Global Polymer Additive Manufacturing Market By Printing Technology (Fused Deposition Modeling, Stereolithography, Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), PolyJet Printing, Digital Light Processing, Multi Jet Fusion, and Others), By Material Type (Thermoplastics, Photopolymers, Composite Polymers, and Others), By Material Form (Filaments, Powders, Liquid Resins, and Pellets / Granules), By Application (Rapid Prototyping, Rapid Tooling, Production Volumes, Injection Molding, Manufacturing Aids, Investment Casting, and Others), By End Use Industry (Industrial And Manufacturing, Automotive, Aerospace And Defense, Healthcare And Medical, Consumer Goods, Energy And Power, and Others), By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Feb 2026
- Report ID: 177568
- Number of Pages: 373
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
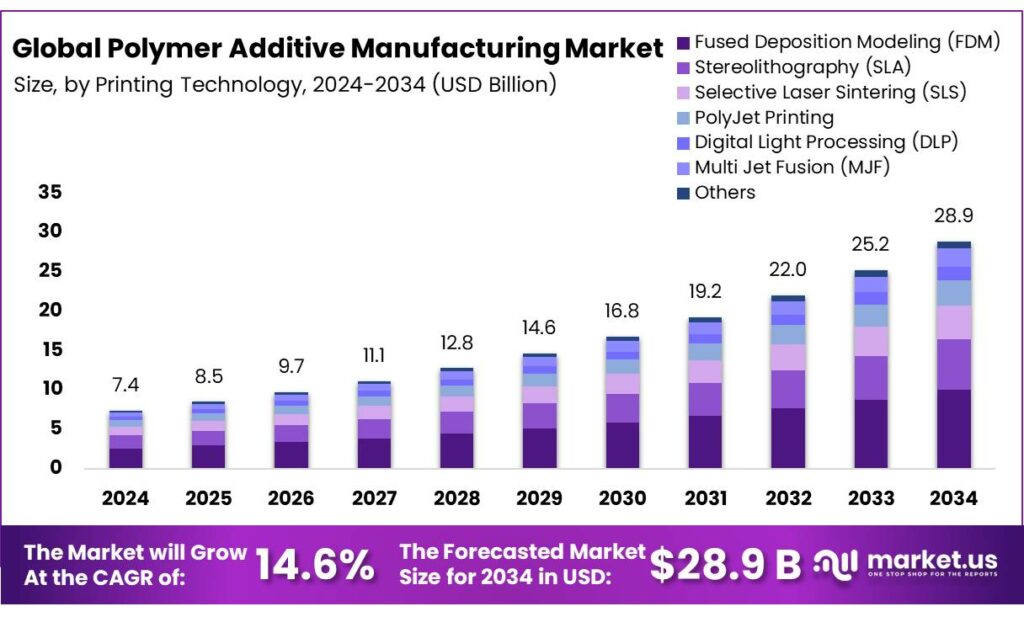
The Global Polymer Additive Manufacturing Market is expected to be worth around USD 28.9 Billion by 2034, up from USD 7.4 Billion in 2024, and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 14.6% from 2025 to 2034. The North America segment maintained 35.8%, supporting a Solar Control Glass value of USD 3.0 Bn.
Polymer additive manufacturing (AM), known as polymer 3D printing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects by joining materials, typically layer by layer, from digital 3D model data. This technology allows for the fabrication of complex, customized geometries that are often unmanageable or expensive to produce using traditional subtractive (machining) or formative (molding) methods.
- The US Department of Energy noted that using high-strength polymer composites can reduce component weight by 10-60% compared to heavy steel parts.
The polymer additive manufacturing market is driven by its versatility in producing lightweight, high-strength components, particularly for industrial and manufacturing applications. In addition, thermoplastics dominate material usage due to their cost-effectiveness, recyclability, and wide range of mechanical properties, while material filaments are preferred for their ease of handling and compatibility with widely used FDM systems.
Similarly, fused deposition modeling (FDM) is the most adopted printing method due to its accessibility, affordability, and ability to produce larger, functional parts with minimal operational complexity. Moreover, polymer additive manufacturing is predominantly applied in rapid prototyping, enabling fast design iteration and functional testing without the need for expensive tooling.
