Global Dicamba Herbicides Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Crop Type (Cereals and Grains, Oilseeds and Pulses, Pastures and Forage Crops, Others), By Physical Form (Liquid, Dry), By Formulation (Salt, Acid), By Time of Application (Post-Emergence, Pre-Emergence) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends, and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Aug 2025
- Report ID: 155660
- Number of Pages: 250
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
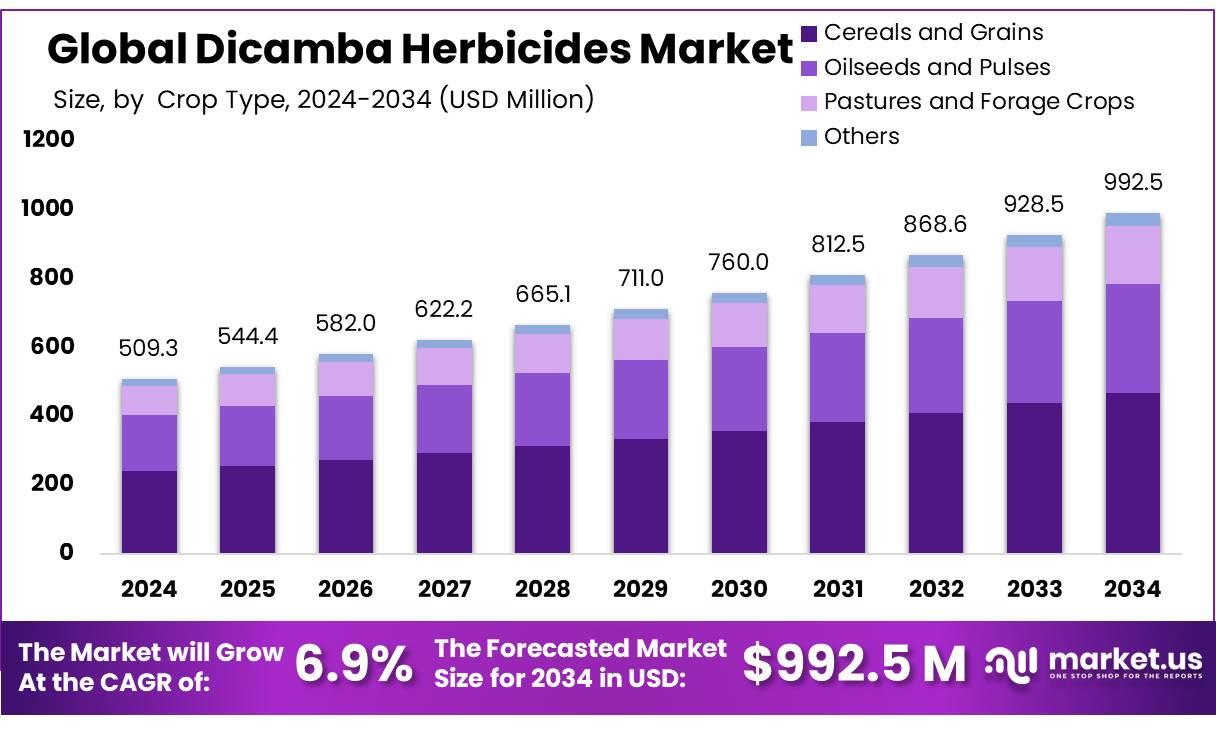
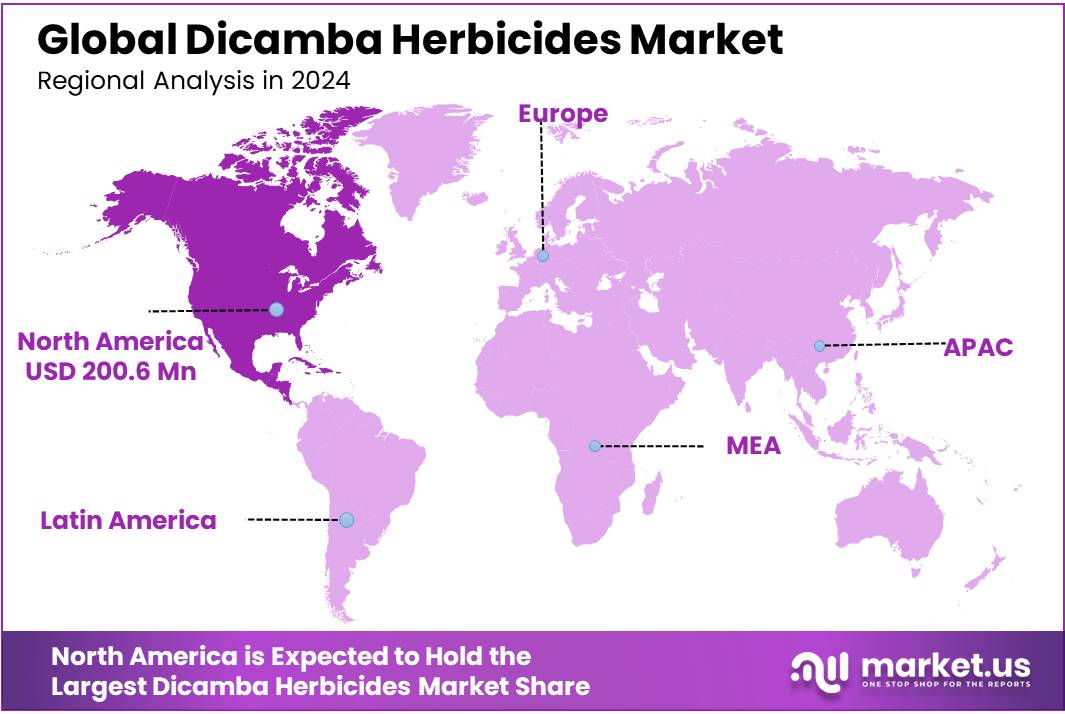
The Global Dicamba Herbicides Market size is expected to be worth around USD 992.5 Million by 2034, from USD 509.3 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 6.9% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 39.4% share, holding USD 200.6 million revenue.
The dicamba herbicide concentrate industry has witnessed significant developments in recent years, driven by the need to manage herbicide-resistant weeds and the adoption of genetically modified (GM) crops. Introduced in 1967, dicamba is a selective systemic herbicide effective against broadleaf weeds. Its application surged following the release of dicamba-tolerant GM crops, notably soybeans and cotton, which facilitated over-the-top (OTT) spraying without harming the crops. This advancement aimed to address the escalating issue of herbicide-resistant weeds, particularly those resistant to glyphosate.
In 2025, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) proposed re-registering dicamba herbicides for use on GM soybeans and cotton, despite previous court rulings in 2020 and 2024 that had vacated such registrations due to environmental concerns. The new proposal includes stringent application restrictions: a maximum of two applications per year, with no more than 1 lb. acid equivalent (a.e.) dicamba per acre annually, and a prohibition on aerial applications. Additionally, it mandates a 240-foot downwind buffer zone and requires the use of drift reduction agents and pH buffering agents during application.
In response to these concerns, regulatory bodies have implemented measures to mitigate risks associated with dicamba use. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has proposed new restrictions on dicamba applications, including temperature cutoffs above 95°F and the use of drift reduction agents when temperatures exceed 75°F . These steps aim to balance the herbicide’s effectiveness with environmental protection.
Key Takeaways
- Dicamba Herbicides Market size is expected to be worth around USD 992.5 Million by 2034, from USD 509.3 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 6.9%.
- Cereals & Grains held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 47.1% share of the dicamba herbicides market.
- Liquid held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 75.8% share of the dicamba herbicides market.
- Salt held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 68.4% share of the dicamba herbicides market.
