Global Infectious Disease Molecular Diagnostics Market Analysis By Product(Instruments (Benchtop instruments, Portable instruments), Reagents & Kits, Services, Others), By Technology(Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), In Situ Hybridization (ISH), Isothermal Nucleic Acid Amplification Technology (INAAT), Chips & Microarrays, Mass Spectrometry, Sequencing, Transcription Mediated Amplification (TMA), Others), By Application(Respiratory Diseases, Tuberculosis, Meningitis, Gastrointestinal Tract Infections, HPV, Sexually Transmitted Infections, Sepsis, Drug Resistance Diseases, Other Infectious Diseases), By End-User(Hospitals, Clinics and Outpatient Diagnostic Centres, Diagnostic Laboratories, Research Institutes) By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Oct 2025
- Report ID: 163576
- Number of Pages: 393
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
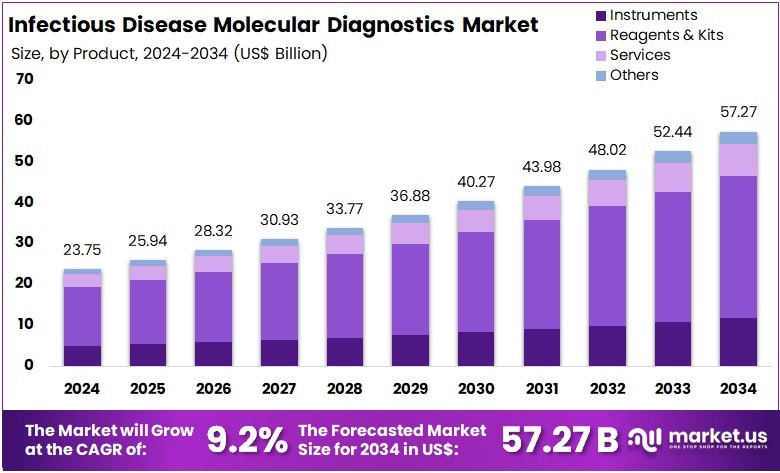
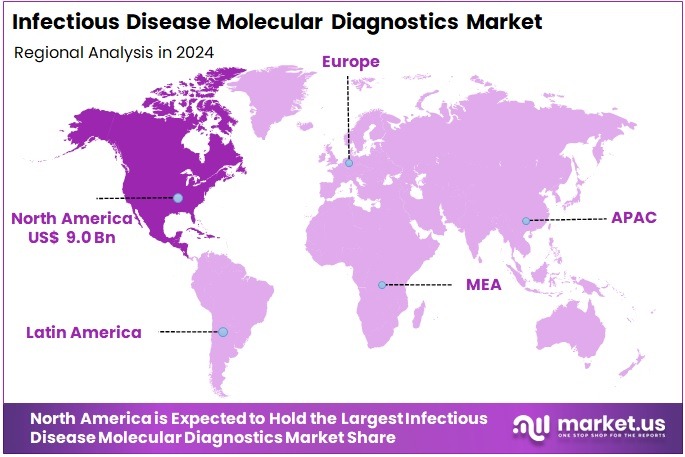
The Global Infectious Disease Molecular Diagnostics Market size is expected to be worth around US$ 57.27 Billion by 2034, from US$ 23.75 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 9.2% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 37.9% share and holds US$ 9.0 Billion market value for the year.
Infectious disease molecular diagnostics refers to advanced methods used to detect pathogens at the genetic level. Techniques such as PCR, real-time PCR, next-generation sequencing, and isothermal amplification are widely used. These methods allow rapid and accurate identification of viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites. According to global clinical practices, they support early diagnosis, treatment monitoring, and public health surveillance across hospitals, laboratories, and point-of-care settings, strengthening timely outbreak control and treatment decisions.
Market demand has been driven by rising communicable disease burdens. According to WHO, 254 million people lived with chronic hepatitis B in 2022. UNAIDS reported 40.8 million people living with HIV in 2024, with 87% aware of their status, indicating sustained testing volumes for diagnosis, staging, and monitoring. WHO also confirmed that 1.25 million people died from tuberculosis in 2023, including 161,000 people living with HIV, while approximately 8.2 million new TB cases were diagnosed that same year.
