Global 2-Methylpropene Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Product (Butyl Rubber, Poly Isobutylene, MMA Monomer, Isooctane, MTBE, Others), By Application (Rubber Manufacturing, Pharmaceuticals, Fuel And Lubricant, Adhesives And Sealants, Antioxidants, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Dec 2025
- Report ID: 169214
- Number of Pages: 252
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
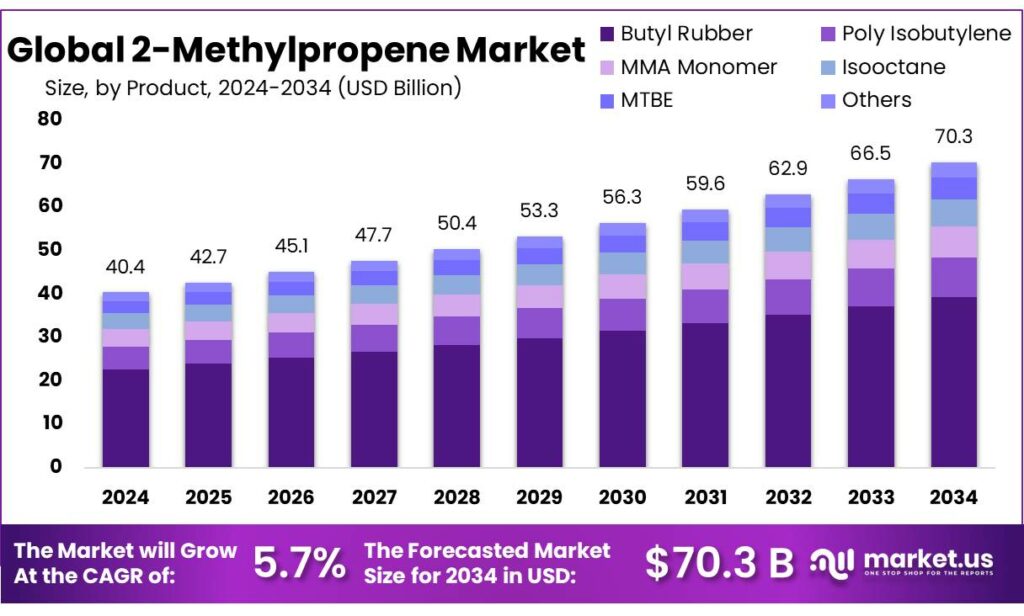
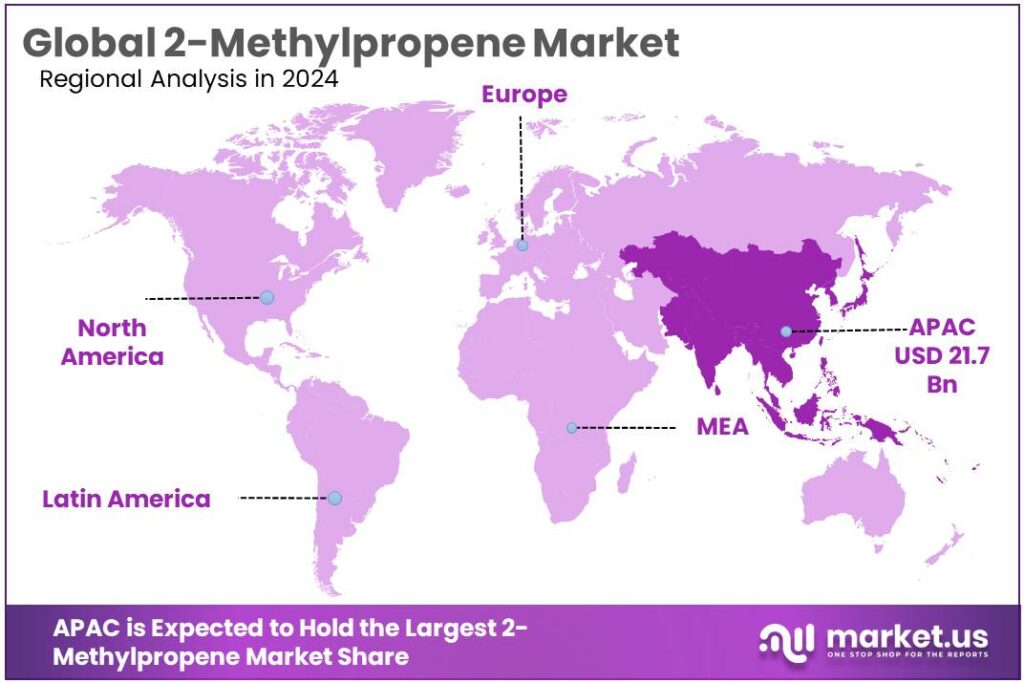
The Global 2-Methylpropene Market size is expected to be worth around USD 70.3 Billion by 2034, from USD 40.4 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 5.7% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, Asia-Pacific (APAC) held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 53.90% share, holding USD 21.7 Billion revenue.
