Company Overview
Ford Motor Statistics: Ford Motor Company engages in the design, manufacturing, distribution, and sale of automobiles across global markets. The company operates in 5 reportable segments: Ford Blue, Ford Model e, Ford Pro, Ford Next, and Ford Credit. The Ford Blue segment focuses on the sale of Lincoln internal combustion engines and Ford hybrid vehicles, along with related accessories, service parts, and digital services designed for retail customers. The Ford Model e segment is dedicated to the development, distribution, and manufacturing of electric vehicles (EVs) and their corresponding parts, accessories, and digital solutions, delivering a complete retail experience for electric mobility customers.
Ford’s Next segment included investments and expenses for business. The Ford Credit segment offers automotive financing products.
The company maintains a global footprint spanning over 125 countries, including Argentina, China, Germany, Canada, Mexico, Romania, Spain, Thailand, Turkey, the U.S., the U.K., Vietnam, and South Africa. As of December 2024, the company operated 375 facilities worldwide, encompassing prototype, testing, manufacturing, and assembly operations across 24 countries, with a total of 41 dedicated production and assembly plants. As of December 2024, the company sold nearly 4,470,000 vehicles globally.
Facts About Ford Motor
- Founded in 1903 by Henry Ford and 11 associate investors, Ford was incorporated with a roughly US $28,000 cash investment from its 12 founders.
- Ford introduced one of the first moving assembly-line manufacturing methods in its Highland Park plant, making large-scale production of the affordable “universal car” possible.
- The famed Ford Model T, introduced in 1908, was designed to be affordable, simple to operate and durable, and became a landmark vehicle in the history of automotive mass production.
- Ford is headquartered in Dearborn, Michigan (USA) and remains a globally operating automobile manufacturer producing cars, trucks, commercial vehicles and luxury vehicles under brands such as Ford and Lincoln.
- The company has long been family-controlled: while the Ford family owns a relatively small equity stake, it retains significant voting power through special share structures.
- Ford has diversified historically: besides passenger cars and light trucks, it has been involved in commercial vehicles, tractors, and other equipment in past decades.
- In more recent years, the company has been restructuring its portfolio and operations to address electric vehicles (EVs), emerging mobility and software-enabled vehicles, in response to industry shifts.
- Ford emphasizes its identity as a “family company” with global reach, stating that its values include service to one another and to customers around the world.
- As part of its historical legacy, Ford’s corporate timeline illustrates key innovations from manufacturing methods through to contemporary mobility endeavours.
History of Ford Motor Company
1800’s
- 1896 – Henry Ford builds his first automobile, the Quadricycle, marking the beginning of his journey in automotive innovation.
- 1899 – Henry Ford partners with investors to establish the Detroit Automobile Company, his first venture into organized car manufacturing.
1900’s
- 1901 – Henry Ford gained national attention by defeating the top racecar driver of the time, proving the performance of his engineering skills.
- 1903 – The Ford Motor Company is officially incorporated, laying the foundation for one of the world’s most influential automakers.
- 1904 – Ford Motor Company of Canada is founded, expanding the company’s reach beyond the U.S. for the first time.
- 1907 – Ford introduces the scripted typeface trademark, creating the iconic logo still recognized today.
- 1908 – Ford opens its first overseas branch in Paris, marking its entry into the global market.
- 1908 – The legendary Model T is introduced, revolutionizing personal transportation through mass affordability.
- 1913 – Ford pioneers the integrated moving assembly line, transforming automobile production efficiency worldwide.
- 1914 – The company introduces the groundbreaking $5 workday, setting a new standard for employee wages.
- 1917 – Construction begins on the River Rouge Complex, which later becomes one of the world’s largest integrated factories.
- 1917 – Ford produces its first-ever truck, expanding its product portfolio beyond passenger cars.
- 1918 – The River Rouge Complex starts manufacturing antisubmarine patrol boats, supporting wartime efforts.
- 1919 – Edsel Ford made Henry Ford the company president, ushering in a new era of leadership.
1920’s
- 1922 – Ford obtains the Lincoln Motor Company, entering the luxury vehicle market.
- 1925 – The company begins the manufacture of Ford Tri-Motor airplanes, diversifying into aviation.
- 1927 – Ford launches the Model A, succeeding the Model T with modern design and improved performance.
- 1932 – Introduction of the flathead V8 engine, setting a new benchmark for affordable power in vehicles.
- 1936 – Ford debuts the Lincoln Zephyr line, combining style, aerodynamics, and performance in the luxury segment.
- 1938 – Ford introduces the Mercury brand, targeting the mid-priced automobile market and expanding its consumer reach.
- 1941 – Ford creates producing Jeeps for the U.S. military.
- 1941 – Ford signs its first labor contract with the UAW-CIO.