- As of 2023, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had cleared over 100 devices made using additive manufacturing technologies, demonstrating regulatory acceptance.
Furthermore, North America leads the market, supported by advanced industrial infrastructure and aerospace and medical applications. Key trends in the market include automation and workflow optimization to improve production efficiency. Challenges remain in high upfront equipment and material costs, while opportunities are emerging in healthcare, where customized implants and surgical tools illustrate the technology’s growing industrial relevance.
- Pilot projects such as NextGenAM have demonstrated that full automation of the additive workflow, including integrating machine operation, part transport, and finishing, can reduce total production costs by as much as 50%.
Key Takeaways
- The global polymer additive manufacturing market was valued at USD 7.4 billion in 2024.
- The global polymer additive manufacturing market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 14.6% and is estimated to reach USD 28.9 billion by 2034.
- On the basis of types of printing technology, fused deposition modeling (FDM) dominated the polymer additive manufacturing market, constituting 34.8% of the total market share.
- Based on the types of materials, thermoplastics dominated the polymer additive manufacturing market, with a substantial market share of around 52.8%.
- Based on the forms of material, filaments led the polymer additive manufacturing market, comprising 40.3% of the total market.
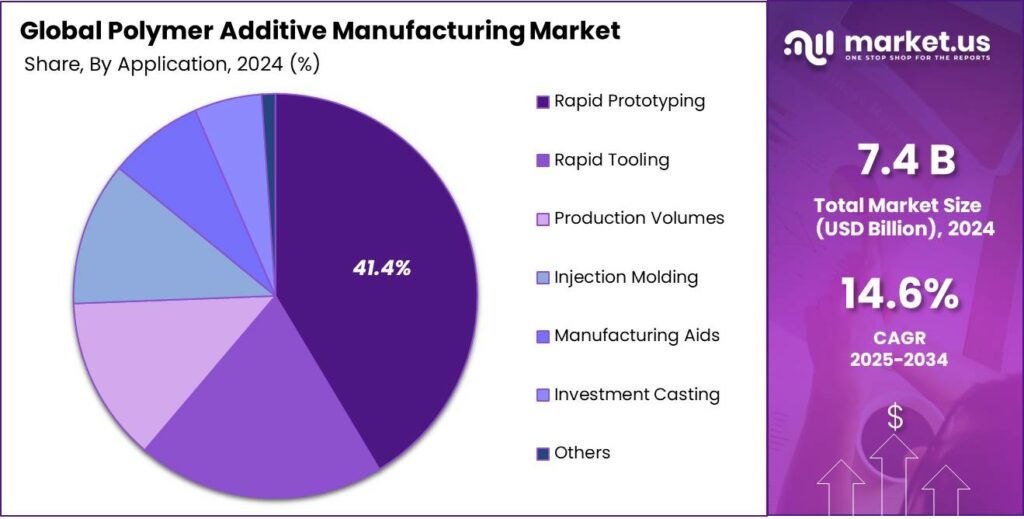
- Among the applications of polymer additive manufacturing, rapid prototyping held a major share in the market, 41.4% of the market share.
- In 2024, 28.9% of polymer additive manufacturing was utilized for industrial and manufacturing uses.
