Global Sustainable Finance Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Investment (Equity, Fixed income, Mixed allocation, Others), By Investor (Institutional investors, Retail investors), By Transaction (Green bond, Mixed-sustainability bond, Social bond, ESG Integrated Investment Funds, Others), By End Use (Utilities, Chemicals, Transport & logistics, Government, Food and beverage, Others), Region and Companies – Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: May 2025
- Report ID: 148041
- Number of Pages: 217
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
- Sustainable Finance Market Size
- Key Takeaways
- Europe Market Growth
- Market Overview
- By Investment Analysis
- By Investor Analysis
- By Transaction Analysis
- By End Use Analysis
- Key Market Segments
- Driver
- Restraint
- Opportunity
- Challenge
- Growth Factors
- Emerging Trends
- Business Benefits
- Key Player Analysis
- Recent Developments
- Report Scope
Sustainable Finance Market Size
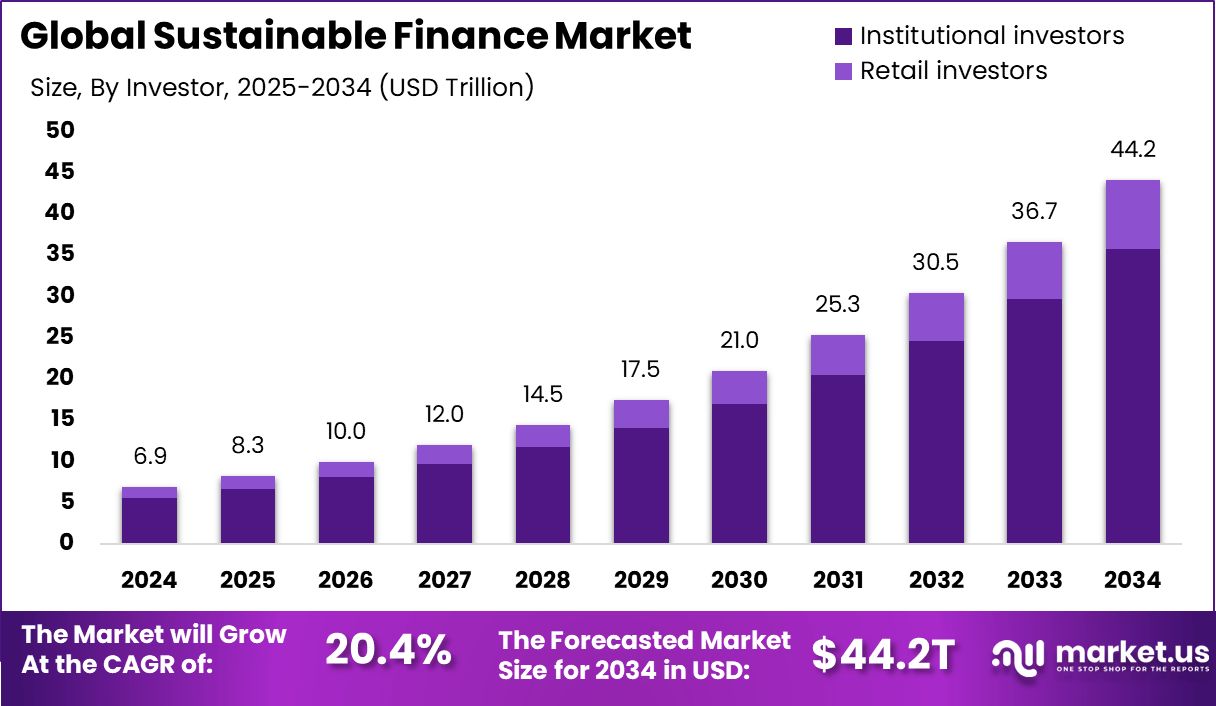
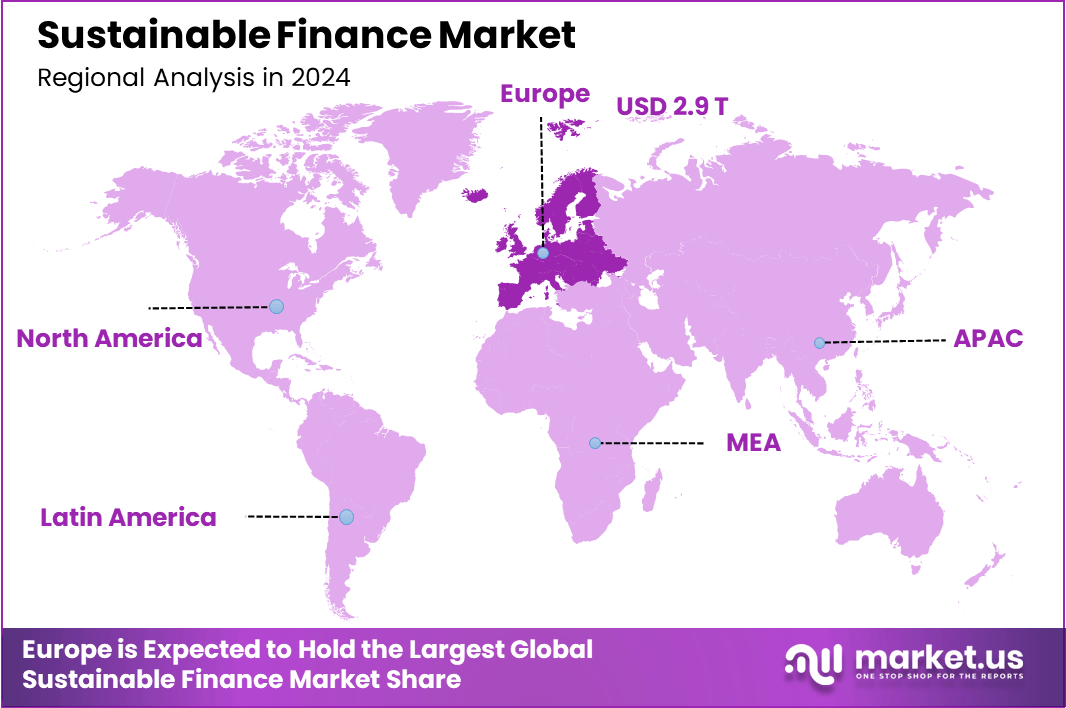
The Global Sustainable Finance Market size is expected to be worth around USD 44.2 Trillion By 2034, from USD 6.9 Trillion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 20.4% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, Europe held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.1% share, holding USD 2.9 Billion revenue.
