Quick Navigation
Overview
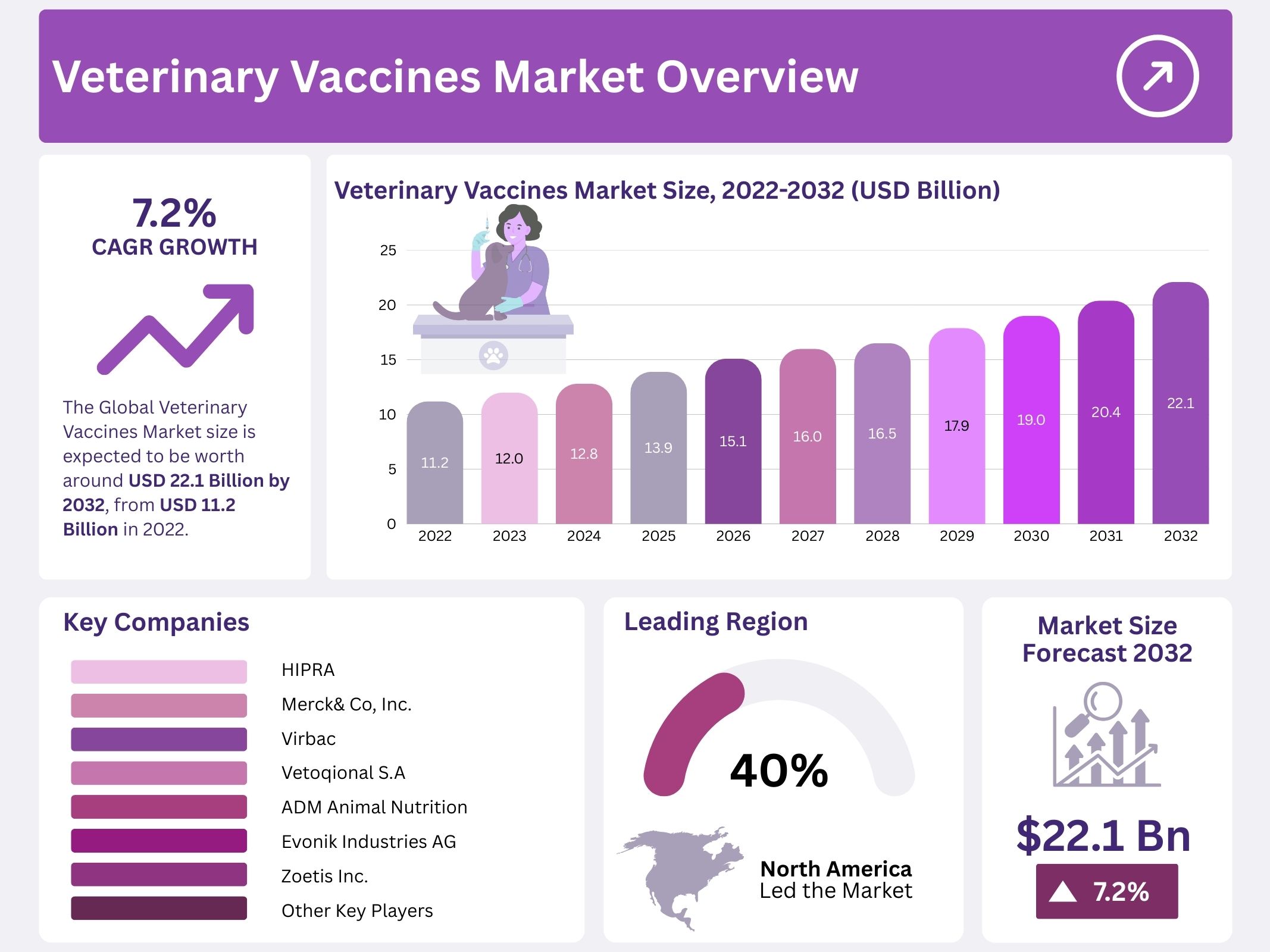
The Global Veterinary Vaccines Market is projected to grow from USD 11.2 billion in 2022 to USD 22.1 billion by 2032. This represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2% over the forecast period. Growth is primarily driven by the rising risk of zoonotic diseases, as approximately 60% of emerging infectious diseases in humans originate from animals, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). Governments and stakeholders are prioritizing prevention at the animal source, ensuring sustained demand for veterinary immunization.
