Global Isopentane Market Size, Share, And Business Benefits By Grade (less than 98%, 98%), By Blending Agent (n-Pentane, Pentane, Cyclopentane), By Function (Blowing Agents, Polyurethane Foam Additives, EPS Additives, Solvents, Propellant, Viscosity Controlling Agents), By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends, and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: November 2025
- Report ID: 164523
- Number of Pages: 355
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
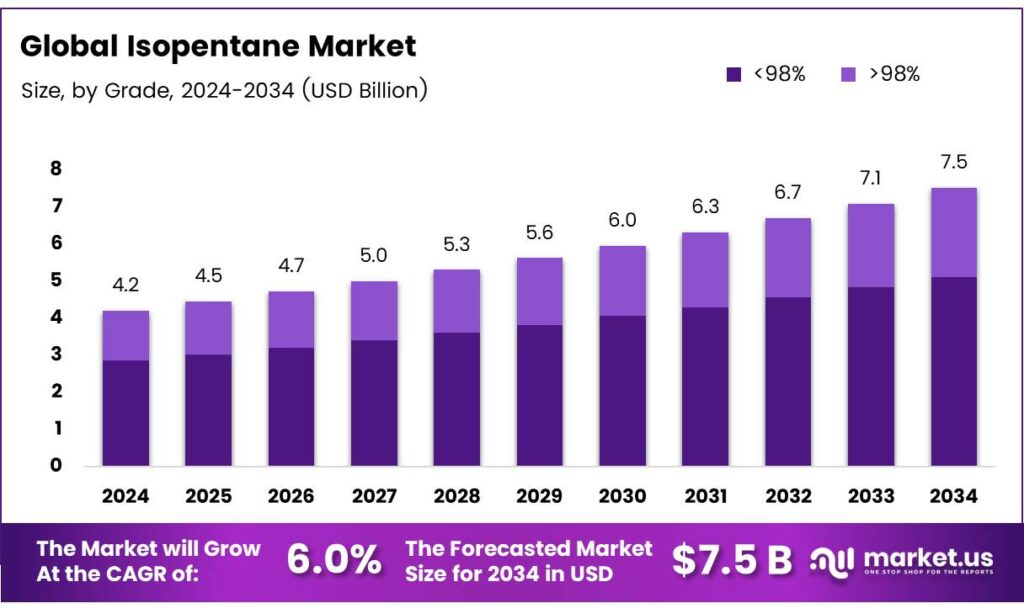
The Global Isopentane Market size is expected to be worth around USD 7.5 Billion by 2034, from USD 4.2 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 6.0% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
Isopentane, also known as 2-methylbutane (C₅H₁₂), is an alkane formed by substituting a methyl group at position 2 of butane. It is an extremely volatile, highly flammable, and colorless liquid with a gasoline-like odor. As the least dense liquid under standard conditions, it floats on water and produces irritating vapors when heated. Its normal boiling point is 82°F (28°C), just above room temperature, causing it to readily evaporate on warm days.
In contrast, isopentane adsorption decreases from 50°C to 250°C before slightly rising at higher temperatures. At low temperatures (80–150°C), alkenes form oligomers on the zeolite’s acid sites, irreversibly trapping within α-cages; isobutene’s oligomers, located near crystallite surfaces, more strongly reduce adsorption capacity. At high temperatures (350–420°C), aromatic and polyaromatic compounds form from alkenes.
For isopentane, only intact molecules are trapped at 50–150°C, indicating slow desorption from narrow pores and significant pore-volume occupation that lowers zeolite capacity. At elevated temperatures, some trapped isopentane converts on weak acid sites into oligomers and aromatics. Isopentane is chilled to 140 K in a Dewar flask using liquid nitrogen in a thick glass cold finger inserted into the flask, with temperature monitored by a thermocouple.
