Global Organophosphate Insecticides Market By Type (Insecticide, Herbicide, Rodenticide, Fungicide), By Active Ingredient (Glyphosate, Parathion, Malathion, Chloropyriphos, Diazinon, Dimethoate, Others), By Application (Grains and Cereals, Pulses and Oilseeds, Commercial Crops, Fruits and Vegetables, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends, and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: June 2025
- Report ID: 151327
- Number of Pages: 219
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
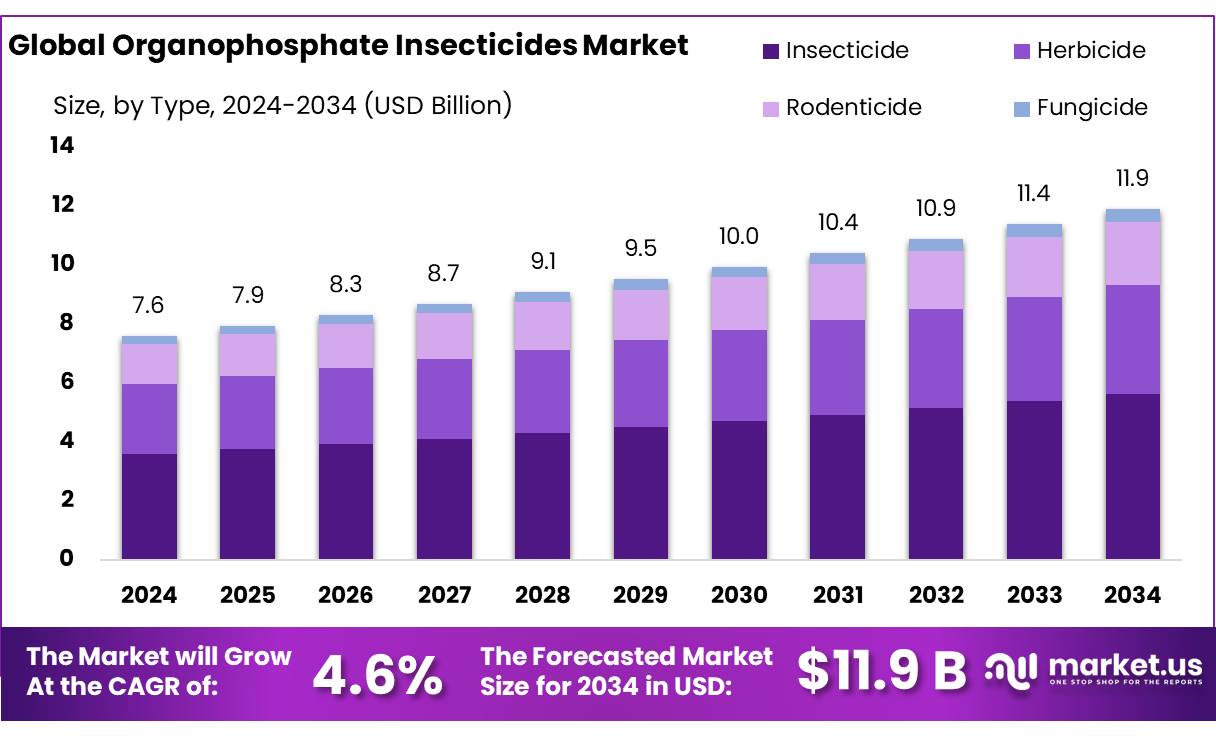
The Global Organophosphate Insecticides Market size is expected to be worth around USD 11.9 Billion by 2034, from USD 7.6 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 4.6% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
The organophosphate insecticides concentrates sector comprises liquid formulations primarily utilized in crop protection, public health vector control, and domestic pest management. These concentrates typically consist of active organophosphate compounds dissolved in solvents to enable mixing with water for spray or fogging applications. The primary industrial synthesis route involves the alcoholysis of phosphorus oxychloride (POCl₃), catalyzed by aluminum or magnesium chlorides, which remains the dominant commercial method for producing organophosphate esters.