One of the strongest accelerators is the “One Health” approach promoted by WHO, CDC, FAO, and the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH). This framework integrates human, animal, and environmental health policies. National adoption of One Health strategies has created coordinated programs, greater funding, and stronger vaccine distribution networks. This alignment has translated into more consistent procurement of veterinary vaccines, strengthening long-term demand across regions. Policy-driven commitments remain critical in stabilizing the market environment.
Disease elimination programs provide further momentum for vaccine uptake. The WHO-led “Zero by 30” initiative targets the elimination of dog-mediated rabies deaths worldwide by 2030. With rabies causing nearly 59,000 human deaths annually, vaccination of dogs remains the most effective preventive measure. Global efforts have mobilized donor funding, strengthened veterinary supply chains, and expanded community vaccination drives. This has increased procurement by both governments and private sector partners, ensuring long-term demand sustainability in the canine vaccine segment.
The continued threat of transboundary animal diseases also reinforces vaccine adoption. Recurring outbreaks of highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI), with documented spillover into mammals, have had significant economic impacts on poultry industries. Authorities such as the USDA’s Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS) have responded with integrated control measures that include targeted vaccination. Similar efforts in Europe, guided by EFSA and WOAH reports, have ensured steady investment in avian vaccines. As outbreaks persist, demand for preventive immunization remains resilient and programmatically reinforced.
Production Expansion, AMR Policies, and Regulatory Support
The expansion of global meat and animal-protein production has become a central driver for the veterinary vaccines market. OECD-FAO estimates indicate world meat output reached about 365 million tonnes in 2024, with poultry as the dominant segment. Rising production volumes have increased the economic value at risk from animal diseases. Vaccination is being widely adopted as a cost-effective safeguard against productivity losses and trade restrictions, providing measurable returns for producers and securing long-term growth in vaccine demand across livestock and poultry sectors.
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) policies are further strengthening vaccine adoption. WHO and FAO recommend reducing routine antibiotic use in animal husbandry, advocating prevention as a substitute. National governments and international organizations are aligning strategies to curb AMR by promoting vaccination. This shift is reducing reliance on prophylactic antibiotics and fostering greater demand for effective immunization programs. As AMR emerges as a global threat to both human and animal health, preventive vaccination stands out as a sustainable and scalable solution.
Improvements in public vaccination guidelines are enhancing implementation efficiency. FAO has developed detailed manuals for livestock campaigns and avian influenza control, providing standardized procedures for cold chain management, dosage schedules, and monitoring. These technical playbooks help reduce wastage, improve coverage, and increase government confidence in allocating budgets for routine and emergency vaccination programs. As these field practices become institutionalized, vaccination programs achieve greater reliability, supporting consistent procurement and reinforcing trust among international donors and multilateral agencies.
Regulatory clarity in major markets is enabling innovation and accelerating uptake. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has issued comprehensive guidelines for veterinary immunologicals and continues to authorize new vaccines. Such frameworks reduce risks for developers and encourage investment in novel vaccine platforms and broader indications. Coupled with strong surveillance systems, such as those led by USDA/APHIS, national authorities are able to quickly detect outbreaks and trigger vaccination responses. This tighter link between surveillance and immunization ensures predictable, programmatic vaccine demand that supports sustained global market expansion.
Key Takeaways
- The veterinary vaccines market is projected to reach USD 22.1 billion by 2032, expanding steadily at a compound annual growth rate of 7.2%.
- Advancements in veterinary vaccine technologies, including DNA and recombinant solutions, are improving vaccine stability, administration convenience, and overall adoption in global markets.
- Recombinant vaccines are anticipated to lead market growth due to higher safety and efficacy, supported by manufacturers’ increasing investments in advanced production methods.
- Rising global pet ownership and animal adoption have established companion animals as the dominant market segment in veterinary vaccines.
- Parenteral administration remains the leading delivery route, offering intramuscular, subcutaneous, and intradermal options to ensure efficient vaccine efficacy in animals.
- Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome accounts for the largest disease indication market share, reflecting its widespread prevalence across animal populations.
- Veterinary clinics dominate distribution channels, while pharmacies and drug stores are witnessing notable growth in delivering vaccine accessibility.
- Rising awareness about zoonotic diseases, coupled with advanced vaccine innovations, continues to drive demand and market expansion worldwide.
- North America leads the market, supported by high zoonotic disease prevalence and favorable compensation policies that encourage widespread vaccine uptake.
- Europe holds the second-largest share, driven by supportive government guidelines, pet insurance growth, and improved animal healthcare infrastructure.