Industrially, isopentane serves as a solvent, aerosol propellant, and blowing agent for expanded polystyrene. It is a building-block chemical in synthesizing chlorinated derivatives, amyl-naphthalene, and isoprene. It behaves like a slightly larger cylindrical molecule in structural comparisons. Isopentane has been detected in urban air and exhibits physical properties closely aligned with other light alkanes, though its branched structure influences volatility and density.
Key Takeaways
- The Global Isopentane Market is projected to grow from USD 4.2 billion in 2024 to USD 7.5 billion by 2034 at a 6.0% CAGR.
- Less than 98% purity grade dominated the By Grade segment in 2024 with 68.3% share due to cost-performance balance.
- n-Pentane led By Blending Agent segment in 2024 with a 33.9% share for enhancing foam uniformity and volatility.
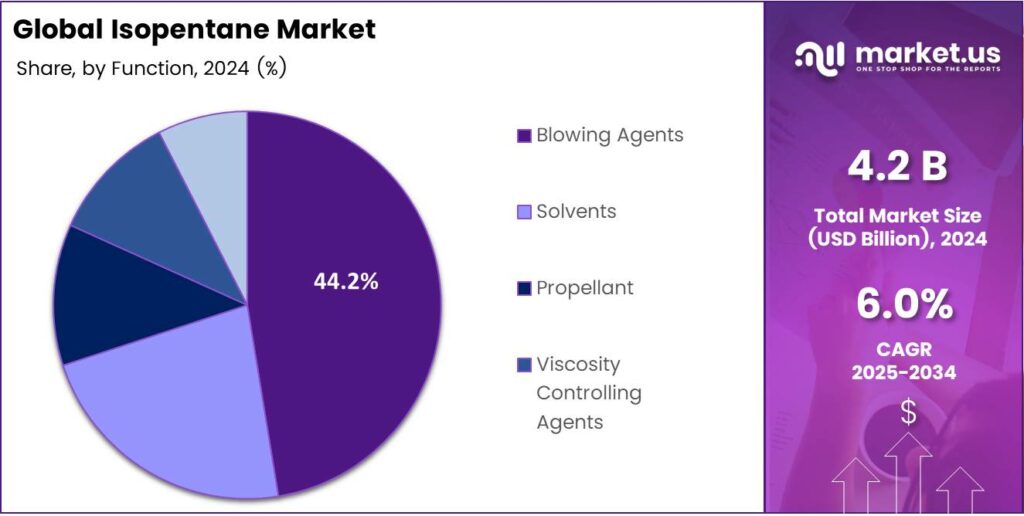
- Blowing Agents held the top position in the By Function segment in 2024 with 44.2% share, essential for EPS and polyurethane insulation.
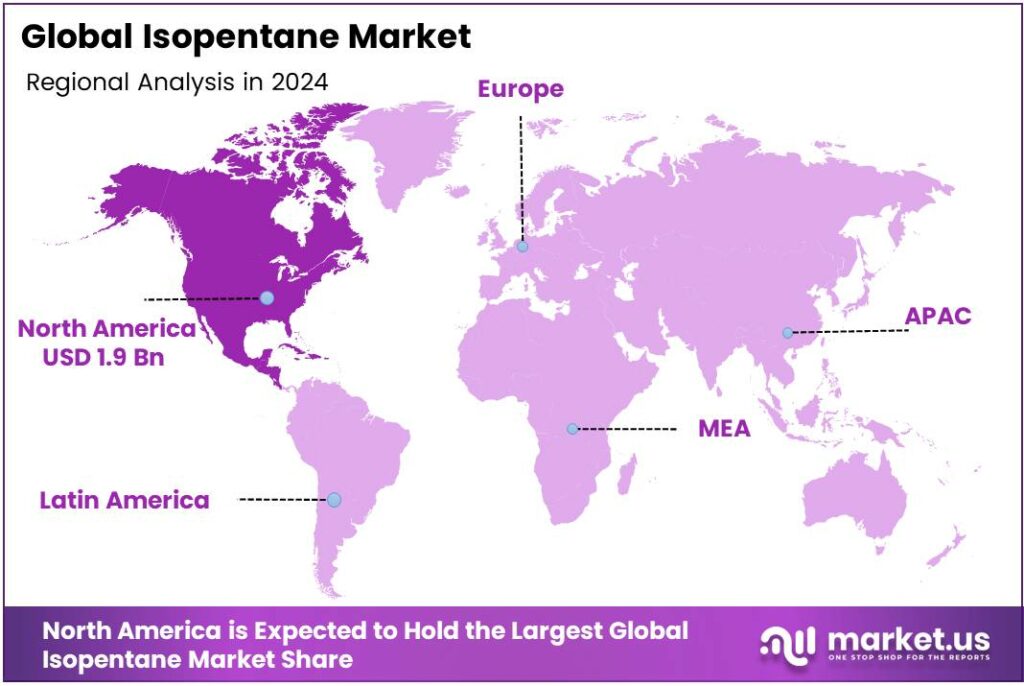
- North America commanded 46.9% market share in 2024, valued at USD 1.9 billion, driven by mature sectors and substitution trends.
