Company Overview
Tesla Statistics: Tesla, Inc. develops, designs, manufactures, sells, and leases high-performance electric vehicles along with energy generation and storage systems. The company also provides services supporting its products. Tesla follows a direct-to-consumer model, operating a global network of showrooms, service centers, body shops, Supercharger stations, and Destination Chargers to enhance customer accessibility and promote the adoption of sustainable transportation.
Tesla’s operations are structured into 2 main reporting segments: automotive and energy generation and storage. The automotive segment encompasses the design, development, manufacturing, sales, and leasing of electric vehicles, as well as the sale of automotive regulatory credits. It also includes revenue from services such as used vehicle sales, non-warranty maintenance, body repair, parts sales, paid Supercharging, insurance, and retail merchandise. The energy generation and storage segment focuses on the design, manufacture, installation, sales, and leasing of solar power and energy storage solutions, along with related services and the sale of solar energy system incentives.
The company maintains a strong international presence with manufacturing facilities across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and the Middle East. In 2024, Tesla produced approximately 1.77 million consumer vehicles and delivered around 1.79 million units globally. During the same year, the company deployed 31.4 GWh of energy storage products, reflecting its expanding role in the renewable energy sector. Tesla also emphasizes workforce development, hiring nearly 4,000 university and community college students annually for internships worldwide. In 2024, the company expanded its graduate program to new campuses, hiring over 800 graduates, and in 2025, Tesla plans to employ more than 1,000 participants across its factories to support growing operations and innovation efforts.
Facts About Tesla
- Tesla, Inc. is headquartered in Austin, Texas, and is a vertically-integrated company designing, building, selling, and servicing electric vehicles and energy products.
- The company was founded in July 2003 by Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning, originally under the name Tesla Motors.
- Tesla is named in honour of the inventor Nikola Tesla.
- The company’s mission is to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy through electric vehicles and renewable energy products.
- Tesla’s product portfolio includes electric cars such as the Model S, Model 3, Model X, Model Y, the Cybertruck, and Semi, as well as home and grid energy storage products and solar products.
- Tesla has become one of the largest automakers by market capitalisation and holds a significant share of the battery-electric vehicle (BEV) market globally.
- The company has multiple “Gigafactories” in the United States, China, and Europe to enable large-scale production of vehicles and battery/energy storage systems.
- Tesla uses over-the-air (OTA) software updates for its vehicles, enabling it to deliver new features and fixes without customers visiting service centres.
- Tesla’s battery technology uses multiple cell formats, and the company has been working to reduce the cost per kWh of battery packs, a major competitive advantage.
- The company sells vehicles directly to consumers (rather than via a traditional franchised dealer network) in many markets.
- Tesla’s energy business includes storage products like the Powerwall (for homes) and Megapack (for utilities,) and solar-roof-type generation solutions.
History of Tesla
- 2003: Tesla Motors was established with the mission to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy.
- 2008: Tesla introduced the Roadster, its first electric sports car, marking a breakthrough in EV technology. In the same year, SpaceX’s Falcon 1 became the first privately developed liquid-fueled rocket to reach orbit.
- 2012: Tesla launched the Model S, which received Consumer Reports’ Best Overall Car award and Motor Trend’s Ultimate Car of the Year recognition.
- 2015: Tesla released the Model X SUV, becoming the first SUV in history to earn 5-star safety ratings across all NHTSA categories and subcategories.
- 2016: Tesla acquired SolarCity, transforming into the world’s first vertically integrated sustainable energy company, and began developing the Solar Roof for renewable energy generation.
- 2017: Tesla started Model 3 deliveries, offering more than 320 miles of range, and unveiled the Tesla Semi, expected to save about $200,000 in fuel over one million miles. In parallel, SpaceX achieved reusability milestones by successfully re-flying both a Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon spacecraft.
- 2018: SpaceX launched Falcon Heavy, the most powerful operational rocket globally, capable of lifting heavy payloads into space.
- 2019: Tesla unveiled the Cybertruck, combining superior performance with truck utility, and began Model Y deliveries. In the same year, SpaceX’s crew-capable Dragon spacecraft completed its first demonstration mission.
- 2020: SpaceX made history by transporting NASA astronauts to the International Space Station aboard the Crew Dragon spacecraft, marking the beginning of commercial spaceflight operations.
- Post-2020: Tesla expanded its energy product range with Powerwall, Powerpack, and Megapack for residential, commercial, and utility applications. Meanwhile, SpaceX advanced Starship, a fully reusable spacecraft designed for lunar and Martian missions, and expanded Starlink’s global broadband network.
