Global Chicory Ingredients Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Product Type (Inulin, Oligofructose, Chicory Flour, Roasted Chicory), By Form (Powder, Liquid), By Application, Food and Beverages, Dietary Supplements, Pharmaceuticals, Animal Feed, Others), By Distribution Channel ( Supermarkets/Hypermarkets, Online Retail, Specialty Stores, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Oct 2025
- Report ID: 162633
- Number of Pages: 228
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
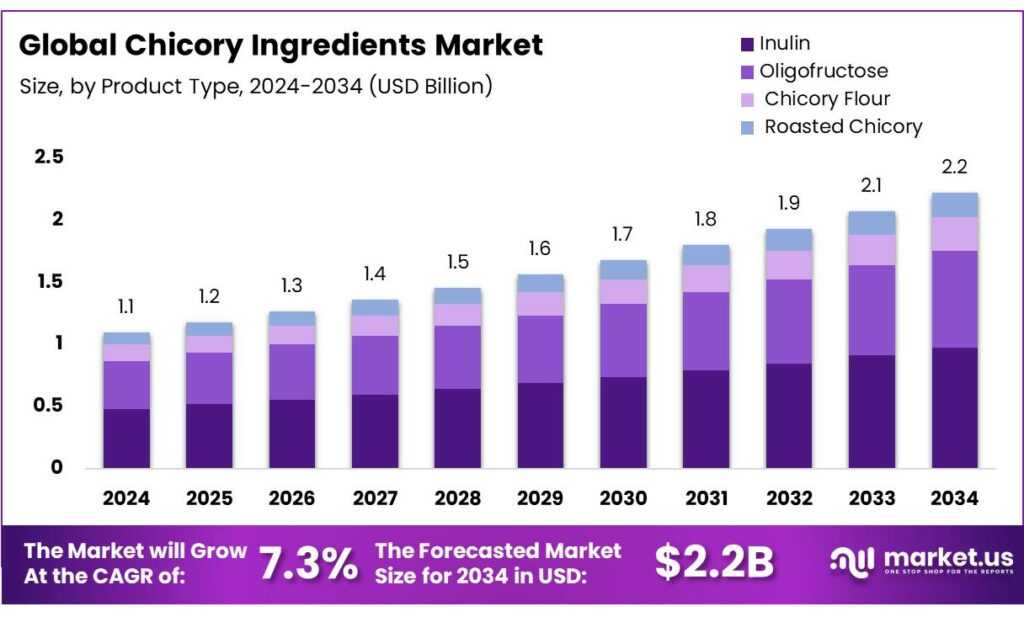
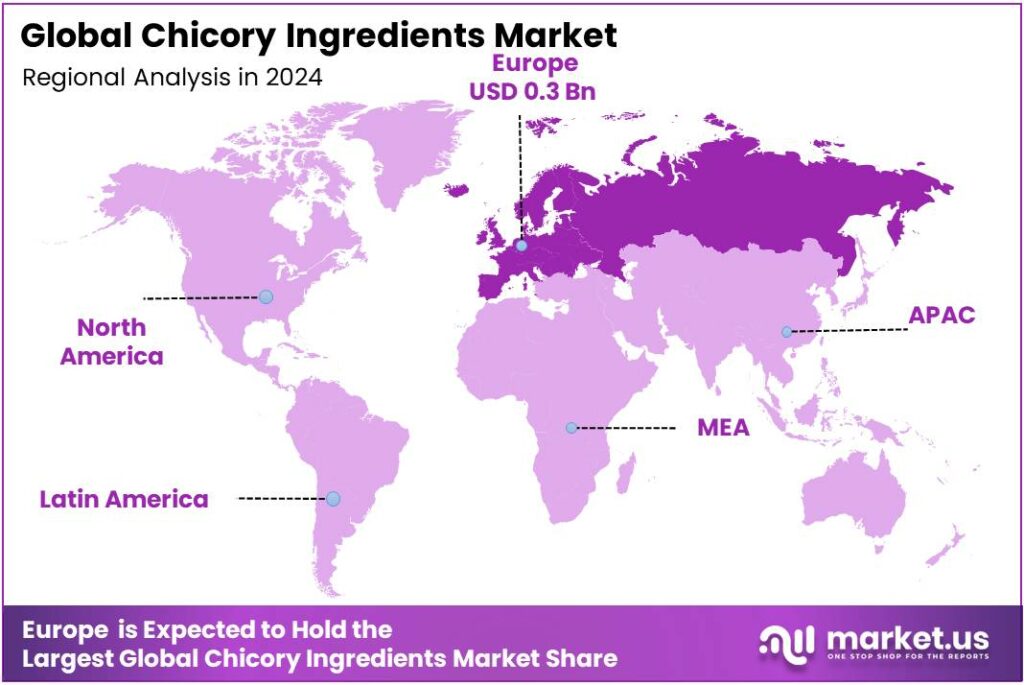
The Global Chicory Ingredients Market size is expected to be worth around USD 2.2 Billion by 2034, from USD 1.1 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 7.3% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024 European held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 34.9% share, holding USD 0.3 Billion in revenue.
