Early Toxicity Testing Market Analysis By Type (In-vivo, In-vitro, In-Silico), By Application (Pharmaceuticals, Diagnostics, Foods and Beverages, Chemicals, Cosmetics, Others) By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: April 2025
- Report ID: 147624
- Number of Pages: 375
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
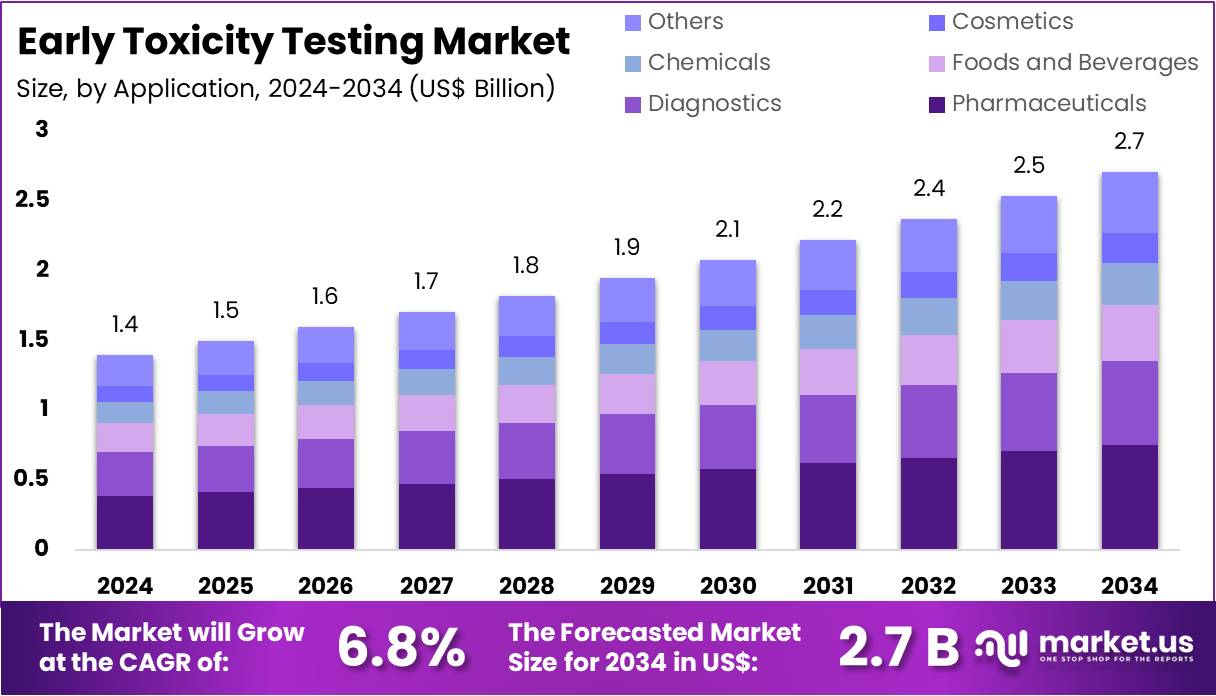
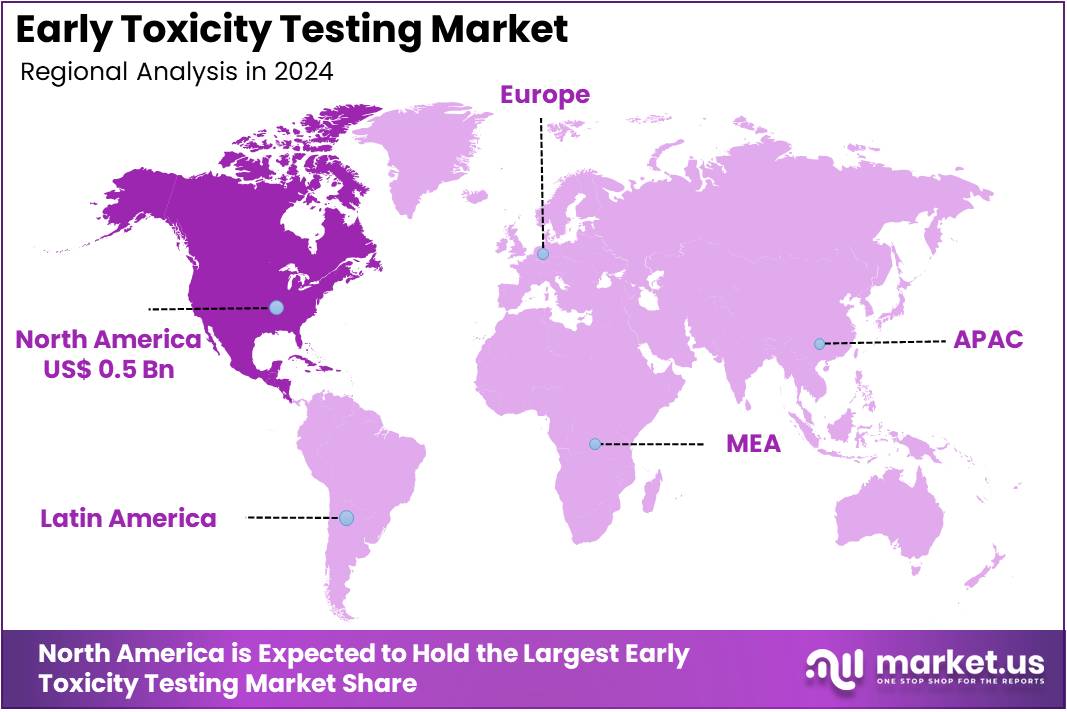
The Global Early Toxicity Testing Market size is expected to be worth around US$ 2.7 Billion by 2034, from US$ 1.4 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 6.8% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 39.2% share and holds US$ 0.5 Billion market value for the year.
Early toxicity testing plays a crucial role in the development of investigational new drugs (INDs) and the registration of chemical substances. This process ensures that regulatory standards set by agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) are met. It helps identify potential risks before a compound reaches human clinical trials, thereby improving safety and minimizing costly failures in later development stages.
According to FDA requirements, IND applications must include detailed preclinical safety data. These data come from pharmacological and toxicological studies, particularly in animal models, to show that a drug is reasonably safe for initial human use. The studies must demonstrate that the benefits outweigh the potential risks. As per FDA guidance, this safety evidence is critical to justify moving a drug candidate into clinical testing, ensuring compliance and minimizing harm to human participants.
Innovative approaches are reshaping early toxicity evaluations. In vitro methods, such as MTT, MTS, and ATP assays, are now widely used to assess cell viability and metabolic activity. For example, neutral red uptake evaluates membrane integrity, while ELISA-based cytokine assays detect inflammatory responses. These techniques offer reliable, ethical alternatives to animal testing by providing controlled, repeatable results on cellular toxicity. They form a foundation for efficient, early-stage toxicology screening in drug development.
