Global Oligonucleotide API Market Analysis By API Type (Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASO), Short Interfering RNA (siRNA), MicroRNA (miRNA), Aptamers, CpG Oligonucleotides, Others), By Manufacturing (In-house, Outsourced), By Application (Therapeutics, Diagnostics, Research, Others), By End-User (Pharmaceutical companies, Biotechnology companies, Academic & research institutes, Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs), Others) By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Nov 2025
- Report ID: 166440
- Number of Pages: 327
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
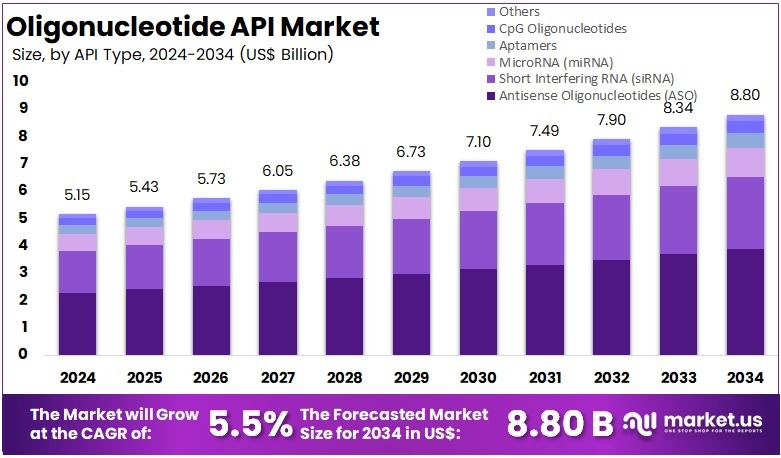
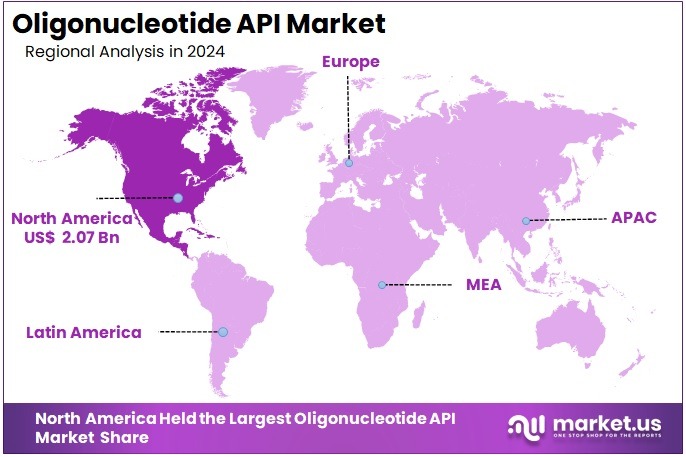
The Global Oligonucleotide API Market size is expected to be worth around US$ 8.8 Billion by 2034, from US$ 5.15 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 5.5% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 40.2% share and holds US$ 2.07 Billion market value for the year.
The global market for oligonucleotide active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) has been expanding due to rising demand for gene-targeted and RNA-based medicines. According to recent assessments, oligonucleotide APIs consist of short synthetic nucleic acid sequences that regulate gene expression or protein synthesis. Their use in antisense therapies, siRNA drugs, and molecular diagnostics has increased. This growth has been supported by precision medicine trends, rising clinical trial activity, and steady investment in genetic research across major regions.
A study by PubMed Central reported that regulators in the US and EU have approved around 20 oligonucleotide medicines, including one aptamer, nearly a dozen antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), and several siRNA drugs. For instance, the FDA approved nusinersen for spinal muscular atrophy and multiple exon-skipping ASOs for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. In 2023, the FDA also cleared Qalsody (tofersen) for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis linked to SOD1 mutations. These approvals have strengthened demand for GMP-grade oligonucleotide APIs.