This rising trend is driven by increasing awareness of environmental and social challenges, prompting investors and institutions to prioritize Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) considerations in their financial decisions. The integration of ESG factors is becoming a standard practice, influencing investment strategies and risk assessments across the financial sector.
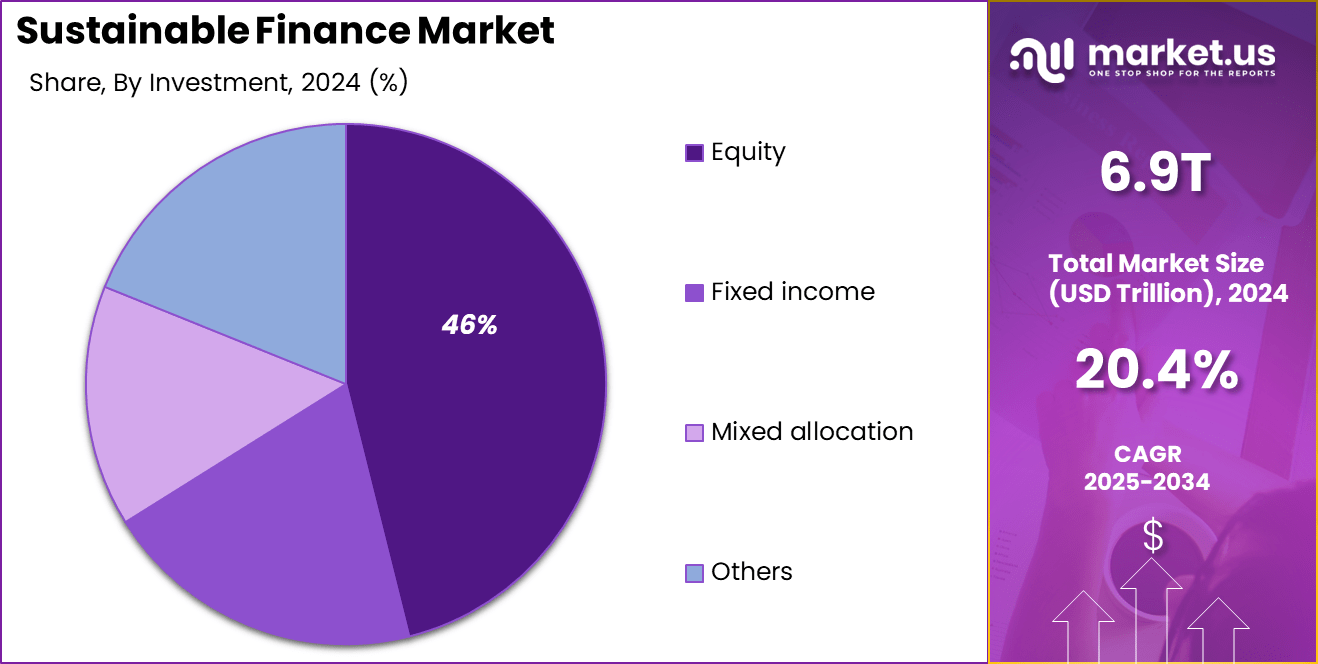
Fixed income instruments, particularly green and social bonds, have emerged as dominant components within the sustainable finance landscape, accounting for approximately 41% of the market share in 2024. These instruments are favored for their potential to deliver stable returns while funding projects with positive environmental and social impacts.
Institutional investors play a pivotal role in this market, holding a substantial 79% share in 2024. Their long-term investment horizons and substantial capital allocations enable them to influence corporate behaviors and promote sustainability practices on a broad scale .
Regionally, Europe leads the sustainable finance market, underpinned by robust regulatory frameworks and a strong commitment to sustainability goals. The European Union’s initiatives, such as the Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR), have fostered transparency and accountability, encouraging investments in sustainable projects.
Technological advancements, including the application of artificial intelligence and machine learning, are enhancing the analysis and reporting of ESG data. These technologies facilitate more accurate assessments of sustainability metrics, aiding investors in making informed decisions.
Key Takeaways
