Global Feed Enzymes Market Size, Share, And Business Benefits By Source (Microorganism, Plant, Animal, By Form, Dry (Liquid, Others), By Type (Phytase, Carbohydrase, Protease, Others), By Livestock (Poultry, Swine, Ruminants, Aquatic Animals, Others), By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends, and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: August 2025
- Report ID: 144720
- Number of Pages: 303
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
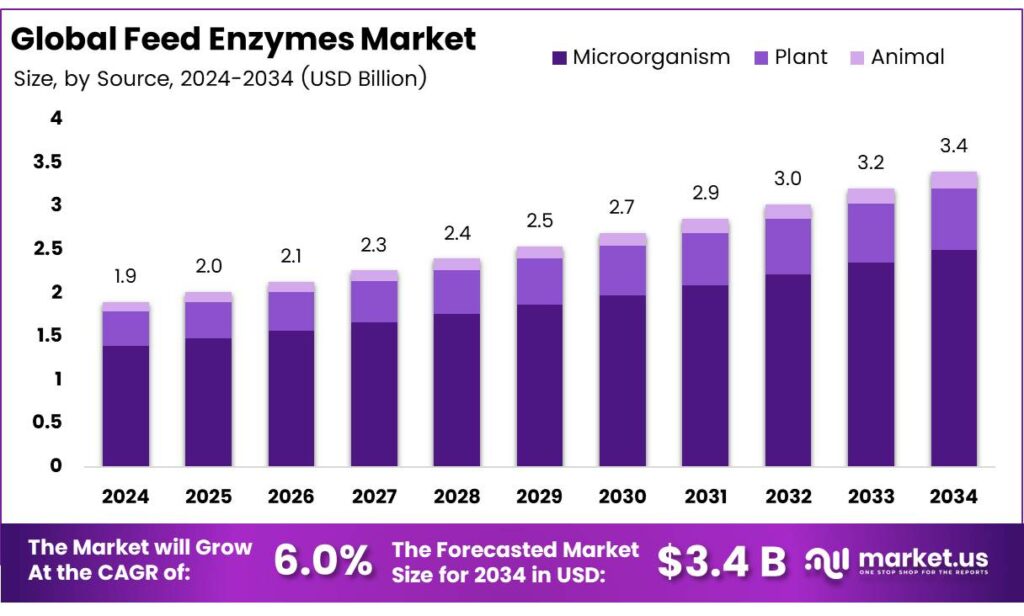
The Global Feed Enzymes Market size is expected to be worth around USD 3.4 billion by 2034, from USD 1.9 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 6.0% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
Feed enzymes are biological catalysts that enhance the digestibility of animal feed by breaking down complex nutrients into simpler forms. They are increasingly being adopted in poultry, swine, ruminant, and aquaculture nutrition to improve feed efficiency, lower production costs, and support sustainable farming practices. Their role is becoming more critical as the global livestock industry works to balance rising protein demand with environmental and regulatory challenges.
The Feed Enzymes Market is valued at approximately USD 850 million, with swine and poultry as the primary segments, followed by ruminants and aquacultured species like fish and shrimp. Pet food is excluded from this analysis. The feed enzymes market grows at 6%–8% annually, varying by region. Within the USD 15 billion global feed additives market, enzymes represent less than 10%, with vitamins, synthetic amino acids, and minerals holding larger shares.
Up to 70% of animal production costs come from feed, yet about 30% of nutrients remain undigested. Our enzymes, first introduced to animal feed over 30 years ago, are a proven solution to maximize efficiency. Continuously improved, they enhance nutrient absorption, improve digestibility, and reduce the impact of antinutritional factors, allowing you to get more from less.
Animal feed enzymes are incorporated into feed to improve digestibility, promote growth, and support environmental sustainability. As animals often fail to digest 15%–20% of feed due to complex components, enzymes optimize energy and micronutrient release from consumed materials. The P equivalency of phytase (840 FTU kg⁻¹ ≈ 1.0 g kg⁻¹ P) is slightly lower than practical estimates suggest. Studies indicate phytase hydrolyzes about 45% of phytate in broiler diets, likely an overestimation.
