Global Thin Film Batteries Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Battery Type (Disposable, Rechargeable), By Voltage (Below 1.5 V, 1.5 V to 3V, Above 3 V), By Application (Wearables, Medical, Consumer Electronics, Smart Cards, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends, and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Dec 2025
- Report ID: 168852
- Number of Pages: 207
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
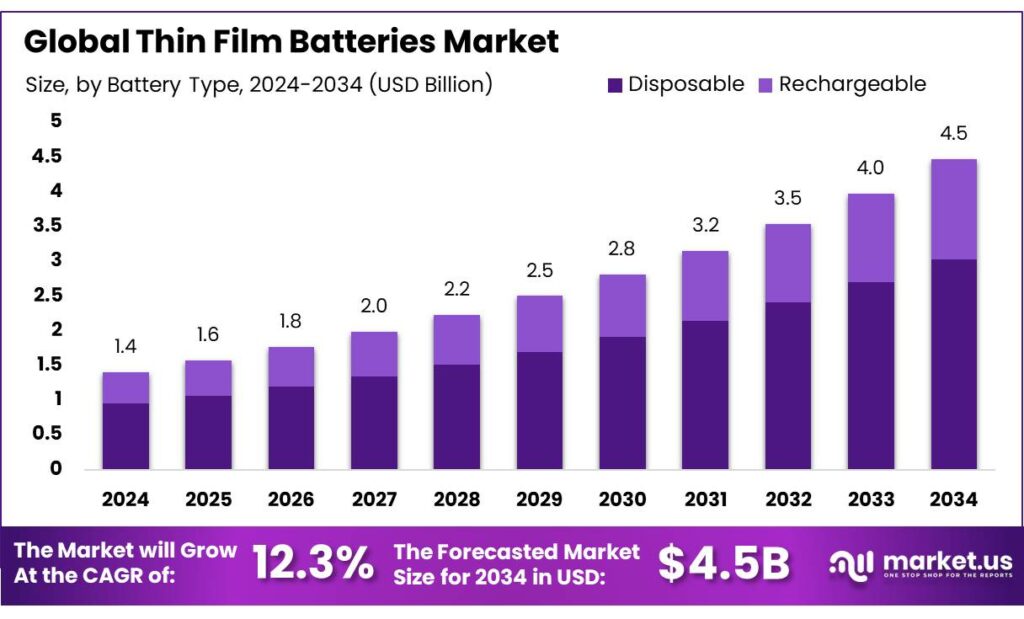
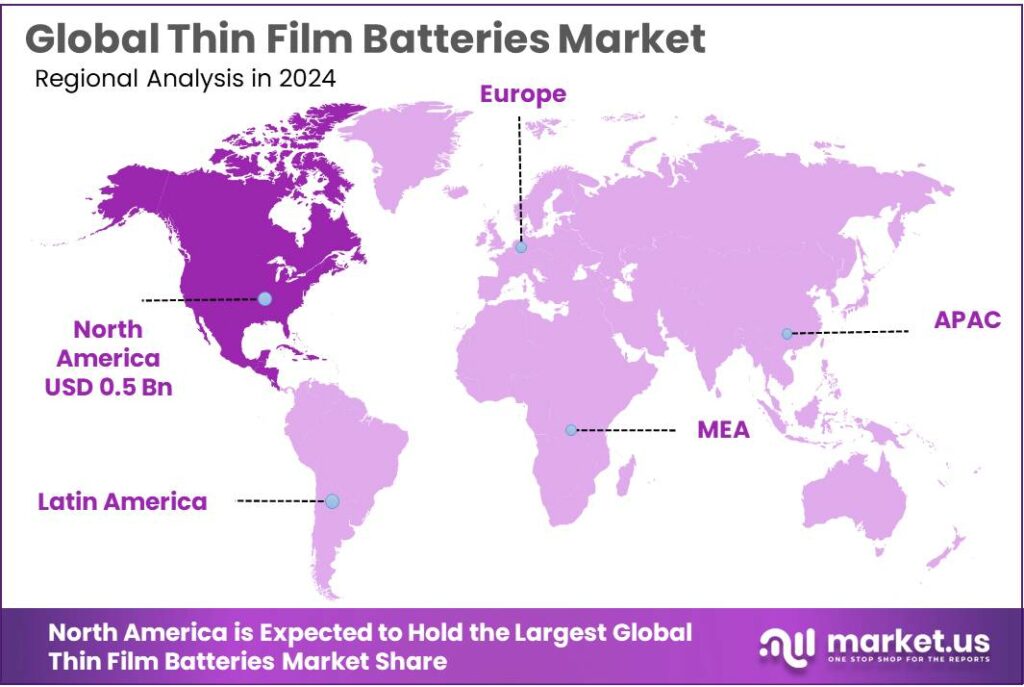
The Global Thin Film Batteries Market size is expected to be worth around USD 4.5 Billion by 2034, from USD 1.4 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 12.3% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 41.8% share, holding USD 0.5 Billion revenue.