2-Methylpropene (isobutene) is a light C₄ olefin produced mainly from steam-cracked C₄ streams and refinery dehydrogenation units. It is a key building block for fuel oxygenates such as methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE), high-octane alkylate, polyisobutylene (PIB) and butyl rubber. Industry sources indicate that annual global production of isobutene now exceeds 10 million metric tons. This firmly positions 2-methylpropene within the core petrochemical value chain linked to mobility, construction, adhesives and specialty elastomers.
The current industrial scenario for 2-methylpropene is tightly linked to gasoline and petrochemical demand. In the United States, finished motor gasoline consumption averaged 8.95 million barrels per day in 2023, highlighting the large pool of fuel into which MTBE/alkylate components derived from 2-methylpropene can be blended. U.S. gasoline exports averaged 0.90 million barrels per day in 2023, about 10% of domestic consumption, further underlining the scale of high-octane blending markets relevant to isobutene-based components.
- The International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates that petrochemical feedstocks already account for about 12% of global oil demand, and this share is expected to rise with ongoing plastics and elastomer growth.
Key demand drivers include robust petrochemical expansion in Asia and the continuing need for high-octane, low-aromatics gasoline components. The IEA notes that in 2023 China’s demand for petrochemical feedstocks such as naphtha, LPG and ethane averaged 1.7 million barrels per day more than in 2019, illustrating how rapidly feedstock-intensive capacity is growing in a single market. As 2-methylpropene is a critical precursor for MTBE/ETBE and butyl rubber, this upstream expansion supports investments in C₄ separation and isobutene derivative units.
Key Takeaways
- 2-Methylpropene Market size is expected to be worth around USD 70.3 Billion by 2034, from USD 40.4 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 5.7%.
- Butyl Rubber held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 56.3% share of the 2-Methylpropene market.
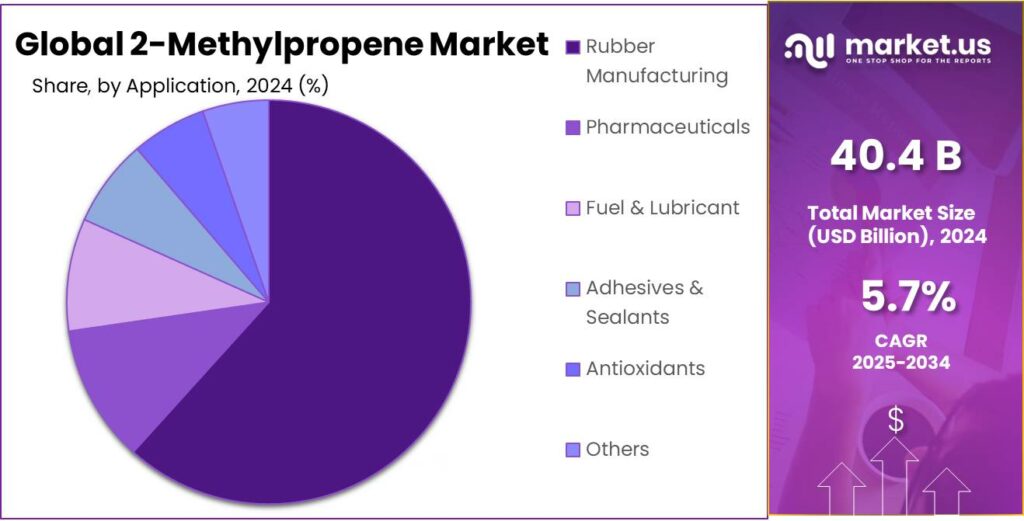
- Rubber Manufacturing held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 61.7% share of the 2-Methylpropene market.