Expansion in global food demand and intensification of cropping systems remain primary growth engines. The UN FAO has estimated that roughly 25% of global food contains residual pesticide traces, indicating ongoing and substantial pesticide deployment. The need for vector control—especially in regions affected by malaria or dengue—also sustains demand for organophosphate concentrates.
Regulatory patterns are shifting: in the U.S., the Food Quality Protection Act (FQPA) of 1996 enforced stricter tolerance settings, especially for vulnerable populations, which catalyzed reformulation efforts toward reduced-risk alternatives. Concurrently, the EPA’s Reduced-Risk Initiative encourages approval of safer insecticide options to replace traditional organophosphates.
Government initiatives and monitoring programs: The U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Pesticide Data Program (PDP) monitors residues in food, analyzing over 310,000 samples and 42 million data points, ensuring consumer safety compliance.
In the U.S., the FQPA (August 3, 1996) reformed pesticide tolerances, emphasizing health-based standards and special protection for infants and children. The EPA’s Pesticide Environmental Stewardship Program (PESP), launched in 1994, offers up to USD 50,000 annually per region to promote integrated pest management (IPM) and safer alternatives, achieving a 30% reduction in high-risk pesticide use over 1.2 million acres between 2003-2006. Similarly, the Strategic Agriculture Initiative (SAI) has provided USD 1.5 million in competitive grants annually to support growers transitioning away from hazardous pesticides.
Key Takeaways
- Organophosphate Insecticides Market size is expected to be worth around USD 11.9 Billion by 2034, from USD 7.6 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 4.6%.
- Insecticide held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 47.3% share in the global organophosphate insecticides market.
- Glyphosate held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 34.9% share in the organophosphate insecticides market.
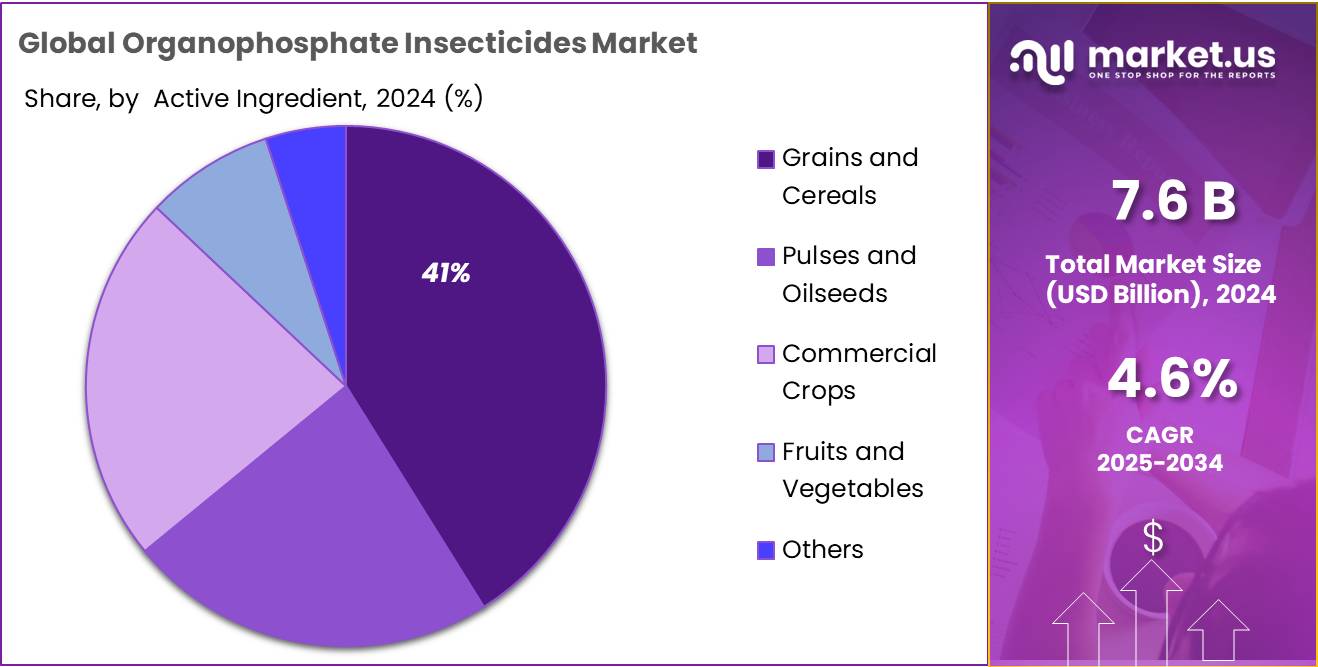
- Grains and Cereals held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 41.2% share in the global organophosphate insecticides market.