By Grade Analysis
Less than 98% dominates with 68.3% due to its cost-effectiveness and broad applicability in industrial processes.
In 2024, Less than 98% held a dominant market position in the By Grade Analysis segment of the Isopentane Market, with a 68.3% share. This lower purity grade thrives because it balances affordability and performance, suiting large-volume uses like solvent extraction and foaming. Industries favor it for reducing costs without sacrificing essential functionality, propelling its lead.
Demand surges as manufacturers scale operations efficiently. The 98% grade targets niche applications needing refined quality. It minimizes contaminants, ensuring superior results in sensitive processes such as pharmaceutical intermediates. While trailing the leader, it gains traction where precision matters most. Growth stems from evolving standards that prioritize consistency in high-end products.
By Blending Agent Analysis
n-Pentane dominates with 33.9% due to its seamless integration and enhanced blend stability.
In 2024, n-Pentane held a dominant market position in the By Blending Agent Analysis segment of the Isopentane Market, with a 33.9% share. This agent excels by improving mixture volatility for better foam uniformity in insulation. Formulators choose it for reliable expansion control, driving efficiency in production lines. Its compatibility boosts overall blend performance across sectors.
Pentane acts as a versatile blender, adapting to various ratios for custom needs. It strengthens formulations in packaging foams, enhancing durability and lightness. This segment expands as industries seek flexible options to meet diverse specifications. Innovation here fuels steady adoption.
Cyclopentane emerges as a sustainable blender, lowering global warming potential in mixes. It supports eco-conscious foaming, aligning with green regulations. Though smaller, it accelerates growth amid environmental pressures. Users transition to it for compliant, high-efficiency blends.
By Function Analysis
Blowing Agents dominate with 44.2% due to their critical role in foam creation and expansion.
In 2024, Blowing Agents held a dominant market position in the By Function Analysis segment of the Isopentane Market, with a 44.2% share. This primary use generates gas for cell formation in EPS and polyurethanes, vital for insulation. It enables lightweight structures, cutting material use while maintaining strength. Market leaders rely on it for scalable, energy-saving solutions.
Polyurethane Foam Additives refine foam properties like flexibility and thermal resistance. They integrate to optimize density, ideal for cushions and panels. This function grows with construction booms, providing durable, insulating materials. Enhancements here drive product innovation.
EPS Additives fine-tune bead pre-expansion for polystyrene molding. They ensure even gas distribution, yielding robust packaging foams. Adoption rises in logistics for cost-saving, protective designs. This segment supports efficient, recyclable applications.