Thin film batteries are ultra-thin, solid-state electrochemical cells in which active materials and solid electrolytes are deposited as micrometre- or even sub-micrometre-scale layers on substrates such as silicon, glass, metal foils or flexible polymers. They deliver high cycle life, low self-discharge and excellent safety, making them ideal for miniaturised electronics, smart cards and implantable medical devices. Laboratory cells based on LiCoO₂ have already demonstrated around 0.2 mAh/cm² capacity while still providing about 70% of that capacity at high current densities of 2 mA/cm², underscoring their ability to support pulse loads in compact formats.
- Industrial development of thin film batteries sits within a rapidly expanding global battery ecosystem. The International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates that global energy storage capacity must reach about 1,500 GW by 2030, with batteries providing 90% of the increase and their capacity rising 14-fold to roughly 1,200 GW. In parallel, EV battery demand is projected to grow from roughly 1 TWh in 2024 to more than 3 TWh by 2030, driven primarily by electric cars.
Demand-side drivers for thin film batteries are tightly linked to the miniaturisation of electronics and the Internet of Things (IoT). Recent reviews show that thin-film and printed batteries are increasingly selected for autonomous wireless sensors, MEMS/CMOS devices and flexible medical wearables, where conformal, millimetre-scale power sources are needed. Thin-film Li-ion cells using LiPON solid electrolytes, for example, have been demonstrated with electrolyte thicknesses below 100 nm and ionic conductivities around 6.5 × 10⁻⁷ S/cm at 35°C, supporting robust solid-state operation on complex surfaces.
Policy and funding frameworks for next-generation batteries also indirectly support thin-film technologies. In the United States, the Department of Energy’s Advanced Materials and Manufacturing Technologies Office announced USD 25.54 million in December 2024 for 11 “Platform Technologies for Transformative Battery Manufacturing” projects, explicitly targeting nanolayered films and advanced manufacturing concepts that are highly relevant to thin-film processes. Japan’s New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) has allocated about JPY 151 billion under its Green Innovation Fund for next-generation batteries and motors, with targets of achieving volume energy densities of 700–800 Wh/L for solid-state-type storage batteries by 2030.
Government programs and public R&D funding reinforce this industrial base. The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) has awarded around USD 2.5 million over three years for thin-film platforms to advance solid-state energy storage science, explicitly targeting safer, more efficient rechargeable batteries. In parallel, DOE’s Microbattery Design Prize allocates a USD 1.1 million federal prize pool to accelerate microbattery commercialization, with at least eight new design concepts supported under Phase I selections.
Key Takeaways
- Thin Film Batteries Market size is expected to be worth around USD 4.5 Billion by 2034, from USD 1.4 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 12.3%.
- Rechargeable held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 67.9% share of the global thin film batteries market.
- 1.5 V to 3 V held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 49.2% share of the global thin film batteries market.
