Hydropower Market By Type(Public, Private), By Capacity(Micro Hydropower, Small Hydropower, Large Hydropower), By Technology(Reservoir, Pumped Storage, Run-of-River, Others), By Component(Civil Construction, Electrical, Mechanical Equipment, Power Infrastructure, Others), By Region and Key Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2024–2033
- Published date: Apr 2024
- Report ID: 117880
- Number of Pages: 272
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
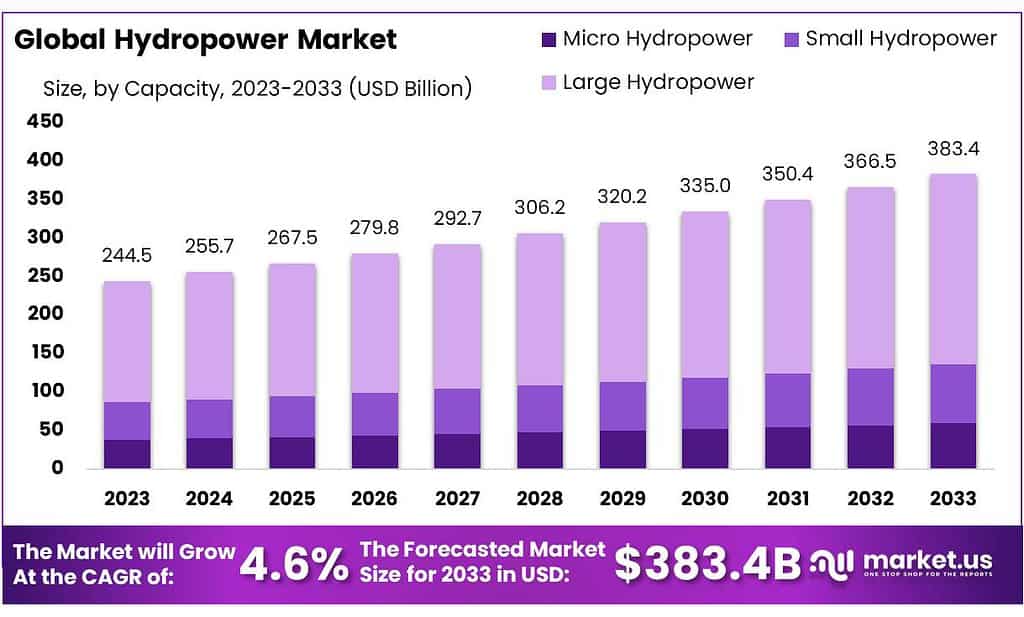
The global Hydropower Market size is expected to be worth around USD 383.4 billion by 2033, from USD 244.5 billion in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 4.6% during the forecast period from 2023 to 2033.
The hydropower market refers to the global industry surrounding the development, deployment, and utilization of hydropower as a renewable energy source. Hydropower, also known as hydroelectric power, harnesses the energy produced by moving water, typically through the construction of dams, to generate electricity. This sector is an integral part of the broader renewable energy market, offering a clean, sustainable, and often cost-effective power generation option.
The market encompasses various components, including the design, construction, and operation of hydropower facilities, the manufacture and supply of turbines and other essential machinery, maintenance services, and the regulatory and policy framework that governs hydropower development and operation. It also involves the study and mitigation of environmental and social impacts associated with hydropower projects.
The growth of the hydropower market can be attributed to its critical role in meeting global energy demand, reducing reliance on fossil fuels, and contributing to sustainable development goals. However, its expansion is closely tied to addressing the associated environmental and social challenges through innovative solutions and regulatory frameworks.
Key Takeaways
- Market Growth: Expected to reach USD 383.4 billion by 2033 from USD 244.5 billion in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 4.6%.
- Public Sector Dominance: Public segment captures over 85% market share, driven by government investments and renewable energy focus.
- Large Hydropower Superiority: Facilities over 30 MW hold 64.5% market share, supplying stable electricity to national grids.