Segmental Analysis
Automotive
- Tesla manufactures 5 consumer vehicle models: the Model 3, Model S, Model X, Model Y, and Cybertruck, each designed to cater to different customer segments while maintaining high performance and sustainability standards.
- The Model 3 is a four-door mid-size sedan engineered for ease of manufacturing and priced to appeal to the mass market.
- The Model Y is a compact SUV built on the Model 3 platform, offering seating for up to seven adults and combining versatility with efficiency.
- The Model S is a full-size luxury sedan, and the Model X is a mid-size SUV, both featuring Tesla’s longest driving ranges and highest performance specifications within their respective categories.
- Tesla also began limited production and deliveries of the Tesla Semi in 2022, marking its entry into the commercial electric vehicle sector aimed at sustainable freight transport.
- The company continues to innovate across upcoming vehicle programs, including the purpose-built Robotaxi (Cybercab). It is advancing its proprietary Full Self-Driving (FSD) (Supervised) technology known as FSD (Capability) in regions such as the Middle East, Europe, and Asia-Pacific to support the next generation of autonomous mobility solutions.
- Automotive sales revenue declined by $6.03 billion, or 8%, for the year ended December 31, 2024, compared to 2023, mainly due to a lower average selling price across vehicles, driven by strategic price reductions and competitive financing programs introduced during the year.
- The decline also reflected a drop of about 22,000 deliveries of Model 3 and Model Y combined, attributed to market mix and demand variations.
Moreover