Key Takeaways
- The Global Feed Enzymes Market is projected to grow from USD 1.9 billion in 2024 to USD 3.4 billion by 2034, with a CAGR of 6.0%.
- Microorganism-based enzymes dominated in 2024, holding a 73.4% market share due to cost-effective, high-yield solutions.
- Dry formulations led in 2024 with a 68.9% share, favored for longer shelf life and ease of handling.
- Phytase enzymes held a 41.1% market share in 2024, driven by enhanced nutrient absorption in animal feed.
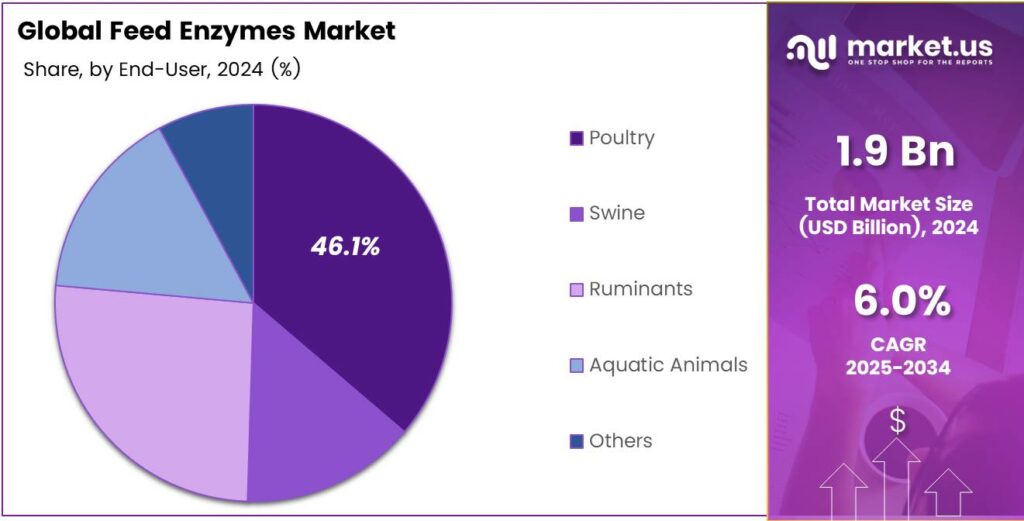
- The poultry segment captured a 46.1% market share in 2024, fueled by global demand for chicken and eggs.
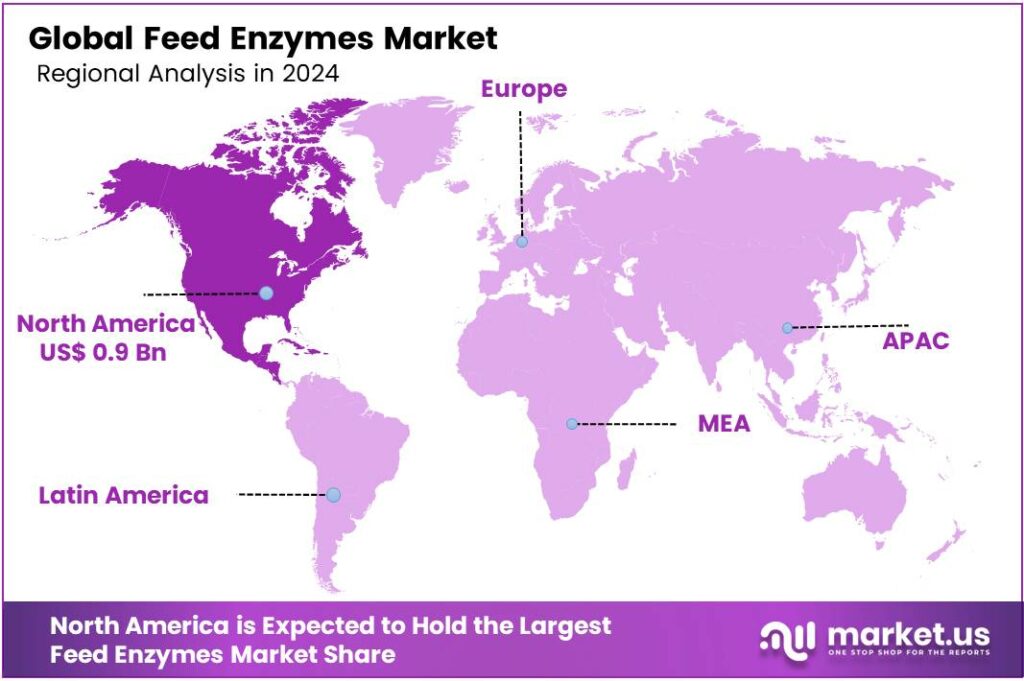
- North America led with a 47.8% revenue share (~USD 0.9 billion) in 2024, driven by the advanced livestock sector and regulations.
