Global Sustainable Marine Fuel Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Туре (Hydrogen, Ammonia, Methanol, Biofuels, Others), By Application (Tankers/Carriers, Barges/Cargo Vessels, Tugboats, Defense Vessels, Ferries, Yachts, Cruise Ships, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends, and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Sep 2025
- Report ID: 153311
- Number of Pages: 316
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
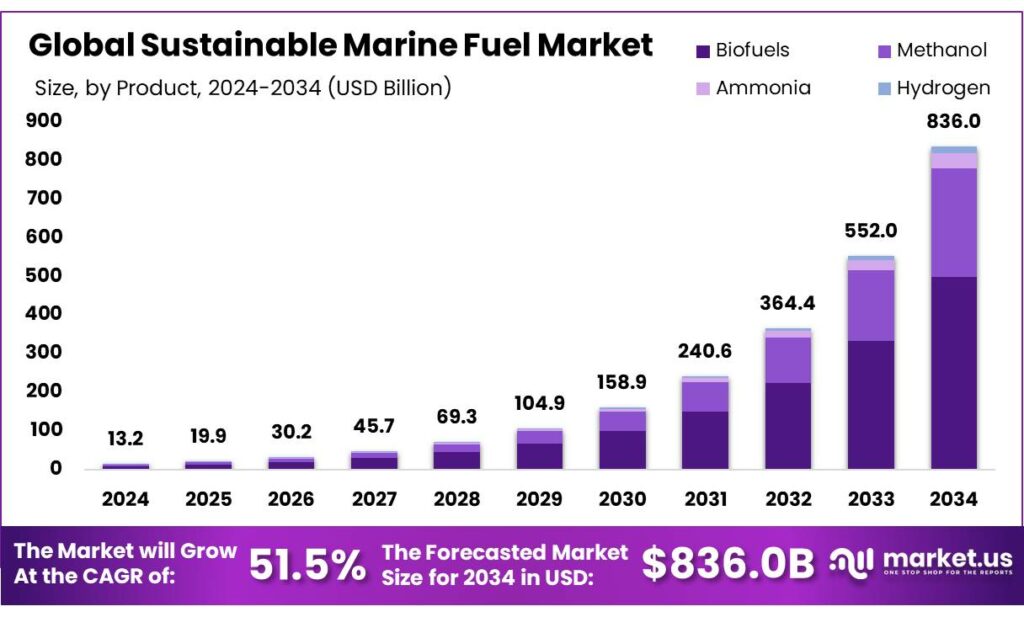
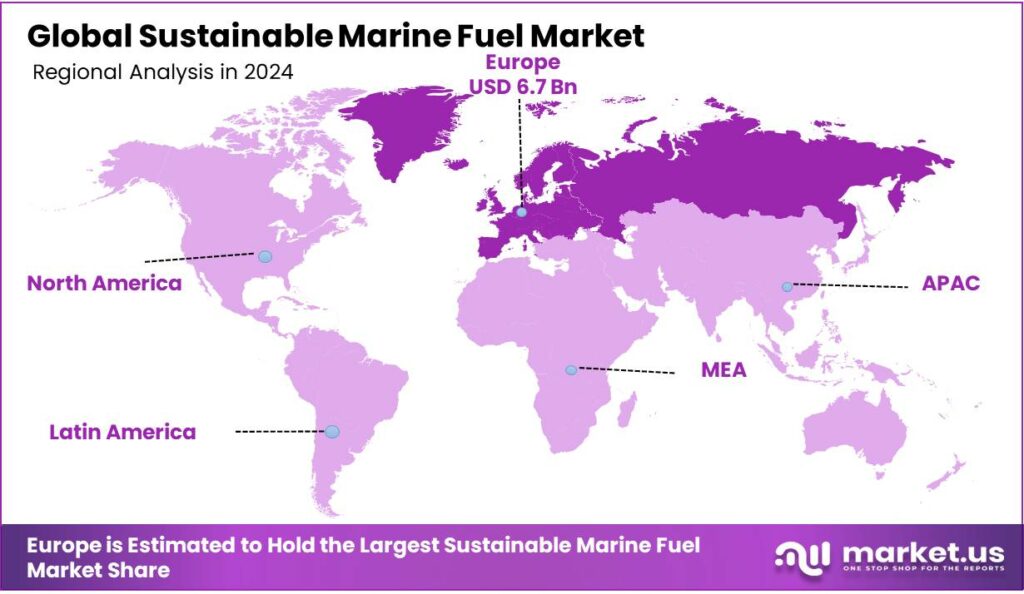
The Global Sustainable Marine Fuel Market size is expected to be worth around USD 836.0 Billion by 2034, from USD 13.1 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 51.5% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, Europe held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 51.0% share, holding USD 6.7 Billion revenue.