- These decreases were partially offset by an increase of roughly 19,000 deliveries from other models, largely supported by the production ramp-up of the Cybertruck.
- Tesla also recognized $596 million in revenue from its Full Self-Driving (FSD) (Supervised) software following the release of new features in 2024, contributing to overall segment performance.
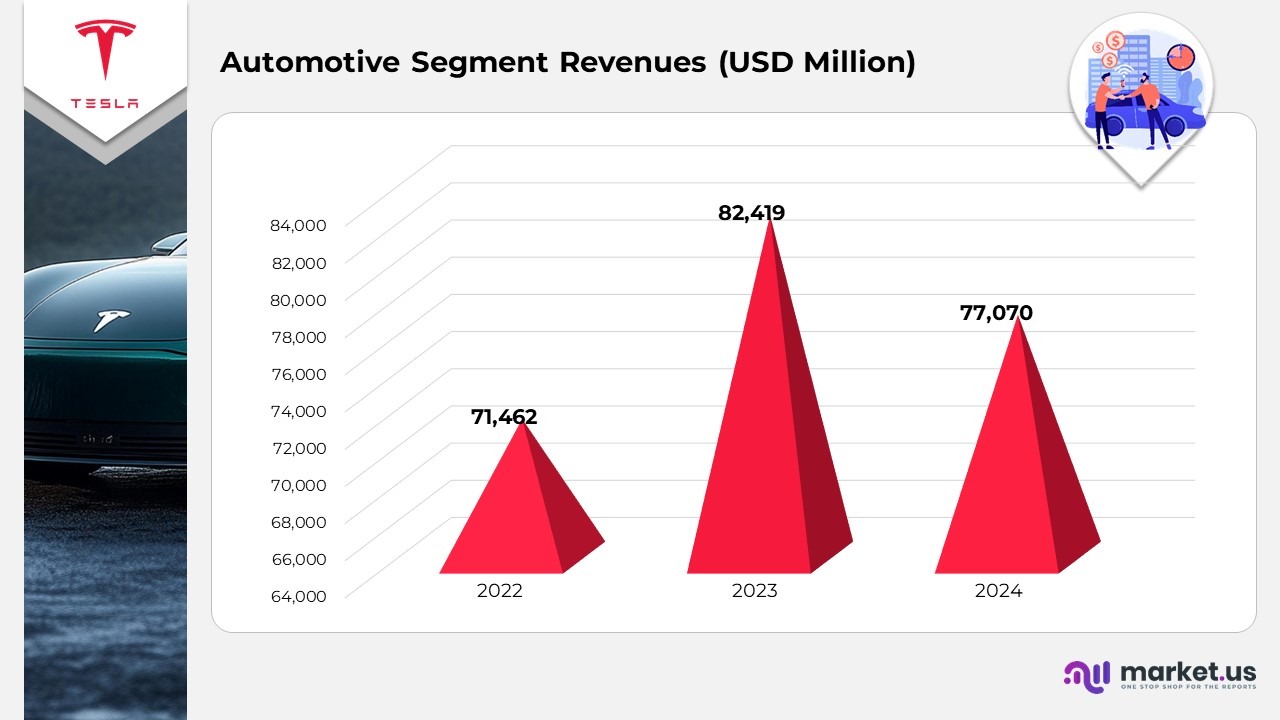
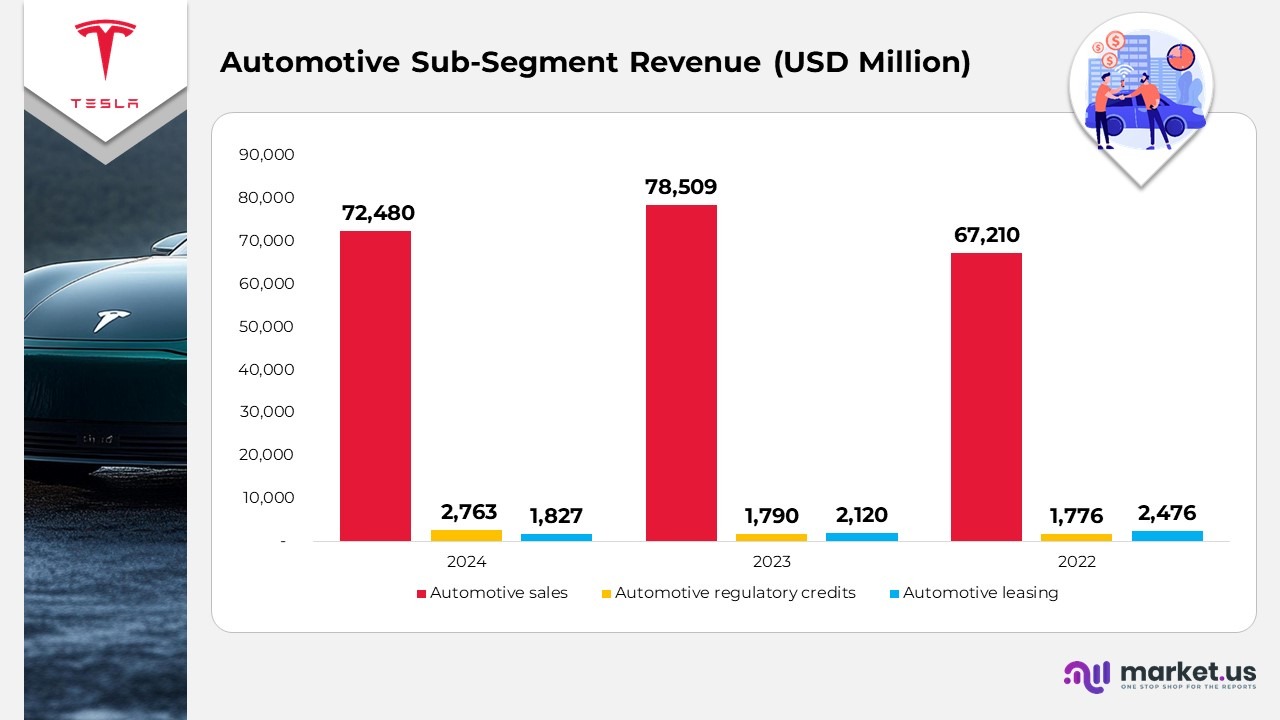
- In 2024, Tesla’s automotive sales revenue reached $72,480 million, a decrease from $78,509 million in 2023, yet higher than $67,210 million in 2022, indicating the effects of targeted pricing strategies and evolving product composition.
- Revenue from automotive regulatory credits amounted to $2,763 million in 2024, rising from $1,790 million in 2023 and $1,776 million in 2022, underscoring consistent growth driven by global emission compliance programs.
- Automotive leasing revenue was recorded at $1,827 million in 2024, down from $2,120 million in 2023 and $2,476 million in 2022, reflecting Tesla’s continued emphasis on direct-to-consumer sales and innovative ownership options.
- The cost of automotive leasing revenue declined by $265 million, or 21%, for the year ended December 31, 2024, compared to 2023, mainly due to a reduction in direct sales-type leasing costs resulting from fewer vehicle deliveries and a lower volume of lease buyouts relative to prior periods.
- The cost of services and other revenue rose by $2.09 billion, representing a 27% increase in 2024 compared to 2023, driven by higher volumes of used vehicle sales at reduced acquisition costs, as well as growth in insurance services, paid Supercharging, parts sales, and non-warranty maintenance and collision repairs.