- Market Expansion: The global sustainable finance market is projected to grow from approximately USD 6.9 trillion in 2024 to USD 44.2 trillion by 2034, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20.4%.
- Regional Leadership: Europe maintained a leading position in 2024, accounting for over 43% of the global market share, with revenues surpassing USD 2.9 trillion.
- Equity Investments: Represented about 47.9% of sustainable finance activities in 2024, indicating strong investor confidence in sustainable equities.
- Green Bonds: Continued to be a dominant instrument, comprising approximately 57.7% of sustainable debt issuance in 2024.
- Investor Demographics: Institutional investors were predominant, contributing to approximately 80% of sustainable finance investments in 2024, underscoring the sector’s appeal to large-scale investors.
- Sectoral Focus: The utilities sector was a significant recipient of sustainable loans, accounting for about 18% of the total sustainable loan activity in 2024.
Europe Market Growth
In 2024, sustainable finance held a dominant market position in Europe, capturing more than a 43.1% share, which translated into approximately USD 2.9 Trillion in revenue. This leadership can be primarily attributed to the region’s aggressive policy frameworks and well-structured regulatory ecosystem.
The European Union’s early implementation of the Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR) and the EU Taxonomy for Sustainable Activities created a transparent foundation for investors, ensuring credibility in ESG-related investment decisions.