Computational methods, or in silico toxicology, are also becoming important. These models predict the toxic potential of chemical substances using biological and chemical structure data. A notable example is the ToxCast Program by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), which screened 1,065 chemicals and achieved an accuracy of 79–82% for developmental toxicity prediction. Although sensitivity was below 67%, specificity exceeded 84%, showing strong potential in replacing some animal testing methods.
The eTOX project, a European initiative, has also advanced in silico tools. It utilized curated toxicology reports to develop predictive models for drug development, improving data reliability. Meanwhile, organ-on-a-chip (OoC) technologies have emerged as cutting-edge tools. These microfluidic systems mimic human organ functions more accurately than animal models. For instance, liver-on-a-chip devices have replicated species-specific drug toxicities and shown alignment with human clinical outcomes. This innovation supports more human-relevant toxicity testing.
Regulatory bodies are recognizing OoC potential. For example, the FDA accepted a liver-on-a-chip platform into its ISTAND program to assess drug-induced liver injury (DILI) risk. A study published in 2022 estimated that using these devices in DILI testing could generate over $3 billion annually for the pharmaceutical industry. Besides financial impact, these tools support ethical commitments by reducing animal use and offering more predictive data, thereby strengthening the overall drug development process.
Key Takeaways
- The global Early Toxicity Testing market is projected to reach approximately US$ 2.7 Billion by 2034, growing from US$ 1.4 Billion in 2024.
