Global Feed Plant-Based Protein Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Type (Concentrates, Isolates, Others), By Source (Soy, Wheat, Pea, Sunflower, Others), By Livestock (Poultry, Pets, Swine, Ruminants, Aquatic Animals) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends, and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Aug 2025
- Report ID: 155101
- Number of Pages: 285
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
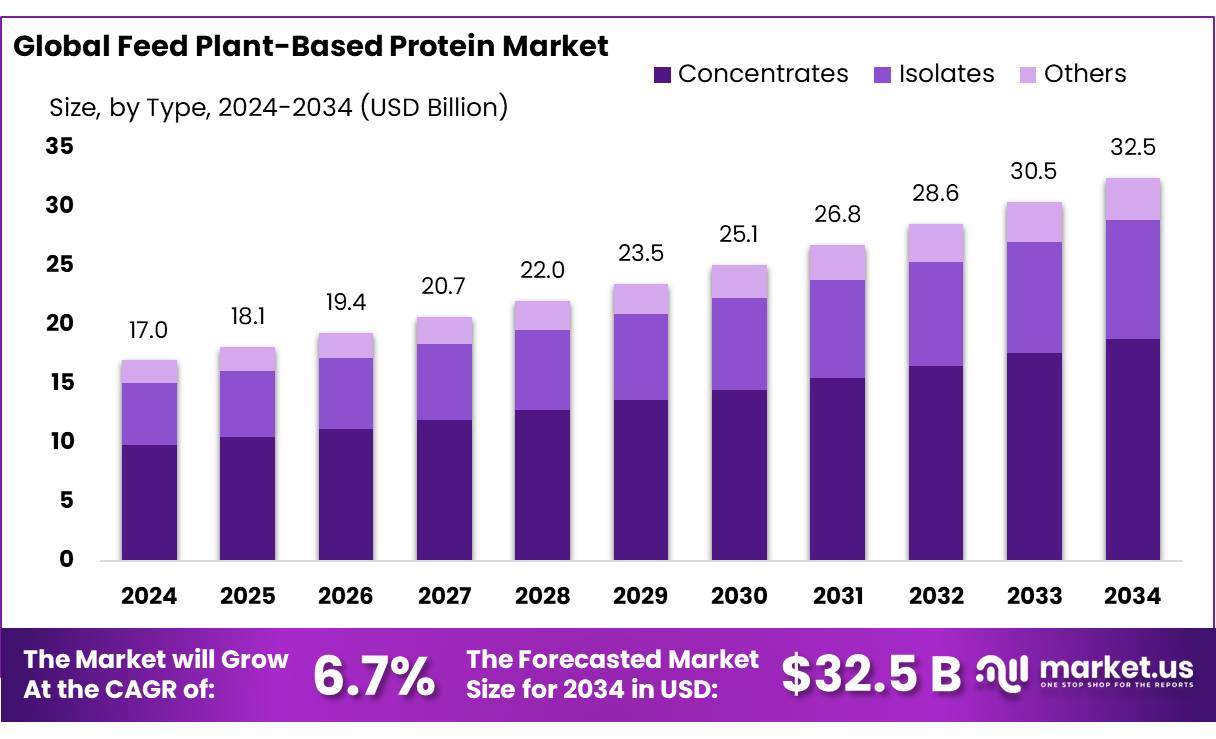
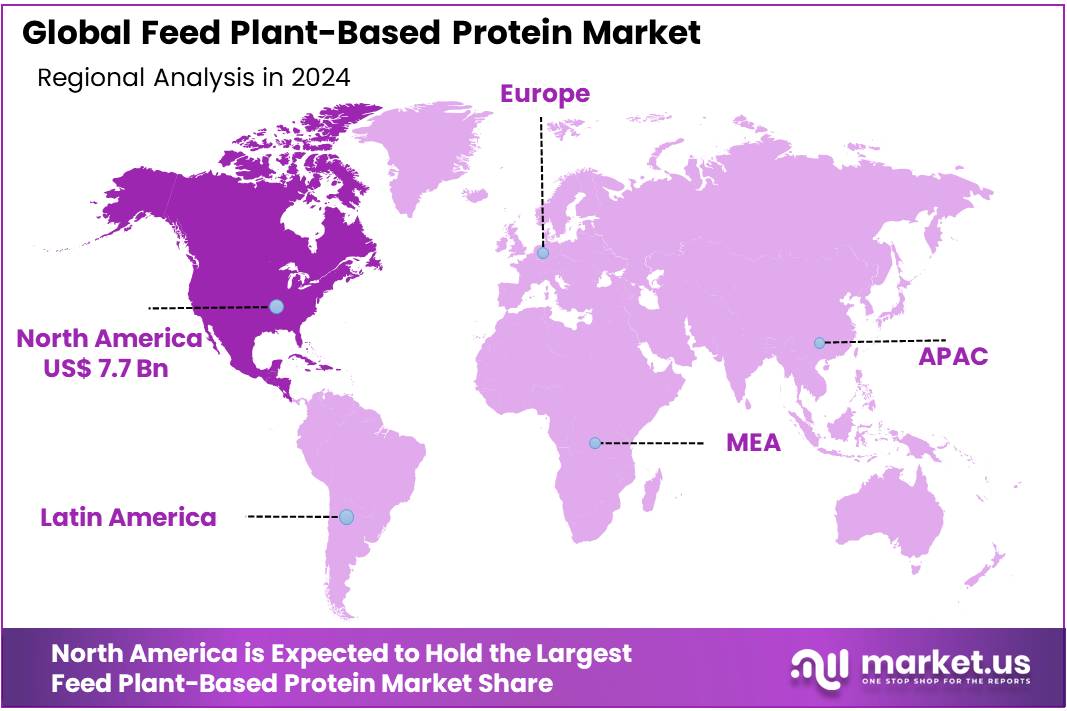
The Global Feed Plant-Based Protein Market size is expected to be worth around USD 32.5 Billion by 2034, from USD 17.0 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 6.7% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 45.6% share, holding USD 7.7 Billion revenue.
The demand for plant-based protein concentrates in India is being propelled by several factors. Health-conscious consumers are increasingly adopting plant-based diets, seeking alternatives to animal proteins due to concerns over health and sustainability. This trend is evident in the rise of plant-based food startups and the expansion of plant-based product offerings in the market. For instance, GoodDot, an Indian alternative protein company, has scaled its operations to produce 65,000 plant-based meat substitutes daily.
In 2022, India’s non-animal derived protein market accounted for 1.9 thousand tonnes, with soy protein concentrate leading the segment at 49.4% market share, followed by soy protein isolate at 36.1%. The growing awareness of lactose intolerance and the environmental impact of animal agriculture are propelling the shift towards plant-based alternatives in both human and animal nutrition.
Several factors are propelling the demand for plant-based protein concentrates in India. Health-conscious consumers are increasingly adopting plant-based diets to manage lifestyle-related diseases and promote overall well-being. Additionally, the growing awareness of lactose intolerance and the environmental impact of animal agriculture are influencing dietary choices. The Indian plant-based food market reached INR 300 crore (~USD 36 million) in 2024, with dairy alternatives outpacing meat substitutes in growth.
Government initiatives have further bolstered the industry’s growth trajectory. The Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF), established in 2020 with an allocation of INR 15,000 crore, aims to enhance private sector investment in developing animal husbandry infrastructure, including feed plants.
Additionally, the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY), launched in 2019, focuses on reducing infrastructural gaps in the fisheries sector, indirectly supporting the feed industry by promoting sustainable aquaculture practices. Additionally, the Prime Minister Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana, launched in July 2025 with an annual outlay of ₹24,000 crore, focuses on crop diversification, sustainable farming, and improved access to credit, benefiting around 1.7 crore farmers.
