Company Overview
Tata Motors Statistics: Tata Motors Limited is a leading global automobile manufacturer offering a comprehensive range of vehicles, including cars, buses, trucks, utility vehicles, and defense vehicles. The company operates through 2 primary business segments: Automotive and Other Operations.
The Automotive segment encompasses the entire spectrum of activities related to vehicle design, manufacturing, assembly, sales, and service, along with car financing and the sale of accessories and spare parts. This segment is further divided into 4 key sub-segments: Tata Passenger Vehicles, Jaguar Land Rover (JLR), Tata Commercial Vehicles, and Vehicle Financing. The Other Operations segment covers the company’s information technology and insurance brokerage services.
Tata Motors has a strong global footprint, with a presence in 125 countries, supported by over 9,400 customer touchpoints, 7 assembly plants, 3 design studios, 25 manufacturing sites, and 9 R&D centers spread across regions such as ASEAN, MENA, SAARC, Latin America, and Sub-Saharan Africa.
As of March 31, 2023, the company’s structure included 90 consolidated subsidiaries, 2 joint operations, 4 joint ventures, and 11 equity-accounted associates, along with their respective subsidiaries. Its key operational hubs are located in the United Kingdom, South Korea, Thailand, South Africa, and Indonesia, with design centers in Italy and the UK. Tata Motors’ vehicles are marketed extensively across Africa, the Middle East, South and Southeast Asia, Australia, and South America, reinforcing its position as a global automotive powerhouse.
Facts About Tata Motors
- Founded in 1945 as Tata Engineering and Locomotive Company (TELCO).
- Headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra, India.
- A core company of the Tata Group conglomerate.
- Initially produced locomotives before entering the automotive industry in 1954.
- Manufactures passenger cars, trucks, buses, vans, coaches, military vehicles, and construction equipment.
- Acquired Jaguar Land Rover (JLR) from Ford in 2008, marking its entry into the global luxury car market.
- Listed among the Fortune Global 500 companies.
- Has manufacturing and R&D facilities across India, the UK, South Korea, Thailand, South Africa, and Indonesia.
- One of India’s largest commercial vehicle manufacturers and a leading player in passenger vehicles.
- Introduced the Tata Indica in 1998, India’s first fully indigenous passenger car.
- Pioneered India’s electric mobility ecosystem with vehicles like Nexon EV, Tiago EV, and Tigor EV.
- Owns a significant market share in India’s electric vehicle segment.
- Focuses on sustainability through EVs, alternative fuel vehicles, and carbon-neutral production.
- Exports vehicles to over 125 countries worldwide.
History of Tata Motors
1900’s
- 1945: Tata Motors entered the industrial sector by starting the production of locomotives and engineering equipment after acquiring the I. Railway Workshop, laying the foundation for its future in heavy engineering.
- 1948: Partnered with Marshall Sons (UK) to manufacture steam road rollers, establishing an early presence in industrial mobility solutions.
- 1954: Achieved a significant breakthrough with the production of its first commercial truck (TMB 312), officially marking its entry into automotive manufacturing.
- 1964: Broadened its product portfolio with the 1210 vehicle series manufactured at the Jamshedpur plant, strengthening its dominance in the commercial vehicle market.
- 1969: Transitioned from TELCO to Tata Motors, adopting a unified brand identity that reflected its growing ambitions and diversified operations.
- 1975: Unveiled the Tata 1210 semi-forward model, enhancing performance and flexibility in the heavy vehicle category.
- 1983: Began mass production of heavy commercial vehicles, expanding operations to meet India’s industrial and logistics needs.
- 1986: Launched the Tata 407, which became one of the most successful light commercial vehicles known for its reliability and endurance.
- 1989: Introduced the Tata Multi-Utility Vehicle (MUV), expanding its offerings in the utility transport segment.
- 1991: Developed and launched Tata Sierra, India’s first indigenously designed SUV, marking a milestone in the domestic passenger vehicle industry.
- 1992: Entered the family car segment with the Tata Estate, designed as a comfortable and versatile station wagon.
- 1994: Rolled out the Tata Sumo, a robust and dependable multi-utility vehicle that became widely popular across India.
- 1995: Proved its engineering excellence during the Geneva–Bombay Rally, covering nearly 8,000 miles without any mechanical failure.
- 1998: Created history with the launch of the Tata Safari, India’s first homegrown SUV, and the Tata Indica, the nation’s first fully indigenous passenger car.
2000’s
- 2002: Launched the Tata Indigo, India’s first locally designed and manufactured sedan, expanding its passenger car lineup.
- 2004: Introduced the Tata Novus under the Tata Daewoo collaboration and the Indigo Marina, signaling global ambitions.
- 2005: Released Globus and Starbus fully built buses, alongside Tata Ace—India’s first mini-truck—and the Tata TL 4×4 utility vehicle, strengthening its presence in multiple segments.