Rare diseases represent one of the largest unmet needs driving market expansion. The WHO notes that its ICD-11 classification already includes roughly 5,500 rare diseases. A landmark analysis by BioMed Central estimated that rare diseases affect 3.5–5.9% of the global population, equal to 263–446 million individuals, often summarized as about 300 million people. For example, many of these conditions stem from single-gene mutations, making siRNA and ASO drugs suitable therapeutic tools. As diagnosis improves, the need for clinical and commercial-scale API manufacturing rises.
Supportive regulatory frameworks continue to reduce development risks. The EMA issued a dedicated guideline for oligonucleotide development in 2024, covering quality, analytics, and manufacturing controls. In parallel, the FDA released guidance for individualized ASO products and shared technical views on impurity control and LC–MS analytical methods. According to regulatory experts, clearer standards increase confidence among developers and CDMOs, encouraging investments in new synthesis lines, advanced analytical laboratories, and large-scale manufacturing capacity.
Technology Trends and Clinical Expansion
Technological advances in oligonucleotide chemistry, delivery, and analytics continue to shape market growth. Reviews show that several generations of backbone and sugar modifications have improved stability and binding efficiency. For example, GalNAc-conjugated siRNA enables targeted liver delivery and supports multiple approved products. According to FDA technical insights, advanced analytical platforms such as high-resolution mass spectrometry and HILIC methods support detailed impurity profiling. These innovations improve yields and lower costs, enhancing scalability.
The therapeutic scope for oligonucleotides is expanding. Initially focused on ultra-rare genetic disorders, the modality is now being applied to neurological, metabolic, and hepatic diseases. For instance, studies highlight the use of antisense oligonucleotides to modulate proteins linked to neurodegeneration. NIH sources also describe siRNA drugs for lipid disorders and liver conditions. Research activity in oncology is increasing as well, where gene-silencing approaches target tumor-driving mutations. This broader adoption increases batch size requirements and strengthens API demand.
Personalized and “n-of-1” therapies represent another emerging growth factor. ClinicalTrials.gov lists several single-participant studies in which customized ASOs are developed for unique mutations. The FDA has issued targeted guidance for these individualized programs. Although such therapies require smaller API volumes, they demand rapid GMP-compliant production, modular equipment, and digital quality systems. According to industry observations, this trend supports the adoption of flexible, multi-product manufacturing platforms.
Clinical development momentum remains strong. Numerous interventional trials continue to assess ASO and siRNA drugs across indications such as epilepsy, hereditary lipid disorders, liver diseases, ALS, and various cancers. Regulators have noted that ASOs and siRNAs now represent an established therapeutic platform supported by extensive non-clinical and clinical data. Public research programs by NIH and global health organizations further encourage gene-targeted innovations. These funding flows increase early-stage candidates and maintain steady demand for high-quality oligonucleotide APIs required for preclinical, Phase I, II, and III supplies.
Key Takeaways
- The global oligonucleotide API market is projected to reach nearly US$ 8.8 billion by 2034, rising steadily from US$ 5.15 billion in 2024 at a 5.5% CAGR.
- Antisense oligonucleotides were identified as the leading API type in 2024, accounting for over 44.2% of total market share due to strong therapeutic adoption.
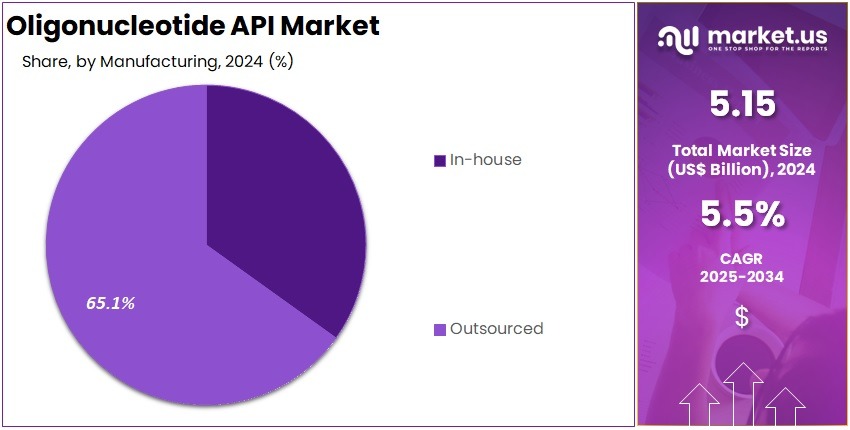
- In-house manufacturing was observed as the primary production approach in 2024, securing more than 65.1% share owing to improved control, quality assurance, and cost efficiency.