Key Takeaways
- Feed Plant-Based Protein Market size is expected to be worth around USD 32.5 Billion by 2034, from USD 17.0 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 6.7%.
- Concentrates held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 57.9% share.
- Soy held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 48.2% share.
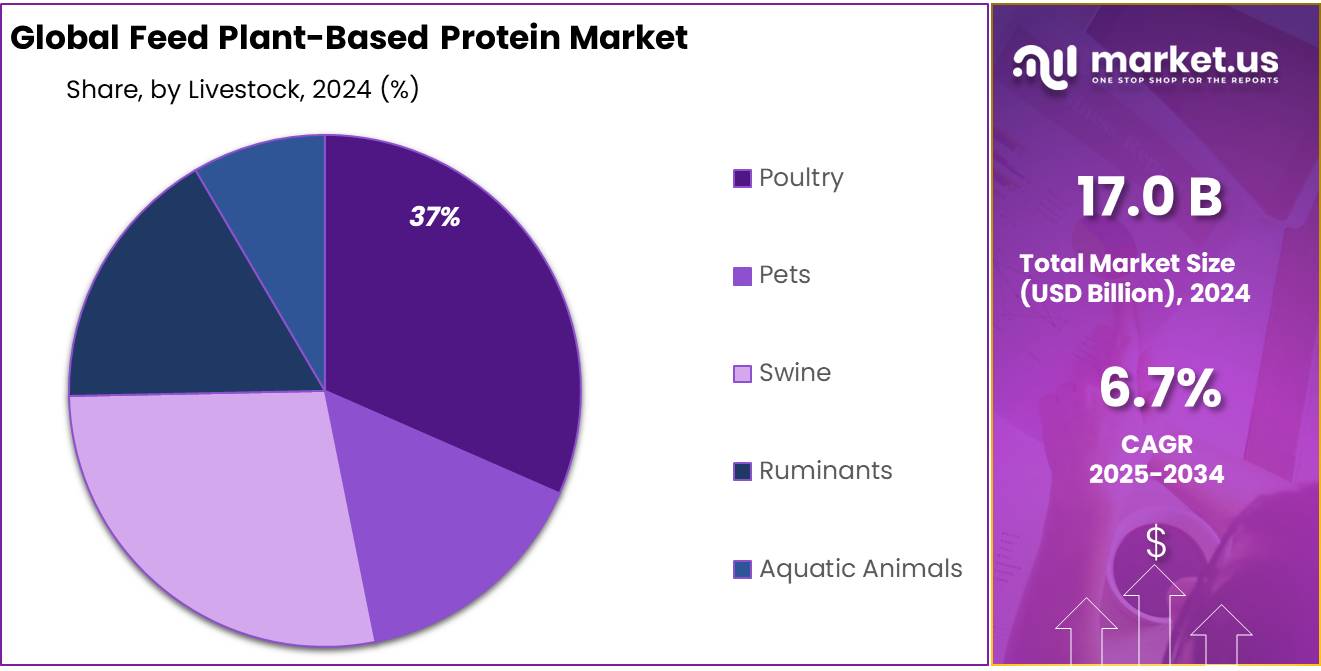
- Poultry held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 37.4% share.
- North America stands as the leading region in the global feed plant-based protein market, commanding a significant share of approximately 45.6%, equating to a market value of around USD 7.7 billion.
By Type Analysis
Concentrates lead with 57.9% on proven nutrition and value
In 2024, Concentrates held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 57.9% share. Buyers favored this type for its reliable amino-acid profile, higher digestibility versus raw meals, and consistent performance across poultry, aqua, and young-animal diets. Formulators leaned on concentrates to tighten feed conversion and stabilize outcomes when raw material quality varied. The segment also benefited from robust oilseed processing, which ensured steady availability of soy, rapeseed/canola, and pea protein streams used to produce concentrate-grade inputs. Procurement teams highlighted the ease of compliance and documentation around sustainability, helping large feed mills satisfy customer and regulatory expectations without complicating supply chains.