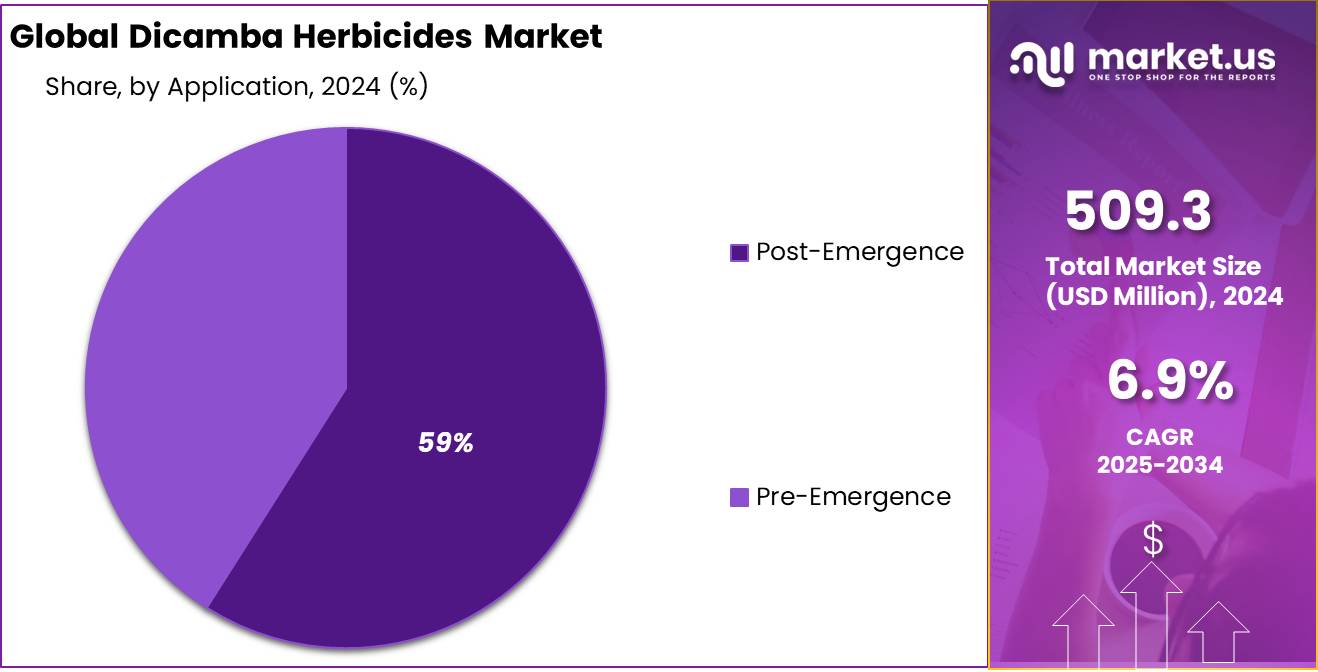
- Post-Emergence held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 59.5% share of the dicamba herbicides market.
- North America stands out as the dominant regional hub, capturing 39.4% of the market share valued at approximately USD 200.6 million.
By Crop Type Analysis
Cereals & Grains lead strongly at 47.1% in 2024
In 2024, Cereals & Grains held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 47.1% share of the dicamba herbicides market—a clear signal that this crop category remains the backbone of dicamba demand. Growers of wheat, barley, and other grains leaned heavily on dicamba concentrates to manage challenging weeds and protect yield, particularly in areas where resistance to glyphosate had become a real headache. Farmers tell us they appreciate dicamba’s reliable broadleaf control, and because cereals and grains span vast acreage, even small changes in planting patterns or application practices can shift demand noticeably. This share implies that nearly half of all dicamba usage is focused on cereal and grain systems, spotlighting this segment as both a performance driver and a strategic frontier for future product improvement—from better drift control to more pasture-friendly formulations.
By Physical Form Analysis
Liquid form leads emphatically at 75.8% share in 2024
In 2024, Liquid held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 75.8% share of the dicamba herbicides market. This tells us something important: most growers truly prefer liquid formulations. Why? Well, liquid concentrates mix easily with water, spread consistently through sprayers, and let farmers adjust the dose on the go—especially helpful when battling weeds like glyphosate-resistant pigweeds or ragweeds. Because dicamba is often used in tightly timed post-emergence applications, having a user-friendly liquid helps reduce mistakes and ensures accurate coverage. That preference drives not just convenience, but real confidence on the field.
By Formulation Analysis
Salt formulation takes the lead at 68.4% share in 2024
In 2024, Salt held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 68.4% share of the dicamba herbicides market—making it the go-to choice for most growers. Salts like DGA and BAPMA have become particularly popular because they’re much less volatile than acid forms, which helps reduce drift and off-target damage. Farmers often tell me they feel more confident using salt formulations, especially when weather conditions are tricky or neighboring fields are sensitive.