Chicory ingredients—primarily inulin and oligofructose derived from Cichorium intybus roots—have matured from niche fibers into multifunctional tools for sugar reduction, texture, and prebiotic benefits. Industrial chicory is concentrated in Northwestern Europe; Belgium is repeatedly identified as the leading producer of inulin chicory, with cultivation footprints also in the Netherlands and Chile, underscoring a stable raw-material base for processors.
The industrial scenario spans farm yields, extraction capacity, and regulatory clarity. Agronomically, root chicory delivers about 45 t/ha with an average 17% inulin content, metrics that support efficient extraction economics when scaled. Demand signals are visible in trade data: the United States imported 1,283,520 kg of HS 110820 inulin from China in 2023, illustrating active downstream use in foods and supplements and the globalized nature of supply. On the policy side, the EU’s Regulation (EU) No 1169/2011 anchors common definitions for nutrition information, including dietary fiber, aiding consistent labeling for chicory-fiber-containing foods across Member States.
- In the U.S., FDA’s Daily Value for dietary fiber is 28 g/day, a benchmark that brands target when formulating with inulin for fiber claims.
On the regulatory front, the category benefits from clear safety and use frameworks in major markets. In the EU, the European Food Safety Authority concluded that consuming ≥ 12 g/day of “native chicory inulin” increases stool frequency and helps maintain normal defecation—an authorized wording widely used by brand owners. In the U.S., FDA has repeatedly issued “no questions” letters for chicory-derived inulin and ingredients: GRN 118 covers inulin from chicory root used broadly in foods, while GRN 830 allows incorporation up to 42% by weight in specified categories, supporting versatile formulation at meaningful inclusion levels.
Key driving factors are nutrition gaps and clean-label reformulation. In the U.S., fiber is under-consumed: analyses aligned with the Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2020–2025 show ~90% of women and 97% of men do not meet recommended intakes—leaving a large addressable need for fiber-enriched foods. Manufacturers also lean on chicory fiber to cut sugars while maintaining mouthfeel, enabled by FDA’s fiber definition in 21 CFR 101.9 and related guidance clarifying which added fibers can be declared as dietary fiber on labels. Upstream, processors have publicly committed capital to expand chicory-fiber capacity—e.g., a >40% planned global capacity increase announced to meet rising demand—signaling confidence in sustained utilization.
Policy and funding tailwinds are material. In Europe, the Horizon 2020 CHIC program channelled € 6,999,596.25 of EU contributions to chicory innovation, accelerating genetics and process efficiency for inulin value chains. In India, the Pradhan Mantri Formalisation of Micro Food Processing Enterprises (PMFME) scheme offers a 35% credit-linked capital subsidy to modernize micro-processing—including chicory roasting, grinding, and extraction—while common-facility infrastructure is funded under the same umbrella.
Key Takeaways
- Chicory Ingredients Market size is expected to be worth around USD 2.2 Billion by 2034, from USD 1.1 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 7.3%.
- Inulin held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.9% share of the global chicory ingredients market.
- Powder held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 74.8% share of the global chicory ingredients market.