Antimicrobial resistance further reinforces growth. WHO estimated antimicrobial resistance caused 1.27 million deaths in 2019 and contributed to 4.95 million deaths. Study by WHO highlighted widespread resistance in South-East Asia and Eastern Mediterranean Regions. For instance, stewardship programs now require rapid pathogen and resistance gene detection. This shift favors molecular platforms and syndromic PCR panels for timely therapy decisions, hospital infection control, and antimicrobial surveillance to protect healthcare outcomes globally.
Respiratory disease dynamics support recurring testing. For example, CDC surveillance continues to track COVID-19, influenza, and RSV, with expectations that respiratory testing will not return to pre-2020 levels. Multiplex PCR systems and confirmatory pathways remain in use. Dengue activity has also surged, with WHO reporting cases doubling year-over-year through 2024 across all regions. This expansion into new geographic areas, including parts of Europe, increases PCR assay procurement and laboratory capacity investments to confirm arboviral infections.
Global Policy, Funding, and Epidemiological Drivers of Molecular Diagnostics
Regulatory pathways and policy frameworks support innovation. In the United States, the FDA Emergency Use Authorization pathway accelerates test availability during emergencies. For instance, extensive EUA listings were published for SARS-CoV-2 molecular assays. In Europe, the In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (EU 2017/746) will be fully consolidated in 2025, requiring stronger clinical evidence and post-market oversight. These requirements are expected to increase manufacturer spending on validation and drive long-term industry consolidation through quality-driven competition.
Public funding continues to strengthen diagnostic infrastructure. The NIH Rapid Acceleration of Diagnostics initiative financed technology scale-up during COVID-19, establishing lasting capacity for rapid assay development beyond the pandemic. For example, global mechanisms such as the Global Fund COVID-19 response allocated about USD 1.0 billion for diagnostics since 2020, enabling low- and middle-income nations to secure PCR systems and consumables. These investments reinforce permanent laboratory capabilities and maintain test demand for priority pathogens.
Global disease trends confirm persistent diagnostic needs. WHO reported that the share of global deaths from communicable diseases rose to 28.1% in 2021, up from 23.0% in 2020, returning to levels seen in 2005. Between 1996 and 2023, a total of 3,013 infectious-disease outbreaks were recorded globally, including 1,305 respiratory, 436 vector-borne, and 469 food- or water-borne outbreaks. For instance, WHO noted 191,000 children under 15 died from TB in 2023, including 122,000 HIV-negative children under five.
Regional surveillance highlights ongoing threats. In 2024, CDC documented 16 measles outbreaks in the United States, with 69% of 285 confirmed cases (198 cases) linked to outbreak clusters. Study by ECDC in November 2024 cited active alerts for dengue, chikungunya, avian influenza, West Nile virus, and poliovirus in wastewater. According to WHO’s World Health Statistics 2025, 431 million people gained essential health-service access by end-2024, but only 637 million became better protected from health emergencies, signaling continued need for molecular testing investment.
Key Takeaways
- The global infectious disease molecular diagnostics market is projected to reach US$ 57.27 Billion by 2034, rising from US$ 23.75 Billion in 2024 at 9.2% CAGR.
- Reagents and kits represented the leading product category in 2024, securing more than 60.8% share within the infectious disease molecular diagnostics market.
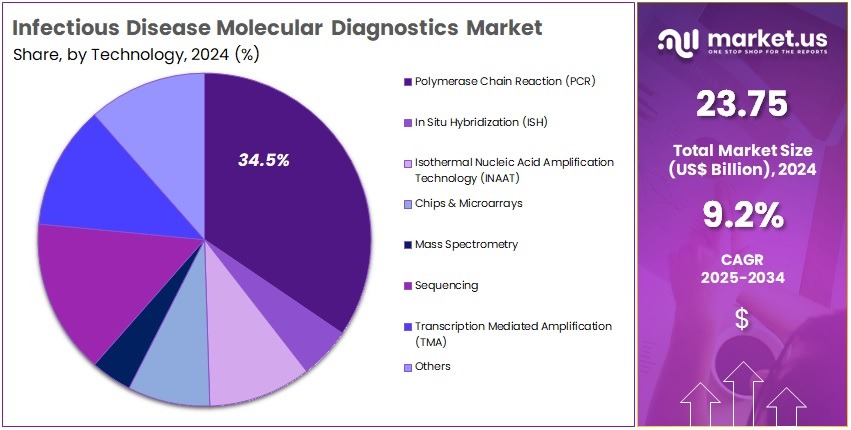
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) technology accounted for the largest technology share in 2024, exceeding 34.5% within the global infectious disease molecular diagnostics space.