- 2007: Entered the mass transport market with Tata Magic and Tata Winger, catering to small and commercial transport needs.
- 2008: Introduced the Tata Indigo CS, the world’s first sub-4-metre sedan, blending compactness with functionality.
- 2009: Launched landmark products including the Tata Nano (world’s most affordable car), Tata Prima heavy trucks, Jaguar Land Rover in India, and the Tata Manza.
- 2010: Rolled out the Tata Aria, India’s first crossover SUV with 4WD, merging power with luxury.
2011’s
- 2011: Expanded its small commercial lineup with Tata Venture, Magic Iris, and Ace Zip, aimed at efficient urban transport.
- 2012: Introduced the Tata Safari Storme, an upgraded SUV offering superior design and performance.
- 2014: Released the Tata Zest, a stylish compact sedan integrating advanced safety and connectivity features.
- 2015: Partnered with Marcopolo to launch the Magna luxury coach and unveiled the Tata Bolt, a sporty hatchback powered by the Revotron 1.2T engine.
- 2016: Introduced the Tata Tiago, a compact car that gained massive popularity for its contemporary design and fuel efficiency.
- 2017: Expanded its product line with Xenon Yodha, Starbus Hybrid, Hexa, Tigor, Tigor EV, Tata Nexon, and launched the performance sub-brand TAMO.
- 2018: Added new products such as Tata Ace Gold, Nexon AMT, Ultra trucks, Harrier SUV, and Winger 15S, advancing both commercial and passenger vehicle innovation.
- 2019: Showcased its technological prowess at the Geneva Motor Show with the debut of Ziptron EV technology, Nexon EV, and the Altroz Voice Bot.
- 2020: Launched Signa 5525 and Signa 4825.TK heavy trucks, the Altroz (5-star GNCAP rated), and introduced ZConnect smart connectivity systems.
Recent
- 2021: Achieved a record milestone by unveiling 21 commercial vehicles in a single day and launching the Ultra Sleek range.
- 2022: Pioneered the introduction of India’s first hydrogen fuel cell buses in partnership with Indian Oil and rolled out the Tata Ace EV, advancing sustainable transport.
- 2023: Enhanced its SUV and EV lineup with updated versions of Safari, Harrier, and Altroz Racer, while scaling hydrogen fuel technologies.
- 2024: Consolidated its leadership in electric mobility with the ADAS-equipped Nexon EV and launched the Altroz Racer, symbolizing next-gen innovation.
- 2025: Recognized as India’s No.1 EV brand, Tata Motors took vehicle safety to new heights with the launch of the Nexon.EV featuring ADAS technology.
- 2025: Presented its ‘Future of Mobility’ vision at the Auto Expo 2025, focusing on connected, sustainable, and intelligent transportation.
(Source: Company Website)
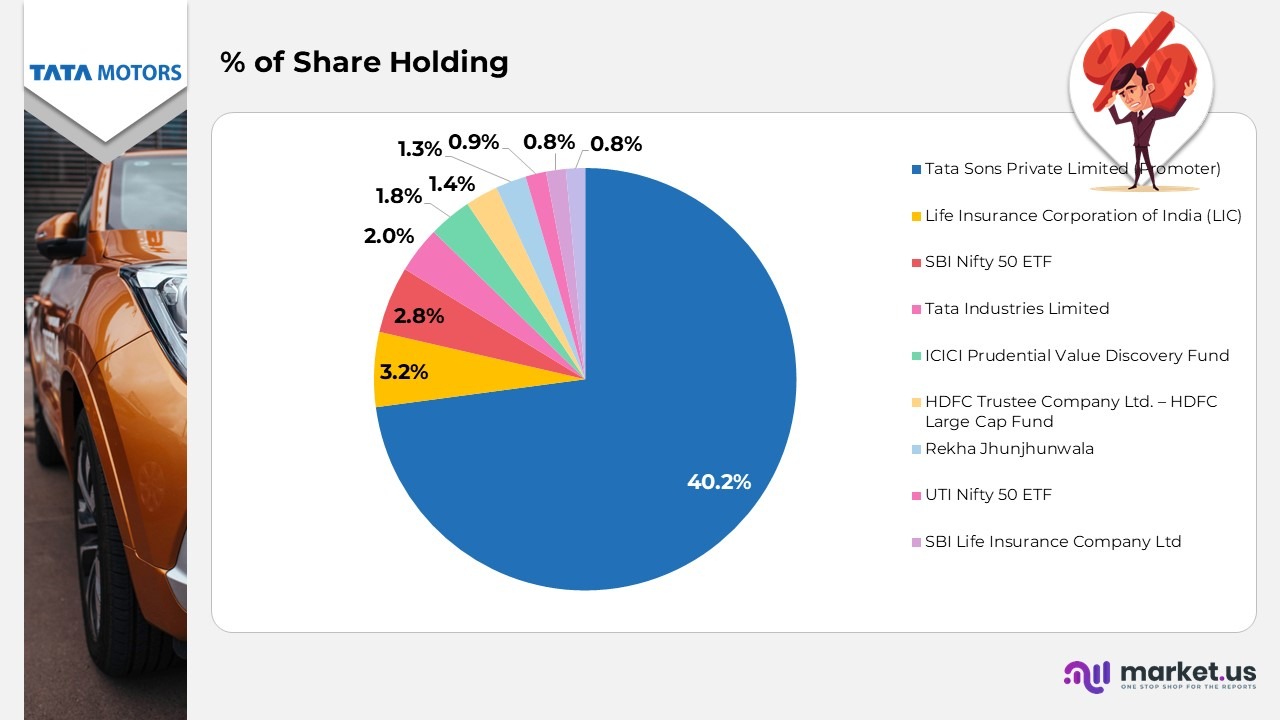
Shareholders Analysis –
- Tata Sons Private Limited (Promoter) remained the dominant shareholder with 1,47,82,63,541 equity shares, representing 16% of total ownership, underscoring its strong promoter backing and strategic control over the company.
- Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC) held 11,59,56,632 shares, equivalent to 15%, maintaining its long-standing investment partnership with the Tata Group.
- SBI Nifty 50 ETF owned 10,39,62,004 shares, amounting to 82%, reflecting Tata Motors’ notable representation within India’s key stock market indices.
- Tata Industries Limited retained a strategic holding of 7,22,03,630 shares, translating to 96%, demonstrating continued support from within the Tata Group’s portfolio companies.
- ICICI Prudential Value Discovery Fund controlled 6,69,94,537 shares, or 82%, signifying strong confidence from institutional investors in the company’s financial and operational performance.
- HDFC Trustee Company Ltd. – HDFC Large Cap Fund owned 5,07,37,455 shares, representing 38%, highlighting the fund’s consistent exposure to Tata Motors as a leading large-cap investment.
- Rekha Jhunjhunwala, a well-known individual investor, held 4,77,70,260 shares, or 30%, reflecting her substantial personal investment and confidence in Tata Motors’ long-term prospects.
- UTI Nifty 50 ETF accounted for 3,19,59,760 shares, equating to 87%, reaffirming Tata Motors’ inclusion in prominent passive investment portfolios.
- SBI Life Insurance Company Ltd owned 3,04,46,963 shares, corresponding to 83%, indicating continued institutional faith from the life insurance sector.
- Vanguard Total International Stock Index Fund held 2,99,27,560 shares, or 81%, representing growing interest from global investors and reinforcing Tata Motors’ international investment appeal.
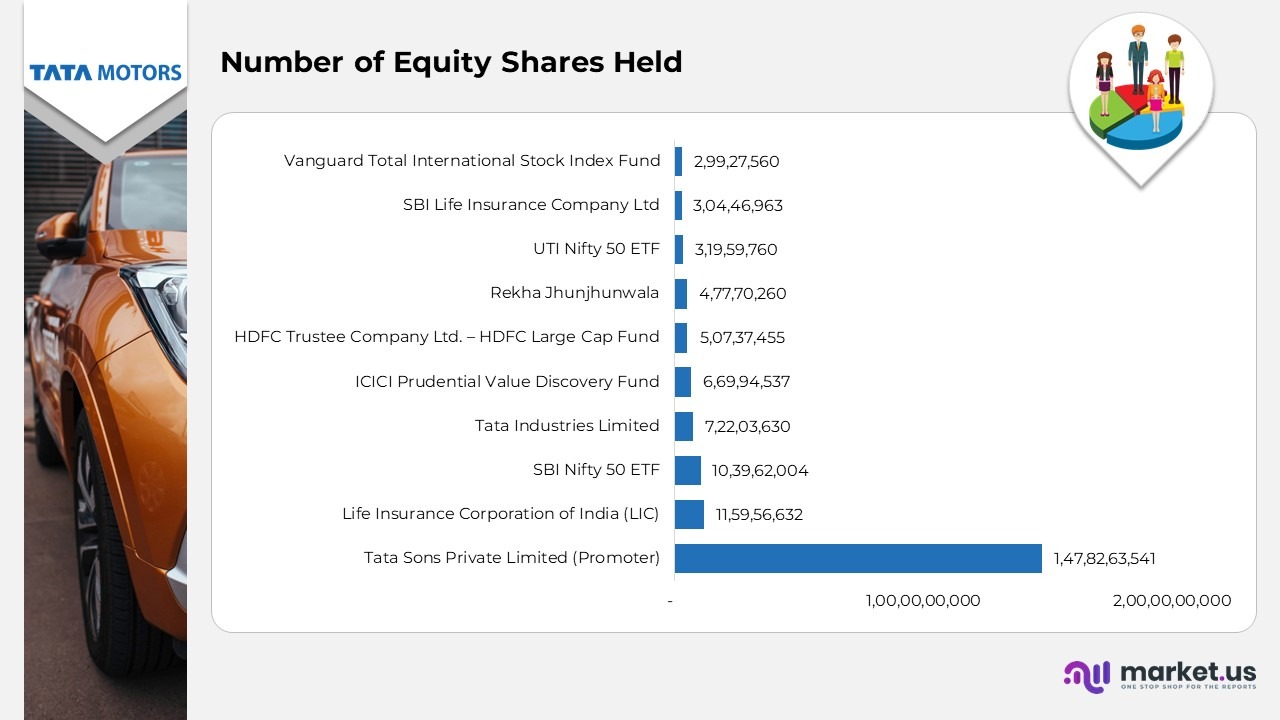
(Source: Tata Motors Limited Annual Report)
Employee Analysis
- As of December 2024, Tata Motors had a total workforce of 58,442 employees, comprising permanent staff and factory workers, reflecting the company’s strong operational presence and diverse talent base across its global network.