Energy Generation and Storage
- Tesla offers Powerwall and Megapack as part of its advanced lithium-ion energy storage portfolio, addressing both residential and large-scale energy demands.
- The Powerwall is designed for homes and small businesses, enabling customers to store and utilize electricity for backup power or to optimize energy use from renewable sources. It is distributed both directly by Tesla and through authorized channel partners.
- The Megapack serves commercial, industrial, and utility-scale clients, with each unit capable of being combined to create large energy storage installations reaching gigawatt-hour (GWh) scale capacity.
- Tesla continues to enhance its energy management software, integrating real-time monitoring, control, and optimization features that allow users to remotely manage and dispatch stored energy across diverse markets and applications.
- Energy generation and storage revenue rose by $4.05 billion, representing a 67% increase for the year ended December 31, 2024, compared to 2023, reflecting strong growth in large-scale energy projects.
- The surge was primarily driven by a 7 GWh rise in Megapack and Powerwall installations, highlighting the expanding adoption of Tesla’s battery storage solutions across residential, commercial, and utility sectors.
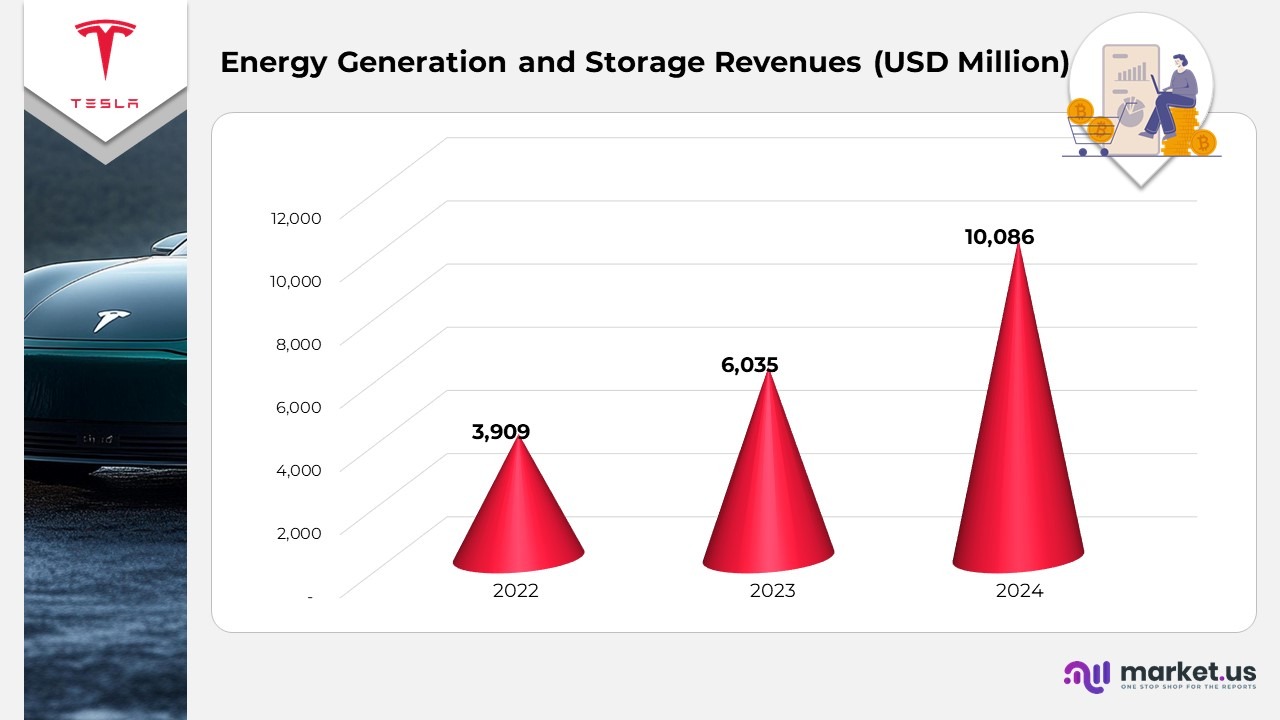
(Source: Tesla Annual Report)
Financial Analysis
Annual Revenue
- In 2024, Tesla recorded total revenues of $97.69 billion, marking a growth of $917 million from the previous year, driven by steady demand for electric vehicles and energy solutions.