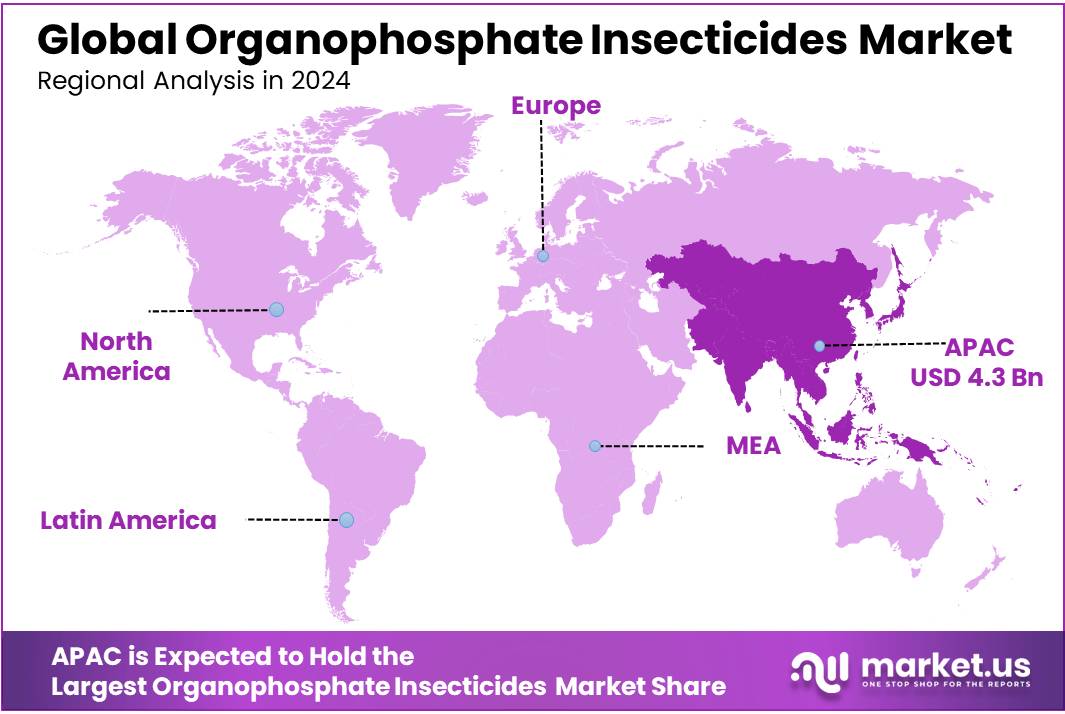
- Asia-Pacific (APAC) region held a dominant position in the global organophosphate insecticides market, accounting for more than 57.3% of the total market share, with a valuation of approximately USD 4.3 billion.
By Type
Insecticide dominates with 47.3% share in 2024 due to its widespread use in crop protection and public health programs.
In 2024, Insecticide held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 47.3% share in the global organophosphate insecticides market. This strong performance is mainly driven by the increasing need for effective pest control in agriculture, especially in countries with intensive farming practices. Organophosphate-based insecticides remain widely used due to their fast-acting nature and broad-spectrum efficacy against various insects.