- Respiratory disease applications captured the top position in 2024, representing over 22.1% of the overall infectious disease molecular diagnostics market.
- Hospitals dominated end-user demand in 2024, holding more than 40.8% share for infectious disease molecular diagnostic procedures.
- North America led the global market in 2024, achieving a 37.9% share valued at approximately US$ 9.0 Billion.
Product Analysis
In 2024, the Reagents & Kits section held a dominant market position in the Product Segment of the Infectious Disease Molecular Diagnostics Market, and captured more than a 60.8% share. This segment benefited from frequent testing needs. It supported high-volume usage in clinical laboratories. The growing burden of infectious diseases also contributed to strong adoption. The expansion of point-of-care testing further supported demand. Increased availability of disease-specific assay panels improved utilization across healthcare settings.
Instruments accounted for a notable share. Benchtop instruments demonstrated strong usage in centralized laboratories due to higher throughput capacity. Portable molecular instruments gained traction in near-patient testing environments. Rising demand for rapid and reliable diagnostic workflows supported instrument deployment. Innovations in automation and real-time PCR platforms strengthened market penetration.
The Services segment experienced steady growth. Outsourcing of molecular testing services increased among smaller healthcare facilities. Service providers offered advanced test portfolios and faster turnaround times. The rise in laboratory partnerships, external quality programs, and technical support services contributed to segment expansion.
The Others category, including consumables and software, represented a supplementary share. Growth in data management and workflow integration needs encouraged adoption of software solutions. Standard laboratory consumables observed stable demand due to routine diagnostic processes. The trend toward digital diagnostics and connected laboratory ecosystems is expected to enhance future growth prospects across this product group.
Technology Analysis
In 2024, the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Section held a dominant market position in the Technology Segment of the Infectious Disease Molecular Diagnostics Market, and captured more than a 34.5% share. PCR continued to lead due to high accuracy and rapid results. It was widely used for respiratory viruses, HIV, hepatitis, and tuberculosis. In Situ Hybridization (ISH) maintained steady adoption. ISH supported tissue-level pathogen detection in complex diagnostic cases. Its application stayed strong in advanced pathology laboratories and cancer-related infection analysis.
The Isothermal Nucleic Acid Amplification Technology (INAAT) segment saw faster adoption. This growth was supported by its ability to deliver rapid detection in decentralized settings. INAAT enabled sensitive testing without advanced laboratory systems. Chips and Microarrays also contributed to growth. These systems offered high-multiplex detection. They supported large-scale surveillance studies and multi-pathogen screening. Mass Spectrometry gained gradual traction. It enhanced advanced pathogen identification and supported clinical microbiology workflows.
Sequencing technologies achieved strong momentum. Declining costs and enhanced bioinformatics supported adoption. Sequencing offered full-genome insights and antimicrobial resistance analysis. Transcription Mediated Amplification (TMA) strengthened its role in centralized labs. It was highly used for HIV, hepatitis, and sexually transmitted infection testing. Other emerging technologies, including digital PCR and CRISPR-based systems, advanced in sensitivity and speed. Growth across segments was supported by rising infectious disease monitoring, point-of-care expansion, and continuous technology innovation in diagnostic platforms.
Application Analysis
In 2024, the Respiratory Diseases Section held a dominant market position in the Application Segment of Infectious Disease Molecular Diagnostics Market, and captured more than a 22.1% share. This leadership was driven by high rates of respiratory infections. Molecular tests offered rapid and accurate pathogen detection. Strong demand for influenza, RSV, and COVID-19 testing also supported growth. Wider adoption in hospitals and clinics boosted usage. Point-of-care systems improved testing access. These factors maintained strong segment dominance.