By Source Analysis
Soy leads with 48.2% for its rich protein profile
In 2024, Soy held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 48.2% share. Its lead came from a unique combination of high protein content, balanced amino-acid profile, and global availability that feed manufacturers trust. Large-scale soybean crushing in key producing regions such as the United States, Brazil, and Argentina ensured a dependable supply of soy meal and concentrates, allowing formulators to meet the nutritional needs of poultry, swine, and aquaculture without compromising consistency. The versatility of soy also played a role—its proteins fit easily into diverse feed formulations, whether for commercial livestock or specialty animal diets.
By Livestock Analysis
Poultry dominates with 37.4% on strong feed efficiency gains
In 2024, Poultry held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 37.4% share. This lead was driven by the sector’s high demand for consistent, nutrient-dense feed formulations that support rapid growth rates and efficient feed conversion. Broiler and layer operations relied heavily on plant-based protein ingredients such as soy concentrates and pea protein to deliver balanced amino-acid profiles while controlling feed costs. The poultry industry’s short production cycles made it more sensitive to feed quality, pushing producers to adopt premium protein sources that enhance growth performance and flock health.
Key Market Segments
By Type
- Concentrates
- Isolates
- Others
By Source
- Soy
- Wheat
- Pea
- Sunflower
- Others
By Livestock
- Poultry
- Pets
- Swine
- Ruminants
- Aquatic Animals
Emerging Trends
Technological Advancements in Plant-Based Feed Proteins
The feed industry is witnessing a significant transformation driven by technological advancements that enhance the efficiency and sustainability of plant-based proteins. Innovations such as precision fermentation, extrusion technologies, and enzymatic processing are revolutionizing the production of plant-based feed ingredients, making them more cost-effective and nutritionally comparable to traditional animal-based proteins.
Precision fermentation, for instance, allows for the production of high-quality proteins by utilizing microorganisms to ferment plant sugars, resulting in protein-rich biomass. This method not only increases the yield of protein per unit of raw material but also reduces the environmental footprint associated with traditional protein extraction methods.
- According to a report by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), such biotechnological approaches are pivotal in developing sustainable protein sources for animal feed, aligning with global goals to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote resource-efficient agricultural practices.
Extrusion technology, another significant advancement, involves cooking and shaping plant materials under high pressure and temperature to create feed pellets with desirable textures and digestibility. This process enhances the palatability and nutritional value of plant-based feeds, making them more attractive to livestock and poultry. The FAO highlights that improving the quality of plant-based feeds is essential for optimizing animal health and productivity, thereby supporting sustainable livestock farming systems.
These technological advancements are supported by various government initiatives aimed at promoting sustainable agricultural practices. For example, the European Union’s Green Deal and Farm to Fork Strategy emphasize the development and adoption of sustainable food systems, including the use of alternative proteins in animal feed. Similarly, the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) has been investing in research and development of alternative protein sources, including plant-based proteins, to enhance food security and sustainability.
Drivers
Rising Demand for Sustainable Protein Sources
The growing demand for sustainable protein sources is a major driving factor for the feed plant-based protein market. As the global population continues to increase, the pressure to feed more people with environmentally sustainable practices becomes more critical. Traditional livestock farming is resource-intensive, requiring vast amounts of water, land, and feed. Plant-based proteins, on the other hand, offer a much more sustainable alternative, requiring fewer resources to produce, making them an attractive option for animal feed.
- According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), the livestock sector is responsible for about 14.5% of global greenhouse gas emissions, contributing significantly to climate change. With climate change becoming a key concern globally, governments and industries are seeking alternative solutions to reduce the environmental footprint of agriculture.
This is where plant-based proteins come into play, as they require less water, land, and energy compared to animal-based proteins. As a result, plant-based proteins, including peas, soy, and canola, are being increasingly utilized in animal feed to reduce the ecological impact of traditional protein sources.