Regional Analysis
North America accounted for the largest share of the global veterinary vaccines market, holding nearly 40%. The growth in this region is attributed to the rising dominance of zoonotic diseases and the availability of favorable compensation programs. Increased awareness among pet owners regarding preventive healthcare is further strengthening market penetration. The presence of advanced veterinary research centers, along with significant investment in animal health, continues to drive adoption. These factors position North America as a leading region in terms of both demand and revenue share.
Europe emerged as the second-largest market for veterinary vaccines during the review period. The region benefits from strong government guidelines and the widespread approval of pet insurance policies. Growth is also supported by an increasing number of veterinary clinics and the availability of advanced healthcare infrastructure across key countries. Rising companion animal ownership in nations such as Germany, France, and the United Kingdom strengthens vaccine uptake. These combined elements create favorable conditions for continued expansion in the European veterinary vaccines market.
The Asia–Pacific region is expected to experience the fastest growth over the forecast period. Rising disposable incomes are encouraging higher expenditure on veterinary services, while awareness of protective animal healthcare is also increasing. The region hosts a substantial cattle population, which generates consistent demand for livestock vaccination programs. Additionally, government initiatives to support animal health management are contributing to rising adoption levels. By contrast, Latin America and the Middle East & Africa are forecasted to show steady growth, driven primarily by rising pet adoption trends.
Segmentation Analysis
The global veterinary vaccines market is segmented into multiple product types, including live attenuated, inactivated, toxoid, recombinant, subunit, conjugate, and DNA vaccines. Conventional inactivated and live attenuated vaccines continue to account for a dominant share. However, recombinant vaccines are projected to expand at the fastest CAGR due to their efficacy, safety, potency, and purity. Manufacturers’ ability to produce advanced recombinant formulations at scale, combined with the immune system’s improved focus on significant antigens, positions this segment as the most promising growth driver during the forecast period.
Based on animal type, the market is categorized into porcine, poultry, livestock, companion animals, aquaculture, and others. Among these, the companion animal segment held the largest share and is projected to expand at a robust CAGR. The growth is driven by rising global pet ownership, increased animal adoption, and higher awareness among pet owners. Non-governmental organizations also support companion animal vaccination programs. Simultaneously, livestock vaccines are witnessing demand due to government restrictions on antibiotic use in animals intended for food, increasing reliance on immunization for safe animal-based products.
The market is also segmented by route of administration into oral, parenteral, and others. The parenteral segment, comprising intramuscular, subcutaneous, and intradermal vaccination, dominates revenue generation. It remains the most widely adopted and traditional mode of immunization, further strengthened by technological advancements in delivery devices. Although parenteral routes dominate, oral vaccines are gaining momentum in research and development, with a particular focus on mucosal vaccination approaches. These innovations are expected to support long-term diversification in administration methods, although parenteral routes will maintain leadership in the forecast period.
By disease indication, porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome accounted for the largest market share due to its high prevalence. Other important areas include avian influenza, rabies, coccidiosis, swine pneumonia, brucellosis, canine parvovirus, anaplasmosis, distemper, and foot and mouth disease. In terms of distribution channels, veterinary clinics captured the highest share, as vaccinations are usually conducted in small-scale settings. Veterinary hospitals accounted for the second-largest share, particularly in complex cases requiring advanced care. Pharmacies and drug stores also show growth potential, supported by rising online sales and institutional demand for veterinary vaccines worldwide.
Key Players Analysis
Eli Lilly and Company, Intervet Inc., and Elanco, Inc. are strengthening their global presence through regional expansions and new product launches. Strategic collaborations are being pursued to enhance competitiveness in the market. The focus is on expanding into emerging regions and consolidating operations in developed markets. Large enterprises are also supporting these strategies by investing in the capabilities of leading players. This approach is enabling them to gain resilience against market pressures and sustain a competitive edge in the animal health sector.
The market is witnessing a growing emphasis on inorganic strategies. A significant example is Elanco’s acquisition of Bayer’s Animal Health Division. This move has positioned Elanco to capture a larger share of revenue while consolidating its leadership. Such acquisitions are reshaping the competitive landscape by enabling companies to access advanced product portfolios and established distribution networks. These initiatives are expected to drive higher growth and improve profitability for leading companies while intensifying competition among industry participants.
Prominent players in the market include Merck & Co., Inc., Zoetis, Inc., Vetoquinol S.A., ADM Animal Nutrition, and Evonik Industries AG. These companies are actively engaged in technological advancements, nutritional innovations, and veterinary solutions. Their strategies focus on diversifying product offerings, ensuring supply chain efficiency, and addressing rising consumer demand for safe and sustainable animal health products. Continued innovation and investment in research and development are expected to secure strong growth prospects, while collaborations and partnerships are likely to strengthen global market reach.