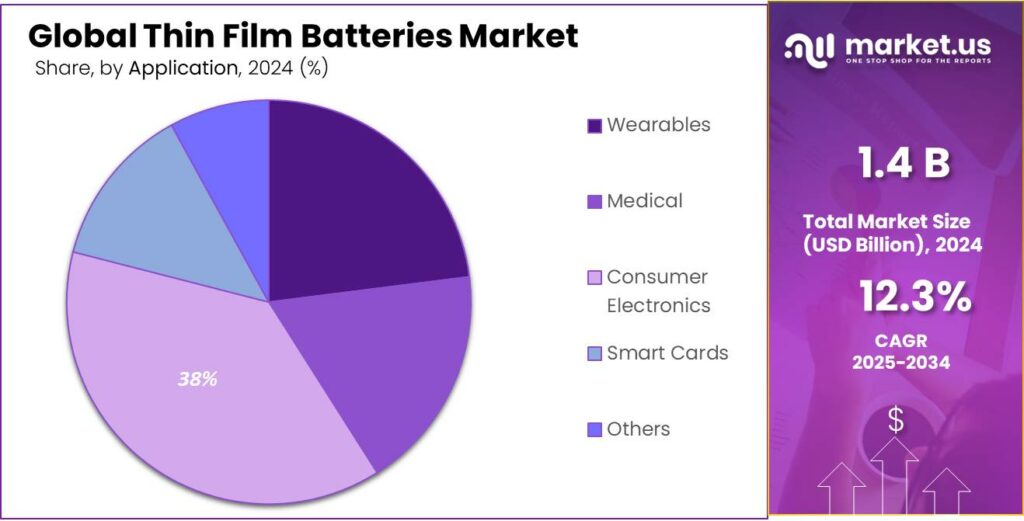
- Consumer Electronics held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.3% share of the global thin film batteries market.
- North America accounted for a dominant 41.8% share of the global thin film batteries market, representing a value of approximately USD 0.5 billion.
By Battery Type Analysis
Rechargeable leads with 67.9% — driven by high reuse potential and growing demand in portable electronics.
In 2024, Rechargeable held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 67.9% share of the global thin film batteries market. This segment’s leadership is attributed to the rising demand for energy storage solutions that can be reused multiple times, reducing waste and overall cost for end users. Rechargeable thin film batteries are widely used in wearable devices, IoT applications, medical devices, and small consumer electronics due to their compact size, lightweight design, and reliable power output. Their ability to support multiple charge-discharge cycles makes them more cost-effective and environmentally friendly compared with primary batteries, encouraging adoption across diverse sectors.
In 2025, demand for rechargeable thin film batteries is expected to grow steadily, driven by the continued expansion of smart wearable devices, miniaturized electronics, and energy-efficient IoT solutions. Advances in materials and manufacturing technologies, along with rising consumer awareness about sustainability, are further expected to reinforce the dominance of rechargeable batteries in the thin film battery market.
By Voltage Analysis
1.5 V to 3 V leads with 49.2% — preferred for compact electronics and low-power applications.
In 2024, 1.5 V to 3 V held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 49.2% share of the global thin film batteries market. This voltage range is widely adopted due to its suitability for low-power devices such as sensors, wearable electronics, medical devices, and small IoT applications. The consistent voltage output, reliability, and compatibility with miniature circuits have made this segment the preferred choice among manufacturers seeking compact and energy-efficient solutions.
In 2025, demand for 1.5 V to 3 V thin film batteries is expected to grow steadily, supported by the increasing proliferation of miniaturized electronic devices and the rising adoption of smart, connected products. Advances in thin-film technology, longer battery life, and improved safety features are also expected to strengthen the segment’s share, ensuring its continued leadership in the market.
By Application Analysis
Consumer Electronics leads with 38.3% — driven by rising demand for compact and reliable power sources.