- The organization also employed over 48,000 contractual personnel, ensuring flexibility in its production systems and operational efficiency across various manufacturing facilities.
- An investment of ₹39.53 crore was directed toward training and development programs, underscoring Tata Motors’ commitment to skill enhancement, technical proficiency, and leadership growth across all levels.
- More than 3,27,471 hours were devoted to specialized learning and development sessions for management professionals, highlighting the company’s emphasis on building a culture of continuous learning and performance excellence.
- Through its Health and Safety initiatives, Tata Motors strengthened workplace safety standards and employee wellness measures, fostering a secure, inclusive, and healthy working environment for its entire workforce.
(Source: Tata Motors Limited Annual Report)
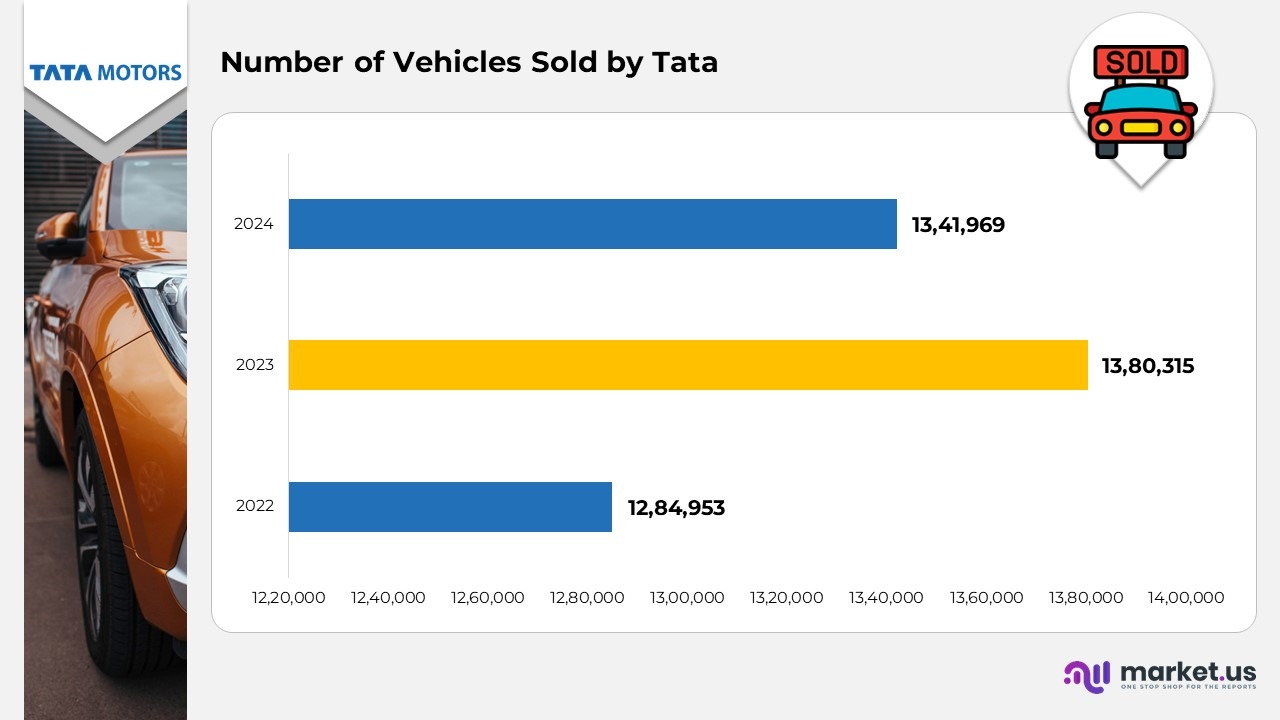
Number of Vehicles Sold by Tata
- In December 2024, Tata Motors reported total sales of 13,41,969 vehicles, demonstrating a strong performance across both domestic and international markets, supported by growing demand across multiple vehicle categories.