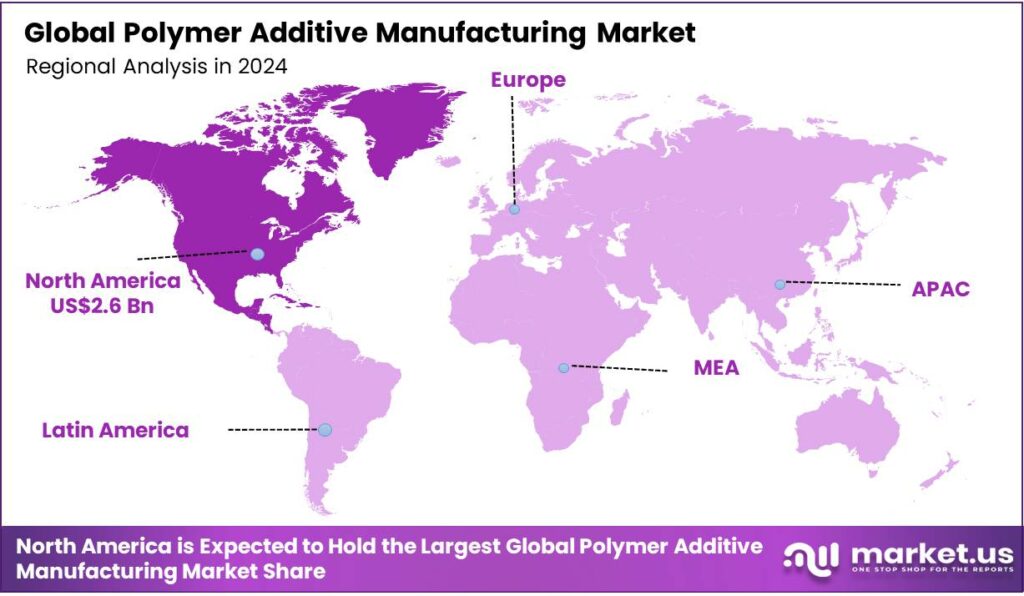
- In 2024, North America was the most dominant region in the polymer additive manufacturing market, accounting for 34.9% of the total global consumption.
Printing Technology Analysis
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) Printing Technology is a Prominent Segment in the Market.
The polymer additive manufacturing market is segmented based on printing technology into fused deposition modeling (FDM), stereolithography (SLA), selective laser sintering (SLS), polyjet printing, digital light processing (DLP), multi-jet fusion (MJF), and others. The fused deposition modeling (FDM) printing technology led the market, comprising 34.8% of the market share, due to its accessibility, cost-effectiveness, and versatility. FDM machines are relatively affordable and easy to operate, making them accessible for a broad range of industries, from prototyping to low-volume production.
Additionally, the material options available for FDM, including thermoplastics, are diverse and cost-efficient, offering practical solutions for both functional parts and prototypes. In contrast, methods such as SLA and SLS typically require more expensive equipment, specialized materials, and greater operational complexity. Similarly, FDM’s ability to produce larger parts in a variety of shapes and its lower maintenance requirements contribute to its widespread adoption across various sectors.
Material Type Analysis
Thermoplastics Dominated the Polymer Additive Manufacturing Market.
On the basis of material type, the polymer additive manufacturing market is segmented into thermoplastics, photopolymers, composite polymers, and others. The thermoplastics dominated the polymer additive manufacturing market, comprising 52.8% of the market share, due to their versatility, ease of processing, and cost-effectiveness. Unlike photopolymers, which require specialized equipment such as UV light for curing, thermoplastics can be easily extruded and processed in a variety of 3D printing technologies, making them more accessible.
Additionally, thermoplastics are recyclable, enhancing their sustainability appeal. Composite polymers and photopolymers, while offering specific advantages in terms of strength or detail resolution, often come with higher material costs and processing complexities, which limit their widespread use compared to thermoplastics.
Material Form Analysis
Polymer Additive Manufacturing Products Are Often Made from Material Filaments.
Based on the material form, the polymer additive manufacturing market is divided into filaments, powders, liquid resins, and pellets/granules. The material filaments dominated the polymer additive manufacturing market, with a notable market share of 40.3%, due to their ease of handling, compatibility with widely available 3D printers, and cost-effectiveness. Filaments are straightforward to load into FDM-based printers and require less post-processing compared to powders or liquid resins, which may need additional curing or specialized equipment.
Additionally, they tend to be more stable and have longer shelf lives than resins, which can degrade or harden if improperly stored. Similarly, filaments are generally less messy, simplifying the manufacturing process. Furthermore, they are available in a wide range of materials, including standard and composite polymers, which makes them versatile for various applications. In contrast, powders and resins often require more specialized equipment and handling procedures, limiting their broader adoption.
Application Analysis
Rapid Prototyping Held a Major Share of the Polymer Additive Manufacturing Market.