- Therapeutic applications represented the largest usage area in 2024, capturing above 48.7% share as clinical demand for targeted oligonucleotide-based treatments continued to expand.
- Pharmaceutical companies remained the chief end users in 2024, contributing over 44.5% share because of extensive R&D pipelines and increasing investment in nucleic acid-based products.
- The opioids category dominated the drug class segment in 2024, holding more than 48.5% share, reflecting its broad utilization in oligonucleotide-driven research and development activities.
- In 2024, North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 40.2% share and holds US$ 2.07 Billion market value for the year.
API Type Analysis
In 2024, the Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASO) held a dominant market position in the API Type segment of the Oligonucleotide API Market, and captured more than a 44.2% share. Strong adoption was driven by targeted genetic therapies. Higher clinical success rates also supported growth. ASO molecules gained traction due to precise sequence targeting. Their use expanded across rare diseases and neuromuscular disorders. Continuous investment in gene-modulating platforms strengthened demand. The segment maintained clear leadership throughout the year.
The siRNA segment secured a notable share. Growth was supported by the wider use of RNA interference. Advancements in delivery systems improved clinical outcomes. Increasing application in metabolic and rare disorders also boosted demand. The miRNA segment showed steady uptake. Its growth was driven by research activity and biomarker development. Rising use in early-stage programs reinforced adoption. Aptamers also advanced due to high affinity binding. Their role in diagnostics and imaging supported continued market penetration.
CpG oligonucleotides expanded at a moderate pace. Their progress was linked to vaccine adjuvant development. Strong interest in immune activation supported demand. Broader use in oncology programs added momentum. The Others segment reported additional growth. Innovation in RNA-editing tools and splice-modulating constructs contributed to this trend. New nucleic acid chemistries improved design efficiency. Advances in synthesis and purification enhanced production quality. These developments strengthened the overall competitiveness of all emerging oligonucleotide API types.
Manufacturing Analysis
In 2024, the ‘In-house’ held a dominant market position in the Manufacturing Segment of the Oligonucleotide API Market and captured more than a 65.1% share. This leadership was influenced by strong internal quality systems. Secure production settings also supported segment strength. The preference for controlled environments increased reliance on internal units. Growing demand for precise synthesis enhanced this position. Companies favored internal teams for sensitive steps. This trend continued as regulatory needs became stricter across regions.
The Outsourced segment accounted for a smaller share but showed steady growth. Rising dependence on contract manufacturers supported this trend. Many firms preferred outsourcing to lower infrastructure costs. This practice was observed among small and mid-sized developers. Increased access to specialized synthesis technology strengthened the model. Service providers offered scalable systems for complex production. This supported broader adoption of outsourcing. The segment benefited from improved technical capabilities and expanding global service networks focused on oligonucleotide production.
Both segments were influenced by expanding therapeutic pipelines. Growth in nucleic acid therapies shaped manufacturing choices. Rising cases of chronic and genetic disorders increased demand for high-quality APIs. Companies focused on efficiency, scalability, and compliance. This encouraged balanced use of internal and external units. Market dynamics shifted as new treatment platforms advanced. The push for reliable supply chains also guided strategies. Overall, manufacturing decisions were shaped by evolving scientific needs and regulatory expectations across key markets.
Application Analysis
In 2024, the ‘Therapeutics’ held a dominant market position in the Application Segment of the Oligonucleotide API Market, and captured more than a 48.7% share. This leadership was driven by strong demand for advanced RNA and DNA therapies. The segment benefited from wider clinical adoption. Growth in rare disease treatment also supported higher uptake. Increased research activity in gene modulation strengthened its appeal. Expanding development pipelines maintained steady momentum. This trend is expected to continue.