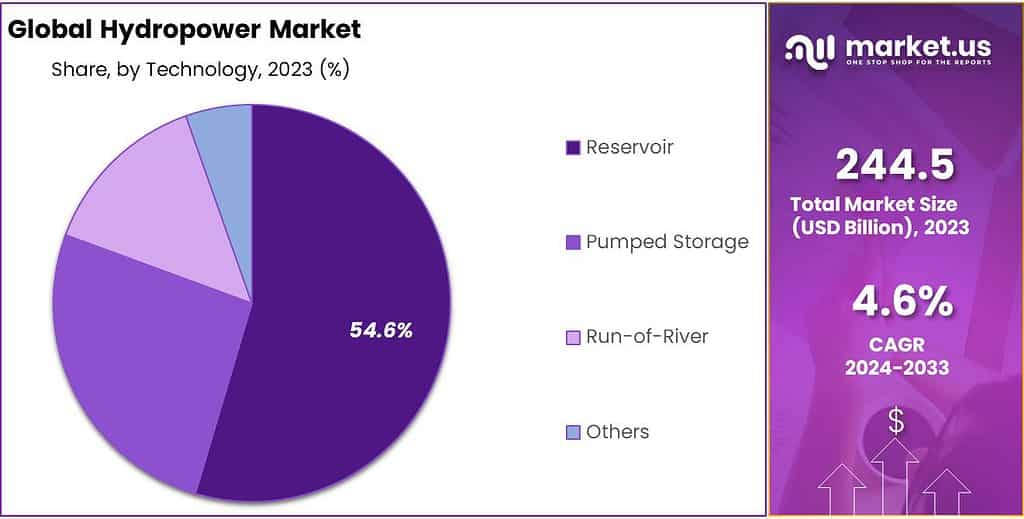
- Technology Advancements: Reservoir technology dominates with 54.6% share, while pumped storage and run-of-river solutions gain traction.
- Capacity Distribution: Large Hydropower leads with 64.5% share, followed by Small Hydropower and Micro Hydropower, catering to diverse energy needs.
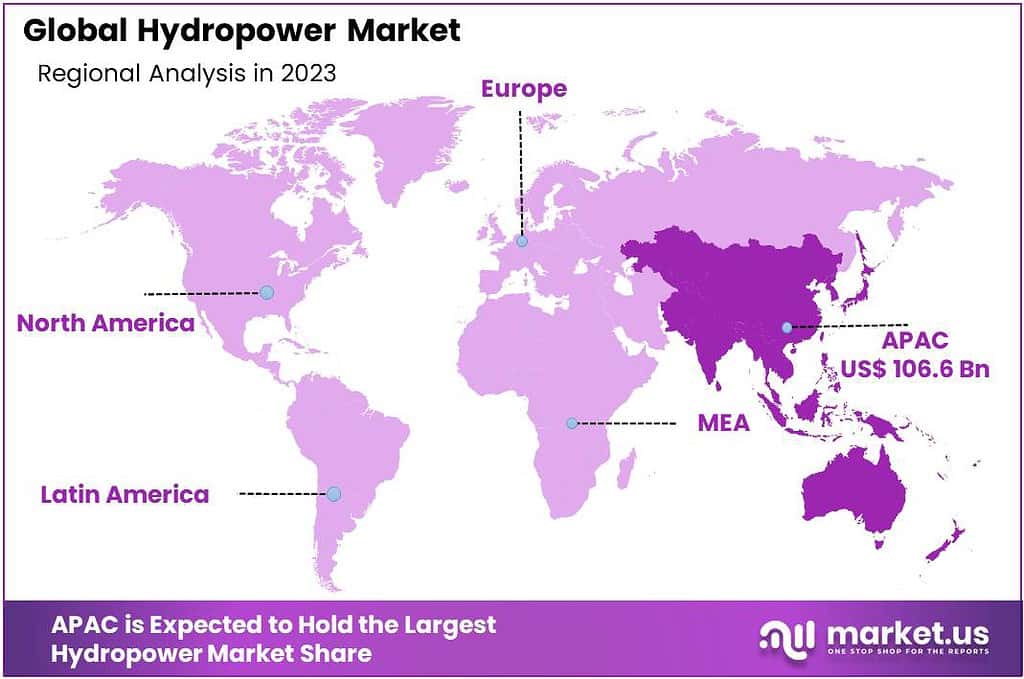
- Global Trends: Asia Pacific leads with 43.6% market share, driven by renewable energy demand and infrastructure development.
- Hydropower accounts for around 16% of the world’s total electricity generation.
- In 2023, the world’s tallest hydropower station, the Baihetan Dam in China, with a height of 289 meters, became fully operational.
By Type
In 2024, the Public segment held a dominant position in the hydropower market, capturing more than an 85% share. This segment primarily includes projects owned and operated by government entities or public utilities.