- 1942 – Ford halts civilian car production to focus on military manufacturing.
- 1943 – Edsel Ford passes away; Henry Ford resumes as company president.
- 1945 – Henry Ford II becomes the president of Ford Motor Company.
- 1948 – Ford announces the F-Series truck lineup.
- 1948 – Ford launches the 1949 Ford, the first postwar American car design.
1950’s
- 1954 – Ford debuts the Thunderbird.
- 1954 – Ford starts crash testing its vehicles.
- 1956 – Ford grow into a publicly traded company.
- 1956 – Continental Division introduces the Continental Mark II.
- 1957 – Ford launches the Edsel.
- 1959 – Ford Motor Credit Company is established.
- 1964 – The Ford Mustang goes on sale.
- 1965 – Ford releases the Transit in Europe.
- 1965 – Ford-Philco engineers develop NASA’s Mission Control Center.
- 1966 – Ford GT40 wins the 24 Hours of Le Mans.
- 1970 – Ford introduces three-point self-adjusting seatbelts.
- 1976 – Ford of Europe launches the Ford Fiesta.
- 1978 – Ford unveils the downsized Panther platform.
- 1980 – Phillip Caldwell becomes Ford’s first non-family CEO.
- 1981 – Ford launches the fifth-generation Escort.
- 1985 – Ford introduces the aerodynamic Taurus.
- 1986 – Ford implements modular assembly lines.
- 1990 – Ford introduces the Explorer SUV.
- 1993 – Ford launches the Mondeo global sedan.
- 1996 – Ford develops the Ranger Electric Vehicle.
- 1998 – Lincoln introduces the Navigator luxury SUV.
2001’s
- 2001 – Bill Ford becomes CEO, refocusing on core automotive operations.
- 2003 – Ford celebrates its 100th anniversary.
- 2004 – Ford announces the GT supercar.
- 2006 – Alan Mulally becomes President and CEO; launches the One Ford plan.
- 2007 – Ford introduces SYNC, a voice-activated connectivity system.
