Global Food Grade Cellulose Market Size, Share, And Industry Analysis Report By Product Type (Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC), Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC), Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose (HPMC), Methylcellulose (MC)), By End Use (Food and Beverages, Pharmaceuticals and Nutraceuticals, Food Processing), By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends, and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: January 2026
- Report ID: 175735
- Number of Pages: 257
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
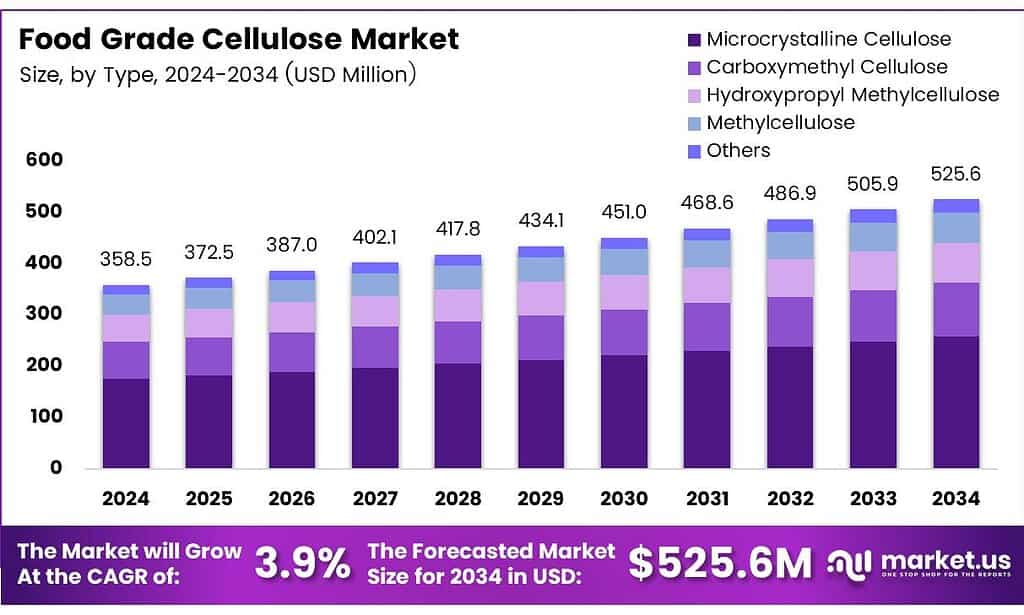
The Global Food Grade Cellulose Market size is expected to be worth around USD 525.6 million by 2034, from USD 358.5 million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 3.9% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
The Food Grade Cellulose Market refers to a specialized segment of the food ingredients industry centered on cellulose-based additives that enhance texture, stability, viscosity, moisture retention, and fiber enrichment. These ingredients, such as MCC, CMC, HPMC, and cellulose gum, are widely used in bakery, dairy, beverages, plant-based foods, sauces, and functional nutrition products.
The Food Grade Cellulose Market continues expanding as manufacturers seek clean-label stabilizers suitable for modern formulations. Consumers prefer safer, plant-derived additives that improve product quality without altering taste, and cellulose solutions fit this shift. Additionally, growing demand for low-fat and high-fiber products keeps strengthening the ingredient’s relevance across global food systems.
- High-purity CMC achieved 99.99% purity—surpassing the standard 99.5% benchmark—indicating strong progress in quality enhancement. This advanced CMC delivered a 2.4 g/g yield, DS 2.41, 5.11 g/g water holding capacity, and 1.59 g/g oil holding capacity, making it suitable for food and pharmaceutical additives.
Additionally, research on corn husk cellulose conversion demonstrated promising efficiency gains. Recovered ethanol through distillation exceeded 90%, and optimized reactions achieved a maximum CMC yield of 240.5%. Notably, CMC output increased as particle size decreased, showcasing technical opportunities in sustainable processing and waste valorization.
Furthermore, opportunities continue to increase as companies explore efficient conversion of agricultural byproducts into high-value cellulose derivatives. This shift supports circular economy models and lowers raw material dependence. Improved yields and optimized processing enhance supply stability, making cellulose derivatives more affordable and appealing for large-scale food and nutraceutical applications.