The demand for plant-based protein in animal feed is also fueled by consumer preferences shifting toward sustainable and eco-friendly products. For example, a report by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) suggests that shifting towards plant-based diets, even for animal feed, could reduce greenhouse gas emissions significantly. As awareness of sustainability issues rises, animal feed manufacturers are looking for ways to meet both consumer demand and regulatory requirements. This includes adopting plant-based protein sources, which are seen as a more ethical and environmentally friendly option.
In addition, several government initiatives are promoting the shift to sustainable agricultural practices. For instance, the European Union has introduced policies that encourage the use of plant-based proteins in the food and feed sectors. The EU’s Green Deal aims to make Europe the first climate-neutral continent by 2050, and promoting plant-based proteins is a key part of this strategy. Likewise, in the United States, the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) is supporting research into the potential of plant-based proteins, providing funding for programs that promote sustainable agricultural practices and reduce the carbon footprint of food production.
Restraints
Supply Chain Constraints in Plant-Based Protein Feed
One of the significant challenges hindering the widespread adoption of plant-based proteins in animal feed is the strain on supply chains. As demand for sustainable protein sources grows, sourcing sufficient quantities of plant-based proteins like peas, soy, and canola becomes increasingly difficult. These ingredients are essential for producing high-quality animal feed, but their availability is limited, leading to potential shortages and price volatility.
The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) has highlighted that the agricultural capacity of peas is particularly limited, especially in Europe, where demand already outstrips supply. This imbalance between demand and production capacity can result in higher prices for plant-based proteins, making them less competitive compared to traditional animal-based protein sources. Such economic pressures can deter animal feed manufacturers from transitioning to plant-based alternatives, slowing the shift towards more sustainable feeding practices.
Moreover, disruptions in the global supply chain, such as those caused by geopolitical tensions or natural disasters, can exacerbate these challenges. For instance, the COVID-19 pandemic demonstrated how vulnerable supply chains are to unexpected shocks, leading to delays and increased costs in obtaining necessary raw materials. These disruptions can have a cascading effect on the production of plant-based proteins, further limiting their availability for animal feed.
Addressing these supply chain constraints requires a multifaceted approach. Investing in agricultural research to develop higher-yielding plant varieties, improving logistics and storage infrastructure, and fostering international trade agreements can help alleviate some of these pressures. Additionally, encouraging the development of alternative protein sources, such as insect-based proteins, could diversify the supply and reduce dependence on traditional plant-based ingredients.
Opportunity
Government Support for Plant-Based Protein Feed
Governments worldwide are increasingly recognizing the importance of plant-based proteins in animal feed as a sustainable solution to global food security and environmental challenges. This recognition has led to various initiatives aimed at promoting the production and utilization of plant-based proteins in animal feed.
For instance, the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) has highlighted that the global alternative proteins market is projected to grow to a value of at least USD 290 billion by 2035. This growth is supported by investments from governments in countries like the United States, Denmark, the European Union, Finland, Israel, and the United Kingdom, which are funding research and development in alternative proteins.
In Canada, the government has been investing in legume farming since the 1970s, including research and development of diversified cropping systems and the adoption of improved cultivars. The Pulse Canada organization of farmers and exporters has an ambitious “25 by 2025” strategy to increase the value of their crops by getting 25% of pulse production into new, higher-value markets and uses by 2025.
Similarly, Denmark has developed a national policy and finance commitments to a plant-based food plan for health, environment, and food security reasons. This includes improving plant-protein food supply chains, including nitrogen-fixing pulse protein crops, and providing investment for farmers to reskill, re-equip, and connect to distribution networks to facilitate the plant-based transition.