Analyst Viewpoint
Investing in the feed enzymes market offers a compelling opportunity, driven by the global push for sustainable livestock production and rising demand for high-quality animal protein. Feed enzymes, like phytases and proteases, enhance nutrient absorption in animals, reducing feed costs and environmental impact, a win-win for farmers and eco-conscious consumers.
The global demand for meat is surging, fueled by population growth and rising incomes in regions like the Asia-Pacific. Investors can tap into this growth through companies innovating in enzyme solutions or startups focusing on precision nutrition. The appeal lies in the market’s alignment with consumer trends toward ethical farming and reduced antibiotic use, making it a socially responsible investment with strong return potential.
Technological advancements, like CRISPR-based enzyme engineering, are game-changers but require hefty R&D investment, which smaller players may struggle to fund. Consumer skepticism about genetically modified enzymes could also dampen adoption in some markets. Despite these challenges, the market’s trajectory looks promising, with innovations like data-driven enzyme blends boosting efficiency and sustainability, appealing to both farmers and environmentally aware investors.
By Source
Microorganisms Lead Feed Enzymes Market with 73.4% in 2024
In 2024, Microorganism held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 73.4% share in the global feed enzymes market. This strong dominance is attributed to the ability of microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, and yeast to produce high-yield, cost-effective, and stable enzyme solutions tailored for animal nutrition.
These microbial sources are highly efficient in producing enzymes like phytase, protease, and carbohydrase, which enhance nutrient absorption and improve the digestibility of animal feed. With the increasing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly enzyme production, microorganisms remain the preferred source due to their scalability and adaptability in industrial fermentation processes.
By 2025, this segment is expected to continue its leadership as livestock producers increasingly shift toward enzyme-rich diets to improve feed efficiency and reduce feed costs. Microbial enzymes are also gaining traction in poultry and swine feed formulations, where improved nutrient utilization directly impacts animal growth performance.
By Form
Dry Form Leads Feed Enzymes Market with 68.9% in 2024
In 2024, Dry held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 68.9% share in the global feed enzymes market. The preference for dry formulations is mainly driven by their longer shelf life, ease of handling, and better stability during storage and transportation compared to liquid forms.
Dry enzymes are widely used in poultry, swine, and ruminant feed, as they can be conveniently mixed into premixes and compound feed without losing effectiveness. Their compatibility with high-temperature feed processing, especially during pelleting, makes them a preferred choice for large-scale commercial feed producers.
The demand for dry feed enzymes is expected to remain strong as livestock farmers and feed manufacturers continue to prioritize efficiency and cost-effectiveness in feed preparation. The durability of dry forms under varying climatic conditions also supports their use in regions with limited cold-chain facilities, further boosting their adoption.
By Type
Phytase Dominates Feed Enzymes Market with 41.1% in 2024
In 2024, Phytase held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 41.1% share in the global feed enzymes market. The strong demand for phytase is mainly due to its proven ability to break down phytic acid in animal feed, thereby improving phosphorus availability and overall nutrient absorption.
This not only enhances animal growth and performance but also reduces the need for inorganic phosphorus supplements, lowering feed costs for farmers. Phytase is particularly significant in poultry and swine feed, where it helps optimize digestion and supports stronger bone development.