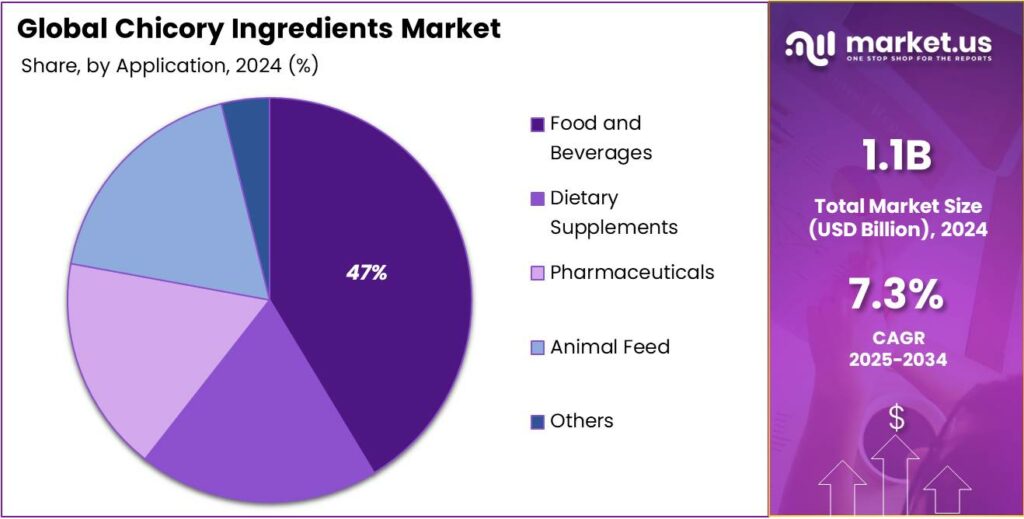
- Food and Beverages held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 47.3% share of the global chicory ingredients market.
- Supermarkets/Hypermarkets held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 48.6% share of the global chicory ingredients market.
- European region, the Chicory Ingredients market registered a share of 34.90%, corresponding to approximately USD 0.3 billion in 2024.
By Product Type Analysis
Inulin Leads the Chicory Ingredients Market with 43.9% Share in 2024
In 2024, Inulin held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.9% share of the global chicory ingredients market. The segment’s leadership was supported by the rising preference for natural dietary fibers and prebiotic ingredients across the food and beverage industry. Inulin, extracted primarily from chicory root, has gained significant acceptance due to its dual functionality—it acts as a soluble dietary fiber and an effective fat and sugar replacer in processed foods. The ingredient’s clean-label appeal and compatibility with health-conscious consumer trends have further reinforced its industrial importance.
Strong demand was observed from bakery, dairy, and beverage manufacturers integrating inulin to improve product texture and nutritional value. Its prebiotic properties, which support gut microbiota balance and digestive wellness, have contributed to increased use in dietary supplements and fortified foods. The global focus on reducing sugar intake has particularly enhanced inulin’s commercial value, as manufacturers adopt it as a natural alternative to artificial sweeteners and synthetic bulking agents.
By Form Analysis
Powder Form Dominates the Chicory Ingredients Market with 74.8% Share in 2024
In 2024, Powder held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 74.8% share of the global chicory ingredients market. This strong dominance was driven by the product’s superior stability, longer shelf life, and easy incorporation into a wide range of food, beverage, and dietary supplement formulations. The powder form of chicory ingredients, particularly inulin and roasted chicory root powder, has become the preferred choice among manufacturers due to its convenient handling, high solubility, and compatibility with dry mix products such as instant beverages, bakery goods, and nutritional blends.
The demand for chicory powder increased significantly in 2024, especially from health-conscious consumers seeking natural sources of prebiotic fiber and caffeine-free beverage alternatives. Food processors adopted powder forms for their ease of transportation and lower moisture content, which ensures product consistency and quality across applications. Additionally, the format’s ability to blend seamlessly with other natural ingredients has expanded its industrial utility in both the food and pharmaceutical sectors.
By Application Analysis
Food and Beverages Lead the Chicory Ingredients Market with 47.3% Share in 2024
In 2024, Food and Beverages held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 47.3% share of the global chicory ingredients market. This dominance was primarily supported by the increasing consumer preference for natural and functional ingredients in everyday diets. Chicory-derived inulin and fibers are widely used in bakery, confectionery, dairy, and beverage formulations to enhance texture, sweetness, and nutritional value without adding excess calories. Their ability to serve as natural fat and sugar substitutes has made them essential in the development of healthier, reduced-sugar food products.