- An annual growth rate of 6.8% is expected for the Early Toxicity Testing market during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
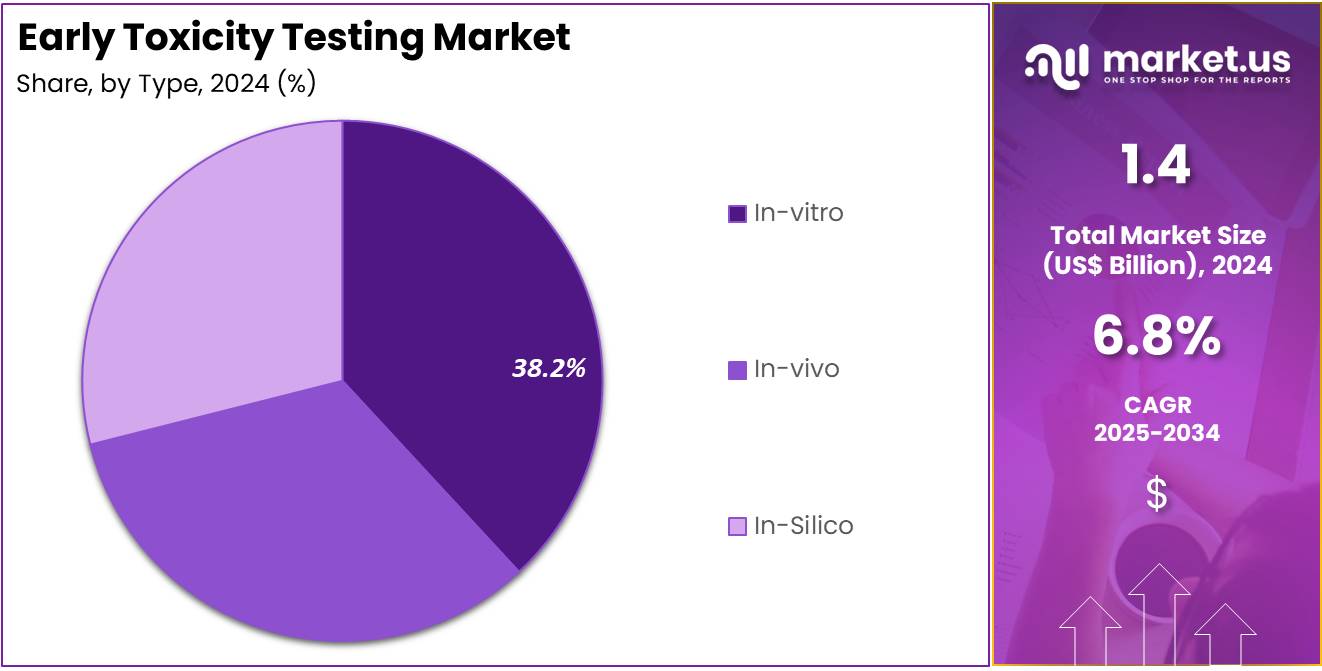
- In 2024, the In-vitro testing method led the Type segment, accounting for over 38.2% of the total market share.
- The Pharmaceuticals sector dominated the Application segment in 2024, capturing more than 28.4% share of the Early Toxicity Testing market.
- North America emerged as the leading region in 2024, holding a 39.2% market share valued at around US$ 0.5 Billion.
Type Analysis
In 2024, the In-vitro section held a dominant market position in the Type Segment of the Early Toxicity Testing Market, and captured more than a 38.2% share. This growth was supported by the increasing use of lab-based cell and tissue models for early toxicity screening. In-vitro methods are less expensive and faster than traditional approaches. They also reduce animal use, aligning with ethical standards. Regulatory agencies are promoting these models to improve accuracy in early drug development stages.
The In-vivo segment also accounted for a significant share of the market. Despite ethical concerns, animal-based models continue to be used for assessing systemic toxicity. These models are critical for evaluating organ-specific effects that in-vitro methods cannot replicate. In-vivo testing remains a regulatory requirement in later preclinical phases. Advances in animal welfare practices and imaging technologies are further contributing to its sustained relevance in toxicology research.
The In-silico segment is showing notable growth due to rising interest in computational prediction models. These tools use data-driven algorithms to estimate toxicity based on chemical structure and biological interactions. Although not yet fully accepted for regulatory approval, In-silico methods help reduce lab costs and testing time. With improvements in artificial intelligence and machine learning, the role of these tools is expected to increase. They offer a non-invasive, scalable solution for early-stage screening.