Their continued application in both food crop production and public health programs—such as mosquito control for diseases like malaria and dengue—has helped sustain demand. The dominance of this type is expected to continue into 2025, supported by government-led vector control initiatives and the need for reliable crop yield protection in developing economies.
By Active Ingredient
Glyphosate leads with 34.9% share in 2024, driven by its broad-spectrum weed control and cost efficiency.
In 2024, Glyphosate held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 34.9% share in the organophosphate insecticides market by active ingredient. Its leadership is largely due to its strong effectiveness in controlling a wide range of weeds and pests across different types of crops, especially in large-scale farming. Farmers continue to favor glyphosate-based formulations for their reliability, low application cost, and compatibility with various cropping systems.
Despite ongoing discussions around regulatory restrictions in some regions, its usage has remained high in countries with large agricultural outputs. The trend is expected to hold steady through 2025, particularly in developing economies where cost-effective pest solutions are crucial.
By Application
Grains and Cereals dominate with 41.2% share in 2024 owing to high pest exposure and large-scale cultivation.
In 2024, Grains and Cereals held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 41.2% share in the global organophosphate insecticides market by application. This dominance is strongly linked to the widespread cultivation of crops like wheat, rice, and corn, which are often vulnerable to pests such as borers, aphids, and beetles.
Farmers in both developed and developing regions rely on organophosphate formulations to protect these staple crops and minimize harvest losses. The high economic value of grains and the critical role they play in food security have made pest control a top priority, especially in high-output agricultural economies. This trend is expected to remain stable into 2025, with rising demand from Asia and Latin America further supporting the segment’s leading position.
Key Market Segments
By Type
- Insecticide
- Herbicide
- Rodenticide
- Fungicide
By Active Ingredient
- Glyphosate
- Parathion
- Malathion
- Chloropyriphos
- Diazinon
- Dimethoate
- Others
By Application
- Grains and Cereals
- Pulses and Oilseeds
- Commercial Crops
- Fruits and Vegetables
- Others
Drivers
Stricter Food Safety Regulations Are Increasing Organophosphate Use
Pest attacks remain one of the biggest threats to global food security. The United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) reports that 20–40% of global crop production is lost annually due to pests. To avoid these losses while meeting growing food demand, farmers often rely on effective and affordable solutions like organophosphate insecticides.
As global food trade expands, exporting nations are under pressure to meet the residue limits set by various importing countries. For example, Canada invested CAD 560,000 in its Agri-Food Sustainability Initiative to help farmers implement safer crop protection methods that still allow them to meet strict export standards. While such programs aim to reduce overall pesticide dependence, they also validate the use of regulated, safer organophosphates where appropriate.
In the U.S., regulatory measures like the Food Quality Protection Act (FQPA) introduced stricter residue thresholds, especially protecting vulnerable groups such as children. This resulted in phasing out some highly toxic organophosphates while permitting the continued use of others under tight supervision. Rather than completely eliminating these chemicals, the goal is safer, responsible usage.
Restraints
Regulatory Restrictions and Toxicity Concerns Pose a Major Restraint
Globally, growing concerns over the toxicity of organophosphate (OP) insecticides have driven substantial regulatory restrictions. Between 2010 and 2019, the global use of OPs in vector control, such as to combat malaria, dropped by nearly 50%, reflecting shifts toward less harmful alternatives as health risks became clearer. This decline has been influenced by mounting scientific evidence linking OP exposure to acute and chronic health effects in both humans and wildlife.
For instance, the World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that around 3 million agricultural workers in developing nations experience severe pesticide poisoning annually, with about 18,000 fatalities. In Sri Lanka, the prohibition of the most toxic Class I OPs—parathion, methylparathion, monocrotophos, and methamidophos—between 1985 and 1995 led to a 40–50% reduction in suicide rates by self-poisoning from 1995 to 2002. Such outcomes have prompted other countries to follow suit.