The Tuberculosis segment recorded solid adoption. High disease prevalence in developing countries supported consistent test demand. Molecular platforms helped deliver faster tuberculosis results. Public health programs played a major role in screening expansion. The Meningitis segment advanced due to urgent diagnosis needs. Molecular tools improved early pathogen identification. Faster results helped reduce treatment delays. Gastrointestinal infection testing also increased. Multiplex testing enabled simultaneous pathogen detection. Clinical laboratories favored high-sensitivity methods.
HPV testing witnessed notable growth. Increased awareness of cervical cancer screening programs drove higher test numbers. Molecular HPV platforms offered strong accuracy. Sexually transmitted infection testing also expanded. Rising disease burden encouraged screening. Accurate detection through molecular tests supported better treatment decisions. Sepsis testing gained attention in emergency care. Rapid molecular diagnosis supported timely intervention. Drug-resistant disease testing increased due to rising antimicrobial resistance. Other infectious disease tests also showed steady integration. Broader access to advanced diagnostics improved detection rates.
End-User Analysis
In 2024, the Hospitals Section held a dominant market position in the End-User Segment of Infectious Disease Molecular Diagnostics Market, and captured more than a 40.8% share. Hospitals were reported as the primary setting for advanced molecular testing due to high patient admissions and strong clinical infrastructure. Rapid diagnosis needs in emergency and critical care supported strong test adoption. Automated PCR platforms and skilled laboratory teams were also identified as major contributors to accuracy and fast results. Continuous investment in hospital laboratories sustained the lead.
Clinics and Outpatient Diagnostic Centres were noted as key contributors to market expansion. Their role grew due to rising demand for fast and affordable diagnostic services. Outpatient settings increasingly used compact molecular platforms to support routine infection screening. High adoption for respiratory and sexually transmitted infections strengthened segment performance. Convenience, short waiting times, and expanding ambulatory care services supported growth. Collaboration between clinics and independent diagnostic networks further increased test reach and market penetration.
Diagnostic Laboratories were recognized for their role in providing high-volume molecular testing. Centralized facilities processed large sample loads and offered broad test menus, including multiplex and advanced genetic panels. Investments in high-throughput systems enhanced efficiency and output. The segment served hospitals, community screening programs, and corporate health services. Research Institutes also contributed by advancing innovation and developing new assays. These centres focused on emerging pathogens and antimicrobial resistance research. Academic and industry partnerships supported ongoing progress in infectious disease diagnostics.
Key Market Segments
By Product
- Instruments
- Benchtop instruments
- Portable instruments
- Reagents & Kits
- Services
- Others
By Technology
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
- In Situ Hybridization (ISH)
- Isothermal Nucleic Acid Amplification Technology (INAAT)
- Chips & Microarrays
- Mass Spectrometry
- Sequencing
- Transcription Mediated Amplification (TMA)
- Others
By Application
- Respiratory Diseases
- Tuberculosis
- Meningitis
- Gastrointestinal Tract Infections
- HPV
- Sexually Transmitted Infections
- Sepsis
- Drug Resistance Diseases
- Other Infectious Diseases
By End-User
- Hospitals
- Clinics and Outpatient Diagnostic Centres
- Diagnostic Laboratories
- Research Institutes
Drivers
Rising Infectious Disease Burden and Need for Rapid Detection
The increasing global burden of infectious diseases has strengthened adoption of molecular diagnostic platforms. Despite a decline in mortality, infectious diseases remain a major health challenge. The demand for rapid, accurate detection is rising as emerging and re-emerging pathogens continue to threaten global health security. The growth of the market can be attributed to higher awareness, improved laboratory infrastructure, and prioritization of early diagnosis to limit transmission. Molecular testing is viewed as essential for timely clinical decisions and outbreak control.
Although mortality linked to infectious diseases declined from approximately 12.7 million in 2000 to nearly 8.2 million in 2019, the disease burden remains significant worldwide. Increased surveillance and early treatment have reduced death rates. However, persistent viral and bacterial threats continue to require advanced diagnostics. Molecular techniques provide high sensitivity and specificity. These tools are increasingly selected over conventional methods due to faster turnaround and superior pathogen identification. Their role in supporting public health programs is expanding.