Diagnostic applications recorded stable growth during the period. Demand increased due to wider use of oligonucleotide probes in molecular tests. Adoption in infectious disease screening also expanded. Advancements in PCR workflows reinforced steady usage. The Research segment showed consistent progress as well. Higher investment in genomic studies supported its expansion. Rising interest in gene expression tools drove usage. Academic and industry programs maintained steady momentum across global R&D environments. This supported ongoing market development.
Other applications contributed a modest share to the market. These included agriculture, forensics, and several industrial uses. Demand increased gradually as synthetic biology gained wider acceptance. Growth was supported by expanding niche projects in applied sciences. Rising interest in customized oligonucleotides helped broaden adoption. Use in analytical workflows also advanced. Although the segment remained smaller, its long-term outlook stayed positive. Steady development across specialized fields strengthened market participation and created incremental opportunities.
End-User Analysis
In 2024, the Pharmaceutical Companies held a dominant market position in the End-User Segment of the Oligonucleotide API Market and captured more than a 44.5% share. Their lead was supported by strong demand for nucleic acid-based drugs. Rapid growth in targeted therapies also strengthened this position. Expansion of clinical programs increased API consumption. Precision medicine initiatives further accelerated adoption. Continued regulatory progress for oligonucleotide therapeutics reinforced high usage across major product pipelines.
Biotechnology companies accounted for a notable share of the market. Their growth was driven by active research in RNA and DNA-based platforms. Investment in gene modulation technologies supported rising API needs. The presence of specialized biotech firms added momentum. Academic and research institutes also contributed steadily. Higher funding in genomics and molecular biology increased their utilization. Frequent purchases for assays, discovery activities, and laboratory applications sustained consistent use of oligonucleotide APIs across diverse research programs.
Contract Manufacturing Organizations showed strong growth due to rising outsourcing trends. Their capacity to deliver high-volume synthesis supported industry needs. Investments in advanced production technologies improved efficiency. The Others segment, including diagnostic developers and specialty laboratories, also expanded. Increased adoption of probe-based testing encouraged demand. Custom synthesis requirements further supported this group. Overall, broad end-user participation strengthened market growth. Advancing nucleic acid technologies continued to create steady opportunities across all application areas.
Key Market Segments
By API Type
- Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASO)
- Short Interfering RNA (siRNA)
- MicroRNA (miRNA)
- Aptamers
- CpG Oligonucleotides
- Others
By Manufacturing
- In-house
- Outsourced
By Application
- Therapeutics
- Diagnostics
- Research
- Others
By End-User
- Pharmaceutical companies
- Biotechnology companies
- Academic & research institutes
- Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs)
- Others
Drivers
Expansion of Genetic Medicine as a Key Driver for Oligonucleotide API Demand
The rising adoption of genetic medicine has been driving sustained growth in demand for oligonucleotide APIs. The expansion of therapeutic applications has been supported by advances in molecular biology and improved delivery platforms. As more genetic disorders are targeted through nucleic acid–based interventions, the requirement for high-quality oligonucleotide inputs has risen consistently. This trend has strengthened the role of oligonucleotide APIs as foundational components for emerging therapeutic pipelines. The market has therefore been experiencing continuous capacity expansion to meet growing development needs.
Personalized therapies have become a significant catalyst for market growth. The shift toward patient-specific and mutation-specific treatment approaches has increased the use of custom oligonucleotides. These molecules are being integrated into targeted interventions designed to address individual genetic profiles. As the therapeutics portfolio diversifies, manufacturers have been required to develop flexible and scalable production systems. The rise of precision medicine has thus contributed to heightened demand for advanced synthesis technologies and reliable API supply infrastructures across global markets.
Antisense oligonucleotides and siRNA-based products have further accelerated commercial-scale manufacturing requirements. Their expanding clinical success has encouraged wider research investment and accelerated regulatory approvals. As product pipelines mature, large-volume production capabilities have gained strategic importance. This has resulted in a growing emphasis on quality control, cost-efficient synthesis, and robust process optimization. The commercial momentum of these nucleic acid therapies continues to strengthen API demand, positioning oligonucleotide manufacturing as a central driver of growth within the broader genetic medicine landscape.