Application Analysis
In 2024, the Pharmaceuticals Section held a dominant market position in the Application Segment of Early Toxicity Testing Market, and captured more than a 28.4% share. This was mainly due to the rising demand for preclinical drug safety evaluations. Regulatory bodies require detailed toxicity profiles before drugs enter human trials. Pharmaceutical companies are adopting early-stage testing to prevent costly failures. In addition, the shift toward reducing animal testing is encouraging the development of alternative in vitro and computational models.
The diagnostics segment is showing notable growth in the early toxicity testing market. This is largely driven by the expansion of molecular diagnostics and biomarker testing. These diagnostic tools must be validated for safety before clinical use. The increase in personalized medicine and companion diagnostics is also creating a greater need for toxicity validation. Diagnostic firms are investing in safer testing environments. Early-stage toxicity screening ensures that diagnostic reagents do not cause adverse effects in human samples.
Cosmetics, chemicals, and food and beverage industries are also contributing to the market’s expansion. Regulatory restrictions on animal testing in regions like the European Union are driving demand for alternative toxicity testing methods. These industries are adopting cell-based and tissue-engineered assays for safety evaluation. Food and beverage companies, in particular, use early testing to meet safety standards and protect public health. Other applications include agriculture, where toxicity testing is used to assess the environmental impact of crop protection chemicals.
Key Market Segments
By Type
- In-vivo
- In-vitro
- In-Silico
By Application
- Pharmaceuticals
- Diagnostics
- Foods and Beverages
- Chemicals
- Cosmetics
- Others
Drivers
Rising R&D Investments in Drug Discovery
Rising investments in drug discovery R&D are playing a crucial role in boosting the demand for early toxicity testing. Pharmaceutical and biotech companies are prioritizing safety screening in the early stages to reduce the risk of late-stage clinical trial failures. Early toxicity testing supports this approach by identifying adverse effects at the cellular and molecular level before candidate drugs enter expensive clinical phases. This proactive strategy helps improve research efficiency and reduce the high costs associated with failed drug development cycles.
According to Deloitte, the world’s top 20 pharmaceutical companies collectively spent USD 145 billion on R&D in 2022–2023, up from USD 139 billion in 2021–2022. This consistent rise reflects a strategic shift toward improving drug safety profiles from the earliest stages of development. Early toxicity testing methods, including in vitro assays and organ-on-a-chip models, are becoming standard tools in preclinical pipelines. These tools enable rapid and reliable identification of potential toxicities, accelerating informed go/no-go decisions.
Companies such as Merck & Co. and Novartis illustrate this trend with significant R&D expenditure increases. Merck & Co. raised its R&D investment to USD 30.5 billion in 2023, up from USD 13.5 billion in 2022. Similarly, Novartis reported a 23.9% rise, spending USD 11.37 billion in 2023. These figures indicate a strong industry-wide commitment to innovation and safety. As a result, the market for early toxicity testing is expected to expand, supported by robust funding and a growing focus on preclinical drug evaluation.
Restraints
High Cost and Complexity of Advanced Testing Technologies
The adoption of advanced early toxicity testing technologies is hindered by their high costs and operational complexity. These technologies, such as in vitro and in silico models, are essential for accurate and early detection of toxic effects in drug candidates. However, their implementation demands significant financial investment and technical expertise. This creates barriers, particularly for small and mid-sized companies and institutions in developing economies, where access to advanced infrastructure and skilled personnel remains limited.
The cost of conducting comprehensive toxicity assessments is substantial. For example, a full toxicological evaluation of a single pesticide may range from $8 million to $16 million and could take up to eight years to complete. In the case of nanomaterials, estimates in the United States suggest that evaluations can cost between $250 million and $1.2 billion. These high figures highlight the financial burden associated with safety testing and demonstrate how they act as a restraint on the broader adoption of such technologies.