By 2025, the role of phytase is expected to grow further as livestock producers and feed manufacturers continue to adopt sustainable feeding practices. Its contribution to reducing phosphorus excretion also supports environmental goals by minimizing nutrient runoff and its negative impact on soil and water systems.
By Livestock
Poultry Leads Feed Enzymes Market with 46.1% in 2024
In 2024, Poultry held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 46.1% share in the global feed enzymes market. The strong dominance of this segment is due to the rising demand for chicken meat and eggs worldwide, which has created a consistent need for efficient and cost-effective feed solutions.
Enzymes such as phytase, protease, and carbohydrase are widely used in poultry diets to improve nutrient digestibility, enhance gut health, and support faster weight gain. By breaking down complex feed components, enzymes help reduce feed conversion ratios, making poultry production more profitable and sustainable.
The poultry segment is expected to maintain its lead as consumer preference for white meat continues to grow in both developed and emerging economies. The cost-effectiveness of enzyme-supplemented feed is also encouraging widespread adoption, particularly in large-scale poultry farms. Furthermore, increasing restrictions on antibiotic growth promoters in feed are pushing producers to rely more on enzymes as natural performance enhancers.
Key Market Segments
By Source
- Microorganism
- Plant
- Animal
By Form
- Dry
- Liquid
- Others
By Type
- Phytase
- Carbohydrase
- Protease
- Others
By Livestock
- Poultry
- Swine
- Ruminants
- Aquatic Animals
- Others
Drivers
Boosting Feed Efficiency and Lowering Costs
One of the most compelling reasons feed enzymes are increasingly used in animal nutrition is their significant impact on boosting feed efficiency, which directly translates to cost savings for farmers and feed producers. When added to animal feed, particularly carbohydrases and proteases, these enzymes can help animals gain between 1 % and 7 % more body weight, while also improving the feed conversion ratio (FCR) by approximately 1 %.
This means farmers essentially need less feed to get the same, or even better, production outcomes. It’s a clear win-win: animals grow faster and more efficiently, feed costs drop, and environmental waste is reduced. This isn’t just a lab finding—it’s grounded in real-world application. Many producers are actively incorporating enzyme blends into diets to optimize resource use and keep operations sustainably profitable.
Restraints
Regulatory Hurdles: A Key Restraint for Feed Enzymes
One of the most significant hurdles holding back the wider adoption of feed enzymes is the complex and often lengthy regulatory approval process. While these enzymes offer clear benefits, navigating the rules set by government bodies can be both time-consuming and expensive, especially for smaller producers.
Government regulations and approvals that must be obtained before the use of feed enzymes constitute one of the market’s most significant obstacles at present. In many countries, feed additives like enzymes must pass stringent safety and efficacy tests before they can be used in livestock diets. This involves extensive documentation, lab trials, and sometimes even field studies, which adds both cost and delay.
Opportunity
A Major Growth Factor: Rising Demand for Animal Protein
One of the clearest reasons feed enzymes are gaining momentum is their role in meeting the world’s growing appetite for high-quality animal protein. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) projects that production of animal proteins will grow by around 1.7% per year between 2010 and 2050, while meat production itself is expected to climb nearly 70% in that same timeframe.
That’s a huge push in demand, and animal producers are under pressure to be more efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective. Enzymes make a real difference here. By helping livestock digest nutrients better, they boost feed conversion efficiency so fewer raw materials are needed to produce the same amount of meat, eggs, or dairy. It’s about doing more with less, and it’s exactly what the industry needs right now.
Trends
Emerging Factor: Sustainability Push Through Environmental Goals
One major emerging driver for the feed enzymes market comes from the rising tide of sustainability regulations, especially in places like Europe, aimed at slashing nutrient pollution from livestock farming. The push to lower environmental impact in farming has given feed enzymes new importance not only for smart farming but also to meet legal requirements. With livestock operations under pressure, enzyme use offers a practical, ready-to-deploy tool that improves digestibility and aligns with “green” farming mandates.