Access gaps in low-income regions highlight unmet needs. A large share of populations in sub-Saharan Africa still lack basic diagnostic services, reinforcing demand for scalable and reliable solutions. Expansion of decentralized molecular testing and digital platforms is enabling better healthcare delivery. Investments from governments and global health agencies encourage deployment of point-of-care molecular tests. Market growth is supported by increasing initiatives to strengthen health systems, improve diagnostic access, and ensure early disease detection. This trend positions molecular diagnostics as a cornerstone of infectious disease management.
Restraints
High Capital and Infrastructure Barriers
High capital investment requirements and steady operational costs are significantly restricting the adoption of advanced infectious disease molecular diagnostics. System installation, regular maintenance, and consumable expenses create financial burdens. These burdens are intensified in low-resource markets where funding limitations exist. Access to these systems remains concentrated in advanced healthcare settings. As a result, cost-sensitive regions face challenges in upgrading laboratory capabilities. These constraints continue to limit technology penetration in emerging economies.
Limited laboratory infrastructure and reimbursement barriers further hinder adoption across resource-constrained healthcare systems. Many facilities lack advanced laboratory space, power stability, and biosafety requirements. This infrastructure gap prolongs dependence on traditional diagnostic workflows. In many regions, reimbursement frameworks do not adequately support molecular testing costs. Delayed payment cycles increase financial strain on hospitals and laboratories. This situation discourages investment in innovative solutions even when clinical need is clear.
Global evidence reinforces these structural barriers. Reports indicate poor availability of molecular tests for priority infectious pathogens outside COVID-19. Many regions do not have reliable diagnostic access across different levels of healthcare service. Scientific reviews highlight limited trained personnel and logistical challenges in remote and low-resource settings. These factors make deployment complex. Point-of-care molecular solutions face similar obstacles due to supply chain gaps. Consequently, market growth is restrained despite rising infectious disease burden and technological advancements.
Opportunities
Point-of-Care Molecular Expansion
The market is expected to benefit from expanding point-of-care molecular testing solutions. Deployment in primary healthcare centers and rural locations is increasing access to rapid and accurate infectious disease diagnostics. Portable and automated systems are enabling decentralised testing, supporting early detection and timely treatment decisions. The growth of compact molecular platforms is expected to improve market penetration, driven by rising investments in technology and expanded healthcare infrastructure in low-resource settings.
Digital molecular diagnostic devices are strengthening this opportunity. Sample-to-answer, mobile-connected platforms are improving accessibility by offering laboratory-quality testing outside traditional facilities. These systems support rapid decision-making and more efficient disease management. Their adoption in underserved areas is projected to expand as connectivity improves and digital health ecosystems advance. Enhanced diagnostic accuracy and ease of use are also expected to support wider utilisation, especially in regions where laboratory capacity remains limited.
Innovations in rapid molecular diagnostics are contributing to improved infectious disease control across disciplines. Breakthroughs in resistance detection and pathogen identification are enabling faster clinical responses. This technology is expected to play a key role in combating emerging and persistent infections. Integration of rapid molecular assays into routine care supports better antimicrobial stewardship and controlled disease transmission. As healthcare systems prioritise early detection and prevention, demand for advanced molecular solutions is likely to increase, reinforcing long-term market growth.
Trends
Shift Toward Multiplex Molecular Platforms and Genomic Surveillance
A strong movement toward multiplex and syndromic panel testing has been observed in infectious disease molecular diagnostics. The adoption of high-throughput PCR systems and real-time PCR is increasing. These platforms allow simultaneous detection of multiple pathogens, improving diagnostic accuracy and speed. The change is driven by clinical needs for rapid and reliable results. It has been supported by rising infectious disease burdens and the need for precise patient management in hospital and public health settings.
Integration of next-generation sequencing is accelerating. NGS is being used for genomic surveillance and variant tracking in emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases. The growth of genomic platforms has been supported by epidemiological monitoring programs and global pathogen surveillance initiatives. Increasing volumes of sequencing data are enabling better outbreak detection and response. As a result, laboratories are adopting hybrid workflows that combine PCR-based assays with sequencing-based confirmation and analysis.