Among the applications, 41.4% of the total global consumption of polymer additive manufacturing is for rapid prototyping. Polymer additive manufacturing is most widely used for rapid prototyping as it enables fast, flexible, and cost-effective iteration of designs. It allows engineers to quickly produce functional or visual models directly from CAD files, facilitating design validation, fit testing, and concept evaluation without the need for expensive molds or tooling.
The polymer AM can produce complex geometries with minimal setup time, making it ideal for testing multiple design variants efficiently. Additionally, the mechanical properties of common polymer materials are often sufficient for prototypes but may not meet the durability or thermal requirements needed for end-use production parts, tooling, or casting applications, reinforcing their primary use in prototyping rather than high-volume manufacturing.
End Use Industry Analysis
Industrial & Manufacturing Uses Accounted for a Significant Portion of the Polymer Additive Manufacturing Market.
The polymer additive manufacturing market is categorized by end-use industry into industrial & manufacturing, automotive, aerospace & defense, healthcare & medical, consumer goods, energy & power, and others. Industrial & manufacturing uses account for 28.9% of the total global usage of polymer additive manufacturing, as these sectors can readily leverage its flexibility, customization, and rapid prototyping capabilities across diverse production needs. Industrial use often involves creating jigs, fixtures, assembly aids, and functional prototypes, where the mechanical requirements of polymers align well with operational demands.
Unlike specialized sectors such as aerospace or healthcare, which require stringent certification, biocompatibility, or extreme material performance, industrial applications are less constrained by regulatory or material limitations. Furthermore, industrial users benefit from shorter design-to-production cycles and the ability to iterate on tooling and parts quickly, making polymer AM an efficient solution for process optimization, pilot production, and low-volume functional components.
Key Market Segments
By Printing Technology
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
- Stereolithography (SLA)
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
- PolyJet Printing
- Digital Light Processing (DLP)
- Multi Jet Fusion (MJF)
- Others
By Material Type
- Thermoplastics
- Polylactic Acid (PLA)
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
- Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PETG)
- Polyamide
- PA6
- PA11
- PA12
- Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)
- Polycarbonate (PC)
- Polyether Ether Ketone / Polyether Ketone Ketone (PEEK / PEKK)
- Photopolymers
- Composite Polymers
- Others
By Material Form
- Filaments
- Powders
- Liquid Resins
- Pellets / Granules
By Application
- Rapid Prototyping
- Rapid Tooling
- Production Volumes
- Injection Molding
- Manufacturing Aids
- Investment Casting
- Others
By End Use Industry
- Industrial & Manufacturing
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Healthcare & Medical
- Consumer Goods
- Energy & Power
- Others
Drivers
Industrial Demand for Lightweight and High-Strength Parts Drives the Polymer Additive Manufacturing Market.
The increasing industrial demand for lightweight and high-strength parts is a critical driver of the polymer additive manufacturing market. Sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices have recognized the value of polymers in producing high-performance components with reduced weight, contributing to improved fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and enhanced mechanical properties.
Aerospace companies, including Boeing and Airbus, have adopted polymer AM technologies for producing lightweight parts to improve fuel efficiency. For instance, Boeing utilizes carbon fiber reinforced polymers (CFRPs) in the production of aircraft structures, citing a 20% reduction in weight compared to traditional materials, thereby enhancing fuel efficiency and operational performance.
Similarly, in automotive manufacturing, companies such as General Motors have explored thermoplastic polymers in additive manufacturing for lightweighting car parts, improving fuel economy, and performance. Furthermore, the medical device industry has embraced polymer AM for producing customized implants and surgical tools, as they offer the required combination of lightness, strength, and biocompatibility.
Restraints
High Upfront Costs Might Pose a Challenge to the Polymer Additive Manufacturing Market.
High upfront costs remain a significant challenge in the polymer additive manufacturing market, particularly for industries seeking to scale production. The initial investment in polymer additive manufacturing systems, including 3D printers and materials, can be substantial. For instance, the U.S.