They already juggle rising energy costs and stricter waste rules. By adding phytase to feed, they cut phosphorus waste and avoid hefty penalties while bettering herd health. That dual benefit makes enzymes feel less like a lab additive and more like a trusted ally. This shift isn’t limited to Europe. Globally, environmental concerns are prompting governments and industry groups to favor solutions that reduce ecological footprints without sacrificing productivity.
Regional Analysis
North America: A Mature Market Holding 47.8% Share Valued at USD 0.9 Billion
The North American region is the dominant force in the global feed enzymes market, accounting for a commanding revenue share of approximately 47.8%, translating to an estimated value of USD 0.9 billion. This leadership is primarily fueled by a highly developed and intensive livestock sector, stringent regulations that promote animal health and reduce environmental impact, and a strong presence of key industry players.
The region’s advanced animal husbandry practices prioritize feed efficiency and optimal nutrient utilization, driving consistent demand for enzyme-based solutions that enhance digestibility and reduce feed costs. Furthermore, growing consumer awareness and demand for antibiotic-free meat and poultry products have accelerated the adoption of feed enzymes as sustainable alternatives to growth promoters.
The United States constitutes the largest market within North America, supported by its massive meat production industry and continual technological advancements in animal nutrition. The well-established regulatory framework, particularly from the FDA and CFIA, ensures product safety and efficacy, fostering innovation and trust among producers. This combination of a mature livestock industry, proactive regulatory standards, and high consumer awareness solidifies North America’s position as the market leader.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
BASF SE is a major force in the feed enzymes market. Its robust portfolio, developed through significant R&D, includes phytases and non-starch polysaccharide (NSP) enzymes, such as xylanase. These products enhance animal nutrition by improving feed digestibility and nutrient availability. BASF leverages its extensive production scale and global distribution network to serve a wide range of livestock producers, strengthening.
Du Pont (Danisco) is a pioneer and one of the largest players in the feed enzymes industry. The company is renowned for its high-performance phytase and carbohydrase products. Its strong commitment to research and development ensures a continuous pipeline of innovative solutions that improve feed efficiency and animal health.
Associated British Foods plc (ABF) holds a significant stake in the global feed enzymes market. AB Vista is particularly recognized for its advanced phytase technology and other specialty enzymes that unlock nutritional value in feed. The company focuses on delivering value-added solutions that enhance animal performance and profitability for farmers.
Top Key Players in the Market
- BASF SE
- Du Pont
- Associated British Foods plc
- Koninklijke DSM N.V.
- Behn Meyer Holding AG
- Adisseo France SAS
- Azelis Holding S.A.
- Novus International Inc.
- Rossari Biotech Ltd.
- Alltech Inc.
Recent Developments
- In 2024, BASF significantly expanded its feed enzyme production capacity at its Ludwigshafen, Germany, facility to increase fermentation output for key enzyme lines such as Natuphos E, Natugrain TS, and Natupulse TS. This expansion enhances BASF’s ability to meet global demand for high-quality feed enzymes.
- In 2025, IFF launched an enzyme blend targeting microbiome-supportive foods, designed to enhance digestive health by improving prebiotic release from plant-based matrices, aligning with global wellness trends and supporting animal nutrition applications.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 1.9 Billion Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 3.4 Billion CAGR (2025-2034) 6.0% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Source (Microorganism, Plant, Animal, By Form, Dry (Liquid, Others), By Type (Phytase, Carbohydrase, Protease, Others), By Livestock (Poultry, Swine, Ruminants, Aquatic Animals, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape BASF SE, Du Pont, Associated British Foods plc, Koninklijke DSM N.V., Behn Meyer Holding AG, Adisseo France SAS, Azelis Holding S.A., Novus International Inc., Rossari Biotech Ltd., Alltech Inc. Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited Users and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- BASF SE
- Du Pont
- Associated British Foods plc
- Koninklijke DSM N.V.
- Behn Meyer Holding AG
- Adisseo France SAS
- Azelis Holding S.A.
- Novus International Inc.
- Rossari Biotech Ltd.
- Alltech Inc.