Scientific literature confirms rapid innovation in nucleic acid detection technologies. A 2023 review highlights advancements in PCR, isothermal amplification, gene chips and high-throughput techniques. Nature also reports rising implementation of syndromic PCR assays that detect multiple pathogens in a single test. These developments reflect industry focus on real-time diagnosis, automation and comprehensive pathogen coverage. The trend has enhanced laboratory throughput, reduced diagnostic turnaround times and supported early disease intervention strategies, strengthening preparedness for global infectious threats.
Regional Analysis
In 2024, North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 37.9% share and holds US$ 9.0 Billion market value for the year. The region’s advantage has been linked to early use of advanced molecular testing technologies and strong healthcare spending. Well-developed clinical labs and systematic reimbursement policies supported faster adoption of new platforms. A continuous push for enhanced diagnostic accuracy encouraged hospitals and labs to invest in modern equipment. These factors strengthened the region’s leadership.
Rising infectious disease cases have influenced molecular diagnostic demand in North America. Frequent influenza seasons, viral outbreaks, and growing antimicrobial resistance increased testing needs. Healthcare providers showed higher preference for reliable and rapid detection tools. Government focus on early diagnosis and infection control also played a key role. Favorable regulatory policies helped faster approval of cutting-edge tests. Increased awareness among clinicians and patients further supported adoption of molecular diagnostics across hospital and outpatient settings.
The United States accounted for the majority share due to a large network of diagnostic laboratories and advanced healthcare facilities. Partnerships among biotech companies, universities, and research centers encouraged constant innovation in molecular test development. Canada demonstrated steady growth, supported by strengthened public health systems and growing interest in point-of-care molecular testing. Investment in high-throughput instruments and decentralized testing continued to rise. Preparedness strategies for future health emergencies are expected to sustain demand and reinforce North America’s leading position in this market.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherland
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- New Zealand
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
The market is shaped by global leaders with strong diagnostic capabilities and wide molecular testing portfolios. Companies such as F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Abbott Laboratories, and Danaher Corporation play a central role due to high-throughput systems and strong reagent pipelines. These players focus on automation, viral load testing, and rapid workflows. Their strategies emphasize expanding assay menus and building scalable platforms. Continuous investments in integrated molecular solutions and near-patient testing systems support solid market penetration in hospitals, reference labs, and decentralized care environments.
A strong competitive edge is observed in rapid and syndromic testing. Cepheid, part of Danaher, leads in near-patient PCR systems with simple workflows and reliable turnaround times. bioMérieux SA also holds a strong position due to its BioFire FilmArray platforms. These systems enable syndromic panels for respiratory, gastrointestinal, and central nervous system infections. Wider clinical adoption is supported by proven accuracy, automated workflows, and growing awareness of antimicrobial stewardship. This segment benefits from strong research backing and clinical validation.
Several diversified diagnostics companies reinforce industry stability. Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Siemens Healthineers AG, and Becton, Dickinson and Company contribute through advanced PCR reagents, automated analyzers, and hospital-based testing instruments. These companies emphasize scalable lab infrastructure and integrated digital connectivity. Their broad product ranges support both centralized and decentralized laboratories. Focus on flexible assay menus, supply reliability, and strong global distribution improves competitiveness. Growth is expected as healthcare providers adopt unified diagnostic ecosystems and automation for improved accuracy and faster reporting.
Additional participants strengthen innovation in multiplex technology, donor screening, and digital diagnostics. Hologic Inc., QIAGEN N.V., Grifols S.A., DiaSorin S.p.A., Seegene Inc., Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc., and Quest Diagnostics remain key contributors. They invest in high-plex molecular platforms, sample-to-result workflows, and nucleic acid testing solutions. Many also support clinical laboratories with specialized assays and laboratory services. Their strategic direction includes developing targeted panels, improving workflow efficiency, and enhancing global presence through collaborations, regulatory approvals, and expanded product launches.
Market Key Players
- F. Hoffmann‑La Roche Ltd. (Roche)
- Abbott Laboratories
- Danaher Corporation (including its subsidiary Cepheid)
- bioMérieux SA
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- Siemens Healthineers AG
- Becton, Dickinson and Company (BD)
- Hologic Inc.