Since dicamba is so timing-sensitive, knowing your chemistry is stable matters a lot—and salts offer that stability. Looking into 2025, the trend seems set to continue: keeping formulations safe, compliant, and effective is top priority, and salt-based dicamba clearly delivers on those fronts. Personally, as someone who loves hearing directly from the field, I see salt formulations as not just a chemical preference, but a real trust-builder between providers, farmers, and regulators.
By Time of Application Analysis
Post-Emergence leads the way with 59.5% share in 2024
In 2024, Post-Emergence held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 59.5% share of the dicamba herbicides market. Farmers prefer post-emergence applications because they allow direct targeting of broadleaf weeds after crops like soybeans, cotton, and corn are already established. This timing is especially effective against fast-growing resistant species such as Palmer amaranth and waterhemp, which threaten yields if not controlled early in the season. The widespread adoption of herbicide-tolerant crop traits further strengthened reliance on post-emergence dicamba, making it the most trusted application window.
Key Market Segments
By Crop Type
- Cereals and Grains
- Oilseeds and Pulses
- Pastures and Forage Crops
- Others
By Physical Form
- Liquid
- Dry
By Formulation
- Salt
- Acid
By Time of Application
- Post-Emergence
- Pre-Emergence
Emerging Trends
Regulatory Reassessment and Proposed Re-Registration of Dicamba Herbicides
A significant trend in the dicamba herbicide market is the ongoing regulatory reassessment and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) recent proposal to re-register dicamba-based herbicides for use on genetically engineered (GE) dicamba-tolerant (DT) crops. This development follows a period of legal challenges and regulatory uncertainty, highlighting the dynamic interplay between agricultural practices, environmental concerns, and regulatory frameworks.
Dicamba, a broad-spectrum herbicide, has been utilized for over 50 years to control broadleaf weeds. Its application surged after 2016 with the introduction of GE crops resistant to dicamba, such as Monsanto’s Xtend soybeans and cotton. These crops allowed for effective post-emergence weed control, addressing issues related to herbicide-resistant weed populations, particularly those resistant to glyphosate. However, the increased use of dicamba led to concerns about its volatility and potential for off-target movement, causing damage to neighboring non-DT crops and natural vegetation.
In 2024, a federal court vacated the EPA’s registration of three dicamba products, citing procedural violations and inadequate consideration of environmental risks. This decision halted the use of dicamba on DT crops for the 2024 growing season. In response, the EPA conducted a comprehensive review and, in July 2025, proposed the re-registration of these dicamba products, incorporating new mitigation measures to address identified risks.
The re-registration proposal has elicited mixed reactions from stakeholders. Agricultural groups, including the American Soybean Association, support the re-registration, emphasizing the importance of dicamba in managing herbicide-resistant weeds and maintaining crop yields. They argue that, with proper application and adherence to guidelines, the risks associated with dicamba can be effectively managed.
Drivers
Increased Demand for Effective Weed Control in Agriculture Drives Dicamba Herbicides Market
The increasing demand for effective weed management in agriculture is one of the primary driving factors for the growth of the Dicamba herbicides market. Dicamba, a broad-spectrum herbicide, is widely used in both conventional and organic farming to control broadleaf weeds in various crops such as soybeans, cotton, and corn. As global food production needs continue to rise due to the growing population, the demand for high-yield crops free from weed competition becomes more critical. This, in turn, drives the usage of herbicides like Dicamba, which are known for their effectiveness in controlling persistent weeds, especially in crop systems resistant to other herbicides.
A key contributing factor to the increasing use of Dicamba is the growing adoption of genetically modified (GM) crops. These crops are engineered to be resistant to specific herbicides, including Dicamba.
- According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), genetically modified crops accounted for over 94% of soybean acreage in the United States by 2024, with Dicamba-resistant varieties playing a significant role in weed control. These herbicides are effective against weeds that have developed resistance to other herbicides, such as glyphosate. The prevalence of glyphosate-resistant weeds in the U.S. has been a major concern for farmers, leading them to increasingly turn to alternative herbicides like Dicamba for efficient control.