- Asia-Pacific (APAC) region asserted a commanding position in the 2-Methylpropene market, holding more than 53.90% of global share and representing approximately USD 21.7 billion.
By Product Analysis
Butyl Rubber dominates with a 56.3% share in 2024
In 2024, Butyl Rubber held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 56.3% share of the 2-Methylpropene market by product type. This considerable share reflects the strong demand for Butyl Rubber in applications requiring resilience, impermeability, and durability. The prevalence of Butyl Rubber can be attributed to its superior material properties—such as resistance to chemicals, weathering, and gas permeability—which make it a preferred choice for tires, inner tubes, sealants, and other industrial uses.
Looking ahead to 2025, the lead of Butyl Rubber is expected to persist as manufacturers continue to prioritize performance characteristics that only specialty rubbers can deliver. Given current consumption patterns and industry preferences, Butyl Rubber is projected to remain the most favored product segment in the 2-Methylpropene market, thereby sustaining its dominant share.
By Application Analysis
Rubber Manufacturing dominates with a 61.7% share in 2024
In 2024, Rubber Manufacturing held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 61.7% share of the 2-Methylpropene market by application. This predominance was driven by the compound’s central role as the monomeric building block for polyisobutylene and butyl rubber, materials that are valued for low gas permeability, chemical resistance, and durability; such properties have supported continued use in tire innerliners, inner tubes, pharmaceutical stoppers, and sealing applications. Production and processing practices were aligned to meet steady industrial demand, and the segment’s leading position is expected to persist into 2025 as manufacturers continue to prioritize material performance in end-use applications.
Key Market Segments
By Product
- Butyl Rubber
- Poly Isobutylene
- MMA Monomer
- Isooctane
- MTBE
- Others
By Application
- Rubber Manufacturing
- Pharmaceuticals
- Fuel & Lubricant
- Adhesives & Sealants
- Antioxidants
- Others
Emerging Trends
2-Methylpropene moving into “quiet” high-barrier food packaging
One of the most interesting recent trends around 2-methylpropene is how its derivatives are finding a stronger, more deliberate role in high-barrier food packaging and sealing systems designed to cut food loss and waste. Polyisobutylene (PIB), made from 2-methylpropene, is being used more often in food and beverage packaging films, resealable closures and sealants because it gives a strong barrier against moisture, oxygen and bacteria and stays flexible at low temperatures.
An industry note on polyisobutene in food and beverage packaging highlights its “high tackiness,” hydrophobic behaviour and FDA-approved food-contact status, describing how it helps keep products fresh in retort pouches, resealable packs and sealing films.
- This technical shift sits on top of a big policy and food-system challenge. FAO’s policy support work now estimates that 13.2% of all food produced is lost in the supply chain after harvest and before retail, while a further 19% is wasted at retail, in food service and in households, based on 2024 UNEP statistics. UNEP’s 2024 Food Waste Index sharpens the picture: in 2022 the world wasted 1.05 billion tonnes of food, equal to 132 kg per person per year, and about one-fifth of all food available to consumers. Of that waste, 60% came from households, 28% from food service and 12% from retail.
For 2-methylpropene producers, this “quiet packaging” trend is a subtle but meaningful shift. Instead of seeing their molecule only as a route to fuel additives or rubber, they are increasingly linked to food-system outcomes: less waste, more reliable cold chains, and better protection for high-value perishables. Given that 1.05 billion tonnes of food were wasted in 2022 and 13.2% of food is still lost before retail, even small percentage improvements in shelf life or damage rates represent huge potential volumes – and a strong, policy-backed argument for continued innovation in PIB-rich films, seals and adhesives made from 2-methylpropene.
Drivers
Growing Use of Food Antioxidants and Packaged Foods
One big, very real driver for 2-methylpropene demand comes from the quiet work it does behind the scenes in our food system. 2-Methylpropene (isobutylene) is a key feedstock for making butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), a synthetic antioxidant widely used to keep fats and oils in foods from going rancid. Industrial chemistry sources describe how BHT is made by reacting p-cresol with isobutylene, showing a direct chemical link between 2-methylpropene and this food-grade preservative.