- During the same period, Tesla reported a net income attributable to common stockholders of $7.09 billion, a decline of $7.91 billion compared to the prior year, mainly reflecting the one-time effect of releasing $6.54 billion in valuation allowances related to U.S. federal and state deferred tax assets recognized in Q4 2023.
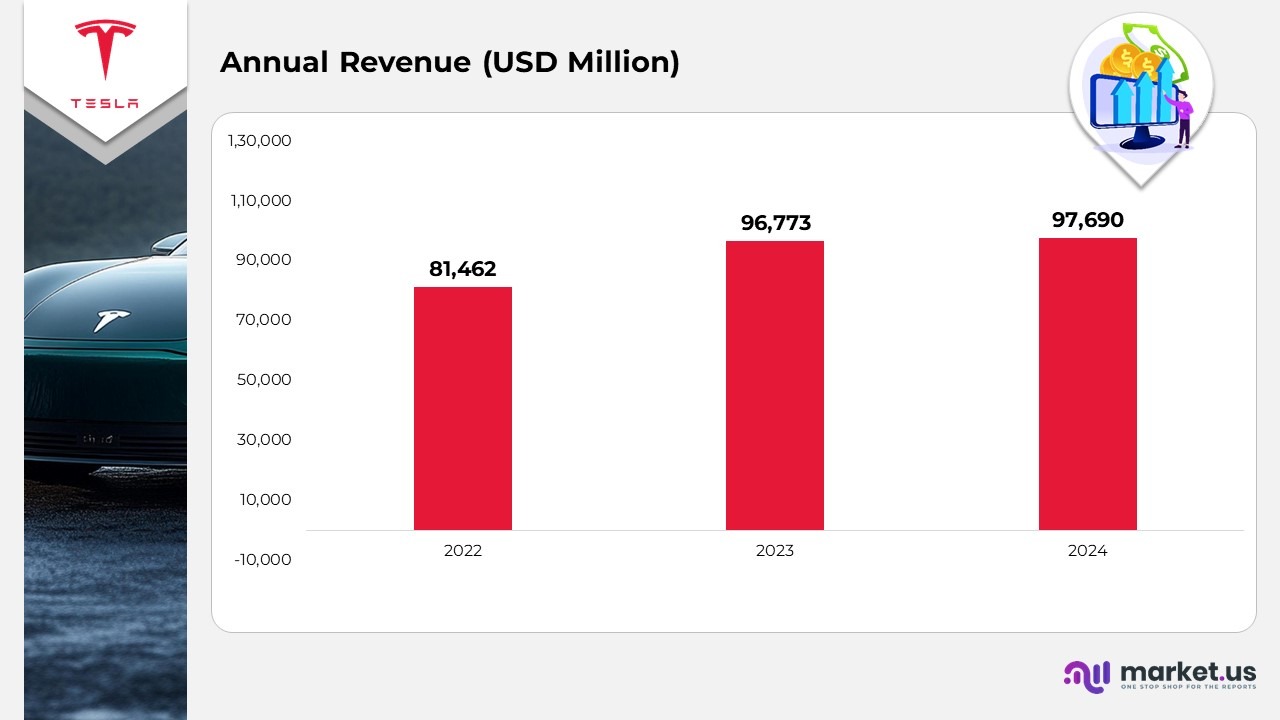
(Source: Tesla Annual Report and SEC Filings)
Geographic Revenue
- In 2024, Tesla recorded $47,725 million in revenue from the United States, an increase from $45,235 million in both 2023 and 2022, indicating steady growth in its core market.
- Revenue from China reached $20,944 million in 2024, compared with $21,745 million in 2023 and $18,145 million in 2022, reflecting a slight dip year over year following earlier expansion.
- Across other international markets, Tesla earned $29,021 million in 2024, marginally lower than $29,793 million in 2023, but well above the $22,764 million reported in 2022, emphasizing the company’s broadening global footprint.