Financial institutions in the region were among the first globally to align with the Paris Agreement goals, integrating climate risk into lending and investment strategies. Additionally, the European Central Bank’s push for green bond standards and sustainable portfolio assessment further accelerated institutional momentum.
Market Overview
Sustainable finance refers to the integration of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations into financial decision-making processes. This approach seeks to promote long-term investments in sustainable economic activities and projects, thereby contributing to the achievement of broader societal goals, such as climate change mitigation and social equity.
Key factors propelling the growth of the sustainable finance market include the increasing frequency of climate-related events, which underscore the financial risks associated with environmental degradation. Additionally, regulatory frameworks, such as the European Union’s Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR), mandate greater transparency in ESG reporting, thereby fostering investor confidence.
Investment opportunities in sustainable finance are diverse, encompassing sectors such as renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and green infrastructure. The transition to a low-carbon economy necessitates substantial capital allocation, presenting avenues for investors to contribute to environmental objectives while achieving financial returns.
The regulatory environment for sustainable finance is evolving, with jurisdictions implementing frameworks to standardize ESG disclosures and prevent greenwashing. For example, the European Union’s taxonomy for sustainable activities provides clear criteria for classifying environmentally sustainable economic activities, thereby guiding investment decisions.
By Investment Analysis
In 2024, the equity segment held a dominant position in the sustainable finance market, capturing approximately 46% of the total share. This prominence can be attributed to investors’ growing preference for long-term capital appreciation and the potential for higher returns associated with equities.
Equity investments allow investors to actively engage in sustainable investing by supporting companies that demonstrate strong environmental, social, and governance (ESG) practices. Moreover, equities offer a higher level of liquidity compared to other asset classes, enabling investors to respond more flexibly to market conditions.
The leading position of the equity segment is further reinforced by the increasing recognition of the financial benefits of sustainability. Companies that effectively manage ESG risks and opportunities are expected to outperform their peers in the long run, making equities an attractive asset class for investors seeking both financial returns and positive impact.
By Investor Analysis
In 2024, the institutional investors segment held a dominant position in the sustainable finance market, capturing approximately 80.07% of the total share. This dominance is attributed to their substantial capital resources and long-term investment horizons, which align well with the objectives of sustainable finance.
Institutional investors, such as pension funds, insurance companies, and sovereign wealth funds, have increasingly integrated Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria into their investment strategies, recognizing the potential for sustainable investments to deliver long-term value and mitigate risks associated with environmental and social factors.
The leading position of institutional investors is further reinforced by their ability to influence corporate behavior through active ownership and engagement. By leveraging their significant equity holdings, institutional investors can advocate for improved corporate governance and sustainability practices within the companies they invest in.
Additionally, their preference for long-term investments supports the funding of sustainable projects that may require extended timeframes to realize returns, such as renewable energy infrastructure and social development programs. This strategic alignment with sustainable finance objectives underscores the pivotal role of institutional investors in driving the growth and maturation of the sustainable finance market.
By Transaction Analysis
In 2024, the green bond segment held a dominant position in the sustainable finance market, capturing approximately 57.7% of the total share. This dominance is attributed to the increasing demand for financing environmentally friendly projects and the growing emphasis on climate change mitigation.
Green bonds have become a preferred instrument for investors seeking to support sustainable initiatives while achieving financial returns. The surge in green bond issuance reflects a broader shift in the financial industry towards integrating environmental considerations into investment decisions.
The leading position of green bonds is further reinforced by supportive regulatory frameworks and investor appetite for transparent and impactful investments. Governments and supranational organizations have played a pivotal role in promoting green bonds through policy incentives and the establishment of green bond standards.
Additionally, the alignment of green bonds with global sustainability goals has attracted a diverse range of investors, including institutional and retail participants. This trend underscores the growing recognition of green bonds as a vital tool in mobilizing capital for sustainable development.
By End Use Analysis
In 2024, the utilities segment held a dominant position in the sustainable finance market, capturing approximately 18% of total sustainable loan activity. This leadership is attributed to the sector’s pivotal role in the global transition to cleaner energy sources and the modernization of energy infrastructure.