- According to the FAO, global agriculture value added increased from about USD 3.9 trillion in 2022 to roughly USD 4.0 trillion in 2023, a growth rate of 2.6% year on year. Even if this is not explosive growth, it shows a very large and steadily expanding base of crops, animal products and oils that need to be moved, processed and stored – all of which benefit from reliable antioxidants such as BHT made from 2-methylpropene.
Food regulators also recognise how central BHT has become in processed foods. The US Food and Drug Administration classifies BHT as “generally recognized as safe” (GRAS) when used within set limits, and allows its use in products ranging from enriched rice to poultry, typically at levels below 0.01% of fat content.
In Europe, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has re-evaluated BHT (E321) and continues to authorise it as a food additive, with exposure assessments based on detailed consumption data in EU diets. The World Health Organization, through JECFA, has set an acceptable daily intake for BHT at 0.3 mg per kg of body weight, giving companies a clear regulatory framework for continued use. These official positions make food manufacturers comfortable planning long-term use of BHT and, by extension, secure demand for its 2-methylpropene feedstock.
- Recent FAO Food Price Index updates underline that, even as prices move up and down, overall volumes remain high. In October 2025, the index stood at 126.4 points, still well below its March 2022 peak but supported by record world cereal production of about 2.99 billion tonnes expected for 2025. High cereal and oilseed output means large flows of grain-based and oil-rich foods, which again need stabilisers and protective packaging.
Restraints
Shift to organic and clean-label food limiting synthetic additives
One important restraining factor for 2-methylpropene is the growing push against synthetic food additives such as BHT, which is made from 2-methylpropene. For years, butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT, E321) has been used as an antioxidant to protect fats and oils. But regulators now look at it much more closely. The European Food Safety Authority re-evaluated BHT and tightened its acceptable daily intake to 0.25 mg per kg of body weight per day, based on new toxicology data. A Norwegian risk assessment also revisited BHT exposure using EFSA, JECFA and IARC evaluations, underlining continuing concern about cumulative intake from different foods and products.
At the same time, the organic and “clean-label” movements have become powerful counter-forces to synthetic antioxidants. FiBL and IFOAM report that global sales of organic food and drink reached almost €135 billion in 2022, and the organic farming area jumped to about 96 million hectares, with more than 4.5 million organic producers worldwide.
- The World of Organic Agriculture shows this trend continuing: global organic farming area in 2023 reached almost 99 million hectares, while retail sales of organic food climbed to nearly €136 billion. These are not niche numbers anymore; they show a huge, growing segment that generally avoids synthetic preservatives like BHT – and therefore indirectly reduces demand for its 2-methylpropene feedstock.
Public policy is reinforcing this shift. Under the European Green Deal’s Farm to Fork strategy, the EU has set a target that at least 25% of agricultural land should be organic by 2030, supported by an action plan to expand organic production and consumption. FAO and EU communications emphasise organic farming’s role in cutting pesticide use and improving soil and biodiversity, pushing food companies to reformulate with “nature-derived” antioxidants such as mixed tocopherols or rosemary extracts instead of BHT.
Opportunity
Cutting food loss with smarter packaging and cold chains
One major growth opportunity for 2-methylpropene sits exactly where food security, climate and packaging meet: the global push to cut food loss and waste. Today, the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) estimates that about 13% of all food produced – around 1.25 billion tonnes – is lost after harvest and before it even reaches retail shelves, while a further 19% – about 1.05 billion tonnes – is wasted in households, food service and retail.
FAO puts the value of this pre-retail loss alone at roughly USD 400 billion per year. For governments and food companies, this is now seen as an unacceptable leak in the system – and it creates clear room for better packaging, sealing and logistics materials, many of which are based on polyisobutylene and other 2-methylpropene derivatives.
From a climate point of view, the pressure is even stronger. The UNFCCC and IPCC both highlight that food loss and waste are responsible for around 8–10% of global greenhouse gas emissions, costing on the order of USD 1 trillion per year in lost value. From a climate point of view, the pressure is even stronger. The UNFCCC and IPCC both highlight that food loss and waste are responsible for around 8–10% of global greenhouse gas emissions, costing on the order of USD 1 trillion per year in lost value.