- The India Passenger Vehicle (PV) segment registered an impressive 11% growth, fueled by the popularity of modern SUVs, compact cars, and expanding electric vehicle offerings.
- Jaguar Land Rover (JLR) recorded a 17% rise in sales of Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) and Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs), reflecting the brand’s strategic progress toward luxury electrification.
- The company sold 64,269 electric vehicles (EVs) during the period, reaffirming Tata Motors’ dominant position in India’s EV segment and its continued focus on advancing sustainable and clean mobility solutions.
(Source: Tata Motors Annual Report)
Segmental Analysis
Automotive
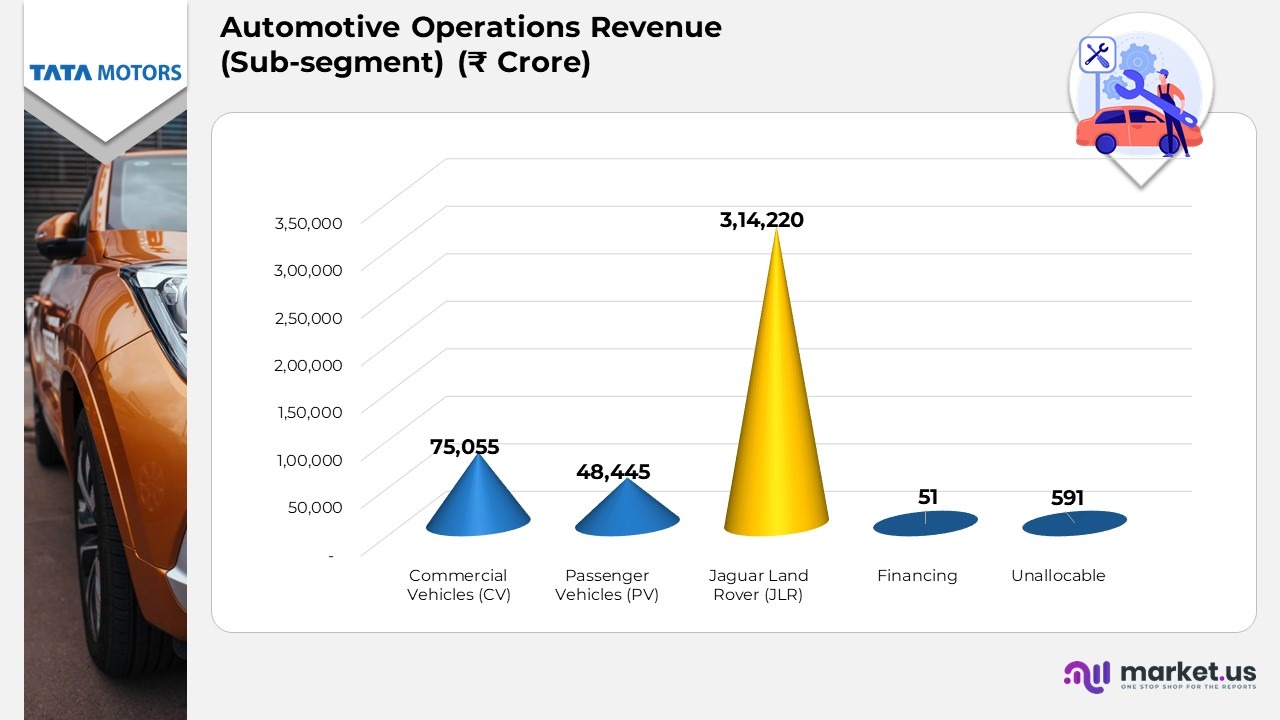
- Commercial Vehicles (CV) reported revenue of ₹78,791 crore in 2023, which eased to ₹75,055 crore in 2024, indicating a marginal contraction in the segment’s sales performance.
- Passenger Vehicles (PV) generated ₹52,353 crore in 2023, dropping to ₹48,445 crore in 2024, reflecting softer consumer demand and market adjustments.
- Jaguar Land Rover (JLR) achieved higher revenue, rising from ₹3,02,825 crore in 2023 to ₹3,14,220 crore in 2024, supported by increased global sales of luxury and electric models.
- The business earned ₹141 crore in 2023, which reduced to ₹51 crore in 2024, signaling a decline in income from financial operations.
- Unallocable segment stayed consistent with ₹593 crore in 2023 and ₹591 crore in 2024, showing stable revenue from ancillary and non-core operations.
Sub-segments
- Tata Commercial Vehicles generated ₹75,055 crore in 2024, compared to ₹78,791 crore in 2023, reflecting a 4.7% decline mainly due to reduced sales volumes. Revenue from vehicle and spare parts sales of commercial vehicles manufactured in India decreased by 5.5%, from ₹71,121 crore in 2023 to ₹67,215 crore in 2024, indicating softer demand in the domestic market.