Key Takeaways
- The Global Food Grade Cellulose Market is valued at USD 358.5 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 525.6 million by 2034, at a CAGR of 3.9% from 2025 to 2034.
- Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC) leads the product type segment with a 45.9% market share.
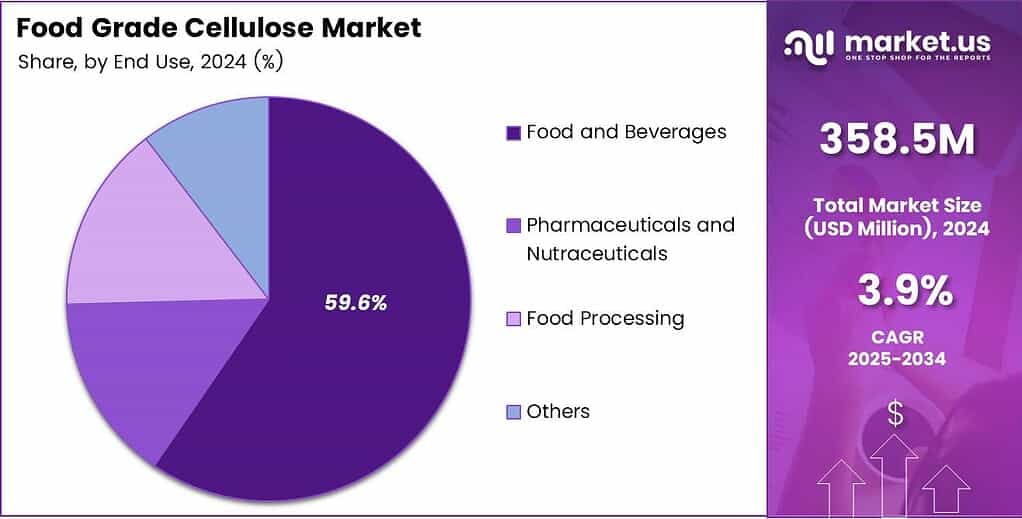
- Food and Beverages dominate the end-use segment with a 59.6% share.
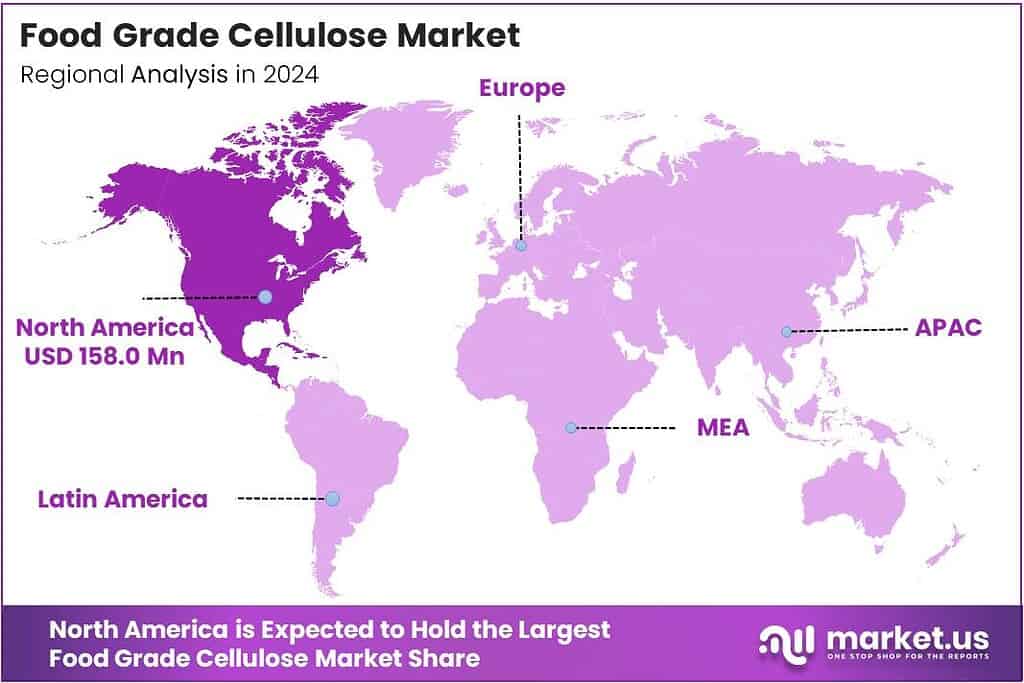
- North America holds the largest regional share at 44.1%, valued at USD 158.0 million.