During 2024, strong demand emerged from beverage manufacturers incorporating chicory extracts as caffeine-free coffee alternatives and functional drink additives. The inclusion of chicory ingredients in dairy products, yogurts, and breakfast cereals also increased, owing to their prebiotic properties that promote gut health. Food companies continued to innovate using chicory fibers to meet growing demand for clean-label, high-fiber, and plant-based formulations.
By Distribution Channel Analysis
Supermarkets/Hypermarkets Lead the Chicory Ingredients Market with 48.6% Share in 2024
In 2024, Supermarkets/Hypermarkets held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 48.6% share of the global chicory ingredients market. This dominance was largely attributed to the wide product availability, organized shelf placement, and strong consumer trust in established retail chains. These stores offer customers a wide variety of chicory-based products—from roasted chicory coffee and instant blends to inulin-enriched foods and dietary supplements—under one roof, which has significantly influenced purchase behavior. The convenience of in-person selection, promotional offers, and product demonstrations further strengthened sales through this channel during the year.
In 2024, the expansion of health-focused food aisles and specialty organic sections within large retail stores supported greater visibility for chicory-based products. Growing awareness of digestive wellness and clean-label ingredients among urban consumers encouraged supermarket buyers to stock more chicory-derived food and beverage products. This trend has been reinforced by global supermarket chains enhancing their private-label offerings that include chicory-based fiber and coffee substitutes.
Key Market Segments
By Product Type
- Inulin
- Oligofructose
- Chicory Flour
- Roasted Chicory
By Form
- Powder
- Liquid
By Application
- Food and Beverages
- Dietary Supplements
- Pharmaceuticals
- Animal Feed
- Others
By Distribution Channel
- Supermarkets/Hypermarkets
- Online Retail
- Specialty Stores
- Others
Emerging Trends
Prebiotic chicory fibers moving into mainstream sugar-reduction
A clear, current trend is the use of chicory-derived inulin and oligofructose as “dual-purpose” ingredients: they add prebiotic fiber for gut health while helping brands cut free sugars without losing body or mouthfeel. Policymakers and health agencies have set numeric anchors that steer this shift. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration fixes the Daily Value (DV) for dietary fiber at 28 g/day, and lists 50 g/day for added sugars on the Nutrition Facts framework—two figures that product developers now design around.
- The World Health Organization recommends keeping free sugars below 10% of energy and says below 5% (~25 g/day) brings additional benefits, pushing retailers and manufacturers toward lower-sugar recipes where soluble fibers can replace bulk and improve texture.
This reformulation wave meets a persistent fiber gap, which makes chicory ingredients’ prebiotic story even more relevant. USDA’s Economic Research Service reports U.S. consumers averaged 8.1 g fiber per 1,000 kcal in 2017–18—only 58% of the recommended 14 g/1,000 kcal density—so most people fall short of fiber guidance. When brands remove sucrose to meet WHO-aligned sugar targets, replacing some of that sugar with chicory inulin lets them restore body, lower net sugars, and contribute fiber toward the 28 g/day DV at the same time.
- The European Food Safety Authority concluded that “native chicory inulin” at least 12 g/day increases stool frequency, supporting normal defecation—a rare, specific physiological claim that can appear on qualified products.
Supply has also professionalized, helping this trend scale. FAOSTAT explicitly tracks “chicory roots” as an agricultural commodity, giving industry and governments a common reference for area and output. Published analyses using FAOSTAT indicate global root-chicory acreage of ~14,500 ha, clustered near extraction hubs—evidence of a stable upstream base that can expand as demand for prebiotic fibers rises.
Drivers
Fiber gap plus sugar-reduction policies are the key driver
The single biggest tailwind for chicory ingredients—especially inulin and oligofructose—is the push to close the dietary-fiber gap while cutting free sugars. The U.S. FDA sets the Daily Value for dietary fiber at 28 g/day, anchoring product development and label claims; this numeric target appears on Nutrition Facts education and reference pages used by industry and regulators. Yet actual intake lags badly. USDA analyses show Americans averaged 8.1 g fiber per 1,000 kcal in 2017–18—only 58% of the recommended 14 g/1,000 kcal density—confirming a shortfall that brands can address with added fibers like chicory inulin.