The global sustainable marine fuel (SMF) market is emerging as a crucial pillar in the decarbonisation of the maritime sector, which currently contributes about 2.5% of global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Without action, this share could rise to 17% by 2050, as international trade and shipping volumes grow.
In response, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) has set ambitious targets to achieve net-zero GHG emissions from shipping by around 2050, with milestones of 20–30% reduction by 2030 and 70–80% by 2040, relative to 2008 levels. Achieving these goals will require a transition away from conventional fossil fuels toward scalable, low-carbon alternatives.
Sustainable marine fuels are central to this transformation. Produced from bio-based feedstocks, recycled carbon sources, or renewable energy pathways (Power-to-X, electrofuels, hydrogen), SMFs must deliver at least 50–60% lifecycle GHG reductions, be free from virgin fossil inputs, and carry independent sustainability certification. While liquid fuels will continue to dominate shipping, electrofuels are expected to lead adoption, complemented by advanced biofuels and methanol.
Government initiatives play a crucial role in accelerating the adoption of Sustainable marine fuel. For instance, the U.S. Department of Energy’s Bioenergy Technologies Office (BETO) is actively engaged in research to enhance the viability of marine biofuels. The U.S. maritime industry consumes an estimated 105 billion gallons of fuel annually, a figure projected to double by 2030 due to expanding global trade. BETO’s efforts aim to increase the production of marine biofuels to meet this rising demand, thereby supporting the industry’s decarbonization goals.
The EU has adopted Regulation (EU)2023/1805 (September 2023), mandating the incorporation of renewable and low-carbon fuels in maritime transport. Additionally, FuelEU Maritime, effective January 2025, will require a 2% reduction in GHG intensity, escalating to 80% by 2050. KPI OceanConnect plans to expand marine biofuel availability to 120 ports to meet demand driven by this policy.
Key Takeaways
- The global Sustainable Marine Fuel (SMF) market is projected to grow from USD 13.1 billion in 2024 to approximately USD 836.0 billion by 2034, reflecting a CAGR of 51.5% over the forecast period.
- Between types, biofuels accounted for the largest market share of 64.2%.
- Among application, tankers/carriers accounted for the majority of the market share at 44.6%.
- Europe was the leading regional market in 2024, holding a commanding 51.0% share of the global SMF market, with its value estimated at approximately USD 6.7 billion.
By Type Analysis
The Sustainable Marine Fuel Market Was Dominated By Biofuels
Based on type, the market is further divided into biofuels, methanol, ammonia & hydrogen. As of 2024, the biofuels dominated the sustainable marine fuel market with a 64.2% share. primarily due to their technological maturity, established supply chains, and compatibility with existing marine engines and infrastructure. Unlike emerging alternatives such as ammonia, hydrogen, or methanol, which often require significant retrofitting of vessels, new fueling systems, or large-scale infrastructure investments, biofuels can be blended with conventional marine fuels and used in current ship engines with minimal modifications.
Additionally, biofuels are already commercially available at scale, derived from diverse feedstocks such as waste oils, residues, and other biogenic sources, which supports both supply security and regional flexibility. Their relatively lower cost compared to other SMF options further strengthens their adoption, especially as operators balance decarbonisation with financial feasibility.
Furthermore, methanol is gaining traction as a marine fuel, but in 2024 its share remained smaller because of limited global supply capacity and the high cost of green methanol production from renewable sources. While methanol engines are being adopted in new builds, the retrofitting of older vessels is expensive. Infrastructure for bunkering methanol is also still developing, restricting widespread adoption.