By Product Type Analysis
Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC) dominates with 45.9% due to its strong functional versatility and widespread approval in global food formulations.
In 2025, ‘Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC)’ held a dominant market position in the ‘By Product Type’ Analysis segment of the Food Grade Cellulose Market, with a 45.9% share. MCC remained widely preferred as a stabilizer and bulking agent, offering texture enhancement and clean-label acceptance across bakery, dairy, and convenience foods globally.
Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC) continued gaining steady traction as formulators used it for superior thickening, moisture retention, and viscosity control. Its performance in sauces, dressings, and frozen desserts supported rising adoption. Furthermore, CMC enabled product consistency and stability, helping manufacturers improve mouthfeel while controlling ingredient costs in highly competitive processed food categories.
Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose (HPMC) has seen increasing usage due to its functional benefits in gluten-free and plant-based food applications. The ingredient supported binding, structure, and thermal stability, improving outcomes in baked items. As consumers increasingly sought texture-rich alternative foods, HPMC became valuable for developing improved formulations that mimic traditional sensory profiles while supporting label transparency.
Methylcellulose (MC) strengthened its niche presence as a heat-induced gelling agent widely used in meat alternatives and specialty processed foods. Its role in emulsification and water binding supported the development of innovative food formats. Additionally, MC’s ability to improve cohesiveness made it an important component in reformulated and hybrid protein products across multiple regions.
By End Use Analysis
Food and Beverages dominate with 59.6% due to their extensive use in texturizing and stabilizing mainstream food products.
In 2025, ‘Food and Beverages’ held a dominant market position in the ‘By End Use’ Analysis segment of the Food Grade Cellulose Market, with a 59.6% share. The segment benefited from growing demand for improved texture, stability, and fiber enhancement in dairy, bakery, beverages, ready meals, and low-calorie food innovations.
Pharmaceuticals and Nutraceuticals increasingly utilized food grade cellulose for controlled release, binding, and tablet integrity. Its natural origin supported expansion in clean-label supplements. Moreover, rising nutraceutical consumption encouraged manufacturers to adopt cellulose ingredients for enhanced formulation stability and consumer-friendly product positioning across global health and wellness markets.
Food Processing applications expanded as cellulose materials assisted in emulsification, moisture control, and structural improvements during large-scale manufacturing. Processors leveraged cellulose to achieve consistency and reduce formulation variability. These functions remained vital in processed meat items, confectionery fillings, sauces, and baking operations where performance reliability strongly influenced product quality.
Other end uses included specialized applications across niche categories requiring tailored cellulose functionalities. These segments grew moderately as manufacturers explored cellulose-based solutions for coating, thickening, or fiber enrichment. Although smaller in share, they provided flexibility for innovation and supported diversification beyond mainstream food and pharmaceutical categories.
Key Market Segments
By Product Type
- Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC)
- Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC)
- Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose (HPMC)
- Methylcellulose (MC)
- Others
By End Use
- Food and Beverages
- Pharmaceuticals and Nutraceuticals
- Food Processing
- Others
Emerging Trends
Growing Use of Cellulose in Fiber Fortification and Texture Enhancement Fuels Market Trends
One of the most noticeable trends in the food-grade cellulose market is its use in fiber fortification. As consumers become more aware of digestive health, brands are increasingly adding cellulose to foods to boost fiber content without affecting taste. This trend is strong in bakery items, cereals, snacks, and beverages.
- Cellulose is also trending as a natural texturizer in dairy alternatives and low-calorie foods. Its ability to mimic creaminess makes it a popular choice for plant-based milks, yogurts, and spreads. In the U.S., the Dietary Guidelines framework ties fiber targets to energy intake, using 14 grams per 1,000 calories as a practical benchmark for planning meals.