- Tata Passenger Vehicles recorded a revenue of ₹48,445 crore in 2024, down from ₹52,353 crore in 2023, representing a 7.5% contraction year-on-year. The revenue from vehicles and spare parts produced in India fell by 4.3%, from ₹50,296 crore in 2023 to ₹48,144 crore in 2024, primarily due to market normalization after strong prior-year growth.
- Vehicle Financing revenue dropped significantly by 63.8%, reaching ₹51 crore in 2024 compared to ₹141 crore in 2023. This decline followed the transfer of Tata Motors Finance Ltd. to Tata Capital Ltd., effective April 1, 2024, as part of the group’s restructuring strategy.
- Jaguar Land Rover (JLR) reported an increase in revenue by 3.8%, rising to ₹3,14,220 crore in 2024 from ₹3,02,825 crore in 2023. This growth included a favorable currency translation impact of ₹11,105 crore due to GBP–INR movement. On a constant currency basis, JLR’s revenue remained steady at £29 billion in both 2024 and 2023, highlighting stable underlying performance in the luxury segment.
(Source: Tata Motors Annual Report)
Other Operations
- Revenue from other operations (before inter-segment eliminations) rose by 5%, reaching ₹6,019 crore in FY25 compared to ₹5,875 crore in FY24, reflecting moderate growth in non-core business activities.