(Source: Tesla Annual Report and SEC Filings)
Business Revenue
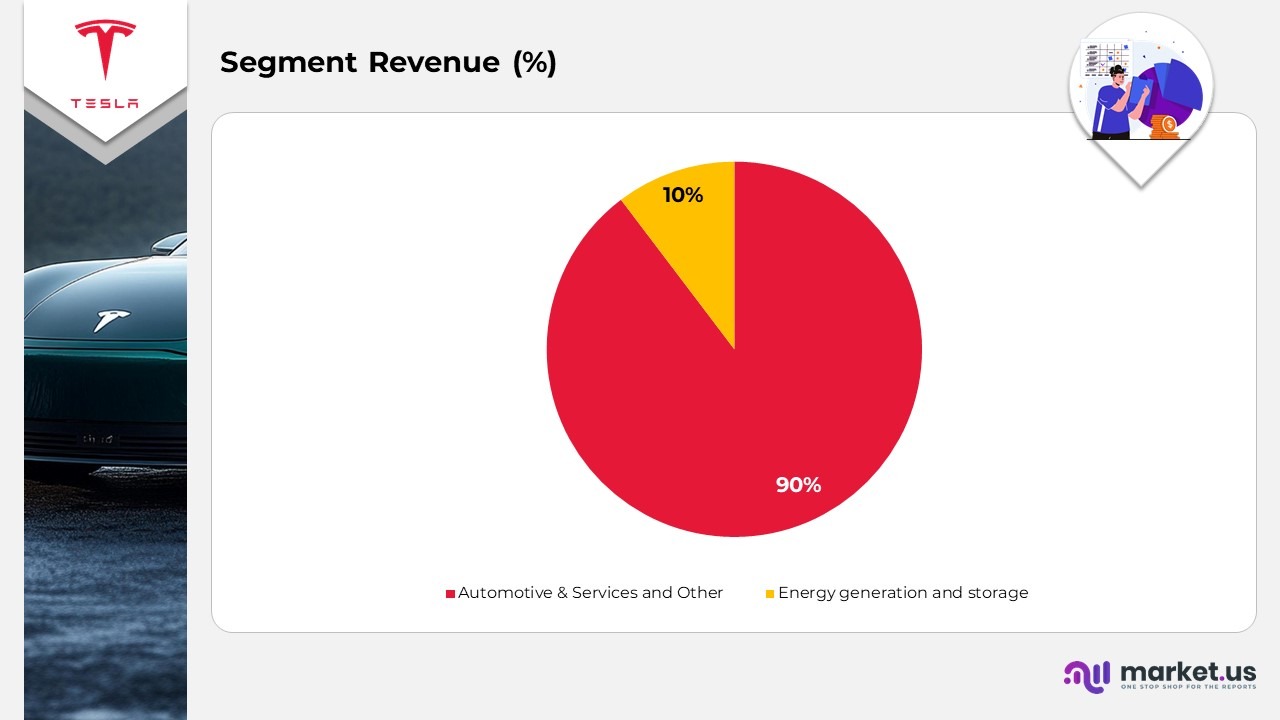
(Source: Tesla Annual Report and SEC Filings)
Research and Development Expenditure
- Research and development (R&D) expenses rose by $571 million, reflecting a 14% increase for the year ended December 31, 2024, compared to 2023, largely due to higher investments in artificial intelligence (AI) initiatives and related technological advancements.
- As a share of total revenue, R&D expenses grew from 4% in 2023 to 5% in 2024, highlighting Tesla’s continued focus on innovation and next-generation product development.
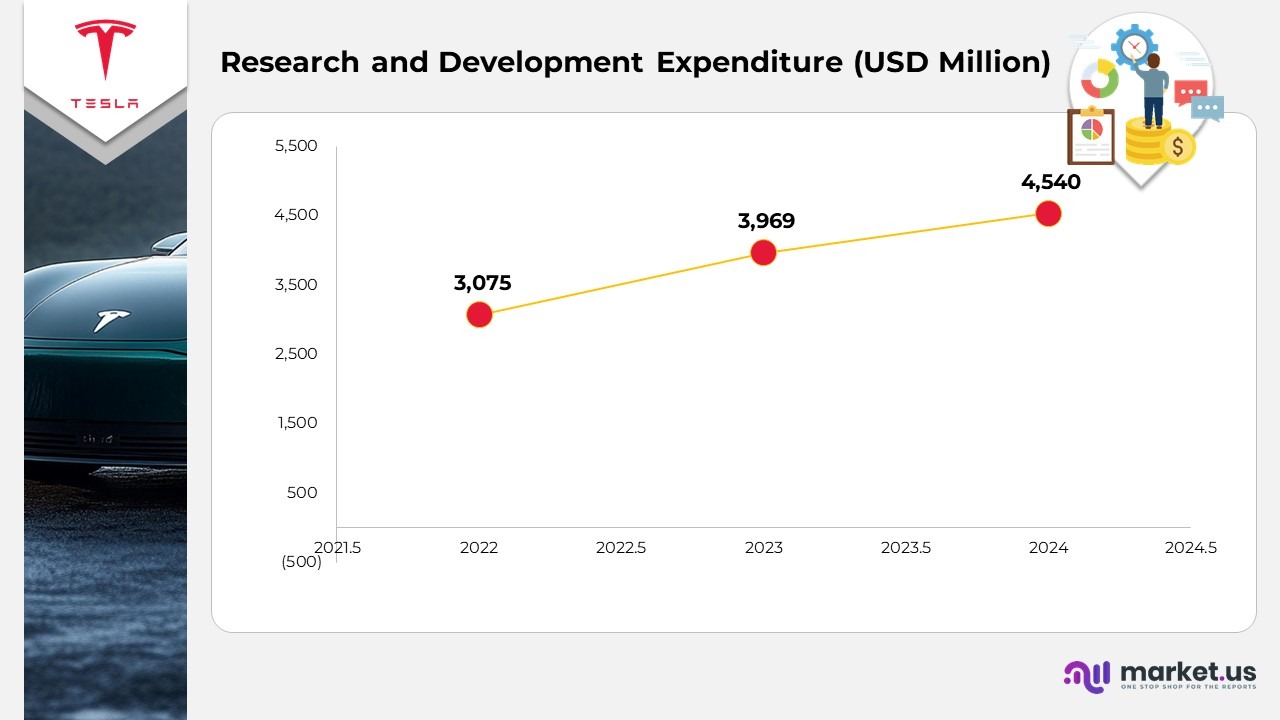
(Source: Tesla Annual Report and SEC Filings)
Tesla Vehicle Deliveries Statistics
- In 2024, Tesla delivered 1,789,226 vehicles, demonstrating continued strong performance despite a slight decline compared to the 1,808,581 vehicles delivered in 2023.
- In Q2 2025, Tesla’s deliveries reached 384,000 units, marking a 29% increase compared to the same period last year, emphasizing the company’s sustained growth and strong demand in key international markets.
- Since its inception, Tesla’s deliveries have grown significantly, from just 22,442 vehicles in 2013 to almost 8 million units in 2024, underscoring its transition from a niche electric vehicle manufacturer to a global leader in the automotive industry.
- The company saw an accelerated growth trajectory starting in 2018, when deliveries surged from 245,491 vehicles to 367,656 units in 2019, marking Tesla’s shift to mass-market vehicle production.
- From 2020 to 2022, deliveries more than doubled from 499,535 vehicles in 2020 to 1,313,851 units in 2022, driven largely by the increased production capacity of Model 3 and Model Y at Gigafactories across the US, Europe, and China.
- In 2021, Tesla crossed a significant milestone by delivering over 900,000 vehicles, a feat reflecting its resilience amidst global supply chain challenges, including the global chip shortage.