- 2009 – Ford launches its turbocharged EcoBoost engine line.
- 2011 – Ford discontinues the Mercury brand.
- 2014 – Mark Fields becomes CEO.
- 2014 – The Mustang celebrates its 50th anniversary.
- 2014 – Ford debuts the 13th generation F-150 with an aluminum body.
- 2016 – Ford Smart Mobility, LLC is established.
- 2016 – Ford celebrates 50 years since its first Le Mans victory.
- 2017 – Jim Hackett becomes CEO.
- 2018 – Ford acquires the Corktown Campus at Michigan Central Station.
- 2019 – Ford unveils the all-electric Mustang Mach-E.
- 2020 – Project Apollo supports pandemic relief efforts.
- 2020 – Jim Farley becomes CEO and launches the Ford+ transformation plan.
- 2020 – Ford launches the all-electric E-Transit.
- 2020 – Ford revives the iconic Bronco SUV.
- 2021 – Ford introduces the all-electric F-150 Lightning.
(Source: Ford Motor Company Website)
Segmental Analysis
Ford Blue
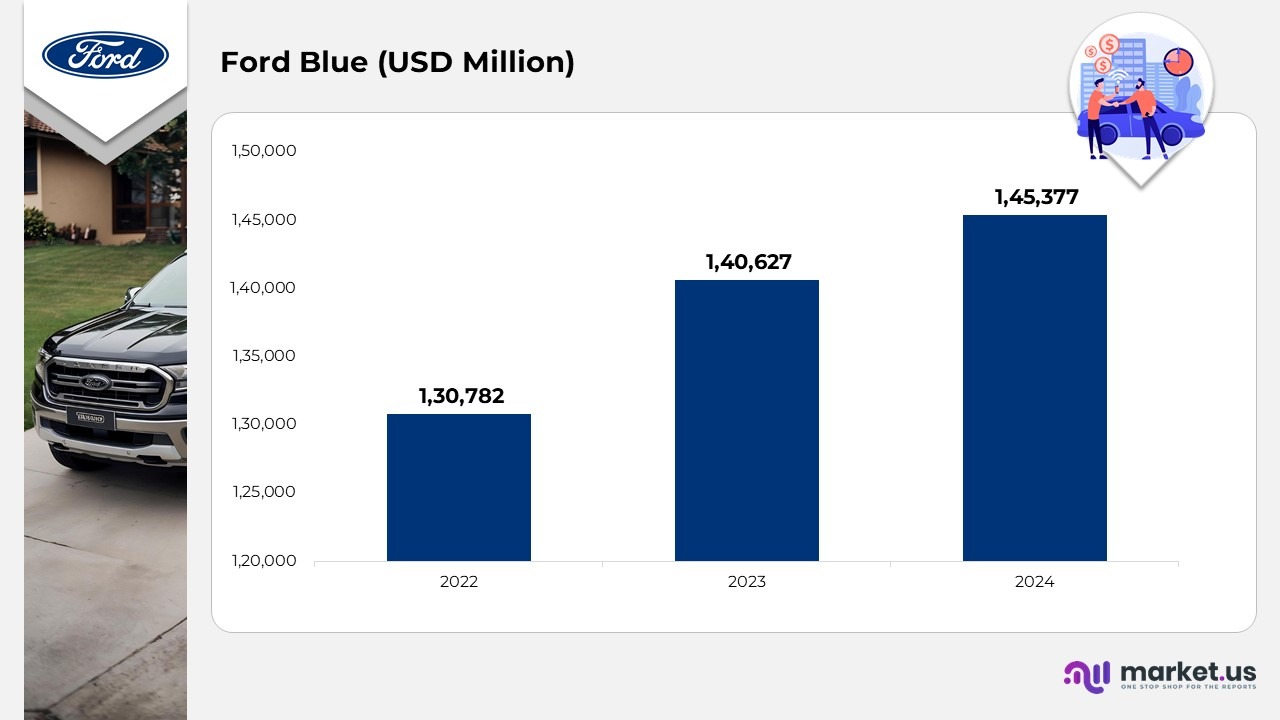
- In 2024, Ford Blue’s sales decreased by 2% compared to the previous year, mainly due to the end of production for the Fiesta in Europe and the Edge in North America. Increased wholesales of the Ranger and Bronco partially offset this decline.
- Ford Blue’s full-year EBIT for 2024 was $5,284 million, a drop of $2,178 million from the previous year, resulting in an EBIT margin of 5.2%.
- The lower EBIT was primarily driven by unfavorable exchange rates, an adverse product mix (especially supplier-related constraints and less F-150s due to the new model launch), reduced wholesales, and higher costs, including increased material costs for new products and advanced warranty expenses.
Ford Blue Revenue
Model E Revenue Statistics of Ford Motor
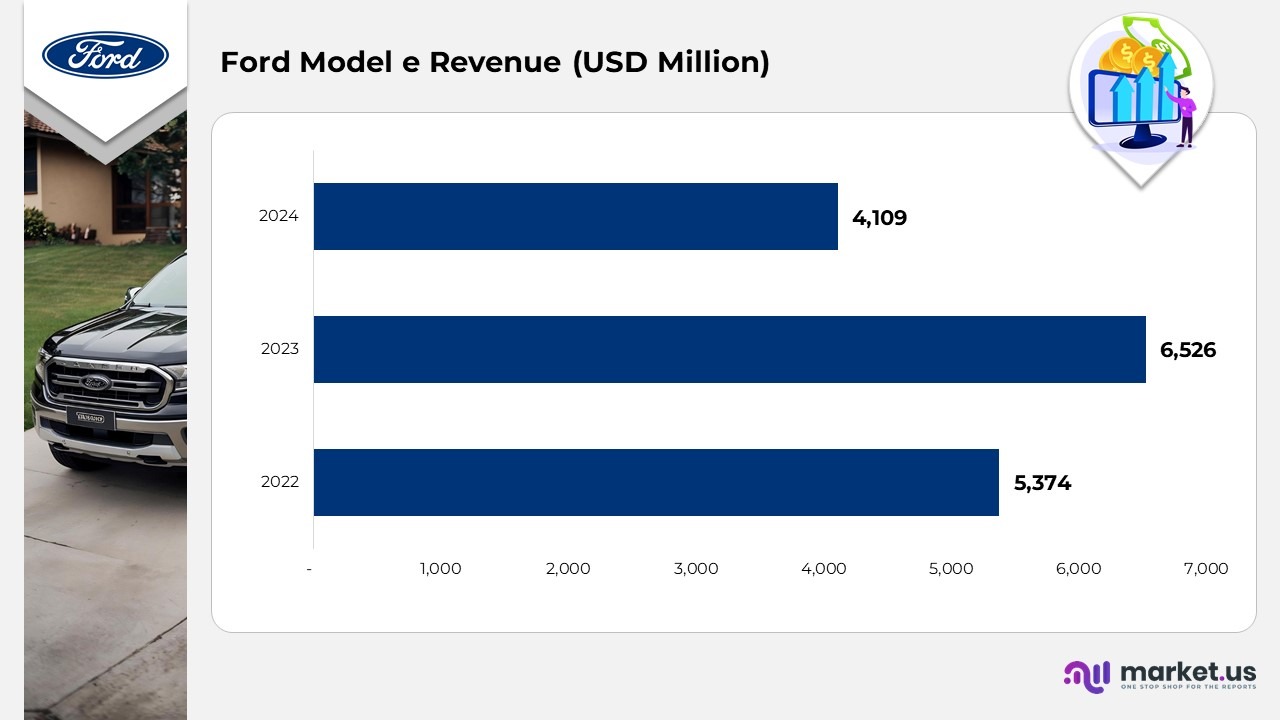
Ford Motor Pro Revenue Statistics
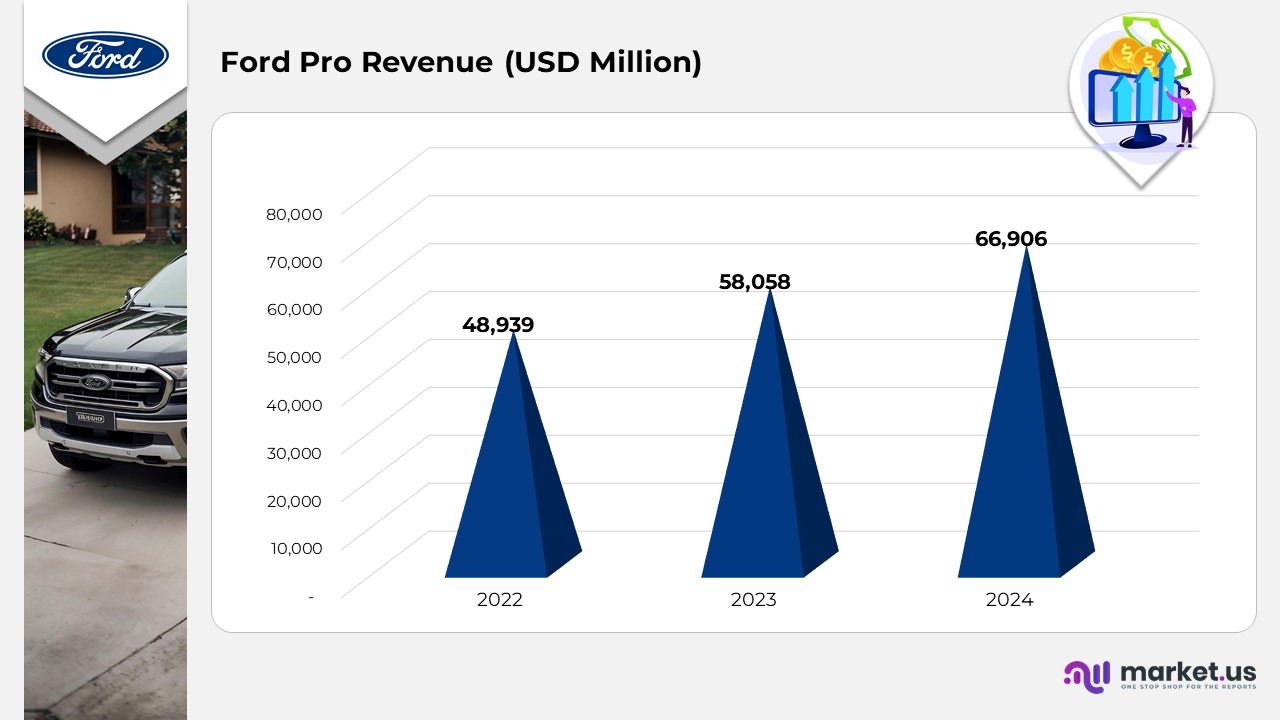
