Global Cellulose Ether and Its Derivatives Market Size, Share Analysis Report Ву Туре (Carboxymethyl Cellulose, Hydroxypropyl Cellulose, Methyl Cellulose, Hydroxyethyl Cellulose, Ethyl Cellulose), By End Use (Pharmaceutical, Food and Beverage, Construction, Personal Care, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Oct 2025
- Report ID: 160512
- Number of Pages: 322
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
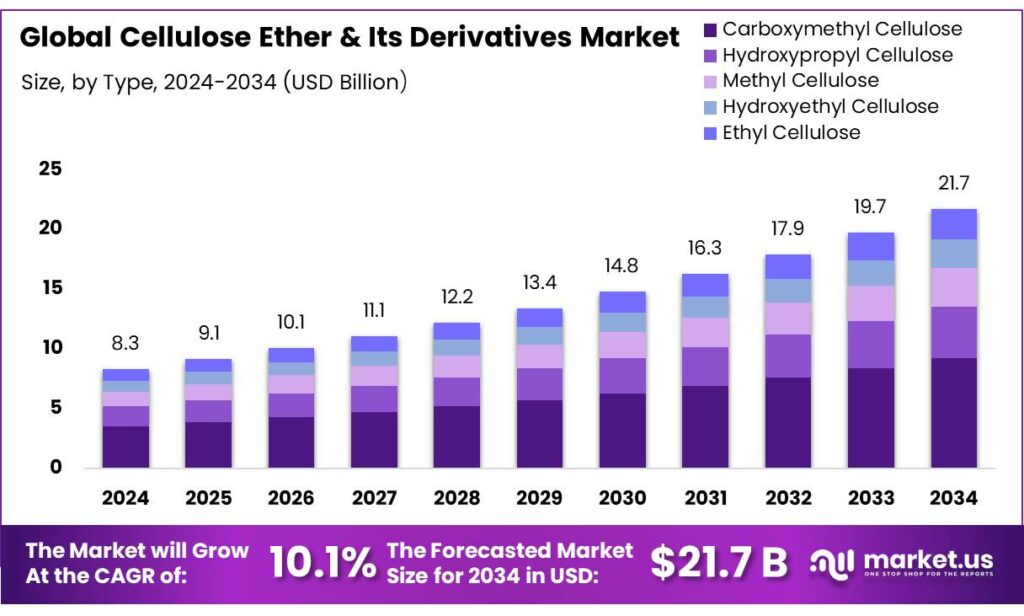
The Global Cellulose Ether and Its Derivatives Market size is expected to be worth around USD 21.7 Billion by 2034, from USD 8.3 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 10.1% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
Cellulose ethers are a family of chemically modified cellulose polymers — including methylcellulose (MC), hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC), carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) and others — that are widely used as thickeners, binders, film-formers and stabilizers across construction, pharmaceuticals, food, personal care and paints. The material’s renewable origin (wood pulp and other cellulosic feedstocks), biodegradability potential and functional versatility have driven steady industrial adoption in value-added formulations.
The industrial scenario is characterized by incremental scale-up of derivative production and diversification of feedstocks. It has been observed that national bioeconomy strategies and biomass assessments are shaping supply security: the U.S. 2023 Billion-Ton assessment indicates that the United States can sustainably produce on the order of 1.1–1.5 billion dry tons per year of biomass under mature-market scenarios, reinforcing the potential feedstock base for cellulosic derivatives and biomanufacturing.
Demand drivers — Demand has been driven by construction and pharmaceuticals. The global construction sector represented a multitrillion-dollar activity base (global construction output was reported near USD 15.46 trillion in 2023), underpinning demand for construction-grade cellulose ethers used in cementitious mortars, tile adhesives and plasters.
At the policy level, government actions have been significant: since the start of the current U.S. Administration, approximately USD 29 billion (and in later reporting USD 46 billion) in public and private investments were reported to support biomanufacturing and the domestic bioeconomy, which indirectly supports cellulose-derivative scale-up and new processing capacity.
Key Takeaways
- Cellulose Ether and Its Derivatives Market size is expected to be worth around USD 21.7 Billion by 2034, from USD 8.3 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 10.1%.
- Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC) held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 42.4% share.