In 2024, Consumer Electronics held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.3% share of the global thin film batteries market. The segment’s leadership is attributed to the widespread use of portable electronic devices, including smartphones, tablets, wearable gadgets, and smart home devices, which require compact, lightweight, and long-lasting power solutions. Thin film batteries provide consistent voltage, high energy density, and a slim form factor, making them highly suitable for miniaturized electronics.
In 2025, demand for thin film batteries in consumer electronics is expected to grow steadily, supported by the rapid adoption of smart wearable devices, IoT gadgets, and flexible electronics. Technological advancements, longer battery life, and enhanced safety features are anticipated to further strengthen this segment’s position, maintaining its lead in the market.
Key Market Segments
By Battery Type
- Disposable
- Rechargeable
By Voltage
- Below 1.5 V
- 1.5 V to 3V
- Above 3 V
By Application
- Wearables
- Medical
- Consumer Electronics
- Smart Cards
- Others
Emerging Trends
Rise of Intelligent Food Packaging Powered by Thin-Film Batteries
A clear latest trend for thin-film batteries is their move into intelligent food packaging and digital food supply chains. Food systems are under pressure to cut waste and prove product safety, and that is pushing demand for ultra-thin, safe power sources that can live inside labels and seals. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) estimates that about one-third of food produced for human consumption is lost or wasted every year, or roughly 1.3 billion tonnes.
Researchers and global agencies increasingly point to packaging and cold-chain management as key levers to reduce waste. FAO notes that about 14% of food is lost after harvest and before reaching retail, often because of poor handling, storage, and temperature control. At the same time, reviews on food packaging show that smart, sensor-enabled packs can directly help prevent loss by monitoring temperature, humidity, and spoilage indicators across the chain.
Digitalization of the cold chain is accelerating this trend. UNCTAD highlights how IoT devices and sensors are now widely deployed to track conditions from farm to fork, using data analytics to reduce loss and keep products within safe ranges. A 2025 study on smart food supply chains notes that IoT-enabled packaging and cold-chain systems are increasingly used to track temperature and humidity and keep food fresh longer.
Policy is reinforcing this direction. Under the EU Farm to Fork Strategy, the EU aims to cut food waste at retail and consumer level by 50% by 2030, and to reach 25% of agricultural land under organic farming. Other EU documents frame legally binding waste-reduction targets as a “historic opportunity” to halve food waste in line with SDG 12.3.
Real-world pilots show how digital tools can transform losses when supported by reliable power. FAO describes how the Twiga Foods platform in Kenya cut typical post-harvest losses for certain produce from about 30% to 4% using better logistics and data-driven distribution. As similar platforms add real-time sensing and traceability, each crate, pallet or pack becomes a candidate for a powered smart tag. Thin-film batteries, with their solid-state design and food-friendly form factor, are emerging as a natural choice in these disposable or semi-disposable devices.
Drivers
Miniaturization of Smart Devices and Sensors Driving Thin-Film Battery Adoption
One of the strongest driving factors for thin-film batteries is the rapid miniaturization of smart devices across healthcare, food monitoring, logistics, and consumer electronics. Modern systems increasingly rely on ultra-small sensors, tags, and control modules that require safe, compact, and maintenance-free power sources. Thin-film batteries meet this need because they are lightweight, flexible, and can be integrated directly onto electronic circuits.
According to the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), solid-state and thin-film battery architectures are a priority area because they eliminate liquid electrolytes, significantly improving safety and allowing use in tightly packed or sensitive environments such as wearable medical and food-contact devices
Growth in connected devices is accelerating demand. The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) reports that global Internet of Things (IoT) connections surpassed 15 billion active devices in 2023, with continued strong growth expected as sensors are embedded deeper into supply chains, healthcare systems, and food quality monitoring platforms . Many of these devices operate at milliwatt power levels and are deployed in locations where battery replacement is impractical. Thin-film batteries offer long operational lifetimes—often 10 years or more in low-power applications—making them well-suited for disposable smart labels, temperature trackers, and biosensors used in food safety and medical diagnostics .