Government initiatives also play a significant role in supporting the use of Dicamba. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has approved the use of Dicamba for certain applications, but only under strict guidelines and regulations to reduce its environmental impact. These guidelines are designed to ensure that the herbicide is applied in a way that minimizes its drift potential, which can impact neighboring crops. The EPA has established the “Pesticide Drift Reduction Technology” program, which aims to reduce off-target movement of herbicides like Dicamba. This program ensures that Dicamba can be used safely without harming other crops, promoting its continued use in the agriculture industry.
Restraints
Environmental Concerns and Regulatory Restrictions Restrain Dicamba Herbicides Market Growth
A significant restraining factor for the Dicamba herbicides market is the growing environmental concerns associated with its use, particularly its potential for drift, which can negatively affect non-target crops and ecosystems. Dicamba is known for its volatility, which means it can easily move off-target when sprayed, leading to unintended damage to neighboring crops. This issue has become a major concern for farmers, especially with the increasing adoption of Dicamba-resistant genetically modified crops.
- The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has highlighted the risks of Dicamba drift, with reports indicating that it has caused damage to millions of acres of crops in recent years. For instance, a study by the National Agricultural Statistics Service (NASS) in 2020 found that approximately 3.6 million acres of non-Dicamba-resistant crops were impacted by Dicamba drift.
To address these concerns, regulatory bodies, including the EPA, have imposed stringent guidelines and restrictions on Dicamba’s usage. In 2020, the EPA issued a rule that required farmers to apply Dicamba only during specific weather conditions, such as when wind speeds are low, and to ensure buffer zones around sensitive crops. These regulatory measures aim to minimize the risk of Dicamba drifting onto adjacent fields and causing crop damage. Despite these precautions, many farmers still face challenges in effectively managing Dicamba applications, especially in regions with unpredictable weather conditions that make it difficult to ensure accurate application.
Additionally, the increasing pressure from environmental advocacy groups and organic farming organizations has led to calls for even tighter regulations on Dicamba. The Organic Trade Association (OTA), for example, has voiced concerns about the potential for Dicamba to damage organic crops, which could result in the loss of certification for organic farms. According to the OTA, approximately 60% of organic farmers in the U.S. have reported crop damage due to herbicide drift, with Dicamba being one of the primary culprits. This has sparked debates about the sustainability of Dicamba usage in agriculture, especially as consumers and retailers increasingly demand sustainable and environmentally friendly farming practices.
Opportunity
Expansion of Genetically Engineered Dicamba-Tolerant Crops Presents Growth Opportunities
The increasing adoption of genetically engineered (GE) dicamba-tolerant crops is a significant growth opportunity for the dicamba herbicide market. These crops are specifically designed to withstand applications of dicamba, allowing farmers to effectively manage broadleaf weeds without harming their crops. The widespread adoption of these GE crops has led to a surge in dicamba usage, presenting both challenges and opportunities for the agricultural sector.
- According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), the adoption of GE dicamba-tolerant crops has been prevalent throughout the United States. In 2019, approximately 88% of cotton acres in Mississippi were planted with dicamba-tolerant varieties, followed by Missouri (85%), South Carolina (83%), and Tennessee (80%) . This widespread adoption underscores the growing reliance on dicamba-tolerant crops for effective weed management.
The adoption of these GE crops has been driven by the increasing prevalence of herbicide-resistant weeds, particularly glyphosate-resistant species. The USDA’s Economic Research Service notes that farmers have observed declines in the effectiveness of glyphosate in all states surveyed. In response, many have turned to dicamba as an alternative herbicide to combat these resistant weeds . This shift has led to a significant increase in dicamba usage, with the U.S. Geological Survey reporting that dicamba use in U.S. agriculture rose from approximately 8 million pounds in 2016 to 30 million pounds in 2019 .