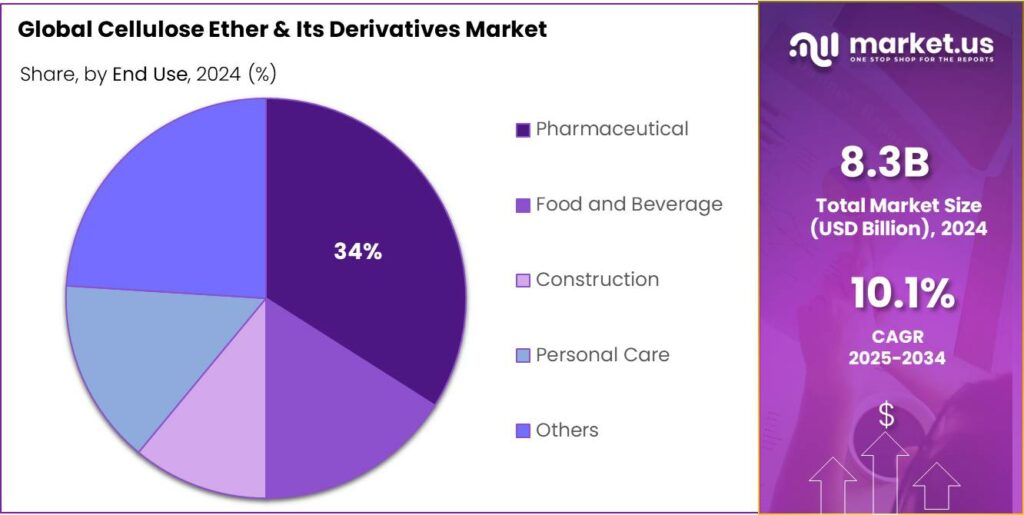
- Pharmaceutical held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 34.8% share.
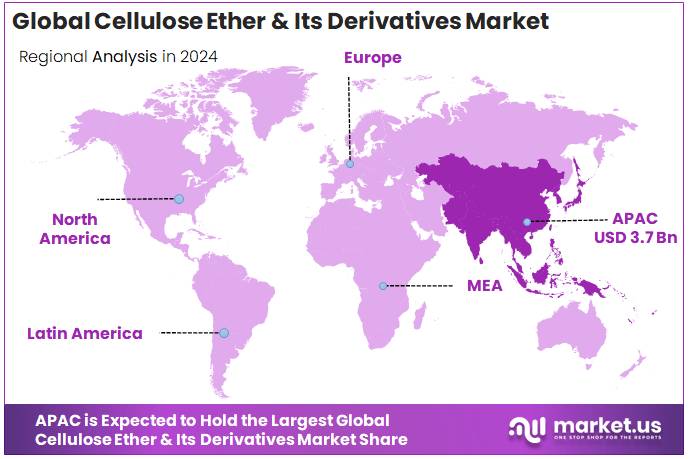
- Asia-Pacific (APAC) region was the clear market leader for cellulose ether and its derivatives, accounting for 44.80% of global demand and representing approximately USD 3.7 billion.
By Type Analysis
Carboxymethyl Cellulose leads with 42.4% market share in 2024 driven by its versatile industrial applications
In 2024, Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC) held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 42.4% share of the global cellulose ether and its derivatives market. This strong position can be attributed to its wide-ranging applications across industries such as food and beverages, pharmaceuticals, personal care, and paper manufacturing. CMC is highly valued for its excellent thickening, stabilizing, and water-retention properties, making it a preferred additive in processed foods, coatings, and cosmetic formulations. During 2024, the food sector accounted for a significant portion of CMC consumption, driven by its use as a texture enhancer and fat substitute in low-calorie products.
In pharmaceuticals, CMC continued to be widely used as a binder and film-forming agent in drug formulations. Year-wise, demand in 2025 is expected to remain strong due to increasing consumer preference for sustainable, bio-based ingredients and the expansion of the processed food industry in Asia-Pacific and Europe. Its cost-effectiveness, non-toxic nature, and compatibility with eco-friendly manufacturing processes have reinforced Carboxymethyl Cellulose’s dominance in the cellulose ether market.
By End Use Analysis
Pharmaceutical sector leads with 34.8% market share in 2024 driven by rising drug formulation demand
In 2024, Pharmaceutical held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 34.8% share of the global cellulose ether and its derivatives market. The growth of this segment was largely supported by the increasing use of cellulose ethers such as Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose (HPMC) and Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC) as excipients in drug formulations. These compounds are widely utilized as binders, stabilizers, and controlled-release agents in tablets, capsules, and ophthalmic solutions. The expanding pharmaceutical manufacturing base in emerging economies like India and China has further accelerated consumption.
The demand for cellulose ethers was reinforced by the rising production of oral solid dosage forms and the growing focus on patient-friendly formulations. Looking ahead to 2025, the segment is expected to maintain steady growth, supported by increasing healthcare expenditure, higher drug approvals, and the adoption of bio-based polymers in pharmaceutical excipients. The biocompatibility, safety, and stability of cellulose ethers have made them indispensable in modern drug delivery systems, sustaining their leading position in the end-use market.