Additionally, routine ecotoxicity testing using vertebrate models can cost about $15,000 per chemical, adding to the cumulative testing burden for product developers. The complexity of advanced testing systems, including their need for precise calibration, validation protocols, and highly trained staff, further escalates operational challenges. These requirements limit the scalability and accessibility of early toxicity testing tools, especially in regions with limited regulatory or research support. This financial and technical hurdle continues to restrict the growth of the global early toxicity testing market.
Opportunities
Adoption of AI and Machine Learning for Predictive Toxicity Models
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into predictive toxicity models presents a strong opportunity in early toxicity testing. These technologies offer improved prediction accuracy for various toxicity endpoints, such as hepatotoxicity and cardiotoxicity. Algorithms like support vector machines and deep neural networks are commonly used. Multi-task deep neural networks, for example, have demonstrated high performance, with AUROC of 91.7%, F1-score of 84.9%, and overall accuracy of 85.4%. Such precision enhances confidence in early-stage drug screening processes.
AI-powered models reduce the reliance on animal-based testing by using computational tools to simulate biological responses. This shift aligns with ethical guidelines while saving time and resources. Predictive models using ML can process large datasets from in vitro, in vivo, and clinical studies. By analyzing these diverse datasets, they detect early signs of toxicity. This helps pharmaceutical firms make better-informed decisions before progressing to costly clinical trials.
The application of AI in early toxicity testing helps mitigate risks associated with drug development. These models detect potential toxicities early, which reduces late-stage clinical failures. As a result, companies benefit from faster time-to-market and lower development costs. Moreover, the use of AI supports pre-market evaluations by identifying adverse human and environmental effects. This ensures only safer drug candidates advance to further stages. The integration of AI tools thus enhances overall efficiency in toxicological research and drug safety assurance.
Trends
Shift Toward Organ-On-A-Chip And 3D Cell Culture Technologies
The shift toward organ-on-a-chip (OoC) and three-dimensional (3D) cell culture technologies is emerging as a transformative trend in early toxicity testing. These advanced platforms replicate human physiological conditions more accurately than traditional 2D cell cultures or animal models. The use of OoC and 3D models enhances the predictive value of preclinical testing by offering deeper insights into human-specific toxicity responses. This trend is gaining traction as pharmaceutical companies seek more reliable, cost-effective, and ethical alternatives for evaluating drug safety in the early stages of development.
Organ-on-a-chip systems are microfluidic devices engineered to replicate the microarchitecture and dynamic functions of human organs. These systems enable simultaneous monitoring of drug metabolism and toxicity within a single, integrated platform. For instance, liver-on-a-chip models have shown improved accuracy in predicting hepatotoxicity, aligning more closely with clinical outcomes. Furthermore, multi-organ-on-a-chip technologies support the study of inter-organ interactions, offering a comprehensive view of systemic toxicity that traditional models cannot deliver.
Three-dimensional cell culture models, such as spheroids and organoids, allow cells to grow in all directions, closely mimicking in vivo environments. These 3D models improve cell differentiation and function, leading to more precise toxicity data. For example, 3D liver cultures are increasingly used to detect drug-induced liver injury, showing higher sensitivity and specificity than 2D cultures. In addition to toxicity evaluation, these models are valuable for studying disease progression and identifying new drug targets, making them essential tools in modern drug development pipelines.
Regional Analysis
In 2024, North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 39.2% share and holds US$ 0.5 Billion market value for the year. This leadership can be explained by the region’s strong pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors. A well-established infrastructure for preclinical research supports the growth. Regulatory agencies such as the FDA have set clear guidelines for early toxicity testing. These regulations encourage companies to adopt safer and faster testing methods during drug development stages.
The United States plays a major role in driving market growth in North America. High spending on research and development has supported innovation in early-stage testing. Many U.S.-based research institutions focus on cell-based and in-vitro models. These methods help reduce reliance on animal testing and offer better predictive accuracy. Government initiatives also promote ethical testing alternatives. Such efforts are helping companies make quicker and more accurate safety decisions in drug discovery.