In India, regulatory action has targeted a range of OPs. As of March 2024, export-only allowances or bans were in place for chemicals such as dichlorvos and phorate, while methamidophos and other highly toxic organophosphates remain strictly controlled. This regulatory intensity stems from documented neurodevelopmental impacts and acute toxicity concerns, particularly affecting children, farmworkers, and non-target species.
Furthermore, policy frameworks such as the U.S. Food Quality Protection Act (FQPA) have mandated a tenfold safety margin for infants and children. The U.S. EPA banned several OPs, including methyl parathion and chlorpyrifos, between 1999 and 2000. Coupled with the European Union’s planned reduction of hazardous pesticide use by 65% by 2030, these regulatory shifts drastically limit OP availability in major markets.
Opportunity
Public Health Risks and Global Bans Limiting Organophosphate Use
Organophosphate insecticides pose serious health threats worldwide, which is driving tighter controls and reducing their market potential. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), there are approximately 3 million cases of organophosphate poisoning and 200,000 deaths every year globally . Beyond fatalities, WHO data also highlights around 740,000 unintentional pesticide poisonings leading to 7,446 deaths, plus roughly 385 million cases of acute pesticide poisoning (including milder exposures) annually. These staggering numbers emphasize how harmful these chemicals can be—not just to farmworkers but to their families and communities.
In many developing nations, organophosphates are easily accessible and often misused, which increases the risk of accidental poisonings and even suicide. Studies show that acute pesticide poisoning is responsible for about one-third of all suicides worldwide, with organophosphates playing a major role in this tragedy. Countries like Sri Lanka saw suicide rates halve after banning highly toxic organophosphates—including WHO Class I agents—demonstrating how effective regulation can safeguard lives.
These grim realities have prompted sweeping bans. Over 112 countries have banned dangerously toxic organophosphates like chlorpyrifos and phorate. The European Union fully banned chlorpyrifos in 2020, and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency followed suit for most agricultural uses in 2022. Such regulatory changes not only reduce supply but also shift farmers toward safer alternatives like pyrethroids and biocontrol methods.
At a human level, these regulations reflect governments’ responsibility to protect public health. Farmers, their families, and healthcare workers bear the emotional and physical burden of exposure and accidental poisonings. Global bans and local policies mean less reliance on these toxic insecticides. As a result, communities experience fewer health crises—leading to cleaner water, safer food, and fewer emergency hospital visits.
Trends
Growing Cereal Cultivation Fuels Demand for Organophosphate Insecticides
The continuous expansion of cereal crop cultivation is creating fresh opportunities for the organophosphate insecticides market. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), pests are responsible for 20–40% of global crop losses each year. With the global population rising, especially in developing regions, the need to safeguard staple crops like rice, wheat, and maize becomes more urgent.
Between 2020 and 2023, FAOSTAT reports that global rice acreage increased from 165.1 million to 168.4 million hectares, while maize grew from 199.6 million to 208.2 million hectares. This expansion is especially pronounced in Asia-Pacific, where India and China alone account for approximately 27.5% of global cereal cultivation area. As more land is cultivated, the risk of pest infestations grows, prompting farmers to rely on effective and affordable solutions like organophosphates.
Government initiatives are also supporting this growth. For instance, China’s Ministry of Agriculture invested 26 billion USD in overseas agricultural projects to modernize farming practices and increase yields. Similarly, Canada allocated CAD 560,000 under its Agri-Food Sustainability Initiative to assist farmers in adopting better crop protection methods.
For countless small farmers, particularly in regions where cereals are critical to both food security and income, having access to reliable pest control allows them to protect their crops, meet international export standards, and improve livelihoods. With supportive policies and advancing technology, organophosphates remain a practical tool in their arsenal—used more safely, efficiently, and effectively.