Global Sustainable Marine Fuel Market, By Type, 2020-2024 (USD Mn)
Type 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 Biofuels 1,596.3 2,419.7 3,671.4 5,572.6 8,455.7 Methanol 784.5 1,177.2 1,771.4 2,671.8 4,043.0 Ammonia 88.6 135.1 206.5 316.4 486.3 Hydrogen 30.5 47.5 74.1 116.0 182.1 By Application Analysis
The Sustainable Marine Fuel Market Was Dominated By the Tankers/Carriers Industry.
Based on the application, the market is further divided into tankers/carriers, barges/cargo vessels, tugboats, defense vessels, ferries, yachts, cruise ships & others. Among them, tankers/carriers accounted for 44.6% of the market share in 2024 due to their dominant role in global maritime trade and their exceptionally high fuel consumption levels. Tankers and bulk carriers are responsible for transporting vast volumes of crude oil, petroleum products, liquefied natural gas (LNG), chemicals, and dry bulk commodities such as coal, iron ore, and grains across continents.
These vessels often operate on long-haul international routes, requiring large quantities of fuel for continuous operations. With the shipping industry under increasing regulatory and environmental pressure to decarbonize, operators of tankers and carriers have been early adopters of sustainable marine fuels to ensure compliance with the IMO’s decarbonization targets and to meet customer and stakeholder expectations for cleaner logistics chains. Their scale of operations provides both the strongest incentive and the largest opportunity to reduce emissions through SMF adoption, making them the most influential application segment in driving demand.
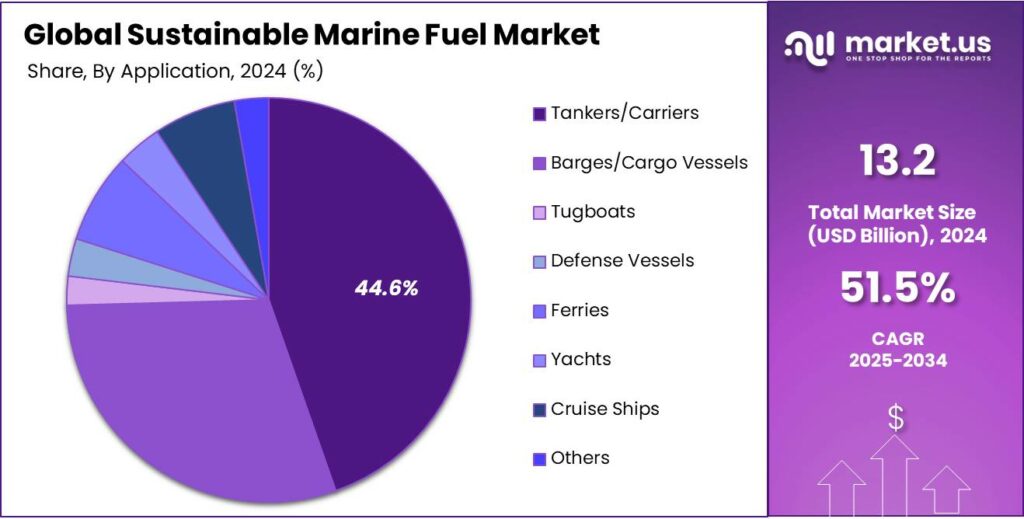
Application 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 Tankers/Carriers 1,045.0 1,612.1 2,485.1 3,826.3 5,877.1 Barges/Cargo Vessels 759.8 1,142.1 1,721.6 2,601.1 3,942.7 Tugboats 68.4 99.0 143.7 209.1 305.3 Defense Vessels 82.9 122.0 180.1 266.5 395.7 Ferries 191.3 284.1 423.3 632.1 947.0 Yachts 97.3 143.7 212.8 315.9 470.5 Cruise Ships 177.2 262.6 390.2 581.2 868.5 Others 77.9 113.7 166.6 244.5 360.2 Key Market Segments
By Туре
- Туре
- Biofuels
- Methanol
- Ammonia
- Hydrogen
By Application
- Tankers/Carriers
- Barges/Cargo Vessels
- Tugboats
- Defense Vessels
- Ferries
- Yachts
- Cruise Ships
- Others
Emerging Trends
Growing Adoption of Methanol-Ready and Dual-Fuel Vessels
The accelerated adoption of methanol-ready and dual-fuel vessels is a significant trend transforming the sustainable marine fuel (SMF) landscape. As regulatory pressure to decarbonize intensifies, shipping companies are investing in flexible propulsion technologies that support both conventional and low-emission fuels, particularly methanol, which has emerged as a strong transitional and future-ready fuel option.