Restraints
Manufacturing Complexity and Regulatory Burden in Oligonucleotide API Production
The market has been facing considerable constraints due to the high complexity associated with oligonucleotide API manufacturing. The production workflow has been dependent on advanced technologies and specialized equipment. These requirements have been increasing operational pressures on manufacturers. Strict contamination control and facility specifications have also been adding to operational burdens. As a result, production efficiency has been affected and expansion plans have been slowed. These challenges have been creating a persistent restraint for market development.
Stringent regulatory expectations have been intensifying the restraint on oligonucleotide API production. Compliance with global quality, safety, and validation standards has been demanding extensive documentation and continuous monitoring. These activities have been consuming significant time and resources. Approval cycles have also been extended due to in-depth regulatory assessments. This environment has been limiting the ability of manufacturers to accelerate output. Consequently, regulatory pressures have been contributing to delays and higher costs across the value chain.
Capacity expansion has been restricted because of the combined impact of manufacturing complexity and regulatory rigor. Contamination-free environments and multi-step validation procedures have been increasing production costs and slowing throughput. Investment requirements for facility upgrades have also been rising. Smaller manufacturers have been facing additional hurdles due to limited budgets and technical capabilities. These factors have been reducing the pace of scale-up activities in the industry. As a result, market growth has been constrained by structural production challenges.
Opportunities
Increasing Adoption Of Automated, Large-Scale Solid-Phase Synthesis Systems
The opportunity for the Oligonucleotide API market is being strengthened by the increasing adoption of automated, large-scale solid-phase synthesis systems. These systems have been improving process consistency and reducing operational variability. Their use has been supporting manufacturers seeking reliable production of complex oligonucleotide sequences. As automation advances, efficiency gains are becoming more visible across development pipelines. This shift has been creating favorable conditions for companies aiming to expand production capacity in regulated environments.
High-throughput synthesis platforms are gaining traction due to their ability to handle rising clinical demand. Their integration has been enabling faster cycle times and higher batch output. Manufacturers are benefiting from technology that supports rapid scale-up without compromising quality. This development has been important as the number of oligonucleotide-based therapeutics in development continues to increase. The growing need for streamlined production has been positioning advanced synthesis systems as a competitive advantage for API suppliers.
The expansion of GMP-compliant production frameworks has been contributing to this opportunity. Compliance has remained essential for companies serving a widening pipeline of clinical programs. Automated systems support these requirements by improving traceability and meeting stringent regulatory expectations. As clinical studies advance and more candidates progress toward commercialization, demand for reliable GMP-grade APIs has been rising. This environment has been driving investment in next-generation synthesis technologies. It is expected to create long-term growth prospects for manufacturers operating in the oligonucleotide API market.
Trends
Advancement in Chemical Modifications
A strong trend has been observed toward the adoption of chemically modified oligonucleotide formats within the Oligonucleotide API market. The focus has been shifting to phosphorothioate backbones, Locked Nucleic Acids, and advanced conjugated structures. These formats have been designed to enhance molecular stability and improve biological performance. Their integration has been increasing due to rising demand for safer and more durable therapeutic candidates. This transition has shaped development priorities and has strengthened interest in next-generation oligonucleotide technologies.
The growth of modified chemistries can be attributed to their ability to improve resistance to enzymatic degradation and support effective in-vivo delivery. Stability enhancements have been considered essential because unmodified oligonucleotides degrade rapidly in physiological conditions. The introduction of Locked Nucleic Acids and phosphorothioate linkages has been used to enhance half-life and binding affinity. These advancements have supported broader therapeutic applications. As a result, manufacturers have prioritized robust chemical engineering approaches to meet emerging clinical requirements.
The increasing use of conjugated oligonucleotides has been influencing formulation and process development strategies across the market. Conjugation technologies, including ligand-based and lipid-based systems, have been improving cellular uptake and tissue specificity. This improvement has reduced dose requirements and enhanced therapeutic efficiency. The demand for such optimized delivery solutions has driven companies to refine manufacturing processes. Consequently, production workflows have been aligned with advanced modification needs, supporting scalable and reliable Oligonucleotide API development for diverse therapeutic pipelines.