Regional Analysis
Asia-Pacific Leads the Organophosphate Insecticides Market with 57.3% Share, Valued at USD 4.3 Billion in 2024
In 2024, the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region held a dominant position in the global organophosphate insecticides market, accounting for more than 57.3% of the total market share, with a valuation of approximately USD 4.3 billion. This leadership is driven by the region’s vast agricultural footprint, high population density, and the continued reliance on chemical pest control in countries such as China, India, Indonesia, and Vietnam. These nations face significant pest pressure due to their tropical climates and year-round cropping cycles, making insecticide use essential to safeguard food production.
Government programs such as India’s “National Food Security Mission” and various IPM (Integrated Pest Management) schemes have promoted balanced pesticide usage, but organophosphates still dominate due to their cost-efficiency and effectiveness. Additionally, the limited regulatory restrictions in several APAC countries, compared to Western markets, have sustained the demand for these formulations.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
ADAMA is a global crop protection leader delivering diverse insecticide formulations—including organophosphates—through R&D and local-market innovation in over 100 countries. Arising from ChemChina’s acquisition and integration with Syngenta, ADAMA leverages state-of-the-art synthesis and formulation plants in Israel, China, India, and Brazil. With nearly USD 4 billion in annual revenue and a broad portfolio of differentiated products, the company is positioned to meet regional farmer needs and adapt OP concentrations to regulatory and agronomic trends
BASF maintains a broad crop-protection portfolio that includes organophosphate insecticides and other chemistries for soil, foliar, and structural pest control. The company emphasizes R&D-driven solutions—such as Axalion® and Inscalis®—to manage resistance and reduce reliance on legacy chemistries. BASF’s global distribution, strong IPM integration, and focus on product stewardship align OP-based offerings with sustainability standards, helping retain market relevance amid regulatory scrutiny and evolving agronomic needs.
FMC supplies fast-acting OP formulations such as malathion-based concentrates under global distribution networks. The company focuses on public-health and agricultural applications, including vector control and food crops. FMC emphasizes regulatory compliance, investing in short-residue and environmentally safer OP product lines. Recent launches—like Malathion 1000 EC for Brazil—highlight its strategy to tailor OP insecticides to regional crop systems while addressing evolving resistance and sustainability requirements.
Top Key Players in the Market
- ADAMA
- American Vanguard Corporation
- BASF SE
- Bayer AG
- FMC Corporation
- Nufarm Limited
- Sumitomo Chemicals
- Syngenta Crop Protection AG
- UPL Limited
- Valent USA LLC
Recent Developments
Bayer Crop Science reported a 2.0% decline in full-year revenue, bringing total sales to €22.3 billion in 2024. EBITDA before special items decreased 14.2% to €4.3 billion, with the EBITDA margin falling to 19.4%.
In 2024, FMC Corporation, which offers organophosphate-based insecticides alongside its broader crop protection portfolio, recorded USD 4.25 billion in annual revenue—a decline of 5% from 2023—driven by lower pricing and currency effects.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 7.6 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 11.9 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 4.6% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Type (Insecticide, Herbicide, Rodenticide, Fungicide), By Active Ingredient (Glyphosate, Parathion, Malathion, Chloropyriphos, Diazinon, Dimethoate, Others), By Application (Grains and Cereals, Pulses and Oilseeds, Commercial Crops, Fruits and Vegetables, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape ADAMA, American Vanguard Corporation, BASF SE, Bayer AG, FMC Corporation, Nufarm Limited, Sumitomo Chemicals, Syngenta Crop Protection AG, UPL Limited, Valent USA LLC Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Organophosphate Insecticides MarketPublished date: June 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Organophosphate Insecticides MarketPublished date: June 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- ADAMA
- American Vanguard Corporation
- BASF SE
- Bayer AG
- FMC Corporation
- Nufarm Limited
- Sumitomo Chemicals
- Syngenta Crop Protection AG
- UPL Limited
- Valent USA LLC