Utilities have become central to sustainable finance due to their significant investments in renewable energy projects, grid enhancements, and the integration of advanced technologies to meet rising energy demands, particularly from data centers and artificial intelligence applications.
The utilities sector’s prominence is further reinforced by its proactive approach to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) initiatives. A substantial majority of utilities have increased their spending on ESG-related projects over recent years, with many reporting significant investments aimed at reducing carbon emissions and enhancing sustainability.
These efforts align with global sustainability goals and have attracted considerable interest from investors seeking stable, long-term returns associated with infrastructure and energy projects. Moreover, the sector’s resilience and adaptability in the face of evolving energy needs underscore its critical role in the sustainable finance landscape.
Key Market Segments
By Investment
- Equity
- Fixed income
- Mixed allocation
- Others
By Investor
- Institutional investors
- Retail investors
By Transaction
- Green bond
- Mixed- sustainability bond
- Social bond
- ESG Integrated Investment Funds
- Others
By End Use
- Utilities
- Chemicals
- Transport & logistics
- Government
- Food and beverage
- Others
Key Regions and Countries
North America
- US
- Canada
Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherlands
- Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Driver
Regulatory Advancements and Policy Support
The expansion of sustainable finance is significantly propelled by evolving regulatory frameworks and supportive government policies. These measures aim to integrate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations into financial decision-making processes.
For instance, the European Union’s Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR) mandates financial market participants to disclose ESG-related information, enhancing transparency and accountability. Similarly, the United Kingdom’s Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) introduced rules requiring funds labeled as “sustainable” to meet specific criteria, ensuring genuine alignment with sustainability objectives .
Restraint
Inconsistent ESG Data and Reporting Standards
A significant impediment to the growth of sustainable finance is the lack of standardized ESG data and reporting frameworks. The absence of uniform metrics leads to inconsistencies in ESG disclosures, making it challenging for investors to assess and compare sustainability performance across companies and sectors. This data variability hampers informed decision-making and may deter investment in sustainable assets.
Moreover, the proliferation of various ESG rating agencies, each employing distinct methodologies, further complicates the landscape. Investors often encounter divergent ESG scores for the same entity, leading to confusion and potential misallocation of capital. Addressing this restraint necessitates the development and adoption of globally recognized ESG reporting standards to enhance data reliability and comparability.
Opportunity
Growth of Impact Investing
Impact investing presents a substantial opportunity within sustainable finance, focusing on generating measurable social and environmental benefits alongside financial returns. The Global Impact Investing Market size is expected to be worth around USD 1,131.0 Billion By 2034, from USD 377 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 11.6% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
The expansion of impact investing is driven by a growing recognition of the need to address global challenges such as climate change, social inequality, and access to essential services. Investors are increasingly allocating capital to sectors like renewable energy, affordable housing, and healthcare, aiming to achieve positive societal outcomes. This trend underscores the potential of impact investing to mobilize private capital for sustainable development objectives.
Challenge
Political and Economic Uncertainties
Political and economic uncertainties pose significant challenges to the advancement of sustainable finance. Policy shifts, such as changes in government leadership or regulatory rollbacks, can create an unpredictable environment for sustainable investments.
For example, the withdrawal of certain banks from climate-focused alliances and the abandonment of sustainable finance targets by institutions like the Royal Bank of Canada highlight the impact of political dynamics on sustainability commitments.
Additionally, economic factors such as rising interest rates and market volatility can influence investor appetite for sustainable assets. In 2024, climate-focused mutual funds experienced net outflows of approximately USD 30 billion, marking the first year of net withdrawals since at least 2019.
Growth Factors
Climate Imperatives and Investor Demand
The expansion of sustainable finance is significantly propelled by the escalating urgency to address climate change. Natural and human-induced disasters have underscored the economic risks associated with environmental degradation, prompting investors to seek avenues that contribute to a low-carbon economy.