Key Market Segments
By Grade
- Less than 98%
- 98%
By Blending Agent
- Pentane
- Cyclopentane
- n-Pentane
- Others
By Function
- Blowing Agents
- Polyurethane Foam Additives
- EPS Additives
- Solvents
- Propellant
- Viscosity Controlling Agents
- Others
Emerging Trends
Hydrocarbon Blowing Agents Gaining Ground in Insulation Foams
A major trend unfolding in the Isopentane space is its increasing use as a hydrocarbon‑based blowing agent for rigid polyurethane (PU) and expanded polystyrene (EPS) insulation foams, replacing high‑global‑warming‑potential (GWP) fluorinated gases. The move is being driven by strong regulatory pressure in many regions and by a rising emphasis on energy‑efficient construction and building retrofit markets.
- The Flexible and Rigid Foams Technical Options Committee, foam blowing agents are subject to significant regulatory scrutiny, and alternatives to high‑GWP HFCs are rising. Furthermore, the EU F‑Gas Regulation has, the manufacture of foam insulation using HFCs with a GWP > 150. Manufacturers, therefore, are increasingly adopting hydrocarbons like isopentane and normal‑pentane blends as blowing agents.
On the quantitative side, while many reports are commercial market research, production of rigid PU foam using pentane‑based blowing agents has been dominant in Europe. One older study noted that in Germany, pentane was used in more than 90% of flexible‑faced laminates production. The broader insulation market context: in the EU, plastic‑foam insulation accounts for 42% of the thermal insulation market.
Drivers
Regulation‑Driven Shift to Low‑GWP Alternatives
One of the biggest drivers behind the growing demand for Isopentane is the regulatory push away from high global‑warming‑potential (GWP) blowing agents and refrigerants toward more environmentally benign options. In simple terms, governments and international bodies are tightening rules on fluorinated substances, which is opening a window for hydrocarbons like isopentane to take their place.
- The Regulation (EU) on fluorinated greenhouse gases came into effect and codifies the phasing‑out of high‑GWP HFCs in the European Union. The regulation notes that the supply of hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) dropped by 37 % (by weight) and by 47 % (in CO₂‑equivalent), marking a clear transition away from the old chemistries.
Because isopentane is considered a more climate‑friendly option, it is increasingly being adopted as a blowing agent in insulation foams and as a refrigerant alternative. One analysis points out that a major driver of the isopentane market is the increasing demand for energy‑efficient and eco‑friendly refrigeration systems across the residential, commercial, and industrial sectors.
Restraints
Elevated Safety and Environmental Challenges
A significant restraint that looms over the use of Isopentane is its high flammability and environmental hazard profile, which creates added cost, stringent handling requirements, and limits its deployment in many applications. In everyday language, while isopentane has good technical properties, its risk factor is not trivial, and that risk factor becomes a real barrier to wider use.
- The substance presents specific health and environmental hazards. In a fact sheet from the New Jersey Department of Health, the airborne exposure limits for isopentane are shown as 1,000 ppm for an 8‑hour shift under OSHA, and the ACGIH TLV is 600 ppm. These values highlight the need for strong ventilation, monitoring, and protective equipment when using the substance.
Explosion‑proof piping, bonded and grounded containers, vapour‑control equipment, and environmental spill‑prevention measures. That adds to cost and complexity, and can discourage use in minor or low‑margin applications. In emerging markets where regulatory enforcement is weaker or infrastructure is less robust, the safety burden may tip users toward alternatives—even if those alternatives are less efficient.
Opportunity
Escalating Demand in Insulation & Construction Applications
One of the key growth drivers for Isopentane is its rapidly rising use as a blowing agent in insulation foams for the construction and refrigeration sectors, which is directly linked to increasing global efforts towards energy efficiency and decarbonisation. The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), hydrocarbons have become the dominant blowing agents in rigid polyurethane boardstock insulation, replacing many fluorinated gases.
- The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), hydrocarbons accounted for approximately 49% of blowing‑agent consumption, about 69 million lbs in the production of rigid polyurethane foam boardstock, out of a total estimated 141 million lbs of blowing agents used in 1.5 billion lbs of foam production.