Methanol offers a number of advantages for maritime use. It is liquid at ambient temperature, making storage and handling far simpler than cryogenic fuels like LNG or hydrogen. It also produces significantly lower sulfur oxide (SOx), nitrogen oxide (NOx), and particulate matter emissions compared to traditional marine fuels. As of mid-2024, methanol is the second most widely adopted alternative marine fuel after LNG, according to the Methanol Institute, with over 250 methanol-capable ships either in operation or on order globally. Major industry players are actively committing to methanol-fueled fleets.
Drivers
Implementation of Stringent International Maritime Regulations Is Driving The Market Growth.
The growth of the sustainable marine fuel (SMF) market is being propelled by the introduction of stringent international and regional regulations designed to cut greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from shipping.
- The International Maritime Organization (IMO), the sector’s global regulator, updated its GHG Reduction Strategy in July 2023, setting ambitious targets: a 20% cut by 2030, at least 70% by 2040, and net-zero emissions by 2050 compared with 2008 levels. To meet these goals, ship operators are being forced to transition from fossil fuels to sustainable alternatives, including biofuels, methanol, hydrogen, and ammonia.
Supporting this shift, mandatory measures such as the Energy Efficiency Existing Ship Index (EEXI) and the Carbon Intensity Indicator (CII), which came into effect in January 2023, now rate the efficiency and carbon intensity of nearly all cargo and passenger vessels. Ships with poor scores risk fines, operational limits, or loss of business from environmentally conscious customers.
Regional policies are adding further pressure. The European Union is expanding its Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) to cover maritime emissions from 2024, making companies pay for their CO₂ output and creating financial incentives to adopt low-carbon fuels. At the same time, the EU Renewable Energy Directive II (RED II) requires fuels to meet strict sustainability standards, verified through recognized certification schemes such as ISCC EU, while the FuelEU Maritime Initiative will set limits on the annual GHG intensity of ship energy use. Industry leaders are already adapting.
For instance, Maersk launched the first methanol-powered container ship in 2023 and plans a green fleet expansion, while NYK Line and Singapore’s MPA are piloting ammonia-fueled vessels. Together, these regulations and initiatives make sustainable marine fuels not only vital for environmental goals but also essential for long-term competitiveness in global shipping.
Restraints
High Costs Associated with Fuel Production and Distribution Restraint on The Growth to a Certain Extent
One of the most significant barriers to the growth of the sustainable marine fuel (SMF) market is the high cost of production and distribution compared to conventional fossil-based marine fuels. The challenge lies not only in the complex and energy-intensive processes required to produce alternatives like green hydrogen, ammonia, methanol, and advanced biofuels but also in the logistics of transporting and distributing them across global maritime networks.
According to cost assessments by Lloyd’s Register, fuels such as e-ammonia and e-methanol remain considerably more expensive than heavy fuel oil (HFO) or marine gas oil (MGO), with levelized costs highly dependent on renewable electricity prices and electrolyzer efficiency. For example, producing green hydrogen via electrolysis can be three to four times more expensive than conventional fuels, as it requires vast amounts of renewable power and costly infrastructure.
Similarly, life-cycle assessments (LCAs) highlight that while many SMFs achieve zero emissions at the point of combustion, their upstream production processes—such as carbon capture for synthetic fuels or land-intensive feedstock cultivation for biofuels—add significant costs and resource pressures.
These high costs create a structural disadvantage for SMFs, particularly in an industry where fuel accounts for a major share of operational expenses. Until large-scale production, technological innovation, and policy incentives significantly reduce costs, the uptake of sustainable marine fuels will remain constrained, limiting their competitiveness against cheaper fossil alternatives.
Opportunity
Carbon Pricing and Emissions Trading Schemes: Enhancing Economic Viability
The implementation of carbon pricing mechanisms and emissions trading schemes (ETS) represents a major opportunity for accelerating the adoption of Sustainable Marine Fuels (SMFs). By internalizing the environmental cost of greenhouse gas emissions, these measures create strong financial incentives for shipowners and operators to transition away from fossil-based marine fuels.