The significant share can be attributed to large-scale investments in infrastructure development, regulatory support, and a focus on renewable energy sources to meet national energy needs. Public projects often benefit from direct government funding, enabling the construction of extensive facilities like dams and reservoirs, which contribute substantially to the nation’s energy mix.
Conversely, the Private segment, though smaller, played a crucial role in the hydropower market. Private investments are typically directed towards smaller or medium-scale projects, such as run-of-river and pumped storage hydropower plants.
The agility and innovation of private firms allow for the efficient implementation of projects, often in partnership with public entities or through independent initiatives. Despite holding a smaller market share, the private sector’s contribution is vital for technological advancements, operational efficiencies, and the exploration of untapped potential within the hydropower industry.
The dynamics between public and private segments underscore the hydropower market’s complexity and the collaborative effort required to harness water resources sustainably. While the public sector provides foundational strength and stability through large-scale projects, the private sector introduces innovation and flexibility, essential for addressing future energy challenges and opportunities within the hydropower market.
By Capacity
In 2024, Large Hydropower held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 64.5% share. This segment includes facilities with a capacity of more than 30 megawatts (MW). Large hydropower plants, often part of extensive dam projects, are significant power producers, contributing to national grids and providing a stable electricity supply. Their dominance in the market stems from their capacity to generate large amounts of electricity, essential for meeting the energy demands of growing populations and industrial sectors.
Small Hydropower, with installations ranging from 1 MW to 30 MW, held a notable position in the market. This segment is praised for its lower environmental impact and ability to supply electricity to remote and rural areas, supporting decentralized energy systems. Although smaller in capacity compared to large hydropower, small projects are crucial for sustainable development, particularly in regions lacking access to the central power grid.
Micro Hydropower, defined by a capacity of less than 1 MW, although smallest in terms of market share, is increasingly significant for its potential in remote and off-grid applications. These installations are particularly valued for their minimal environmental footprint and their role in empowering local communities by providing reliable and renewable energy sources.
The segmentation of the hydropower market by capacity highlights the diverse roles these plants play in the global energy landscape. While large hydropower continues to be a backbone for many countries’ electricity needs, small and micro installations are indispensable for their flexibility, sustainability, and the unique ability to reach underserved areas.
By Technology
In 2024, Reservoir technology held a dominant market position in the hydropower sector, capturing more than a 54.6% share. This technology involves storing large volumes of water in a reservoir behind a dam, releasing it through turbines to generate electricity as needed. Its leading market position is attributed to its reliability and ability to provide both power generation and water management services, such as flood control and irrigation support.
Pumped Storage followed, serving as a critical technology for energy storage and grid stabilization. By moving water between two reservoirs at different elevations, pumped storage plants can store energy during low demand and release it during peak periods. This technology is increasingly valuable for balancing the variability of other renewable energy sources like wind and solar, making it an essential component of modern energy systems.
Run-of-River technology also played a significant role, especially appreciated for its minimal environmental impact and quick deployment time. Unlike reservoir-based systems, run-of-river hydropower plants generate electricity by channeling flowing river water through a turbine, making them suitable for continuous energy generation without the need for large-scale water storage. This technology is particularly beneficial for areas with consistent water flow, offering a sustainable energy solution with lower ecological footprint.
The segmentation by technology within the hydropower market illustrates the industry’s breadth, from traditional, large-scale projects to innovative solutions addressing the modern energy challenges. Each technology plays a unique role in contributing to the global energy mix, highlighting the importance of continued investment and development across all segments to achieve a sustainable and balanced energy future.
By Component
In 2024, Civil Construction held a dominant market position in the hydropower sector, capturing more than a 42.6% share. This component encompasses the physical structures necessary for hydropower plants, including dams, reservoirs, water conduits, and tunnels. Its significant market share reflects the crucial role of civil construction in the foundational stages of hydropower projects, determining their feasibility, durability, and overall success. The demand for civil construction is driven by the need for robust infrastructure capable of withstanding natural forces and ensuring long-term operational stability.
Electrical components followed, essential for the generation, transmission, and distribution of hydroelectric power. This segment includes generators, transformers, switchgear, and control systems. Electrical components are vital for converting mechanical energy from flowing water into electrical energy, highlighting their integral role in the efficiency and reliability of power production.