- QIAGEN N.V.
- Grifols S.A.
- DiaSorin S.p.A.
- Seegene Inc.
- Bio‑Rad Laboratories Inc.
- Quest Diagnostics Incorporated
Recent Developments
- In October 2024: The Alinity m MPXV assay (a real-time PCR test for the Mpox virus) manufactured by Abbott’s molecular diagnostics arm was added to the World Health Organization Emergency Use Listing (EUL). The assay enables detection of MPXV DNA from human skin lesion swab specimens (clade I/II). This marks a significant step in expanding global access to molecular testing for mpox, particularly in outbreak-affected and underserved regions.
- In September 2024: Roche launched the cobas Respiratory flex test, the first assay using its TAGS technology; the multiplex RT-PCR panel enables tailored detection of up to 12 common respiratory viruses (including influenza A/B, RSV, and SARS-CoV-2) on high-throughput cobas systems.
- In March 2024 (11 March): Cepheid announced that it had received U.S. Food & Drug Administration clearance for Xpert Xpress GBS, a dual-target molecular diagnostic test for intrapartum detection of Group B Streptococcus (GBS) in women. The test returns results as quickly as ~30 minutes and improves sensitivity/strain coverage.
- In April 2023: bioMérieux received U.S. FDA 510(k) clearance for its BIOFIRE® SPOTFIRE® Respiratory (R) Panel Mini, a multiplex PCR-based test detecting five of the most common viral causes of upper respiratory tract infections (SARS-CoV-2, Influenza A, Influenza B, RSV and Rhinovirus) in about 15 minutes. In May 2023 the test also secured a CLIA-waiver in the U.S., enabling use at the point-of-care. This development strengthens the company’s infectious disease molecular diagnostics offering and supports rapid diagnostics in decentralized settings.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) US$ 23.75 Billion Forecast Revenue (2034) US$ 57.27 Billion CAGR (2025-2034) 9.2% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, COVID-19 Impact, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Product(Instruments (Benchtop instruments, Portable instruments), Reagents & Kits, Services, Others), By Technology(Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), In Situ Hybridization (ISH), Isothermal Nucleic Acid Amplification Technology (INAAT), Chips & Microarrays, Mass Spectrometry, Sequencing, Transcription Mediated Amplification (TMA), Others), By Application(Respiratory Diseases, Tuberculosis, Meningitis, Gastrointestinal Tract Infections, HPV, Sexually Transmitted Infections, Sepsis, Drug Resistance Diseases, Other Infectious Diseases), By End-User(Hospitals, Clinics and Outpatient Diagnostic Centres, Diagnostic Laboratories, Research Institutes) Regional Analysis North America – The US, Canada, & Mexico; Western Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Portugal, Ireland, Austria, Switzerland, Benelux, Nordic, & Rest of Western Europe; Eastern Europe – Russia, Poland, The Czech Republic, Greece, & Rest of Eastern Europe; APAC – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia & New Zealand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, & Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Colombia, Chile, Argentina, Costa Rica, & Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – Algeria, Egypt, Israel, Kuwait, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, & Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape F. Hoffmann‑La Roche Ltd. (Roche), Abbott Laboratories, Danaher Corporation (including its subsidiary Cepheid), bioMérieux SA, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Siemens Healthineers AG, Becton, Dickinson and Company (BD), Hologic Inc., QIAGEN N.V., Grifols S.A., DiaSorin S.p.A., Seegene Inc., Bio‑Rad Laboratories Inc., Quest Diagnostics Incorporated Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Infectious Disease Molecular Diagnostics MarketPublished date: Oct 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Infectious Disease Molecular Diagnostics MarketPublished date: Oct 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- F. Hoffmann‑La Roche Ltd. (Roche)
- Abbott Laboratories
- Danaher Corporation (including its subsidiary Cepheid)
- bioMérieux SA
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- Siemens Healthineers AG
- Becton, Dickinson and Company (BD)
- Hologic Inc.
- QIAGEN N.V.
- Grifols S.A.
- DiaSorin S.p.A.
- Seegene Inc.
- Bio‑Rad Laboratories Inc.
- Quest Diagnostics Incorporated