In the United States, the government has integrated lessons learned and the latest evidence into its Global Food Security Strategy, emphasizing equity and inclusion with a particular focus on inclusive agricultural-led economic growth that empowers women, girls, youth, and marginalized communities. An ambitious approach to climate change underpins the strategy, with a focus on climate-smart innovations to help communities vulnerable to the accelerating effects of climate change adapt and thrive while reducing emissions and enhancing carbon storage in soils and agricultural tree cover.
Regional Insights
North America leads with 45.6% share worth USD 7.7 Bn
North America stands as the leading region in the global feed plant-based protein market, commanding a significant share of approximately 45.6%, equating to a market value of around USD 7.7 billion. This dominance is primarily attributed to the region’s robust agricultural infrastructure, heightened consumer awareness regarding sustainable and ethical farming practices, and substantial investments in research and development.
The United States, in particular, plays a pivotal role in this market, driven by a growing preference for plant-based diets among consumers and a surge in demand for alternative protein sources in animal feed. This shift is further supported by government initiatives and policies promoting sustainable agricultural practices. For instance, the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) has been actively supporting research into alternative protein sources, including plant-based proteins, to enhance food security and sustainability.
Canada also contributes significantly to the North American market, with a notable increase in the adoption of plant-based proteins in animal feed. The Canadian government’s emphasis on sustainable agriculture and support for plant-based protein research have facilitated this growth. Moreover, the rising vegan and vegetarian populations in both the U.S. and Canada are influencing the demand for plant-based products, including animal feed.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
AGRANA Beteiligungs-AG, based in Austria, is a leading producer of plant-based proteins, specializing in the development of innovative, sustainable solutions. The company offers a broad range of protein ingredients derived from natural sources like grains and legumes. AGRANA plays a pivotal role in Europe’s plant-based protein sector, with a strong focus on innovation and the adoption of sustainable agricultural practices, supporting its growth in the plant-based food market.
AGT Foods, a prominent global player headquartered in Canada, is one of the largest suppliers of pulses and pulse-based products, including plant-based proteins. With a focus on the food, feed, and ingredient industries, AGT Foods is recognized for its high-quality protein products derived from peas, lentils, and chickpeas. The company’s commitment to sustainable sourcing and processing positions it as a key competitor in the North American plant-based protein market.
Aminola is a major manufacturer of plant-based protein ingredients, particularly known for its high-quality, sustainable protein derived from algae and other plant sources. The company serves various industries, including food, feed, and nutraceuticals, offering a wide range of protein products that cater to the growing demand for plant-based alternatives. Aminola’s focus on innovation and sustainability helps it maintain a competitive edge in the plant-based protein market, particularly in Europe.
Top Key Players Outlook
- AGRANA Beteiligungs-AG
- AGT Foods
- Alltech, Inc
- Aminola
- Avebe UA
- Batory Foods
- Adisseo Co., Ltd
- Cargill, Incorporated
- Emsland Group
- Ingredion Incorporated
Recent Industry Developments
In 2023/2024 Avebe U.A., reported a revenue of €780 million and employed approximately 1,254 individuals.
In 2024, Alltech’s revenue was estimated to be approximately $1 billion, with a workforce of around 6,000 employees worldwide.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 17.0 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 32.5 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 6.7% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Type (Concentrates, Isolates, Others), By Source (Soy, Wheat, Pea, Sunflower, Others), By Livestock (Poultry, Pets, Swine, Ruminants, Aquatic Animals) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape AGRANA Beteiligungs-AG, AGT Foods, Alltech, Inc, Aminola, Avebe UA, Batory Foods, Adisseo Co., Ltd, Cargill, Incorporated, Emsland Group, Ingredion Incorporated Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Feed Plant-Based Protein MarketPublished date: Aug 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Feed Plant-Based Protein MarketPublished date: Aug 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- AGRANA Beteiligungs-AG
- AGT Foods
- Alltech, Inc
- Aminola
- Avebe UA
- Batory Foods
- Adisseo Co., Ltd
- Cargill, Incorporated
- Emsland Group
- Ingredion Incorporated