Mechanical Equipment, comprising turbines, valves, and gates, also played a critical role in the hydropower market. These components are directly involved in the water-to-energy conversion process, with innovations in turbine technology significantly enhancing plant efficiency and environmental compatibility. The mechanical segment is pivotal for the operational performance of hydropower plants, influencing both their energy output and maintenance requirements.
Power Infrastructure, which involves the broader network needed to connect hydropower plants to the grid, held a vital position. This category includes transmission lines and substations, crucial for delivering generated electricity to consumers. The expansion of power infrastructure is key to integrating hydropower into the energy system, ensuring that renewable energy can reach distant markets and contribute to grid stability.
The segmentation by component within the hydropower market illustrates the diverse range of elements that contribute to the development and operation of hydropower plants. From the construction of physical infrastructure to the advanced technologies enabling efficient power generation and grid integration, each component plays a unique role in sustaining the growth and evolution of the hydropower sector.
Key Market Segments
By Type
- Public
- Private
By Capacity
- Micro Hydropower
- Small Hydropower
- Large Hydropower
By Technology
- Reservoir
- Pumped Storage
- Run-of-River
- Others
By Component
- Civil Construction
- Electrical
- Mechanical Equipment
- Power Infrastructure
- Others
Drivers
Global Push for Renewable Energy Sources
A pivotal driver propelling the hydropower market is the global shift towards renewable energy sources, underscored by the urgent need to mitigate climate change and reduce dependency on fossil fuels. This transition is fueled by an increasing recognition of the finite nature of traditional energy resources and the environmental costs associated with their extraction and use.
Governments, businesses, and communities worldwide are actively seeking sustainable and clean energy alternatives, with hydropower emerging as a key solution due to its proven reliability, scalability, and ability to provide a consistent energy supply.
Hydropower, the most established form of renewable energy, offers significant advantages, including low operating costs, long-term sustainability, and the capacity for large-scale energy storage. Unlike other renewable sources such as wind and solar, which can be intermittent, hydropower provides a stable and controllable power output, making it indispensable for balancing the grid and ensuring a steady electricity supply. This is particularly crucial as the world strives to increase the share of renewables in the energy mix, necessitating technologies that can supply base-load power and enhance grid stability.
Moreover, the role of hydropower extends beyond energy generation. It contributes to water management, flood control, and irrigation—services that are increasingly vital in the face of climate change-induced weather variability. The multifunctional nature of hydropower projects, therefore, not only addresses energy needs but also supports adaptation to environmental changes, offering a holistic approach to sustainable development.
The international commitment to the Paris Agreement and the pursuit of Sustainable Development Goals have further catalyzed investments in hydropower. National policies and international frameworks are increasingly supportive, providing financial incentives, regulatory reforms, and technical assistance to expand hydropower capacity.
This policy environment, coupled with technological advancements that reduce environmental impacts and enhance efficiency, has positioned hydropower as a cornerstone of the transition to a renewable energy future.
Despite challenges related to environmental concerns and the social implications of large projects, the hydropower market continues to evolve, with innovations in project design and operation minimizing negative impacts and maximizing benefits. Small-scale, run-of-river, and pumped storage projects are gaining traction, offering more flexible and ecologically sensitive options for harnessing hydropower.
Restraints
Environmental and Social Concerns
A significant restraint impacting the hydropower market is the environmental and social concerns associated with the development of hydropower projects. While hydropower is celebrated for its renewable attributes and capacity to generate clean energy, the construction of large dams and reservoirs has raised substantial environmental issues, including habitat destruction, alteration of river ecosystems, and the displacement of local communities. These concerns have led to increased scrutiny and opposition to new projects, challenging the expansion of hydropower in certain regions.
The ecological impact of large-scale hydropower projects can be profound. Altering the natural flow of rivers affects aquatic ecosystems, disrupting migration patterns of fish and other species, and can lead to the loss of biodiversity. The submersion of large areas of land for reservoirs not only destroys terrestrial habitats but can also result in significant greenhouse gas emissions from decaying vegetation and soil organic matter. These environmental repercussions challenge the green credentials of hydropower, necessitating careful consideration and mitigation strategies in project planning and implementation.
Social implications, particularly the displacement of communities and the loss of lands and livelihoods, further complicate the development of hydropower projects. Large dams have historically led to the relocation of millions of people globally, often without adequate compensation or support for resettlement. The disruption to local economies, cultural heritage, and social structures has sparked opposition and protests against hydropower projects, highlighting the need for inclusive planning and equitable benefit-sharing mechanisms.