Market Key Players
- Elanco Animal Health Incorporated
- Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
- HIPRA
- Merck& Co, Inc.
- Virbac
- Vetoqional S. A
- ADM Animal Nutrition
- Evonik Industries AG
- Zoetis Inc.
- MSD Animal Health
- Hester Biosciences Limited
- Ceva Logistics
- Neogen Corporation Limited
- Biogenesis Bago S A
- Kindered Biosciences, Inc.
- Bayer AG
- Indian Immunologicals Ltd
- Eli Lilly and Company
- Phibro Animal Health Corporation
- Other Key Players
Challenges in Veterinary Vaccines
High Development Costs and Long Timelines
Developing veterinary vaccines is an expensive and time-consuming process. Research and development require safety testing, efficacy studies, and multiple phases of clinical trials. In addition, manufacturers must secure regulatory approvals before a vaccine can enter the market. Each of these steps demands significant financial resources and scientific expertise. The long timelines also increase the risk of delays and higher costs. These challenges make it difficult for smaller firms to compete, leaving only large players with the capacity to invest. As a result, innovation in the veterinary vaccine sector often progresses slowly compared to other healthcare areas.
Regulatory Complexity
Veterinary vaccines must meet strict regulatory standards, which differ across regions and countries. This creates challenges for manufacturers aiming to launch products in multiple markets. Unlike human vaccines, where some harmonization exists, veterinary regulations remain fragmented. Limited global alignment often leads to lengthy approval procedures, delaying product launches and increasing costs. Companies must adapt to different compliance rules, testing methods, and documentation requirements. This complexity reduces efficiency and discourages rapid innovation. As a result, farmers and veterinarians in certain regions face limited access to advanced vaccines. Streamlined regulations and harmonized guidelines could help reduce delays and encourage wider adoption globally.
Cold Chain and Distribution Constraints
Many veterinary vaccines require refrigeration and temperature-controlled transport. This cold chain system is vital to preserve potency and effectiveness. However, ensuring strict temperature control is challenging in rural and resource-limited areas. Power shortages, inadequate storage, and weak logistics networks often disrupt the supply chain. As a result, vaccines lose effectiveness, leading to wastage and reduced coverage. Small-scale farmers are especially affected due to limited access to reliable distribution channels. These constraints slow down vaccination programs and reduce disease control effectiveness. Developing thermostable vaccines and investing in better infrastructure can help overcome this challenge and improve global vaccine accessibility.
Antigenic Variation and Emerging Diseases
Pathogens in animals evolve rapidly, often reducing the long-term effectiveness of vaccines. Viruses and bacteria can mutate, creating new strains that existing vaccines may not control. Zoonotic diseases, which spread between animals and humans, further increase the complexity. Emerging infections demand continuous monitoring and fast vaccine adaptation. However, development cycles are long, making it hard to respond quickly to new outbreaks. This constant antigenic variation forces companies to update vaccines more frequently, increasing costs and delays. Global surveillance systems and new vaccine technologies are essential to address these evolving threats and safeguard both animal and human health.
Limited Awareness and Adoption
In many developing regions, small-scale livestock farmers have limited awareness of vaccination benefits. Lack of education about disease prevention leads to low adoption rates. Cost is another major barrier, as farmers often prioritize immediate expenses over preventive healthcare. As a result, diseases spread more easily, causing economic losses and animal deaths. Limited access to veterinary services further worsens the problem. Awareness campaigns, training programs, and affordable vaccination schemes are needed to address this gap. Expanding outreach and support can increase adoption rates, improve herd health, and reduce long-term disease management costs in emerging markets.
Short Shelf Life and Stability Issues
Many veterinary vaccines have a short shelf life and degrade quickly. If not stored under ideal conditions, they lose potency, leading to wastage and higher costs. This makes it difficult for distributors and farmers to maintain a consistent supply. In regions with poor infrastructure, vaccines often expire before use. Stability issues also limit stockpiling, reducing the ability to respond quickly during outbreaks. Although research into thermostable vaccines is ongoing, adoption remains limited. More investment in vaccine stabilization technologies is required to reduce losses, ensure effective disease prevention, and improve global access to veterinary healthcare solutions.