Key Market Segments
Ву Туре
- Carboxymethyl Cellulose
- Hydroxypropyl Cellulose
- Methyl Cellulose
- Hydroxyethyl Cellulose
- Ethyl Cellulose
By End Use
- Pharmaceutical
- Food and Beverage
- Construction
- Personal Care
- Others
Emerging Trends
Clean-Label and Plant-Based Food Innovations Driving Cellulose Ether Demand
A significant trend shaping the food industry is the increasing consumer preference for clean-label and plant-based products. This shift is compelling food manufacturers to seek natural and transparent ingredients, positioning cellulose ethers—such as hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) and carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC)—as pivotal components in modern food formulations.
In the United States, the clean-label movement is particularly pronounced. A study conducted in partnership with Clear Seas Research found that 99% of European manufacturers consider clean-label products essential to their business strategy, with 87% already incorporating these into their products. This trend is mirrored in the U.S., where consumers are increasingly scrutinizing food labels for transparency and simplicity.
Cellulose ethers play a crucial role in this landscape. Derived from natural plant sources, they serve as effective thickeners, stabilizers, and emulsifiers in various food products. Their versatility allows manufacturers to replace synthetic additives with natural alternatives, thereby meeting the growing consumer demand for clean-label products.
Furthermore, government initiatives are supporting this transition. For instance, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has recognized certain cellulose derivatives as Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) for use in food products, providing manufacturers with the regulatory assurance needed to incorporate these ingredients into their formulations
Drivers
Rising Demand for Clean-Label and Plant-Based Food Products
The increasing consumer preference for clean-label and plant-based food products is a significant driver for the growth of cellulose ethers and their derivatives in the food industry. As consumers become more health-conscious and environmentally aware, there is a growing demand for natural, minimally processed, and transparent food ingredients. Cellulose ethers, such as hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) and carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), align well with these consumer trends due to their plant-based origins and multifunctional properties.
Governments and regulatory bodies are also supporting this shift towards clean-label products. For instance, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has endorsed cellulose derivatives as safe food additives, further boosting consumer confidence in these ingredients. Additionally, initiatives like the European Union’s Green Deal promote the use of sustainable and biodegradable materials in food packaging, indirectly encouraging the use of cellulose ethers.
Governments and regulatory bodies are also supporting this shift towards clean-label products. For instance, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has endorsed cellulose derivatives as safe food additives, further boosting consumer confidence in these ingredients. Additionally, initiatives like the European Union’s Green Deal promote the use of sustainable and biodegradable materials in food packaging, indirectly encouraging the use of cellulose ethers.
In India, the demand for clean-label food products is also on the rise. With a growing middle class and increasing health awareness, Indian consumers are seeking food products with natural ingredients and minimal additives. This trend is prompting food manufacturers in India to incorporate cellulose ethers into their products to meet consumer expectations.
Restraints
Regulatory Challenges and Compliance Costs
The cellulose ether industry, particularly in the food sector, faces significant challenges due to stringent regulatory requirements and the associated compliance costs. These regulations, while essential for ensuring food safety and consumer health, can impose substantial financial and operational burdens on manufacturers.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates food additives under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. For instance, methyl ethyl cellulose (E465) is permitted as a food additive but must adhere to specific usage conditions outlined in 21 CFR § 172.872. These conditions include limitations on the methoxy and ethoxy content and viscosity of the additive, as well as restrictions on its use in standardized foods unless explicitly permitted by the standard of identity.
Similarly, in the European Union, cellulose ethers used in food products must comply with the General Food Law Regulation (EC) No 178/2002, which establishes the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and sets out procedures in matters of food safety. Additives like hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (E464) are evaluated for safety and must be used in accordance with good manufacturing practices.
These regulatory frameworks are designed to protect consumers but can lead to increased costs for manufacturers. The need for extensive testing, certification, and documentation to meet regulatory standards can be resource-intensive. For example, obtaining approval for a new food additive or a new application of an existing additive can involve significant investments in research and development, as well as in compliance with regulatory procedures.
Opportunity
Adoption of Cellulose Ethers in Clean-Label and Plant-Based Food Products
The increasing consumer demand for clean-label and plant-based food products presents a significant growth opportunity for cellulose ethers and their derivatives in the food industry. As consumers become more health-conscious and environmentally aware, there is a growing preference for natural, minimally processed, and transparent food ingredients. Cellulose ethers, such as hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC), carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), and hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC), align well with these consumer trends due to their plant-based origins and multifunctional properties.
In India, the demand for clean-label food products is also on the rise. With a growing middle class and increasing health awareness, Indian consumers are seeking food products with natural ingredients and minimal additives. This trend is prompting food manufacturers in India to incorporate cellulose ethers into their products to meet consumer expectations.
