its venture capital arm, Tyson Ventures, backing companies in plant-based and cultivated meat. Simultaneously, it is working to improve the sustainability of its core animal protein operations through supply chain efficiency and environmental commitments.
Top Key Players in the Market
- Beyond Meat
- General Mills
- Tyson Foods
- Kellogg Company
- Archer Daniels Midland
- PepsiCo
- Cargill
- Campbell Soup Company
- Hain Celestial Group
- The Coca-Cola Company
Recent Developments
- In 2025, Beyond Meat, a pioneer in plant-based meat alternatives, will focus on enhancing product sustainability and health profiles. The company launched its Beyond IV platform, featuring updated Beyond Burger and Beyond Beef products at Erewhon stores.
- In 2025, Tyson Foods emphasized sustainable protein production, integrating environmental stewardship into operations amid financial growth. The company announced plans to eliminate high fructose corn syrup, sucralose, BHA/BHT, and titanium dioxide from U.S. branded products, advancing its mission for safe, affordable, and sustainable food.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 2.0 Billion Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 4.0 Billion CAGR (2025-2034) 7.2% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Product Type (Fruits and Vegetables, Seafood and Seaweed, Cereals and Grains, Mussels, Mushrooms, Others), By Distribution Channel (Hypermarkets/Supermarkets, E-Commerce, Convenience Stores, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Beyond Meat, General Mills, Tyson Foods, Kellogg Company, Archer Daniels Midland, PepsiCo, Cargill, Campbell Soup Company, Hain Celestial Group, The Coca-Cola Company Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited Users and Printable PDF)  Sustainable Food MarketPublished date: October 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Sustainable Food MarketPublished date: October 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Beyond Meat
- General Mills
- Tyson Foods
- Kellogg Company
- Archer Daniels Midland
- PepsiCo
- Cargill
- Campbell Soup Company
- Hain Celestial Group
- The Coca-Cola Company