Opportunities in Veterinary Vaccines
Rising Pet Ownership and Animal Health Awareness
The global rise in pet adoption, especially in urban areas, is fueling demand for companion animal vaccines. More people now view pets as family members, leading to higher spending on preventive care. Vaccines are seen as essential to protect pets from common diseases such as rabies, parvovirus, and distemper. Growing awareness of animal health has made pet owners more proactive. This focus on prevention, instead of treatment, is boosting vaccine uptake. As disposable incomes increase, more households are willing to invest in veterinary services, strengthening opportunities in the companion animal vaccine segment.
Expansion of the Livestock Industry
The livestock industry is growing rapidly due to rising demand for animal-derived food products such as meat, milk, and eggs. This growth increases the need to protect animals from contagious diseases. Vaccination plays a vital role in ensuring food safety and maintaining productivity. Governments worldwide are promoting immunization programs to safeguard national food supplies. Many regions are making livestock vaccination mandatory, particularly for diseases like foot-and-mouth disease. As consumption levels rise, the need for preventive healthcare solutions grows, creating opportunities for vaccine providers to expand their offerings in poultry, cattle, and swine vaccines.
Technological Advancements
Technology is transforming veterinary vaccines by improving safety, efficacy, and convenience. Recombinant, DNA, and vector-based vaccines are gaining popularity due to their ability to provide long-lasting immunity. These innovations reduce side effects and enhance targeted protection against specific pathogens. Diagnostic tools are also advancing, allowing quicker detection of diseases. Early diagnosis helps veterinarians design precise vaccination strategies. The use of biotechnology and nanotechnology in vaccine development is opening new possibilities. As research progresses, next-generation vaccines are expected to dominate the market, making innovation a key driver of growth in veterinary immunization.
Government and NGO Initiatives
Governments and non-governmental organizations are expanding vaccination programs to protect both animals and humans. Large-scale immunization drives against rabies, avian influenza, and foot-and-mouth disease are being launched in many countries. International organizations such as the OIE, FAO, and WHO are actively promoting veterinary vaccine adoption. Their campaigns aim to prevent disease outbreaks, safeguard food supplies, and reduce zoonotic risks. Subsidies and funding support are also increasing, making vaccines more affordable for farmers and pet owners. These initiatives are expected to boost vaccine coverage, driving market growth in both developed and developing regions.
Emerging Markets Growth
Emerging markets such as Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa offer vast potential for veterinary vaccines. These regions have large livestock populations and growing pet ownership. Rising investments in veterinary healthcare infrastructure are improving access to vaccines. Governments and private organizations are working together to expand animal health services. Increasing income levels in these regions are encouraging spending on both livestock and companion animal healthcare. While vaccination rates are still lower than in developed regions, rapid urbanization and awareness programs are bridging the gap. This creates strong growth opportunities for vaccine manufacturers and distributors.
One Health Approach
The One Health approach emphasizes the connection between human, animal, and environmental health. Zoonotic diseases like rabies, avian influenza, and brucellosis show the need for integrated solutions. Vaccination is a powerful tool to control these diseases and reduce cross-species transmission. Collaboration among governments, healthcare providers, and environmental agencies is increasing. Cross-sector partnerships are creating new opportunities for veterinary vaccine development and distribution. By preventing animal diseases, the spread to humans is reduced, improving global health security. This holistic approach strengthens the importance of veterinary vaccines in public health strategies worldwide.
Conclusion
The veterinary vaccines market is on a steady growth path, supported by rising awareness of zoonotic risks, stricter animal health regulations, and global initiatives like the One Health approach. Increasing demand for safe food production, expanding pet ownership, and government-driven vaccination campaigns are shaping the market’s long-term outlook. While high development costs, cold chain limits, and regulatory complexities remain challenges, opportunities lie in advanced technologies such as recombinant and DNA-based vaccines. Emerging economies and growing livestock industries are also creating new growth avenues. Overall, veterinary vaccines are positioned as a vital tool for safeguarding animal health, reducing disease spread, and strengthening global public health systems.
Get in Touch with Us:
Market.us (Powered By Prudour Pvt. Ltd.)
Address: 420 Lexington Avenue, Suite 300, New York City, NY 10170, United States.
Contact No: +1 718 874 1545 (International), +91 78878 22626 (Asia).
Email: [email protected]
View More
Veterinary Electrosurgery Market || Veterinary Software Market || Veterinary Supplements Market || Homeopathic Veterinary Medicines Market || Veterinary Medicine Market || Veterinary Oncology Market || Veterinary Microchips Market || Veterinary Surgical Instruments Market || Veterinary Services Market || Veterinary Drugs Market