For example, the European Union extended its Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) to maritime emissions beginning in January 2024, requiring shipping companies operating in EU waters to purchase allowances for CO₂ emissions. With carbon prices around €90 per ton of CO₂, this policy significantly increases the cost of conventional fuels such as heavy fuel oil, while narrowing the cost gap with lower-carbon alternatives such as biofuels, green methanol, ammonia, and hydrogen.
Globally, more than 70 carbon pricing initiatives are in place or scheduled, covering over 23% of greenhouse gas emissions, and this coverage is expected to expand further. China’s national ETS, though currently limited to the power sector, has strong potential to extend into shipping. Likewise, Japan and Singapore are actively exploring maritime carbon pricing frameworks. These initiatives align with International Maritime Organization (IMO) strategies and could create a level playing field that stimulates investments in SMFs while discouraging continued reliance on fossil fuels.
In addition to direct cost impacts, carbon pricing also generates revenues that can be reinvested in maritime research, development, and infrastructure for low-carbon fuels. Ports such as Rotterdam and Los Angeles are already offering reduced port fees and incentives for ships using cleaner fuels, amplifying the market’s economic attractiveness. As more regions adopt carbon pricing and ETS frameworks, the economic case for SMFs strengthens, positioning them as not only an environmental necessity but also a commercially viable solution for global shipping.
Geopolitical Impact Analysis
Geopolitical Scenerios Of The Sustainable Marine Fuel Market.
The Russia–Ukraine war has profoundly reshaped the global sustainable marine fuel (SMF) market by disrupting traditional energy supply chains, inflating fossil fuel prices, and accelerating the transition toward renewable alternatives. Before the conflict, Russia accounted for 12% of global oil output, but sanctions and trade restrictions led to sharp supply shortages and price volatility, with Brent crude peaking at $139.13/barrel in 2022. This volatility exposed the maritime sector’s vulnerability to fossil fuel dependence and strengthened the economic and strategic rationale for adopting SMFs such as bio-methanol, hydrotreated vegetable oil (HVO), and advanced biofuels.
- Europe, heavily reliant on Russian imports, responded with initiatives such as REPowerEU and reinforced RED II/III targets, prioritizing marine biofuel trials, e-methanol bunkering, and low-carbon shipping infrastructure. In Ukraine, the crisis highlighted energy security concerns, with government plans to scale bioethanol and biodiesel production—potentially yielding up to 2.54 million tonnes of oil equivalent by 2050—positioning the country as a future supplier of advanced fuels.
Globally, the energy shock caused divergent economic impacts: Russia’s GDP contracted sharply, while non-European exporters like Canada and Middle Eastern states benefited, and developed economies absorbed inflation and trade disruptions. These pressures accelerated corporate and governmental efforts to diversify fuel supply chains and invest in circular bioeconomy models using waste- and residue-based feedstocks.
Moreover, disruptions to Ukrainian agricultural exports underscored the risks of relying on first-generation feedstocks, pushing producers in regions like the EU and U.S. to expand waste-based refining capacity. Thus, the war catalyzed both urgency and opportunity, making SMFs central to maritime decarbonization and energy security strategies.
Regional Insights
Europe Held the Largest Share of the Global Sustainable Marine Fuel Market
In 2024, Europe dominated the global sustainable marine fuel market with 51.0% of the total share, primarily due to its aggressive regulatory framework, strong decarbonisation commitments, and rapid deployment of low-carbon fuel infrastructure. The European Union (EU) has positioned itself at the forefront of maritime decarbonisation by extending the EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) to shipping in January 2024, effectively putting a carbon price on maritime emissions and making fossil fuels less economically attractive.
Complementary initiatives such as FuelEU Maritime and RED II/III directives further mandate reductions in the carbon intensity of marine fuels, creating a strong compliance-driven demand for sustainable alternatives like biofuels, methanol, hydrogen, and ammonia. Europe’s dominance is also supported by its advanced port and bunkering infrastructure. Leading ports such as Rotterdam, Antwerp-Bruges, and Hamburg have invested heavily in e-methanol, ammonia, and biofuel facilities, enabling large-scale trials and commercial supply for shipping fleets.