At the same time, global policy is squeezing added sugars, creating room for prebiotic fibers as functional bulking and sweetness-modulating tools. The World Health Organization recommends keeping free sugars below 10% of energy, and notes further health benefits below 5% (~25 g/day); these numeric thresholds guide national reformulation programs and retailer targets worldwide. When formulators remove sucrose or glucose-fructose syrups to meet WHO-aligned limits, they often need soluble fiber to restore mouthfeel and reduce net sugars—precisely the role chicory inulin can play.
Chicory’s advantage is not only regulatory-fit but also claimable function at realistic doses. The European Food Safety Authority concluded that “native chicory inulin” at least 12 g/day “increases stool frequency,” supporting maintenance of normal defecation—a rare fiber claim with cause-and-effect wording that marketers can deploy on qualifying products. In the United States, FDA guidance formally recognizes added isolated/synthetic carbohydrates that demonstrate beneficial physiological effects as “dietary fiber,” and in 2018 the Agency expanded the list of eligible fibers—explicitly aligning labeling with demonstrated outcomes such as increased bowel-movement frequency, glycemic and cholesterol benefits.
Supply-side fundamentals support scale. FAOSTAT tracks “chicory roots (including roots for inulin)” as an agricultural commodity, giving processors and policymakers line-of-sight into area and output; literature using FAOSTAT data estimates ~14,500 ha of root chicory acreage globally, concentrated near extraction hubs—a base that can expand as demand grows.
- For instance, nutrition-label modernization in the U.S. hard-codes the 28 g/day fiber DV into consumer education and compliance materials used by manufacturers, nudging portfolio renovation toward higher-fiber, lower-sugar formulations where chicory ingredients fit naturally.
Restraints
One Major Restraining Factor for Chicory Ingredients – Gastro-intestinal Tolerance and Consumer Acceptance
A significant restraint on the adoption of chicory-derived ingredients (such as inulin and oligofructose from Cichorium intybus roots) lies in their gastrointestinal (GI) tolerance and the impact this has on consumer acceptance. While these fibres are celebrated for their digestive-health benefits, the same mechanism that yields benefit can produce undesirable side-effects when dosage is not managed or product design is weak.
Clinical evidence indicates that even though inulin is generally safe, at higher doses it can provoke symptoms such as gas, bloating, abdominal discomfort, loose stools or diarrhoea. For example, a review of human studies reported that inulin doses exceeding 20-30 g/day led to increased reporting of GI adverse events. Similarly, in one controlled trial it was found that doses of up to 10 g/day for native inulin and 5 g/day for oligofructose were well tolerated in healthy young adults—but GI symptoms increased at higher intakes. What this signals is a relatively narrow “sweet spot” for functional dosing: enough to deliver the claimed benefit.
In practice, the formulator and food manufacturer must strike a delicate balance. When chicory fibers are incorporated into foods (bakery, dairy, beverages) to deliver benefits while reducing sugar or increasing fibre content, the manufacturing process must account for how the added fibre behaves (solubility, viscosity, fermentability) and how consumers’ guts respond. If a product delivers e.g. 15 g of inulin in a single portion to meet the “≥12 g/day” claim, some consumers may experience bloating or excess flatulence. Indeed, one article warns that many consumers “don’t realise how much inulin they are consuming,” and the dose-dependency of symptoms is clear.
From a market-launch perspective, cost in use is also affected by tolerance constraints. Rather than pushing inclusion to e.g., 20 g per serving, formulators may cap additions at 8-10 g per portion to ensure consumer comfort, which may reduce incremental functional claims or ingredient margin. If competitive fibres or fibre blends can achieve higher dosages with fewer GI side-effects, chicory inulin may lose relative appeal.
Opportunity
Rising Gut-Health Awareness Meets Functional Fiber Demand
One of the clearest growth opportunities for chicory-derived ingredients like inulin and oligofructose comes from the escalating global focus on gut health and the role of dietary fiber in preventive nutrition. According to data from the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, higher intake of soluble fiber is linked with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease and improved metabolic health.