The expansion of GE dicamba-tolerant crops offers several growth opportunities for the dicamba herbicide market. First, the increased adoption of these crops necessitates a corresponding increase in dicamba applications, driving demand for the herbicide. Second, the development of new dicamba formulations with reduced volatility and improved drift-reduction characteristics can enhance the effectiveness and safety of dicamba applications, further boosting market growth. Third, as farmers continue to seek effective solutions for herbicide-resistant weeds, the reliance on dicamba-tolerant crops and associated herbicide applications is expected to persist, sustaining long-term demand for dicamba.
Regional Insights
In the global dicamba herbicides market, North America stands out as the dominant regional hub, capturing 39.4% of the market share valued at approximately USD 200.6 million. The region’s leadership is underpinned by its extensive adoption of herbicide-tolerant crops, particularly soybeans and cotton.
According to the USDA, in 2024 nearly 96% of soybean acres and 93% of cotton acres in the United States were planted with herbicide-tolerant seeds, forming a massive user base for auxinic herbicides like dicamba. The demand is also reinforced by the widespread challenge of glyphosate-resistant weeds such as waterhemp and Palmer amaranth, which have compelled farmers across states like Iowa, Illinois, and Arkansas to integrate dicamba-based weed management strategies.
Regulatory dynamics also strongly shape the North American segment. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and state-level agricultural departments have issued evolving guidelines to ensure responsible dicamba use, from volatility-reduction requirements to seasonal cut-off dates, thus creating a structured yet regulated growth environment. In Canada, dicamba use is largely tied to corn and soybean acreage, where farmers are adopting modern formulations to mitigate drift and maximize field productivity.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Syngenta AG plays a significant role in the dicamba herbicides market, focusing on integrated weed management for major row crops like soybeans and corn. The company emphasizes combining dicamba formulations with advanced traits to control resistant weeds. Syngenta has invested in stewardship programs to reduce drift and enhance application safety. With a strong North American footprint and global distribution, it ensures reliable supply chains. The company’s innovation and farmer outreach position it as a reliable leader in auxin herbicides.
Bayer Crop Science is one of the most influential players in dicamba herbicides, closely tied to its Xtend and XtendFlex crop systems for soybeans and cotton. The firm provides low-volatility dicamba formulations integrated with herbicide-tolerant seed traits, strengthening adoption among U.S. farmers battling glyphosate-resistant weeds. Bayer invests heavily in stewardship, digital compliance tools, and regulatory collaboration to maintain market presence. Its leadership in biotechnology traits and herbicide systems makes Bayer central to sustaining dicamba demand across North America.
BASF SE is a key innovator in dicamba herbicides, with its Engenia® herbicide recognized for low-volatility performance in soybeans and cotton. The company supports growers with resistance management tools and robust training initiatives. BASF’s focus is on minimizing drift while offering reliable post-emergence weed control in resistant broadleaf weeds. With extensive R&D and a global crop protection portfolio, BASF plays a vital role in shaping dicamba stewardship programs, ensuring that its solutions align with evolving U.S. EPA regulatory frameworks.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Syngenta AG
- Bayer Crop Science
- BASF SE
- Nufarm Limited
- Alligare LLC
- Helena Chemical Company
- Albaugh Inc.
- UPL
- ADAMA
- FMC
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024, Syngenta Crop Protection, which includes dicamba and other herbicides, recorded sales of USD 13.2 billion, down 13% year-over-year.
In 2024, Bayer Crop Science—which includes dicamba herbicides—reported total sales of €22.3 billion, reflecting a 4.3% drop from the previous year due chiefly to pricing pressures and regulatory headwinds around dicamba use.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 509.3 Mn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 992.5 Mn CAGR (2025-2034) 6.9% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Crop Type (Cereals and Grains, Oilseeds and Pulses, Pastures and Forage Crops, Others), By Physical Form (Liquid, Dry), By Formulation (Salt, Acid), By Time of Application (Post-Emergence, Pre-Emergence) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Syngenta AG, Bayer Crop Science, BASF SE, Nufarm Limited, Alligare LLC, Helena Chemical Company, Albaugh Inc., UPL, ADAMA, FMC Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Syngenta AG
- Bayer Crop Science
- BASF SE
- Nufarm Limited
- Alligare LLC
- Helena Chemical Company
- Albaugh Inc.
- UPL
- ADAMA
- FMC