- By 2023, Tesla set a new record with 1,808,581 vehicles delivered, as electric vehicle adoption accelerated globally, supported by expanding charging infrastructure and government incentives.
- Tesla’s extensive Supercharger network, with thousands of locations worldwide, continues to strengthen its competitive edge by ensuring convenient long-distance travel and enhancing consumer confidence in EV technology.
(Source: CleanTechnica, Tesla)
Tesla’s Vehicle Production Trends
- In 2024, Tesla produced 1,773,443 vehicles, reflecting a 93% decline compared to the 1,845,985 units produced in the previous year.
- In 2014, Tesla’s production was limited to 35,000 vehicles, marking the company’s early phase of production with constrained capacity.
- The following year, 2015, saw a modest growth, with production reaching 51,095 units, as Tesla began scaling its manufacturing processes.
- By 2016, production had grown to 83,922 vehicles, as the company focused on further expanding its production lines.
- In 2017, Tesla produced 100,757 vehicles, continuing its trend of efficiency improvements and increasing its manufacturing output.
- 2018 marked a significant leap, with production reaching 254,530 vehicles, driven by growing demand for the Model 3.
- In 2019, Tesla’s production surged to 365,232 units, reflecting the success of the Model 3 and the broader expansion of the electric vehicle market.
- Despite the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic, 2020 saw Tesla’s production rise to 509,737 vehicles, demonstrating its ability to adapt and persevere.
- By 2021, Tesla surpassed the 930,000-vehicle mark, coming close to producing 1 million vehicles.
- In 2022, production further increased to 1,369,611 units, continuing the strong momentum, fueled by the ongoing success of the Model 3 and Model Y.
- Tesla achieved a record high in 2023, with production reaching 1,845,985 vehicles, reinforcing its dominance in the global electric vehicle market.