Investor demand for transparency and accountability has further fueled this growth. The integration of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria into investment decisions has become a standard practice, with stakeholders increasingly prioritizing companies that demonstrate sustainable practices. This trend not only mitigates risks but also aligns investment portfolios with long-term value creation and societal impact.
Emerging Trends
Regulatory Evolution and Technological Integration
Regulatory frameworks are evolving to enhance the credibility and effectiveness of sustainable finance. In the United Kingdom, the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) implemented new rules in April 2025, requiring funds labeled as “sustainable” to meet specific criteria and adopt one of four official labels: Sustainability Focus, Improvers, Impact, or Mixed Goals. This move aims to curb greenwashing and ensure genuine alignment with sustainability objectives.
Technological advancements are also shaping the sustainable finance landscape. The integration of big data, artificial intelligence, and machine learning enables more accurate assessment of ESG risks and opportunities. These tools facilitate better decision-making by providing insights into complex sustainability metrics, thus enhancing the efficiency and impact of sustainable investments.
Business Benefits
Enhanced Risk Management
Adopting sustainable finance practices offers businesses the advantage of improved risk management. By incorporating ESG considerations into their operations, companies can identify and mitigate potential risks related to environmental regulations, social responsibilities, and governance issues. This proactive approach not only safeguards against regulatory penalties but also enhances resilience against market volatility.
Moreover, companies that prioritize sustainability are better positioned to attract investors and customers who value ethical practices. This alignment with stakeholder expectations can lead to increased brand loyalty, access to new markets, and long-term financial performance. Thus, sustainable finance serves as a strategic tool for businesses aiming to achieve both economic and societal objectives.
Key Player Analysis
In the sustainable finance sector, major players such as JPMorgan Chase & Co., BlackRock, Inc., and Morgan Stanley are actively shaping the industry landscape through continuous mergers, acquisitions, and strategic partnerships. These companies are not only expanding their portfolios but are also aligning their core services with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) priorities.
Their growing focus on responsible investment practices reflects a clear intention to lead the shift towards greener capital allocation. By strengthening their sustainability frameworks and integrating ESG-driven financial tools, these firms are positioning themselves to capture a larger share of the market, while reinforcing their long-term competitiveness in an evolving financial ecosystem.
Sustainable Finance Market Companies
- BlackRock, Inc.
- State Street Corporation
- Morgan Stanley
- UBS
- JPMorgan Chase & Co.
- Franklin Templeton Investments
- Amundi US
- The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation
- Deutsche Bank AG
- Goldman Sachs
Recent Developments
- In October 2024, Standard Chartered introduced sustainable finance versions of its Borrowing Base Trade Loans (BBTL), initially launching in the U.S., UK, UAE, Singapore, South Africa, and Hong Kong. This secured revolving credit facility is designed to support businesses in the commodity sector with tailored, ESG-aligned financing.
- In January 2024, Societe Generale partnered with the International Finance Corporation to expand sustainable finance in developing countries. This collaboration supports the UN SDGs and aims to promote environmental transition through increased green capital flow in emerging markets.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 6.9 Trillion Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 44.2 Trillion CAGR (2025-2034) 20.4% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue forecast, AI impact on market trends, Share Insights, Company ranking, competitive landscape, Recent Developments, Market Dynamics and Emerging Trends Segments Covered By Investment (Equity, Fixed income, Mixed allocation, Others), By Investor (Institutional investors, Retail investors), By Transaction (Green bond, Mixed-sustainability bond, Social bond, ESG Integrated Investment Funds, Others), By End Use (Utilities, Chemicals, Transport & logistics, Government, Food and beverage, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape BlackRock, Inc., State Street Corporation, Morgan Stanley, UBS, JPMorgan Chase & Co., Franklin Templeton Investments, Amundi US, The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation, Deutsche Bank AG, Goldman Sachs Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three license to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- BlackRock, Inc.
- State Street Corporation
- Morgan Stanley
- UBS
- JPMorgan Chase & Co.
- Franklin Templeton Investments
- Amundi US
- The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation
- Deutsche Bank AG
- Goldman Sachs