The clean label movement further supports this trend. Consumers prefer ingredients derived from natural sources, and cellulose fits well within this preference. Companies highlight their natural origin, helping build trust around processed foods. The move toward sustainable ingredients. Cellulose production supports sustainability initiatives because it utilizes renewable plant fibers.
Drivers
Rising Demand for Clean Label and Functional Ingredients Drives Market Growth
Food-grade cellulose is gaining strong traction as consumers shift toward clean-label products. Brands across bakery, dairy, beverages, and plant-based foods prefer cellulose because it comes from natural sources and supports stable textures without synthetic additives. This rising preference for transparency encourages manufacturers to choose cellulose as a multifunctional ingredient.
- Food companies are actively reducing fat, sugar, and calories in products. Cellulose helps maintain creaminess, bulk, and mouthfeel even when traditional ingredients are reduced. In U.S. retail alone, plant-based foods were valued at $8.1 billion in 2024. Even with softer performance—unit sales down 5% and dollar sales down 4% the category is still big enough that formulation improvements can move ingredient volumes in a meaningful way.
The growing popularity of plant-based and vegan foods further supports market expansion. Cellulose provides structure, moisture retention, and stability in plant-based meats, dairy substitutes, and nutrition bars. As these categories grow globally, the demand for cellulose rises alongside them.
Restraints
Rising Raw Material Costs and Supply Fluctuations Limit Market Expansion
One of the major restraints affecting the food-grade cellulose market is the fluctuation in raw material availability. Since cellulose is sourced from plant fibers such as wood pulp, any changes in forestry regulations or supply disruptions can impact the pricing structure. This makes long-term cost planning difficult for manufacturers.
- Another limitation comes from the complex extraction and purification processes required to meet food-grade standards. These processes require advanced technology and strict quality control, which increases production costs. In 2025, 81% of households that bought plant-based foods purchased more than once during the year, which tells manufacturers the market is not just trial-based—it’s habit-forming for a large base of consumers.
Regulatory challenges also play a role. Different countries follow specific guidelines for food additives, and cellulose must meet these criteria before entering the market. Changes in food safety laws can slow approvals or require reformulation, increasing compliance costs.
Growth Factors
Expanding Use in Plant-Based and Nutrient-Enhanced Foods Creates New Opportunities
A major growth opportunity in the food-grade cellulose market lies in the rapid global expansion of plant-based foods. As consumers seek alternatives to dairy and meat, cellulose is becoming essential for improving texture, juiciness, and stability. This makes it a key ingredient for companies developing next-generation plant-based products.
- The World Health Organization’s current healthy diet guidance recommends that people older than 10 aim for at least 25 grams of naturally occurring dietary fibre daily, and it also emphasizes a daily intake of at least 400 grams of fruits and vegetables.
The rising demand for nutrient-enhanced and better-for-you foods also creates room for cellulose-based solutions. Its ability to add fiber without altering flavor or appearance helps brands launch high-fiber snacks, beverages, and bakery goods. This aligns with public health initiatives urging higher fiber intake across populations.
Regional Analysis
North America Dominates the Food Grade Cellulose Market with a Market Share of 44.1%, Valued at USD 158.0 Million
North America holds the leading position in the Food Grade Cellulose Market, accounting for 44.1% of the total share and reaching a valuation of USD 158.0 million. The region benefits from strong demand for clean-label ingredients, a mature processed food industry, and continuous formulation innovation across bakery, dairy, and beverages. Regulatory clarity from the FDA further supports adoption, making North America the center of cellulose-based ingredient utilization.
Europe shows steady growth due to its highly regulated food ecosystem and rising consumer inclination toward healthier, fiber-enhanced foods. The region’s focus on product reformulation to reduce sugars, fats, and additives contributes to higher cellulose incorporation in bakery, confectionery, and ready-to-eat products. Sustainability-driven packaging and stringent quality standards continue to reinforce cellulose use across European industries.