(Source: Tesla)
Tesla’s Supercharger Network Statistics
- As of September 2025, Tesla’s Supercharger network includes 7,702 active stations across 55 countries, further cementing its leadership in the electric vehicle charging space.
- By February 2025, Tesla reached 7,074 Supercharger stations, achieving another significant milestone in expanding its global charging infrastructure.
- As of January 2025, the network expanded to 7,035 stations, surpassing the 7,000 mark, showcasing Tesla’s rapid expansion in the charging network.
- In October 2024, Tesla achieved 6,766 active Superchargers, reflecting consistent growth in its network over the past years.
- By December 2023, Tesla’s network had reached 5,878 Supercharger stations, highlighting a steady and continuous increase in its charging infrastructure to meet the growing demand for EVs.
- As of April 2023, Tesla’s global network included 5,003 active stations, marking a significant achievement in the first quarter of 2023.
- By December 2022, the network had expanded to 4,620 stations, reflecting a marked growth compared to previous years.
- By March 2022, the number of Supercharger stations reached 3,251, continuing the company’s rapid infrastructure expansion.
- By December 2021, Tesla’s Supercharger network reached 3,070 stations, a key milestone in its network expansion.
- In July 2021, the network reached 2,966 stations, as Tesla continued its rapid infrastructure growth to keep up with the growing number of Tesla vehicles.
- By January 2021, the network had expanded to 2,613 active Superchargers, reflecting the increasing demand for EVs.
- By July 2020, Tesla’s network grew to 1,915 Superchargers, continuing its consistent growth trajectory despite global challenges.
- By January 2020, the network reached 1,770 active stations, marking another milestone in Tesla’s charging network development.
Moreover
- In July 2019, Tesla operated 1,594 Supercharger stations, showing increasing demand for electric vehicles globally.
- In January 2019, Tesla had 1,433 Superchargers, continuing to expand its charging infrastructure for growing EV adoption.
- In July 2018, Tesla’s network had grown to 1,314 stations, demonstrating steady progress to meet the increasing adoption of Tesla vehicles.
- In January 2018, the number of Supercharger stations reached 1,133, marking significant progress in global coverage.
- In July 2017, Tesla reached 889 stations, further advancing its global charging network.
- In January 2017, Tesla had 767 Supercharger stations, continuing its steady progress.
- In July 2016, the network grew to 640 stations, reflecting rapid expansion across various regions.
- By January 2016, Tesla’s Supercharger network included 553 stations, marking a phase of aggressive expansion.
- In July 2015, Tesla had 432 active Superchargers, demonstrating significant growth in the network.
- In January 2015, Tesla expanded to 328 stations, furthering its efforts to build a widespread EV infrastructure.
- In July 2014, Tesla’s Supercharger network reached 145 stations, showcasing increasing demand and expansion.
- In January 2014, the network included 84 stations, marking strong early growth.
- In July 2013, Tesla had 15 active Superchargers, initiating its global charging network.
(Source: supercharge.info)
Fun Facts
- Tesla’s first production vehicle, the original Roadster (2008-2012), was the first highway-legal serial electric car using lithium-ion battery cells.
- The company name Tesla was chosen during a date at Disneyland (according to one anecdote) by one of the founders.
- Tesla’s “Falcon wing” doors on the Model X are a distinctive design choice that set it apart from most SUVs.
- Tesla purchased and repurposed the former NUMMI plant in Fremont, California (previously Toyota/GM) in 2010 as its vehicle manufacturing facility.
- Tesla’s logo is said to represent a cross-section of an electric motor, paying homage to electromagnetic engineering.
- Tesla’s vehicles are built with large battery packs mounted under the floor, which lowers the centre of gravity and improves handling.
- While many automakers sell via dealerships, Tesla takes orders online and delivers vehicles largely via its owned outlets.
- Tesla’s energy storage product Megapack has been used in large utility projects, shifting the company beyond cars into grid-scale solutions.
- Tesla heavily machines large castings (“Giga Presses”) to make huge single-piece underbodies, reducing manufacturing complexity.
- Tesla’s strategy included producing high-price, low-volume models (Roadster, Model S) first, to help lower battery costs, then moving into higher-volume, lower-price models (Model 3, Model Y).
Recent Developments
- In July 2025, Tesla partnered with ACKO to redefine car ownership in India.
- In November 2023, Tesla expanded into the pickup truck segment with the launch of the Cybertruck, a full-size electric truck constructed with a stainless steel exoskeleton, combining the ruggedness of a utility vehicle with the acceleration of a sports car.
(Source: Tesla Press Releases)