Department of Energy (DOE) reports that industrial-grade 3D printers for polymer-based additive manufacturing can cost between US$100,000 and US$500,000, depending on the machine’s capabilities and scale. These costs often deter small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) from adopting the technology, despite the potential long-term benefits of reduced waste and design flexibility.
Moreover, material costs add a financial burden. High-performance polymer materials such as PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) and PA12 (Polyamide 12) are significantly more expensive than traditional manufacturing materials. According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), the cost of materials for polymer additive manufacturing can be 3 to 5 times higher than those used in conventional injection molding.
The cost discrepancy is particularly notable in industries such as automotive and aerospace, where high-strength, heat-resistant polymers are required for critical components. These high upfront costs are a primary barrier to wider adoption of polymer AM, limiting its use to industries and companies that can justify the capital expenditure for specialized applications.
Opportunity
Applications of Polymer Additive Manufacturing in the Healthcare Industry Create Opportunities in the Market.
Polymer additive manufacturing has emerged as a transformative opportunity in the healthcare industry, facilitating the production of customized medical devices, implants, and surgical tools. One notable application is in the creation of patient-specific implants. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved several 3D-printed polymer implants, including those made from materials such as PEEK, which are used in spinal and orthopedic surgeries.
These implants, tailored to the patient’s anatomy, reduce the need for extensive surgical modification, improving recovery times and overall surgical outcomes. Additionally, polymer additive manufacturing is advancing the production of surgical guides and tools. These guides are made from biocompatible polymers and are designed to fit the unique contours of individual patients, leading to more accurate procedures and reduced surgical time.
Moreover, the use of polymer additive manufacturing in prosthetics is growing. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) highlights several ongoing research projects focused on developing affordable, custom prosthetic limbs using 3D printing technologies, demonstrating the potential for wide-scale adoption in patient-specific care. These applications underscore the expanding role of polymer AM in enhancing personalized healthcare solutions.
Trends
Shift Towards Automation and Streamlined Workflows.
The shift towards automation and streamlined workflows is a key trend driving advancements in the polymer additive manufacturing market, particularly in industrial applications. The integration of automated processes in AM systems significantly reduces labor costs and improves production efficiency. The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) emphasizes the role of robotics in enhancing the precision and speed of polymer AM, particularly in the aerospace sector, where the production of complex parts demands high repeatability and accuracy.
Similarly, automated post-processing, such as automated cleaning and curing of 3D-printed parts, is gaining traction. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) reports that the incorporation of automated post-processing can reduce the time required for finishing 3D-printed parts by up to 50%, streamlining workflows and enhancing productivity.
Additionally, the adoption of manufacturing execution systems (MES) specialized for 3D printing has significantly reduced administrative bottlenecks. For instance, AMFG’s MES software helped a global IT company reduce quotation times by approximately 80% by replacing manual spreadsheets with automated order-handling solutions.
Geopolitical Impact Analysis
The Geopolitical Reality of Polymer Additive Manufacturing, Including Tariffs, Tensions, and Transformation.
The geopolitical tensions have had a noticeable impact on the polymer additive manufacturing market, influencing supply chains, material sourcing, and international collaboration. As of early 2025, over two-thirds of imports from China are subject to increased duties, including a 34% reciprocal tariff from the US that impacts the landed cost of industrial 3D printers and polymer feedstocks.
The ongoing trade restrictions and political instability, particularly between the United States, China, and Russia, have disrupted the global flow of raw materials critical to the processes. For instance, the U.S. Department of Commerce has imposed export controls on advanced materials such as certain polymers and composite materials to restrict access to strategic technologies, impacting manufacturers reliant on international supply chains.
Additionally, sanctions and trade barriers have prompted many companies to seek localized solutions, spurring investments in domestic polymer AM capabilities. In Europe, the European Commission has recognized the importance of reducing dependency on non-EU countries for high-performance materials and is prioritizing self-sufficiency in advanced manufacturing sectors.
Regional Analysis
North America Held the Largest Share of the Global Polymer Additive Manufacturing Market.