The regulatory and permitting processes for hydropower projects have become increasingly stringent in response to these environmental and social concerns. Securing approvals can involve lengthy environmental impact assessments, public consultations, and negotiations to address the interests of multiple stakeholders. These processes, while necessary for ensuring sustainable and socially responsible projects, can delay or deter the development of new hydropower capacity, impacting the market’s growth.
Moreover, the focus on minimizing environmental and social impacts has led to higher project costs. Investments in environmental mitigation measures, enhanced design features to ensure ecological flow, and compensation for affected communities increase the financial burden of hydropower projects. These added costs can affect the competitiveness of hydropower, particularly when compared to other renewable energy sources that might have lower upfront costs and fewer environmental and social issues.
Opportunity
Integration with Other Renewable Energy Sources
A significant opportunity for the hydropower market lies in its potential for integration with other renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power. This synergy is increasingly important as countries strive to achieve a sustainable, reliable, and diversified energy mix. Hydropower’s unique characteristics, including its storage capabilities and flexibility in generation, make it an ideal partner for intermittent renewable sources, addressing some of the key challenges associated with their integration into the energy grid.
The variable nature of wind and solar energy, dependent on weather conditions and time of day, poses challenges for grid stability and the consistent supply of electricity. Hydropower, particularly pumped storage hydropower, can complement these sources by acting as a natural battery. Excess electricity generated during periods of high wind or solar output can be used to pump water to a higher elevation for storage. When the output from wind and solar decreases, stored water can be released to generate electricity, thus balancing the grid and ensuring a continuous energy supply. This symbiotic relationship enhances the overall reliability and efficiency of renewable energy systems.
Moreover, the integration of hydropower with wind and solar technologies presents opportunities for hybrid renewable energy projects. Such projects can leverage the strengths of each technology, optimizing land use and reducing the environmental footprint associated with energy generation. For instance, floating solar panels on reservoirs represent a novel approach to maximizing the utility of hydropower facilities while adding solar generation capacity without the need for additional land.
This integration also opens avenues for innovation in renewable energy technology and project financing. New business models are emerging that focus on multi-source renewable projects, attracting investment and fostering collaboration between different sectors of the energy industry. Governments and regulatory bodies are increasingly recognizing the value of integrated renewable energy systems, leading to policy frameworks and incentives that encourage such projects.
The opportunity for hydropower to act as a linchpin in the renewable energy transition is not without its challenges, including the need for advancements in grid infrastructure and energy management systems. However, the potential benefits in terms of enhanced energy security, reduced carbon emissions, and economic development are substantial.
Trends
Technological Innovations in Hydropower
A major trend shaping the hydropower market is the rapid advancement and adoption of technological innovations. These developments are not only enhancing the efficiency and environmental sustainability of hydropower projects but are also expanding their applicability in diverse geographical and ecological settings. This trend reflects a broader industry shift towards smarter, more adaptable, and less intrusive hydropower solutions, driven by the dual objectives of meeting growing energy demands and addressing environmental concerns.
One of the key areas of innovation is in turbine technology. Modern turbines are designed to be more fish-friendly, reducing mortality rates among aquatic life and mitigating one of the most significant ecological impacts of hydropower dams. Additionally, these turbines exhibit improved efficiency in energy conversion, capable of generating more electricity from the same amount of water flow. This enhancement not only increases the power output of existing facilities but also makes it feasible to develop new projects in locations with lower flow rates or smaller drops in elevation, previously considered unsuitable for hydropower.
Another significant technological trend is the development of modular and small-scale hydropower systems. These systems can be rapidly deployed with minimal environmental footprint, offering a viable option for remote or underserved communities. The scalability of modular hydropower also allows for a tailored approach to energy generation, matching capacity with local demand and reducing the need for extensive transmission infrastructure.
Pumped storage hydropower (PSH) technology is witnessing innovations that improve its role as an energy storage solution. Advanced PSH systems offer greater flexibility in operation, allowing for quicker response times to changes in electricity demand or supply from intermittent renewable sources like wind and solar. This capability positions hydropower as a critical asset in the transition to a more renewable-based energy grid, providing a reliable means of balancing and storing energy.
Digital technologies, including artificial intelligence and machine learning, are being integrated into hydropower operations to optimize performance and maintenance. Predictive analytics can forecast equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Similarly, real-time monitoring and control systems enhance the operational efficiency and safety of hydropower plants, ensuring optimal performance across diverse operating conditions.