Governments and regulatory bodies are also supporting this shift towards clean-label products. For instance, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has endorsed cellulose derivatives as safe food additives, further boosting consumer confidence in these ingredients. Additionally, initiatives like the European Union’s Green Deal promote the use of sustainable and biodegradable materials in food packaging, indirectly encouraging the use of cellulose ethers.
Regional Insights
APAC leads with 44.80% share (USD 3.7 Bn) in 2024, driven by manufacturing, pharmaceuticals and expanding construction activity
In 2024, the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region was the clear market leader for cellulose ether and its derivatives, accounting for 44.80% of global demand and representing approximately USD 3.7 billion in market value; this position was underpinned by dense population centres, rapid industrialisation and strong downstream demand from pharmaceuticals, construction chemicals and personal-care sectors. Manufacturing activity in APAC accounted for roughly 55% of global manufacturing value added in recent years, providing a broad industrial base that supported demand for cellulose ethers used in adhesives, mortar additives and coatings.
Population and urbanisation trends in the region sustained domestic demand: East Asia and Pacific populations remained large, providing both labour and consumer markets for processed goods. The pharmaceutical sector in APAC—notably India and China—contributed materially to material consumption; India’s pharmaceutical market was projected near USD 65 billion by 2024, supporting higher use of excipients such as HPMC and CMC.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
In 2024, Ashland Global Holdings, Inc. maintained a strong presence in the cellulose ether and derivatives market through its diversified product portfolio, including methylcellulose (MC) and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) used in pharmaceuticals, personal care, and construction. The company emphasized sustainable formulations and bio-based materials, supporting growing eco-friendly demand. With operations spanning over 100 countries and annual sales surpassing USD 2.5 billion in 2024, Ashland’s innovation-driven approach and R&D investments positioned it among the key global cellulose ether producers.
Colorcon continued to dominate the pharmaceutical-grade cellulose ether market segment in 2024, focusing on excipient solutions for controlled drug release and tablet coatings. The company’s products, such as HPMC and ethylcellulose, are widely utilized in solid dosage formulations across global pharmaceutical manufacturing hubs. Colorcon’s collaboration with major drug makers strengthened its global reach, with over 20 manufacturing and technical facilities worldwide. Its focus on compliance with global pharmacopoeias further enhanced its credibility and customer trust in regulated markets.
J.M. Huber Corporation retained a competitive edge in 2024 through its diversified cellulose ether offerings catering to construction, personal care, and food applications. The company’s Huber Engineered Materials division produced cellulose derivatives with high consistency and environmental performance. With more than 4,000 employees and operations in over 20 countries, Huber’s revenue base exceeded USD 3 billion in 2024. Its focus on innovation and circular production practices strengthened its role in sustainable chemical manufacturing.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Ashland Global Holdings, Inc
- Colorcon
- J.M. Huber Corporation
- J. RETTENMAIER SOHNE Gmbh
- Lamberti S.p.A
- LOTTE Fine Chemicals
- Nouryon Chemical Holdings B.V
- DKS Co. Ltd
- Fenchem
- Dow Chemical Company
- Zibo Hailan Chemicals Co. Ltd.
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024, Colorcon advanced its role in the cellulose ether & derivatives sector, especially through its specialty excipients and film-coating systems. The company operates 16 manufacturing facilities worldwide and maintains over 40 global locations to serve its clients in pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, and solid dose formulating.
In 2024, J.M. Huber Corporation reinforced its presence in the cellulose ether & derivatives sector as part of its broader specialty chemicals and engineered materials business. The company employed approximately 4,000 people globally.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 8.3 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 21.7 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 10.1% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered Ву Туре (Carboxymethyl Cellulose, Hydroxypropyl Cellulose, Methyl Cellulose, Hydroxyethyl Cellulose, Ethyl Cellulose), By End Use (Pharmaceutical, Food and Beverage, Construction, Personal Care, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Ashland Global Holdings, Inc, Colorcon, J.M. Huber Corporation, J. RETTENMAIER SOHNE Gmbh, Lamberti S.p.A, LOTTE Fine Chemicals, Nouryon Chemical Holdings B.V, DKS Co. Ltd, Fenchem, Dow Chemical Company, Zibo Hailan Chemicals Co. Ltd. Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Cellulose Ether and Its Derivatives MarketPublished date: Oct 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Cellulose Ether and Its Derivatives MarketPublished date: Oct 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Ashland Global Holdings, Inc
- Colorcon
- J.M. Huber Corporation
- J. RETTENMAIER SOHNE Gmbh
- Lamberti S.p.A
- LOTTE Fine Chemicals
- Nouryon Chemical Holdings B.V
- DKS Co. Ltd
- Fenchem
- Dow Chemical Company
- Zibo Hailan Chemicals Co. Ltd.