Policy signals are also moving in favour of more durable, higher-performance packaging. FAO’s “Food is Never Waste” coalition notes that around 14% of the world’s food, worth about USD 400 billion annually, is still lost in the chain before retail, while another 17% is wasted at and after retail. That is a huge pool of value that governments want to recover. Their guidance is clear: invest in better handling, storage, packaging and processing. At the same time, international climate briefs warn that food loss and waste use almost one-third of the world’s agricultural land and drive avoidable land-use change.
Regional Insights
Asia-Pacific leads with 53.90% share, accounting for USD 21.7 billion in 2024
In 2024, the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region asserted a commanding position in the 2-Methylpropene market, holding more than 53.90% of global share and representing approximately USD 21.7 billion in market value. This dominance can be attributed to concentrated upstream petrochemical capacity and the large presence of downstream end-users in countries such as China and India, where demand for butyl rubber, fuel additives and specialty polymers is substantial.
Rapid industrialization and ongoing expansion of refining and olefin conversion facilities have increased regional feedstock availability, which has supported competitive production economics for isobutylene derivatives and related monomers. The tire and rubber manufacturing sectors in APAC have been a particularly significant demand center, where low gas-permeability materials and sealants are required at scale for automotive and industrial applications.
In parallel, rising consumption in packaging, adhesives and chemical intermediates has reinforced steady off-take across multiple application segments. Investment activity in new polymerization units and capacity debottlenecking projects has been observed, and such capacity additions are expected to sustain the region’s supply advantage and cost competitiveness versus other geographies. Export flows of intermediate products from APAC hubs have also grown, enabling regional producers to serve nearby emerging markets while capturing scale efficiencies.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
SABIC is operated as a diversified petrochemical and polymer manufacturer, and its production platforms have been applied to support the 2-methylpropene ecosystem. Research and application engineering capabilities have been leveraged to develop formulations for rubbers, fuel additives and specialty polymers. Emphasis has been placed on feedstock integration, yield improvement and regional supply reliability to meet industrial demand. Regional manufacturing hubs and commercial channels have been expanded to serve converters and end users, while operational initiatives have been executed to enhance competitiveness.
Mitsubishi Chemical operates across petrochemical, functional material and specialty segments, and its product portfolio has intersected with 2-methylpropene-derived applications. Research-driven development and application engineering have been emphasised to meet performance requirements in sealing, insulation and specialty elastomer markets. Global manufacturing footprints and strategic alliances have been deployed to support consistent supply for multinational customers. Operational improvement programmes and targeted investments in process capability have been implemented to refine product performance and to support long-term customer commitments.
Braskem is recognized for its resin and chemical production in Latin America, and its olefin derivative capabilities have supported regional availability of 2-methylpropene intermediates. Vertical integration into downstream polymer manufacturing has been pursued to capture additional value and to supply regional converters at scale. Investments in operational reliability, maintenance and process technology upgrades have been advanced to improve yields and cost performance. Export flows from regional hubs have been utilised to serve neighbouring markets, while close engagement with converters has been maintained to align production with demand.
Top Key Players Outlook
- LyondellBasell Industries N.V.
- SABIC
- Braskem S.A.
- Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation
- Tosoh Corporation
- Eastman Chemical Company
Recent Industry Developments
- In 2024 Tosoh Corporation reported consolidated net sales of JPY 1,005,640 million (~ US$ 7.9 billion) under its petrochemical, basic-chemicals, and specialty-materials business segments.
- Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation sits at the heart of Mitsubishi Chemical Group Corporation (MCG), which reported consolidated group sales of ¥4,407.4 billion in fiscal year 2024.
- LyondellBasell, one of the world’s biggest chemical and petrochemical firms, reported total revenue of US$ 40.302 billion in 2024.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 40.4 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 70.3 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 5.7% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Product (Butyl Rubber, Poly Isobutylene, MMA Monomer, Isooctane, MTBE, Others), By Application (Rubber Manufacturing, Pharmaceuticals, Fuel And Lubricant, Adhesives And Sealants, Antioxidants, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape LyondellBasell Industries N.V., SABIC, Braskem S.A., Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation, Tosoh Corporation, Eastman Chemical Company Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- LyondellBasell Industries N.V.
- SABIC
- Braskem S.A.
- Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation
- Tosoh Corporation
- Eastman Chemical Company