Ford Next Revenue
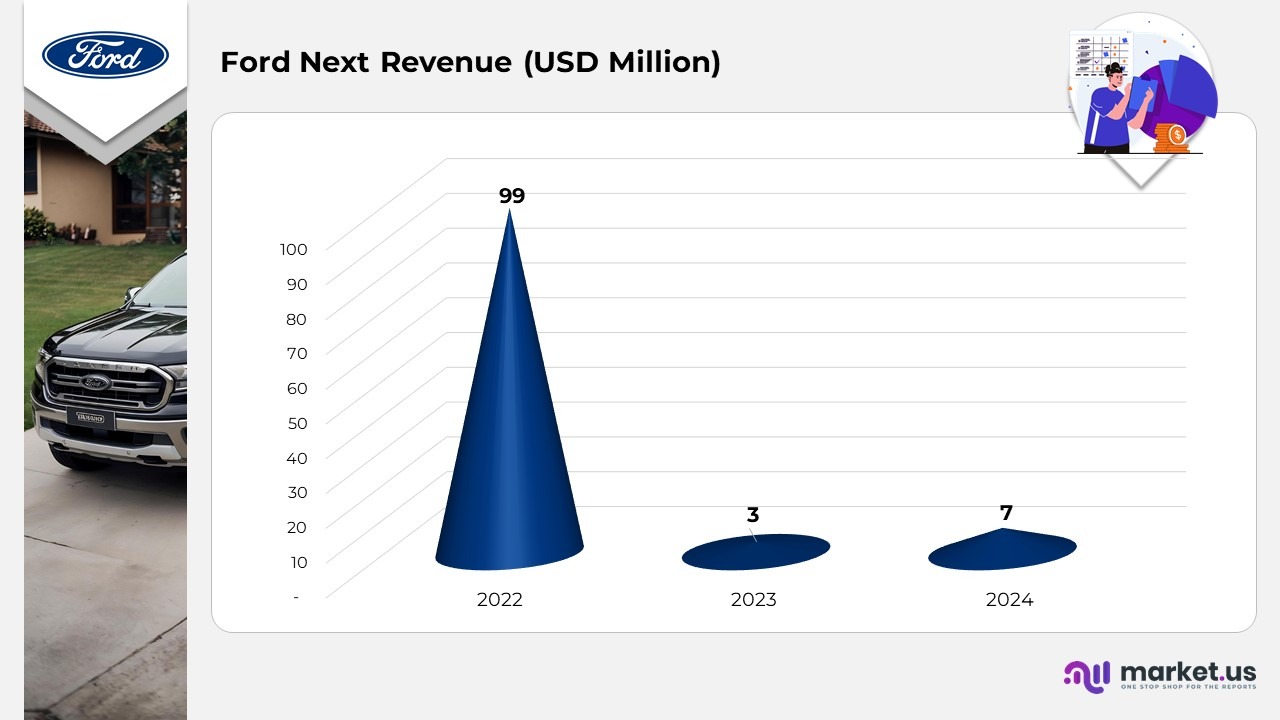
Credit Revenue By Ford
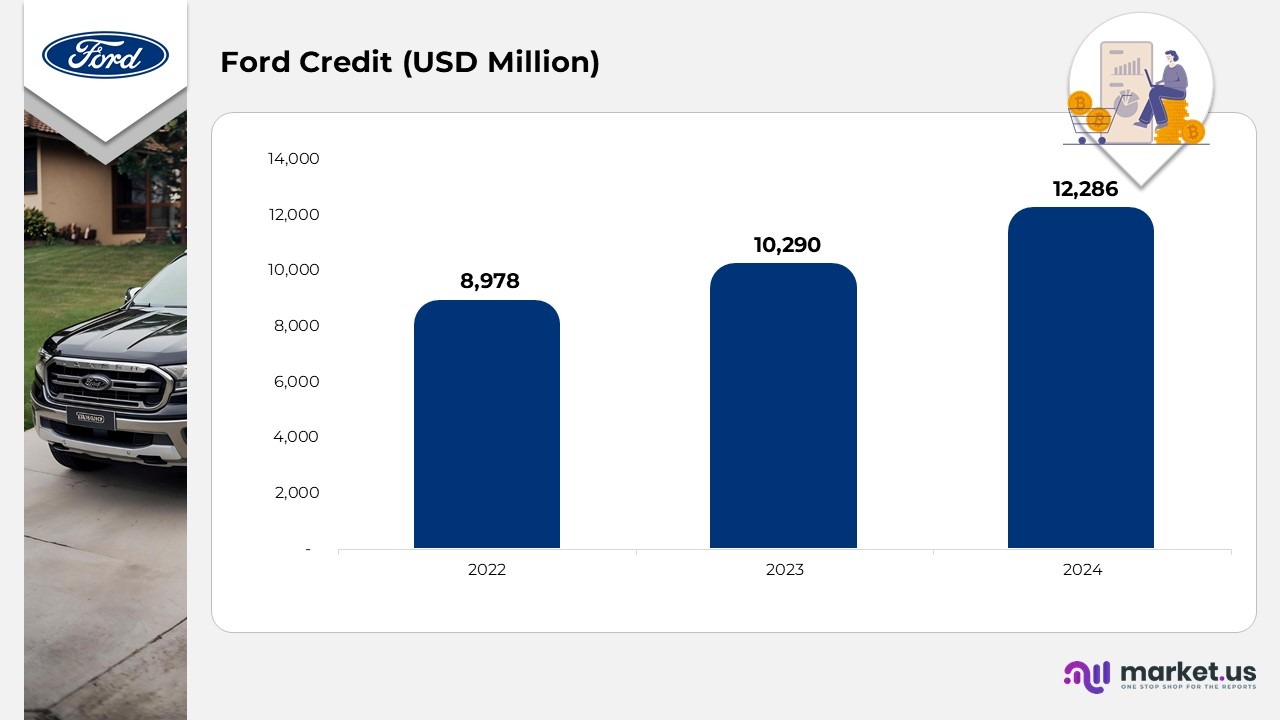
(Source: Ford Motor Company Annual Report, and Company Website)
Financial Analysis
Group Revenues
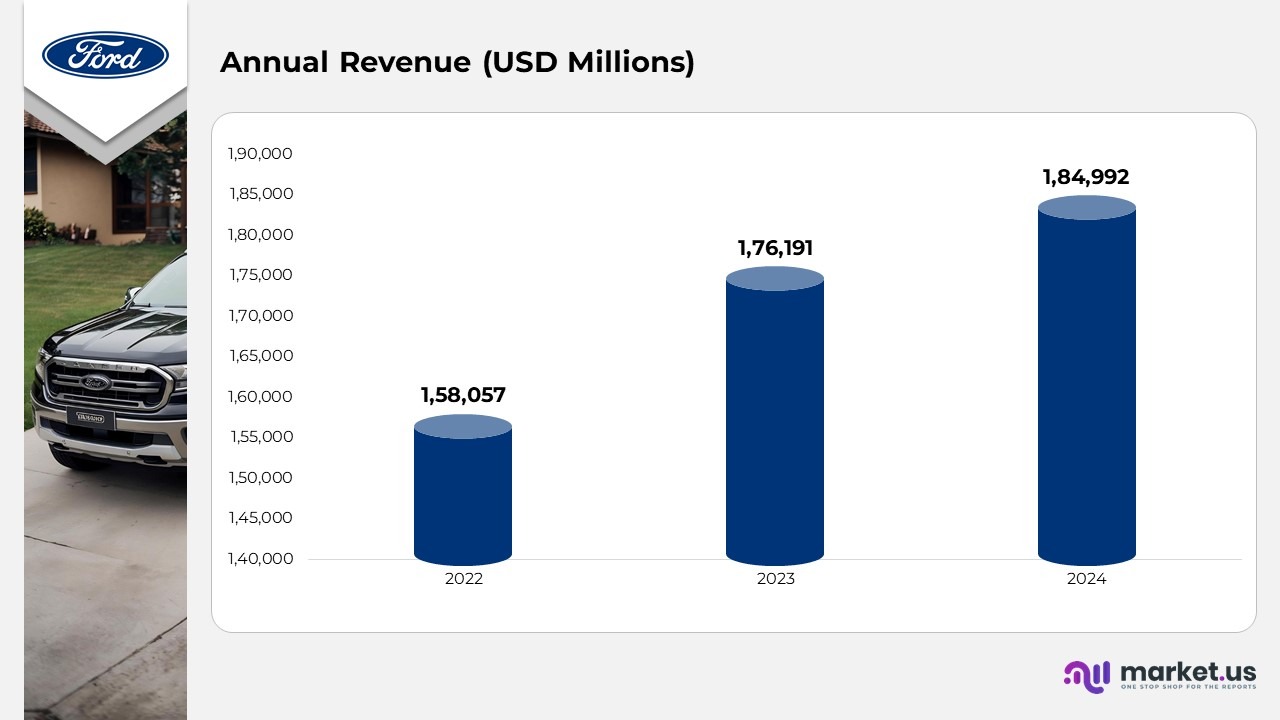
(Source: Ford Motor Company Annual Report)
R&D Expenditure
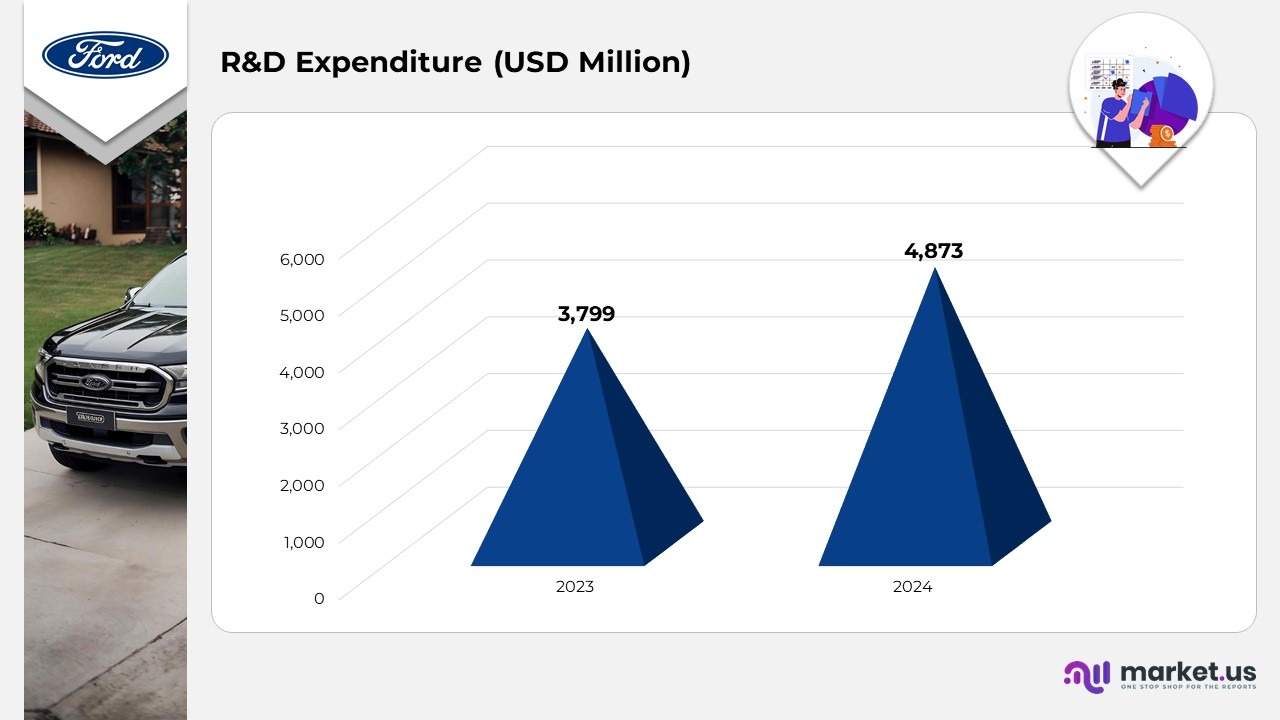
(Source: Ford Motor Company Annual Report)
Business Revenue
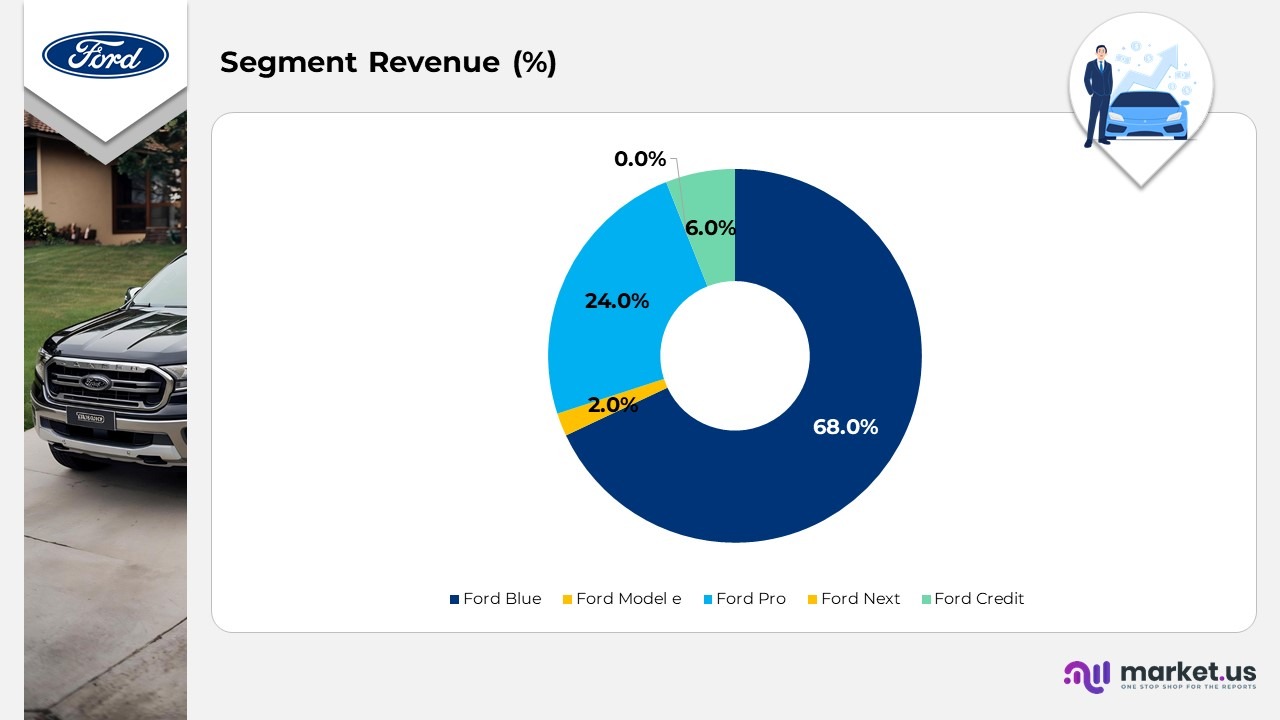
(Source: Ford Motor Company Annual Report)
Geographic Revenue
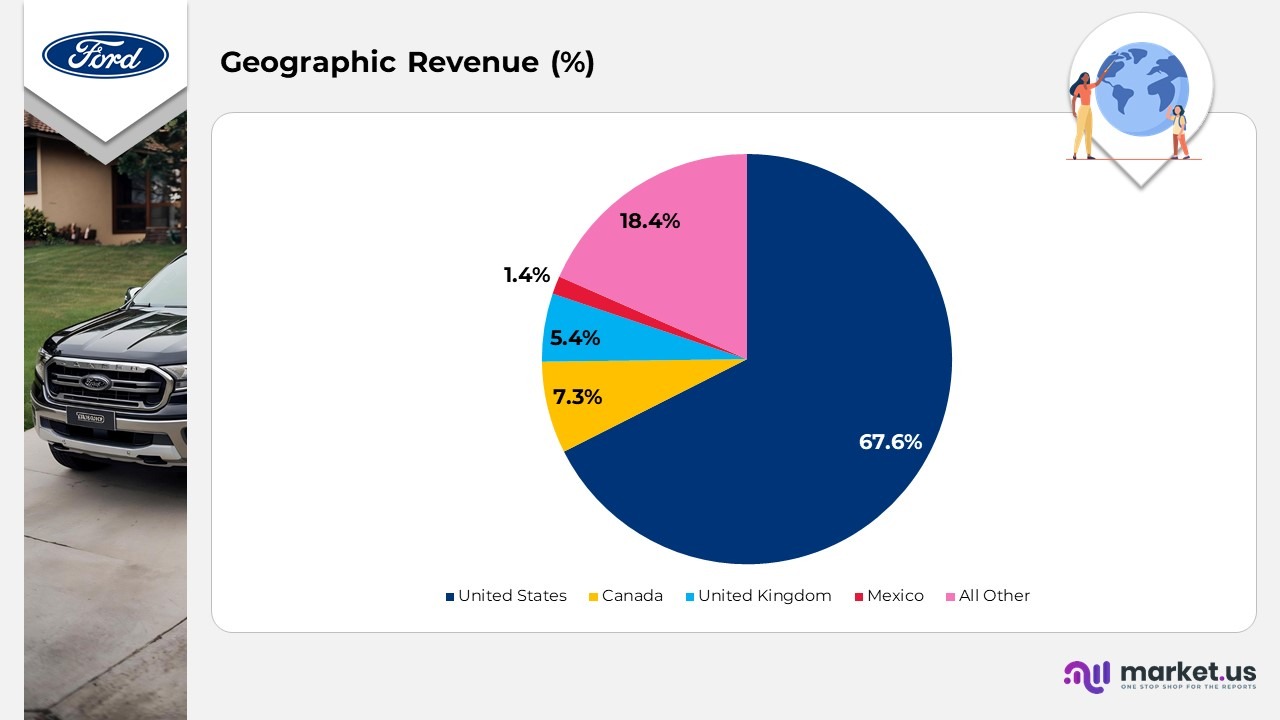
(Source: Denso Corporation Annual Report)
Fun Facts
- The company’s very first vehicle sold was a “Model A” in 1903, purchased by Dr. Pfennig for US $850.
- Henry Ford and Thomas Edison were close friends and went on well-publicised camping trips together between 1914 and 1924.