Regional Analysis
The Asia Pacific region is poised to lead the global hydropower market, claiming a dominant share of 43.6%. This substantial growth is driven by the rising demand for renewable energy sources across key applications such as power generation, water management, and sustainable development initiatives.
Significant increases in hydropower projects within countries like China, India, and several Southeast Asian nations, including Korea, Thailand, Malaysia, and Vietnam, are expected to fuel market expansion throughout the region over the forecast period. This expansion is supported by the area’s growing industrial activities and enhanced focus on renewable energy sources to meet rising energy demands and environmental sustainability goals.
In North America, economic progress, coupled with the expansion of sectors requiring reliable and clean energy sources such as power utilities and large-scale irrigation projects, is anticipated to boost the demand for hydropower. The region’s commitment to renewable energy targets and reducing carbon emissions further supports this demand, establishing North America as a significant market for hydropower.
Europe is forecasted to witness notable growth in the hydropower market as well. This growth is propelled by an increased consumer and industrial shift towards renewable energy sources, alongside strong demand from power utilities, flood control projects, and sustainable water management practices. The European market’s focus on energy security, sustainability, and environmental protection underscores the rising adoption of hydropower solutions.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- The US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia & CIS
- Rest of Europe
- APAC
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- ASEAN
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
The hydropower market features a diverse array of key players, ranging from engineering and construction firms to equipment manufacturers and utility companies. These entities play a critical role in the development, operation, and expansion of hydropower across the globe.
The analysis of these key players typically focuses on their market share, strategic initiatives, product portfolios, geographic presence, and contributions to technological advancements within the sector. Below, we provide an overview of the competitive landscape and highlight some strategic considerations characterizing the hydropower market’s leading entities.
Market Key Players
- China Three Gorges Corporation
- Electricité de France
- State Power Investment Corporation
- Duke Energy Corporation
- Hydro-Québec
- SN Aboitiz Power Group
- Enel Green Power
- RusHydro
- National Hydropower Corporation
- Innergex Renewable Energy Inc.
- Andritz AG
- Brookfield Renewable Partners
Recent Development
In December 2023 China Three Gorges Corporation (CTG): CTG continues to be a leader in hydropower development. Six cascade hydropower stations on the Yangtze River achieved a record daily electricity generation peak. They’re also expanding their renewable energy portfolio beyond hydro, focusing on wind and solar power.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2023) USD 244.5 Bn Forecast Revenue (2033) USD 383.4 Bn CAGR (2024-2033) 4.6% Base Year for Estimation 2023 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2024-2033 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, COVID-19 Impact, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Type(Public, Private), By Capacity(Micro Hydropower, Small Hydropower, Large Hydropower), By Technology(Reservoir, Pumped Storage, Run-of-River, Others), By Component(Civil Construction, Electrical, Mechanical Equipment, Power Infrastructure, Others) Regional Analysis North America – The US & Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia & CIS, Rest of Europe; APAC– China, Japan, South Korea, India, ASEAN & Rest of APAC; Latin America– Brazil, Mexico & Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa– GCC, South Africa, & Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape China Three Gorges Corporation, Electricité de France, State Power Investment Corporation, Duke Energy Corporation, Hydro-Québec, SN Aboitiz Power Group, Enel Green Power, RusHydro, National Hydropower Corporation, Innergex Renewable Energy Inc., Andritz AG, Brookfield Renewable Partners Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the size of Hydropower Market?Hydropower Market size is expected to be worth around USD 383.4 billion by 2033, from USD 244.5 billion in 2023
What CAGR is projected for the Hydropower Market?The Hydropower Market is expected to grow at 4.6% CAGR (2024-2033).Name the major industry players in the Hydropower Market?China Three Gorges Corporation, Electricité de France, State Power Investment Corporation, Duke Energy Corporation, Hydro-Québec, SN Aboitiz Power Group, Enel Green Power, RusHydro, National Hydropower Corporation, Innergex Renewable Energy Inc., Andritz AG, Brookfield Renewable Partners

-
-
- China Three Gorges Corporation
- Electricité de France
- State Power Investment Corporation
- Duke Energy Corporation
- Hydro-Québec
- SN Aboitiz Power Group
- Enel Green Power
- RusHydro
- National Hydropower Corporation
- Innergex Renewable Energy Inc.
- Andritz AG
- Brookfield Renewable Partners