Canada has contributed to regional expansion by supporting research in toxicity screening. National programs have encouraged investment in laboratory automation and new testing platforms. The country’s regulatory bodies also work to align their standards with international practices. This has improved trust in Canadian testing protocols. As a result, both domestic and foreign pharmaceutical firms are showing interest. These combined factors are expected to help North America maintain its leading position in early toxicity testing for the years ahead.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherland
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- New Zealand
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
The Early Toxicity Testing market is shaped by several major players, with Thermo Fisher Scientific leading through its robust platforms for predictive toxicology. The company provides high-content screening, assay development, and integrated analytical workflows. These solutions improve testing accuracy and speed up drug development. Thermo Fisher’s extensive reagent and service portfolio also supports pharmaceutical research. Its continuous investment in automation and innovation reinforces its leadership in the biotechnology and drug discovery industries, positioning the company as a central contributor to early-stage safety profiling.
BD Biosciences plays a critical role in early toxicity testing with its expertise in flow cytometry and cell-based assays. The company offers tools for precise analysis of cellular responses, including apoptosis and immune system profiling. Its single-cell analysis technologies are widely used in preclinical toxicology. These innovations enable detailed evaluation of drug-induced effects. BD’s focus on analytical accuracy and throughput supports its relevance across pharmaceutical and academic research environments, contributing to advancements in early toxicology insights.
Covance, a division of Labcorp, provides comprehensive toxicology services as a leading contract research organization. The company offers both in vitro and in vivo testing, biomarker identification, and pharmacokinetic evaluations. Its global GLP-compliant infrastructure ensures support for regulatory submissions. Covance’s partnerships with drug developers streamline early-phase studies and enhance drug pipeline efficiency. The company’s wide range of services and regulatory expertise makes it a key enabler in safe and effective drug development across international markets.
Agilent Technologies and Bio-Rad Laboratories also contribute significantly to early toxicity testing. Agilent’s chromatography and mass spectrometry tools detect toxic metabolites with high precision. The company emphasizes automation and data analysis, enhancing high-throughput screening. Bio-Rad supports toxicology studies with PCR systems, ELISA kits, and protein analysis platforms. These tools enable standardized and reproducible results. Additional players focus on alternative testing methods, including organ-on-chip and 3D models, addressing ethical and regulatory demands in modern toxicology.
Market Key Players
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- BD Biosciences
- Covance
- Agilent Technologies
- Bio-Rad
- Sigma Aldrich
- Quest Diagnostics
- Charles River Laboratories
Recent Developments
- In September 2024: BD completed the acquisition of Edwards Lifesciences’ Critical Care division, rebranding it as BD Advanced Patient Monitoring. This $3.911 billion transaction expanded BD’s portfolio with advanced monitoring technologies, including AI-enabled clinical decision tools. These innovations are expected to improve patient monitoring and data collection, which are crucial for assessing drug safety and efficacy during early-stage testing.
- In July 2024: Thermo Fisher Scientific finalized its acquisition of Olink Holding AB, a leader in next-generation proteomics solutions, for approximately $3.1 billion. Olink’s proprietary Proximity Extension Assay (PEA) technology, which enables high-throughput protein biomarker discovery, complements Thermo Fisher’s existing life sciences and mass spectrometry offerings. This acquisition is poised to accelerate advancements in protein research, thereby enhancing early-stage toxicity testing and precision medicine initiatives.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) US$ 1.4 Billion Forecast Revenue (2034) US$ 2.7 Billion CAGR (2025-2034) 6.8% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, COVID-19 Impact, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Type (In-vivo, In-vitro, In-Silico), By Application (Pharmaceuticals, Diagnostics, Foods and Beverages, Chemicals, Cosmetics, Others) Regional Analysis North America – The US, Canada, & Mexico; Western Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Portugal, Ireland, Austria, Switzerland, Benelux, Nordic, & Rest of Western Europe; Eastern Europe – Russia, Poland, The Czech Republic, Greece, & Rest of Eastern Europe; APAC – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia & New Zealand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, & Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Colombia, Chile, Argentina, Costa Rica, & Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – Algeria, Egypt, Israel, Kuwait, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, & Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Thermo Fisher Scientific, BD Biosciences, Covance, Agilent Technologies, Bio-Rad, Sigma Aldrich, Quest Diagnostics, Charles River Laboratories Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Early Toxicity Testing MarketPublished date: April 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Early Toxicity Testing MarketPublished date: April 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- BD Biosciences
- Covance
- Agilent Technologies
- Bio-Rad
- Sigma Aldrich
- Quest Diagnostics
- Charles River Laboratories