Asia Pacific is emerging as a high-potential market, driven by rapid urbanization, expanding food processing sectors, and rising demand for affordable functional ingredients. Increased consumption of packaged foods in China, India, and Southeast Asia boosts the adoption of food-grade cellulose in texture improvement and shelf-life enhancement. Growing awareness of dietary fiber also strengthens long-term demand.
The Middle East and Africa region is experiencing a gradual adoption of food-grade cellulose, primarily supported by growth in processed foods, bakery expansion, and rising investment in food manufacturing infrastructure. As regional consumers shift toward convenience foods, manufacturers increasingly turn to cellulose for stabilization and cost-effective formulation improvement. Government efforts to expand domestic food production support further market penetration.
Key Regions and Countries
North America
- US
- Canada
Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
In 2025, the global Food Grade Cellulose Market will be shaped strongly by innovation, clean-label preferences, and rising functional applications across bakery, beverages, dairy alternatives, and nutraceuticals. Leading suppliers continue to advance ingredient performance while scaling production to meet formulation demands driven by stabilizing, thickening, and texturizing needs.
IFF maintains a strategic edge with its broad cellulose portfolio supported by strong R&D pipelines across functional food systems. The company continues to focus on improving texture stability and fiber-enhancement solutions, helping brands strengthen product performance in dairy alternatives and processed foods.
Ashland leverages its strong hydrocolloid technologies, particularly cellulose gum and methylcellulose grades, to support premium mouthfeel and product consistency. Its application-focused approach helps food manufacturers address formulation gaps linked to viscosity control and freeze–thaw stability.
Lamberti S.p.A. strengthens its market position through specialized cellulose derivatives tailored for bakery, sauces, and plant-based categories. Its emphasis on performance differentiation and sustainable processing supports customer needs for reliable, multifunctional ingredients.
Roquette Frères continues expanding its plant-based ingredient ecosystem, with cellulose solutions supporting fiber enrichment and calorie-reduction formulations. The company focuses on natural-origin ingredients and optimized dispersion properties, aligning well with clean-label and health-driven innovation.
Top Key Players in the Market
- IFF
- Ashland
- Lamberti S.p.A.
- Roquette Frères
- Asahi Kasei Corporation
- Kima Chemical Co., Ltd.
- Celotech Chemical Co., Ltd.
- Sigachi Industries
- Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd.
- Ataman Chemicals
Recent Developments
- In 2025, IFF continues to lead in microcrystalline cellulose technology with its Avicel and Lattice brands, which are used in food and industrial applications for binding, stabilization, and suspension. These products meet food-grade specifications and comply with food additive requirements, allowing for use in food contact materials.
- In 2025, Ashland was granted a patent for a substantially anhydrous thickener system in gel form for oral care compositions, incorporating carboxymethyl cellulose or its salts to enhance viscosity and stability in consumer products. Ashland’s Aqualon carboxymethyl cellulose is highlighted in recent studies for improving physical properties in edible films, such as gelatin-based coatings for food applications.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 358.5 Million Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 525.6 Million CAGR (2025-2034) 3.9% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Product Type (Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC), Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC), Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose (HPMC), Methylcellulose (MC), Others), By End Use (Food and Beverages, Pharmaceuticals and Nutraceuticals, Food Processing, Others) Regional Analysis North America (US and Canada), Europe (Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, and Rest of Europe), Asia Pacific (China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, and Rest of APAC), Latin America (Brazil, Mexico, and Rest of Latin America), Middle East & Africa (GCC, South Africa, and Rest of MEA) Competitive Landscape IFF, Ashland, Lamberti S.p.A., Roquette Frères, Asahi Kasei Corporation, Kima Chemical Co., Ltd., Celotech Chemical Co., Ltd., Sigachi Industries, Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd., Ataman Chemicals Customization Scope Customisation for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customisation can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited Users and Printable PDF)  Food Grade Cellulose MarketPublished date: January 2026add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Food Grade Cellulose MarketPublished date: January 2026add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- IFF
- Ashland
- Lamberti S.p.A.
- Roquette Frères
- Asahi Kasei Corporation
- Kima Chemical Co., Ltd.
- Celotech Chemical Co., Ltd.
- Sigachi Industries
- Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd.
- Ataman Chemicals