Food industry digitization is a major contributor. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) highlights that over 30% of global food production is lost annually due to spoilage and supply-chain inefficiencies, driving investment in smart packaging and cold-chain monitoring technologies . Smart food labels using embedded sensors can track freshness, humidity, and temperature in real time. These labels require ultra-thin, non-toxic power sources that can safely operate in direct or indirect contact with food.
Government initiatives further reinforce this driver. The U.S. DOE has allocated USD 2.5 million to research programs focused on advanced thin-film and solid-state batteries, supporting safer, scalable energy storage for electronics and sensor networks. In parallel, the DOE Microbattery Design Prize introduced a USD 1.1 million federal prize pool to accelerate compact battery designs for medical devices, wearables, and smart packaging, directly encouraging thin-film solutions.
Restraints
High Manufacturing Cost and Limited Scalability Restrict Wider Thin-Film Battery Adoption
One major restraining factor for thin-film batteries is their high manufacturing cost combined with limited large-scale production capability. Unlike conventional batteries that use roll-to-roll processes, thin-film batteries depend on vacuum deposition methods such as sputtering and chemical vapor deposition. These processes require cleanroom environments, advanced equipment, and tight quality control, which significantly increases production costs. The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) notes that fabrication costs for solid-state and thin-film batteries remain several times higher than traditional lithium-ion cells due to low throughput and capital-intensive tools .
This cost barrier becomes more evident when thin-film batteries are considered for price-sensitive industries such as food supply chains and smart packaging. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) estimates that more than 30% of global food is lost each year, pushing industries toward smart labels and monitoring solutions to reduce waste . However, large-scale adoption of sensor-enabled food labels depends heavily on unit cost. Thin-film batteries, while technically ideal, often cost several dollars per cell, making them unsuitable for disposable food packaging when compared with low-cost printed or primary batteries .
Material limitations further intensify the restraint. Thin-film batteries rely on high-purity lithium compounds and specialty ceramics, which face supply pressure. According to the IEA, global lithium demand could increase by more than five times by 2030 under clean-energy scenarios, raising concerns about material price volatility and long-term availability. For food-related technologies—where margins are already thin—stable and affordable raw material supply is essential. Any significant fluctuation in material costs directly impacts the financial feasibility of thin-film battery integration.
- Government initiatives acknowledge these challenges but also confirm that solutions are still emerging. The U.S. DOE has funded more than USD 2.5 million in targeted research programs to improve thin-film battery manufacturing efficiency and reduce cost through novel deposition techniques and alternative materials . While promising, these programs remain largely at pilot and laboratory scale, meaning commercial impact will take time.
Opportunity
Expansion of Smart Food Packaging and Cold-Chain Monitoring Creates Strong Growth Opportunity
One of the most promising growth opportunities for thin-film batteries lies in the rapid expansion of smart food packaging and cold-chain monitoring systems. Global food systems are under pressure to reduce waste, improve traceability, and guarantee food safety from farm to consumer.
- According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), nearly 30% of all food produced worldwide is lost every year due to spoilage, improper storage, and inefficient logistics.
To address this problem, food producers and retailers are increasingly adopting smart labels, temperature sensors, freshness indicators, and tracking tags. These devices must be extremely thin, safe, and reliable, as they are often placed directly on food packaging. Cold-chain monitoring is another major driver. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that temperature-controlled logistics are essential for nearly 50% of global food products, including dairy, seafood, vaccines, and fresh produce.
Each shipment often requires multiple low-power sensors to record temperature, humidity, and transit duration. Thin-film batteries are well-suited for these applications because they can operate reliably over long periods at low power levels, often lasting 5–10 years without replacement when paired with low-energy electronics. This reduces maintenance costs and improves data reliability across food distribution networks.
Government initiatives further strengthen this opportunity. In the United States, the Department of Energy (DOE) has highlighted smart sensors and distributed electronics as essential tools for improving supply-chain efficiency and reducing waste. The DOE has committed over USD 2.5 million to research programs focused on advanced thin-film and solid-state battery technologies that support small electronics and sensor platforms.