- Tata Technologies maintained a steady performance with revenue of ₹5,175 crore in FY25, marginally higher than ₹5,126 crore in FY24, indicating stable contributions from its engineering and digital solutions portfolio.
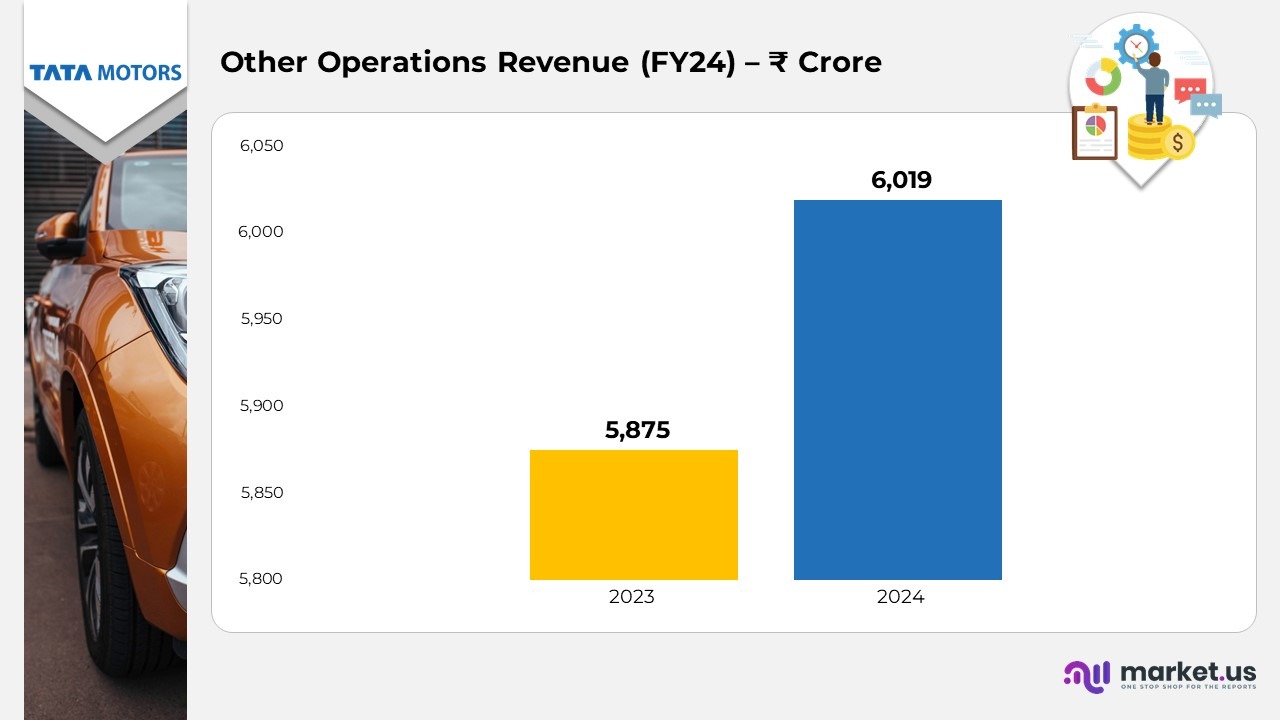
(Source: Tata Motors Annual Report)
Financial Analysis
Annual Revenue
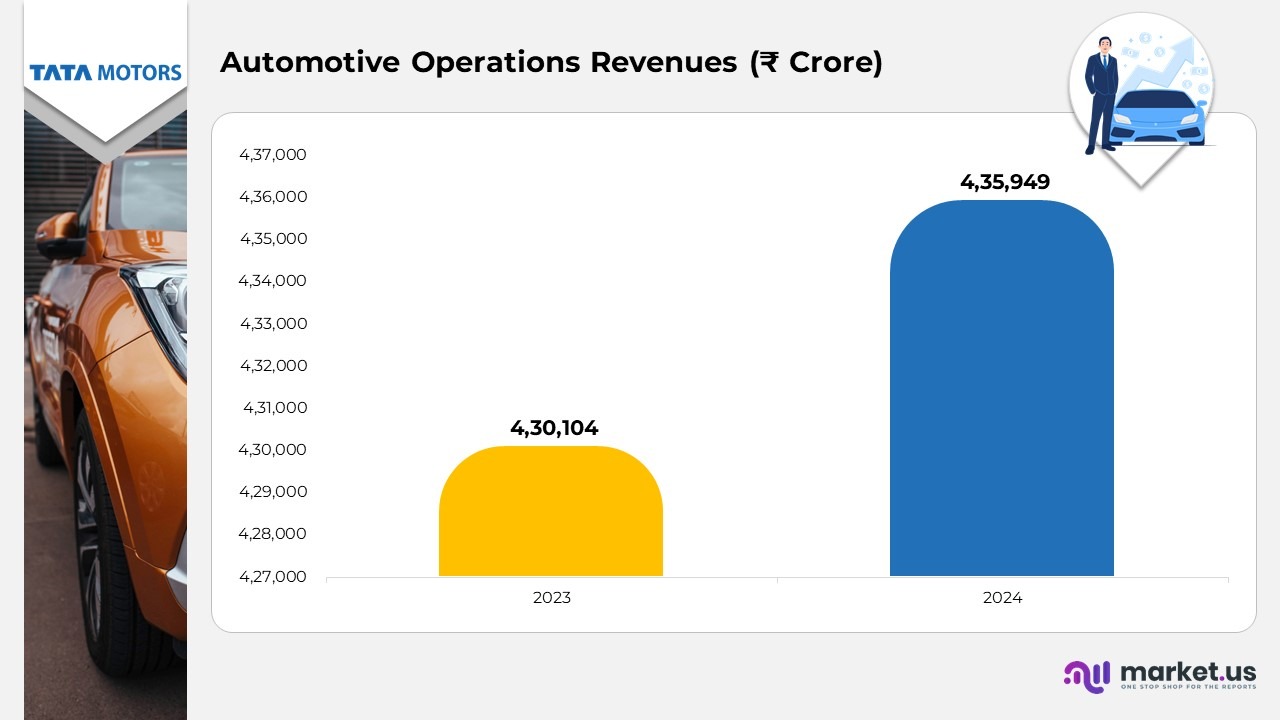
- In 2024, the company reported revenue from operations (excluding discontinued operations) of ₹4,39,695 crore, representing a 1.3% increase compared to ₹4,34,016 crore in 2023, reflecting steady top-line growth.
- The underlying EBITDA margin stood at 13.1% in 2024, slightly lower than 14.1% in 2023, influenced by higher input costs and strategic investments in new technologies.
- The underlying EBIT margin (excluding discontinued operations) remained stable at 7.9% for both 2024 and 2023, indicating consistent operational efficiency and effective cost management.
- Overall, Tata Motors demonstrated sustained revenue growth, operational stability, and continued focus on long-term profitability despite a competitive market environment.