Global Sustainable Marine Fuel Market, By Region, 2020-2024 (USD Mn)
Region 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 North America 467.5 700.4 1,050.7 1,577.2 2,368.9 Europe 1,207.4 1,851.1 2,841.9 4,366.4 6,713.5 Asia Pacific 602.5 902.2 1,353.5 2,032.9 3,056.8 Middle East & Africa 62.5 89.9 129.4 186.5 269.0 Latin America 160.0 235.8 347.9 513.6 758.9 Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
product innovation and robust research & development are the key strategies of major players of sustainable marine fuel market.
To maintain a competitive edge in the sustainable marine fuel (SMF) market, major companies are prioritizing product innovation and robust research & development (R&D). By investing in advanced technologies, they are developing scalable, cost-efficient, and low-carbon fuel solutions such as bio-methanol, ammonia, hydrogen, and waste-based biofuels that meet stringent international regulations.
R&D efforts focus on improving fuel performance, reducing lifecycle emissions, and ensuring compatibility with existing ship engines and bunkering infrastructure. Innovation also extends to partnerships with ports, energy providers, and technology firms, enabling companies to accelerate commercialization, differentiate their offerings, and position themselves as leaders in the global energy transition.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Maersk
- Exxon Mobil Corporation
- Chevron Corporation
- British Petroleum (BP)
- Shell Plc
- TotalEnergies
- FincoEnergies
- Liquid Wind AB
- Methanex Corporation
- Neste Corp.
- Oyj Targray
- Other Key Players
Recent Industry Developments
November, 2024 : Hapag-Lloyd’s vessel Colorado Express has successfully bunkered a B25 bio marine fuel blend supplied by ExxonMobil, which combines Premium HDME 50™ fuel (a 0.10% sulphur Emission Control Area fuel) with 25% waste-based fatty acid methyl esters (FAME) derived from used cooking oil methyl ester (UCOME). This represents a significant advance in the use of sustainable marine fuels.
July 2023: Chevron has achieved a key milestone in sustainable marine fuel, completing 50+ biofuel deliveries at the Port of Singapore since 2022. Following its acquisition of Renewable Energy Group, the company is expanding in marine biofuels, collaborating with global shipowners, and patenting biofuel blending. Derived mainly from waste-based sources, Chevron’s biofuels cut lifecycle emissions and work without engine modifications, offering a practical near-term solution for decarbonizing shipping.
February 2023: Shell and Hapag-Lloyd have entered a multi-year deal to supply LNG for Hapag-Lloyd’s new dual-fuel container ships, with bunkering starting in Rotterdam in late 2023. The partnership also explores alternative fuels like liquefied biomethane and e-methane. LNG use is expected to cut CO₂ emissions by up to 23% and lower particulate matter, highlighting both companies’ commitment to sustainable marine fuels and driving shipping’s transition to a low-carbon future.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) US$ 13.2 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) US$ 836.0 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 51.5% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered Type (Biofuels, Methanol, Ammonia, & Hydrogen), By Application (Tankers/Carriers, Barges/Cargo, Vessels, Tugboats, Defense Vessels, Ferries, Yachts, Cruise Ships & Others) Regional Analysis North America – The US & Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia & CIS, Rest of Europe; APAC– China, Japan, South Korea, India, ASEAN & Rest of APAC; Latin America– Brazil, Mexico & Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa– GCC, South Africa, & Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Exxon Mobil Corporation, Chevron Corporation, British Petroleum (BP), Shell Plc, TotalEnergies, Maersk, FincoEnergies, Liquid Wind AB, Methanex Corporation, Neste Corp., Oyj Targray & oTHERS Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited Users and Printable PDF)  Sustainable Marine Fuel MarketPublished date: Sep 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Sustainable Marine Fuel MarketPublished date: Sep 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Maersk
- Exxon Mobil Corporation
- Chevron Corporation
- British Petroleum (BP)
- Shell Plc
- TotalEnergies
- FincoEnergies
- Liquid Wind AB
- Methanex Corporation
- Neste Corp.
- Oyj Targray
- Other Key Players