- The iconic “Blue Oval” Ford logo was not introduced until 1907—four years after the company’s incorporation.
- Ford used wood scrap from the production of the Model T to make charcoal briquettes.
- The Ford family still holds about 40 % of the voting power in the company, even though their equity share is much smaller.
- In 1965, a Ford Mustang was transported in pieces to the observation deck of the Empire State Building, reassembled there for a photo shoot, and then later removed.
- The company pioneered large-scale mass production through its moving assembly line—this innovation greatly lowered costs and made cars widely accessible.
- Moreover, Ford is considered one of the largest family-controlled businesses in the world despite being publicly traded.
Recent Developments
- In September 2025, Ford teamed up with Service Titan, the software provider supporting the trades industry, to enhance fleet management and vehicle servicing for work vehicles used by tradespeople.
- In March 2025, the company launched LocateFordWorkTrucks.com, a tool designed to help quickly locate upfitted vehicles.
- In January 2024, Ford Motor Company announced the creation of nearly 900 new jobs with the introduction of a third shift at the Michigan Assembly Plant in Wayne to meet the growing demand for the popular Bronco, Bronco Raptor, and the all-new Ranger and Ranger Raptor.
- In March 2023, Ford signed a partnership agreement with PT Vale Indonesia Tbk and Zhejiang Huayou Cobalt Co. to support more sustainable nickel production in Indonesia, contributing to the reduction in electric vehicle battery costs.
- In August 2023, Ford expanded F-150 Lightning production with a plant expansion, aiming to triple its manufacturing output.
(Source: Ford Motor Company Press Releases)