This matters for isopentane because, as one of the hydrocarbon options, it shares in that conversion momentum. With insulation standards tightening globally — especially in regions like Europe where building codes increasingly demand lower‑GWP materials — the substitution cycle accelerates. The coupling of regulation with rising construction and cold‑chain refrigeration infrastructure builds a robust demand pipeline.
Regional Analysis
North America leads with a 46.9% share and a USD 1.9 Billion market value.
In 2024, the North American region emerged as a dominant hub for the Isopentane market, capturing approximately 46.9% share and representing around USD 1.9 billion in value. This notable figure reflects both mature end‑use sectors and accelerating substitution trends across the U.S. and Canada.
The sustained demand emanates primarily from the construction and insulation industries, where isopentane is used as a blowing agent for rigid foam insulation, as well as from the packaging and electronics sectors. In these applications, the push towards energy‑efficient buildings and the phase‑out of high-GWP surfactants bolster the uptake of lower‑GWP hydrocarbons such as isopentane.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) restrictions on hydrofluorocarbons and Canada’s strengthening of chemical‑handling standards indirectly support the transition to hydrocarbon‑based blowing agents, thereby driving regional demand. Growth remains steady as retrofit activity in commercial buildings increases and cold‑chain infrastructure expands.
High‑purity grades and compliance‑certified supply chains add premium cost, which some smaller users view as a barrier. In sum, North America remains the leading regional market for isopentane thanks to its strong industrial base, favourable regulatory tailwinds, and the scale of construction and packaging demand that underpins the nearly half‑share of global consumption.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Shell is a dominant force in the isopentane market. Its strength lies in its integrated supply chain, from upstream extraction to downstream refining and distribution. This vertical integration ensures consistent quality and reliable supply for large-volume buyers. Shell leverages its extensive infrastructure and technical expertise to serve diverse sectors, including polystyrene foam manufacturing and appliance insulation.
ExxonMobil is a leading producer of isopentane, underpinned by its massive refining capacity and advanced petrochemical operations. The company’s strategic advantage is its ability to optimize production within its complex refinery networks, ensuring cost-effectiveness and scale. ExxonMobil supplies high-purity isopentane primarily to the expanding polystyrene and polyurethane foam industries, which are critical for insulation and packaging.
Linde plays a crucial role in the isopentane market as a premier global industrial gases and engineering company. While not a primary producer like oil majors, Linde often supplies high-purity isopentane as a specialty chemical, particularly through its acquisition of BOC and other chemical divisions. Its expertise lies in precise gas and chemical separation, purification, and handling. Linde serves niche applications.
Top Key Players in the Market
- Shell
- ExxonMobil
- Linde
- Mitsubishi Chemical
- INEOS
- TotalEnergies
- Eastman Chemical
Recent Developments
- In 2025, Shell, a major producer of hydrocarbons including isopentane, continues to emphasize sustainable transitions in its chemical portfolio. The company advanced its Energy Transition Strategy, investing heavily in low-carbon hydrocarbons and biofuels to complement traditional outputs like pentane isomers used in foaming and solvents.
- In 2025, ExxonMobil will focus on expanding its hydrocarbon production capabilities, which encompass pentane isomers for petrochemical feedstocks and blowing agents. The company reported record-high value product sales volumes, driven by advantaged growth in Permian Basin and Guyana operations.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 4.2 Billion Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 7.5 Billion CAGR (2025-2034) 6.0% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Grade (less than 98%, 98%), By Blending Agent (n-Pentane, Pentane, Cyclopentane, Others), By Function (Blowing Agents, Polyurethane Foam Additives, EPS Additives, Solvents, Propellant, Viscosity Controlling Agents, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Shell, ExxonMobil, Linde, Mitsubishi Chemical, INEOS, TotalEnergies, Eastman Chemical Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited Users and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Shell
- ExxonMobil
- Linde
- Mitsubishi Chemical
- INEOS
- TotalEnergies
- Eastman Chemical