Regional Insights
North America dominates with 41.8% share, valued at USD 0.5 billion, driven by advanced electronics adoption and strong R&D support
In 2024, North America accounted for a dominant 41.8% share of the global thin film batteries market, representing a value of approximately USD 0.5 billion. The region’s leadership is primarily driven by high adoption of portable and wearable consumer electronics, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and medical electronics, all of which benefit from the compact, lightweight, and reliable power solutions offered by thin film batteries. Strong research and development infrastructure, particularly in the United States and Canada, has enabled manufacturers to innovate in battery design, energy density, and flexible form factors, accelerating the commercial adoption of these solutions.
Government initiatives in North America have also supported market growth. Programs promoting energy efficiency, sustainable electronics, and advanced manufacturing have encouraged domestic production and deployment of thin film batteries in key sectors. Additionally, strategic collaborations between universities, research institutions, and technology companies have fostered rapid innovation, particularly in miniaturized and flexible battery technologies suitable for wearable and medical devices.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Blue Spark Technologies focuses on ultra-thin, flexible printed batteries designed mainly for single-use and low-power applications. The company is well known for its paper-based, solid electrolyte battery technology, which offers high safety and environmental compatibility. Its solutions are increasingly explored in smart packaging, medical patches, and disposable diagnostics. Blue Spark’s strength lies in scalable printing processes and food-safe designs, making it relevant for cost-sensitive applications where ultra-thin form factors and safety are critical.
Enfucell specializes in soft, flexible thin-film batteries optimized for IoT, smart labels, and wearable devices. Its printed battery technology allows integration into compact and curved surfaces without compromising reliability. Enfucell targets applications such as temperature sensors, logistics tracking, and smart packaging, where long life and low power consumption are essential. The company’s focus on environmentally friendly materials and printable manufacturing positions it well as sustainability becomes a stronger requirement across electronics and packaging industries.
LG Chem leverages its deep battery expertise to explore advanced thin-film and solid-state battery technologies. While best known for large lithium-ion systems, the company invests in next-generation materials and compact battery formats for electronics and automotive electronics. LG Chem’s strength lies in materials science, scale, and long-term R&D budgets. Its involvement signals industrial confidence in thin-film batteries as a future complement to conventional batteries, especially for compact, high-reliability electronic applications.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Blue Spark Technologies
- Enfucell
- STMicroelectronics
- LG Chem
- LionVolt
- SAMSUNG SDI Co. Ltd.
- Ilika Plc.
- BTRY AG
- NGK Insulators, Ltd.
- The Kurt J. Lesker Company
Recent Industry Developments
Enfucell’s SoftBattery typically delivers nominal voltages of 1.5 V and 3.0 V and is formulated using zinc–manganese dioxide chemistry with environmentally friendly materials and no heavy metals.
In 2025, LG Chem reported a breakthrough in its solid-electrolyte material development: the new electrolyte design boosted all-solid-state battery performance by up to 50% in high-rate discharge capacity compared with standard cells.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 1.4 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 4.5 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 12.3% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Battery Type (Disposable, Rechargeable), By Voltage (Below 1.5 V, 1.5 V to 3V, Above 3 V), By Application (Wearables, Medical, Consumer Electronics, Smart Cards, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Blue Spark Technologies, Enfucell, STMicroelectronics, LG Chem, LionVolt, SAMSUNG SDI Co. Ltd., Ilika Plc., BTRY AG, NGK Insulators, Ltd., The Kurt J. Lesker Company Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Blue Spark Technologies
- Enfucell
- STMicroelectronics
- LG Chem
- LionVolt
- SAMSUNG SDI Co. Ltd.
- Ilika Plc.
- BTRY AG
- NGK Insulators, Ltd.
- The Kurt J. Lesker Company