In 2024, North America dominated the global polymer additive manufacturing market, holding about 34.9% of the total global consumption, driven by its advanced industrial base, robust R&D infrastructure, and early adoption of innovative manufacturing technologies. In addition, the US government actively promotes additive manufacturing through federal programs, such as the Additive Manufacturing Forward program, which encourages major manufacturers to integrate smaller, U.S.-based suppliers into the AM supply chain.
Furthermore, the National Science Foundation (NSF) committed US$25.5 million in 2025 for R&D and workforce development in future manufacturing, including polymer additive manufacturing applications. The aerospace and defense sectors in the U.S. are major users, leveraging polymer additive manufacturing for functional parts and rapid prototyping. Similarly, the medical sector drives demand, utilizing polymer additive manufacturing for specialized devices with FDA clearance.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- The US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia & CIS
- Rest of Europe
- APAC
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- ASEAN
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Players in the polymer additive manufacturing market focus on innovation in materials development, particularly for high-performance polymers that offer improved strength, durability, and thermal resistance. Additionally, companies emphasize expanding their technological capabilities by advancing 3D printing systems that allow for faster, more precise, and scalable production.
Furthermore, these players focus on collaborations with research institutions and industry partners to enable access to cutting-edge developments and foster cross-industry applications, especially in aerospace, healthcare, and automotive sectors. Moreover, companies are investing in customer-specific solutions, offering tailored products and services to meet the unique needs of clients in diverse industries.
The Major Players in The Industry
- Stratasys
- 3D Systems, Inc.
- EOS GmbH
- HP Inc.
- Formlabs
- Carbon, Inc.
- EnvisionTEC (ETEC)
- The Prodways Group
- Materialise
- Hexagon AB
- Raise 3D Technologies, Inc.
- Anycubic
- Zortrax
- BCN3D Technologies, Inc.
- Markforged
- Other Key Players
Key Development
- In January 2026, EOS, a leading provider of additive manufacturing solutions, revealed plans to strengthen its U.S. manufacturing and logistics infrastructure through a US$3 million investment at its Pflugerville, Texas, facility and the opening of a new warehouse in Belton, Texas.
- In January 2026, Stratasys unveiled its Post Processing Partnership Program, a strategic effort to provide customers with streamlined access to validated post-processing solutions across complete additive manufacturing workflows. Additionally, the company entered into a commercial agreement with PostProcess Technologies, a leader in automated and intelligent post-printing solutions, which became the program’s first participating partner.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) US$7.4 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) US$28.9 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 14.6% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Printing Technology (Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), PolyJet Printing, Digital Light Processing (DLP), Multi Jet Fusion (MJF), and Others), By Material Type (Thermoplastics, Photopolymers, Composite Polymers, and Others), By Material Form (Filaments, Powders, Liquid Resins, and Pellets / Granules), By Application (Rapid Prototyping, Rapid Tooling, Production Volumes, Injection Molding, Manufacturing Aids, Investment Casting, and Others), By End Use Industry (Industrial & Manufacturing, Automotive, Aerospace & Defense, Healthcare & Medical, Consumer Goods, Energy & Power, and Others) Regional Analysis North America – The US & Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia & CIS, Rest of Europe; APAC– China, Japan, South Korea, India, ASEAN & Rest of APAC; Latin America– Brazil, Mexico & Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa– GCC, South Africa, & Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Stratasys, 3D Systems, Inc., EOS GmbH, HP Inc., Formlabs, Carbon, Inc., EnvisionTEC (ETEC), The Prodways Group, Materialise, Hexagon AB, Raise 3D Technologies, Inc., Anycubic, Zortrax, BCN3D Technologies, Inc., Markforged, and Other Players. Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited Users and Printable PDF)  Polymer Additive Manufacturing MarketPublished date: Feb 2026add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Polymer Additive Manufacturing MarketPublished date: Feb 2026add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Stratasys
- 3D Systems, Inc.
- EOS GmbH
- HP Inc.
- Formlabs
- Carbon, Inc.
- EnvisionTEC (ETEC)
- The Prodways Group
- Materialise
- Hexagon AB
- Raise 3D Technologies, Inc.
- Anycubic
- Zortrax
- BCN3D Technologies, Inc.
- Markforged
- Other Key Players