This gap between recommendation and intake opens a strong window of opportunity for food manufacturers and ingredient producers. When consumers consciously look to improve their digestive wellbeing, the kind of fiber that offers both functional food engineering benefits and health-oriented claims becomes especially valuable. The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has already recognized isolated non-digestible carbohydrates that demonstrate physiological benefits as “dietary fiber,” which gives inulin regulatory legitimacy and opens doors for front-of-pack labeling upgrades.
- Government and institutional initiatives amplify this potential further. For example, official dietary guidance in many countries underscores the importance of increased fiber intake—not just for digestibility, but for reducing risks of conditions like hypertension and metabolic disorders. The American Heart Association recommends that adults with hypertension should target more than 28 g/day for women and more than 38 g/day for men of dietary fiber, with each additional 5 g/day linked to measurable health benefit.
Regional Insights
Europe dominates with 34.90% share (USD 0.3 billion) — robust production base and established demand.
In the European region, the Chicory Ingredients market registered a share of 34.90%, corresponding to approximately USD 0.3 billion in 2024. This notable position reflects a combination of mature agricultural production in key countries—such as Belgium, France and the Netherlands—which together contribute significantly to chicory-root cultivation and processing. The region’s robust food and beverage manufacturing base has supported downstream demand for chicory-derived inulin and functional fiber ingredients.
The prevalence of consumer awareness around digestive health and clean-label nutrition within Europe has further bolstered uptake of chicory-based ingredient solutions. Regulatory support for dietary-fibre enrichment and functional claims has assisted companies in extending applications of chicory ingredients into bakery, dairy, beverages and nutraceuticals. Additionally, long-standing supply chains for chicory roots and well-established extraction infrastructure have reduced raw-material risk and enhanced processing efficiencies, thereby enabling competitive production and market penetration within the European context.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Founded in 1852 in Belgium, COSUCRA is a specialist in natural-based ingredients derived from chicory roots and yellow peas. The company produces its signature FIBRULINE™ chicory root fibre and other functional fibres for food, beverage and nutrition markets. It emphasises sustainability via local sourcing (400+ farmers within ~60 km radius) and has invested €45 million in an energy-transition plan targeting a 50% reduction in carbon footprint by 2030.
Beneo, a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Südzucker Group, supplies functional ingredients including chicory-root derived inulin and oligofructose, as well as rice, wheat and beet sugar-derivatives. Its Orafti® inulin portfolio supports digestive health, sugar reduction and clean-label applications across bakery, confectionery, cereals and baby foods. The company announced a multi-million-euro investment to expand its chicory root fibre capacity by over 40%, signalling strong growth intent.
Based in Secunderabad, India, Delecto Foods was established in 2013 and focuses on the cultivation, drying, roasting and processing of chicory roots, with export reach to Russia, Poland, France, Malaysia and other markets. Its offerings include instant chicory powder, roasted chicory cubes/grains and liquid chicory, leveraging local agricultural expertise and targeting cost-sensitive global markets.
Top Key Players Outlook
- COSUCRA Groupe
- Beneo GmbH
- The Tierra Group
- Cargill
- Delecto Foods Pvt. Ltd.
- Reily Foods Company
- Otheres
Recent Industry Developments
As at March 2024 Delecto Foods Pvt Ltd, paid-up capital stood at INR 7.48 crore and its revenue range was reported within INR 25-50 crore for the year.
COSUCRA Groupe Warcoing S.A., headquartered in Warcoing, Belgium, has positioned itself as a specialist supplier of chicory-root based ingredients, particularly the branded FIBRULINE™ chicory root fibre. According to its own disclosures, by 2024 the company had engaged over 400 local farmers within a 60 km radius to source chicory roots.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 1.1 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 2.2 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 7.3% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Product Type (Inulin, Oligofructose, Chicory Flour, Roasted Chicory), By Form (Powder, Liquid), By Application, Food and Beverages, Dietary Supplements, Pharmaceuticals, Animal Feed, Others), By Distribution Channel ( Supermarkets/Hypermarkets, Online Retail, Specialty Stores, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape COSUCRA Groupe, Beneo GmbH, The Tierra Group, Cargill, Delecto Foods Pvt. Ltd., Reily Foods Company, Otheres Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- COSUCRA Groupe
- Beneo GmbH
- The Tierra Group
- Cargill
- Delecto Foods Pvt. Ltd.
- Reily Foods Company
- Otheres