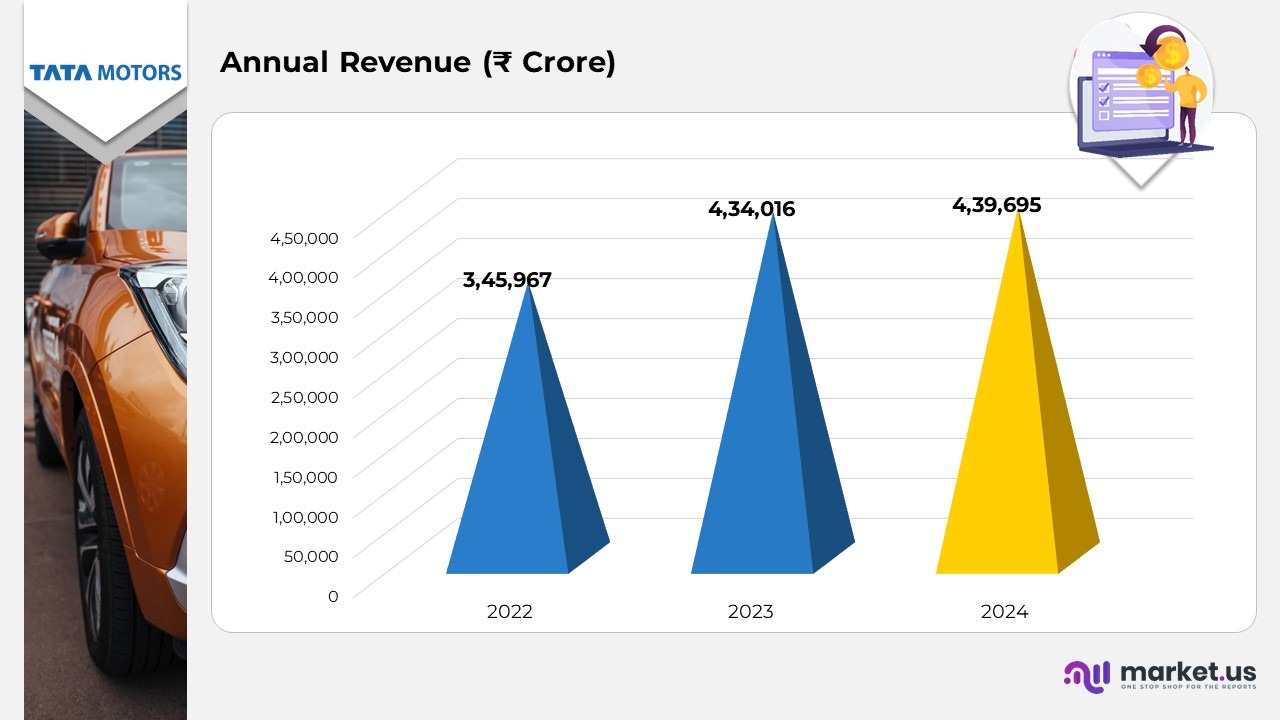
(Source: Tata Motors Annual Report)
Recent Developments
- In September 2025, Tata Motors introduced the Ace Gold+, the most affordable diesel variant in its legendary Ace lineup, priced at ₹5.52 lakh (ex-showroom). Designed for superior performance and efficiency, it offers the lowest Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) in its class, catering to cost-conscious entrepreneurs seeking reliability and value.
- In September 2025, the company launched the Tata LPT 812, a category-defining truck that reimagines customer profitability in its segment. Engineered for enhanced productivity, fuel efficiency, and operational ease, it sets a new standard for uptime and fleet performance.
- In August 2025, Tata Motors rolled out the all-new Tata Winger Plus, a 9-seater premium passenger vehicle built for corporate staff transport and the travel & tourism sector. Priced at ₹20.60 lakh (ex-showroom, New Delhi), it combines modern design, spacious interiors, and advanced connectivity for superior passenger comfort and cost efficiency.
- In August 2025, Tata Motors partnered with DIMO, marking a significant expansion of its footprint in the market while introducing advanced mobility and transport solutions tailored to local needs.
Moreover
- In August 2025, Tata Motors signed a landmark agreement with Green Energy Mobility Solutions Pvt. Ltd., the electric motion subsidiary of Universal Bus Services, to stream 100 Magna EV direct coaches, strengthening its presence in the premium electric passenger transport segment.
- In June 2025, the company launched the Tata Ace Pro, aimed at empowering a new generation of Indian entrepreneurs through enhanced load capacity, performance, and operational efficiency.
- In June 2025, Tata Motors expanded its ‘Recycle with Respect’ initiative by opening new Registered Vehicle Scrapping Facilities (RVSFs) in Lucknow (Uttar Pradesh) and Raipur (Chhattisgarh). These facilities cater to the responsible scrapping of passenger and commercial vehicles, including two- and three-wheelers, from all brands.
- In May 2025, Tata Motors unveiled the All-New Altroz, starting at ₹6.89 lakh, redefining the premium hatchback category with its elegant design, plush interiors, advanced technology, and top-tier safety features that reflect Tata’s commitment to style and performance.
- In May 2025, the company expanded its Registered Vehicle Scrapping Facility (RVSF) network to Kolkata, marking its eighth such facility nationwide. The center is equipped to process passenger, commercial, two, and three-wheeler vehicles, promoting sustainability and circular economy practices across India.
(Source: Tata Motors Press Releases)
Fun Facts About Tata Motors
- The Tata Nano, launched in 2008, was the world’s cheapest car, priced around USD 2,000.
- Tata Motors was the first Indian company to develop a sports utility vehicle — the Tata Sierra — in 1991.
- The Tata Safari, launched in 1998, was one of the first SUVs designed entirely in India.
- Tata Motors’ commercial vehicle, the Tata 407, has been one of the most successful light trucks in India.
- The Indica became a cultural icon in India, known for its tagline “More car per car.”
- Tata Motors developed the world’s first compressed air-powered car prototype with France’s MDI Group.
- The company’s vehicles are used in the Indian Army, emphasizing durability and reliability.
- Tata Motors has produced over 10 million vehicles globally since its inception.
- The company operates a design studio in the UK that has contributed to modern car aesthetics.
- Known for innovation, Tata Motors has been recognized with multiple national awards for engineering excellence.