Regional Analysis
In 2024, the Opioids segment held a dominant market position in the Drug Class Segment of the Oligonucleotide API, capturing more than a 48.5% share. This leadership was supported by rising demand for targeted therapies. Steady progress in nucleic acid research strengthened clinical adoption. Growing interest in precision treatment also encouraged higher usage. Increased funding for advanced drug development created further momentum. As a result, the segment maintained stable expansion and strong acceptance across key therapeutic fields.
The dominance of the segment was reinforced by continuous innovation in molecular platforms. Advancements in synthesis technologies improved output quality and reduced development timelines. Broader application in chronic disease management supported consistent uptake. Regulatory support for emerging oligonucleotide therapies added further stability. Strong collaboration among research institutions strengthened product availability. The segment benefited from rising awareness of advanced treatments, which encouraged healthcare providers to adopt modern therapeutic options across diverse patient groups.
Growing clinical trials involving oligonucleotide-based mechanisms strengthened the segment’s strategic importance. Increased investment from pharmaceutical firms enhanced production capacity and improved supply reliability. Expansion of therapeutic indications boosted long-term outlook. Rising focus on genetic and metabolic conditions created new opportunities. The segment also gained from improved diagnostic capabilities, which supported wider usage. Continuous improvements in safety profiles reinforced confidence among prescribers. Overall demand trends suggested stable and sustained growth.
Healthcare systems increasingly adopted advanced nucleic acid therapies for complex conditions. This trend expanded the use of oligonucleotide APIs in specialized treatment centers. The segment gained traction due to predictable clinical outcomes and growing therapeutic validation. Enhanced formulation processes strengthened efficiency. Increasing integration of high-precision manufacturing supported scalability. Broader acceptance of innovative treatment models improved market penetration. As patient awareness expanded, demand for specialized solutions increased at a steady rate.
Strong research frameworks supported ongoing development across multiple therapeutic areas. Continued investment in modern laboratory infrastructure improved innovation capacity. The segment benefited from collaborative pipelines that encouraged consistent product advancement. Increased focus on personalized medicine helped strengthen its relevance. Wider commercial interest supported stable supply arrangements. As demand for targeted interventions increased, the segment remained central to evolving treatment strategies. Its growth outlook stayed positive due to continuous scientific progress and rising clinical adoption.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherland
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- New Zealand
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
The oligonucleotide API market is shaped by a group of advanced CDMOs and global life-science suppliers. Agilent Technologies holds a strong lead due to its commercial-scale cGMP capacity and proven track record in approved oligonucleotide APIs. Its facilities support multiple modalities such as siRNA and antisense oligos. Growth in therapeutic pipelines has increased reliance on Agilent’s robust quality systems. The company’s regulatory experience, validated processes, and large-scale synthesis capabilities continue to strengthen its competitive position across late-stage and commercial supply.
Ajinomoto Bio-Pharma Services maintains a solid presence with its AJIPHASE® liquid-phase platform and large solid-phase synthesis systems. These enable efficient production of complex and modified oligonucleotides. The company supports early to late-stage programs and provides reliable cGMP manufacturing. Integrated DNA Technologies also contributes significantly, offering high-quality research and GMP-grade oligos for diagnostics and emerging therapies. Its broad modification options and established global footprint allow it to support early development needs. Both players reinforce market growth through flexible capacities and advanced synthesis capabilities.
Thermo Fisher Scientific and Merck KGaA influence the market through integrated technology portfolios. Thermo Fisher provides oligo synthesis services, key reagents, and analytical systems, creating strong end-to-end value. This integrated offering supports both standardized and custom production needs. Merck KGaA strengthens the segment through its high-potency API and bioconjugation expertise. These capabilities are relevant for next-generation conjugated oligonucleotides. Their global manufacturing networks and strict quality systems help meet rising demand for high-purity therapeutic oligos. Their roles support technical advancement and regulatory reliability.
Other key players include Eurogentec, GenScript Biotech, Kaneka Corporation, BioSpring, Avecia, Almac, Lonza, Corden Pharma, and Siegfried. These companies contribute specialized strengths across GMP manufacturing, enzymatic synthesis, large-scale capacity, and analytical development. BioSpring and Avecia remain central in therapeutic-grade oligo production. Corden Pharma and Almac expand through new platforms and capacity additions. GenScript and Eurogentec support both diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Their combined capabilities enhance supply resilience. Their investments support broader adoption of oligonucleotide-based therapies and reinforce global market competitiveness.
Market Key Players
- Agilent Technologies
- Ajinomoto Bio‑Pharma Services
- Integrated DNA Technologies (IDT)
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- Merck KGaA
- Eurogentec
- GenScript Biotech
- Kaneka Corporation
- BioSpring GmbH
- Avecia (Nitto Denko group)
- Almac Group
- Lonza Group
- Corden Pharma International
- Siegfried AG
- Other key players
Recent Developments
- January 2023: Agilent Technologies announced an investment of approximately US$725 million to double its manufacturing capacity for therapeutic nucleic acids (therapeutic oligonucleotides, used as APIs) at its Frederick, Colorado site. The expansion is targeted at meeting rapidly growing demand for high-quality oligonucleotide APIs for nucleic-acid–based therapeutics and is linked to a supplier market for therapeutic oligos estimated at around US$1 billion. The investment is directed toward state-of-the-art large-scale oligo API production for late-stage clinical and commercial supply, directly strengthening Agilent’s position as an oligonucleotide API CDMO partner.
- February 2022: Ajinomoto Bio-Pharma Services announced the development of a new artificial RNA ligase enzyme (ancestral design method) that enables high-productivity formation of double-strand oligonucleotides. In internal comparisons, yield for an siRNA drug substance improved from about 20% to 80% under identical reaction conditions versus a natural RNA ligase, demonstrating significantly higher thermostability and ligation activity, including for fragments containing xenonucleic acids. The company indicates that this enzyme is intended to support more efficient and environmentally friendly enzymatic synthesis of nucleic acid medicines and can be combined with AJIPHASE® and conventional solid-phase synthesis, thereby strengthening the technology base for scalable oligonucleotide API manufacturing.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) US$ 5.15 Billion Forecast Revenue (2034) US$ 8.80 Billion CAGR (2025-2034) 5.5% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, COVID-19 Impact, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By API Type (Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASO), Short Interfering RNA (siRNA), MicroRNA (miRNA), Aptamers, CpG Oligonucleotides, Others), By Manufacturing (In-house, Outsourced), By Application (Therapeutics, Diagnostics, Research, Others), By End-User (Pharmaceutical companies, Biotechnology companies, Academic & research institutes, Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs), Others) Regional Analysis North America – The US, Canada, & Mexico; Western Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Portugal, Ireland, Austria, Switzerland, Benelux, Nordic, & Rest of Western Europe; Eastern Europe – Russia, Poland, The Czech Republic, Greece, & Rest of Eastern Europe; APAC – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia & New Zealand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, & Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Colombia, Chile, Argentina, Costa Rica, & Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – Algeria, Egypt, Israel, Kuwait, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, & Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Agilent Technologies, Ajinomoto Bio‑Pharma Services, Integrated DNA Technologies (IDT), Thermo Fisher Scientific, Merck KGaA, Eurogentec, GenScript Biotech, Kaneka Corporation, BioSpring GmbH, Avecia (Nitto Denko group), Almac Group, Lonza Group, Corden Pharma International, Siegfried AG, Other key players Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Agilent Technologies
- Ajinomoto Bio‑Pharma Services
- Integrated DNA Technologies (IDT)
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- Merck KGaA
- Eurogentec
- GenScript Biotech
- Kaneka Corporation
- BioSpring GmbH
- Avecia (Nitto Denko group)
- Almac Group
- Lonza Group
- Corden Pharma International
- Siegfried AG
- Other key players










