Global Rocket Propulsion Market Size, Share, Industry Analysis Report By Type (Rocket Motors, Rocket Engines), By Fuel Type (Solid Fuel, Liquid Fuel, Hybrid Fuel), By Orbit Type (Low Earth Orbit, Medium Earth Orbit, Geostationary Earth Orbit, Beyond Geosynchronous Earth Orbit), By Vehicle Type (Unmanned, Manned), By End-use (Defense & Civil, Commercial), By Region, Global Opportunity Analysis, Future Outlook and Industry Trends Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Sept. 2025
- Report ID: 158825
- Number of Pages: 375
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
- Rocket Propulsion Market size
- Key Insight Summary
- Market Overview
- Investment and Business Benefits
- By Type Analysis
- By Fuel Type Analysis
- By Orbit Type Analysis
- By Vehicle Type Analysis
- By End-Use Analysis
- Emerging Trends
- Growth Factors
- Regional Trends
- Key Market Segments
- Driver Analysis
- Restraint Analysis
- Opportunity Analysis
- Challenge Analysis
- Competitive Analysis
- Recent Developments
- Report Scope
Rocket Propulsion Market size
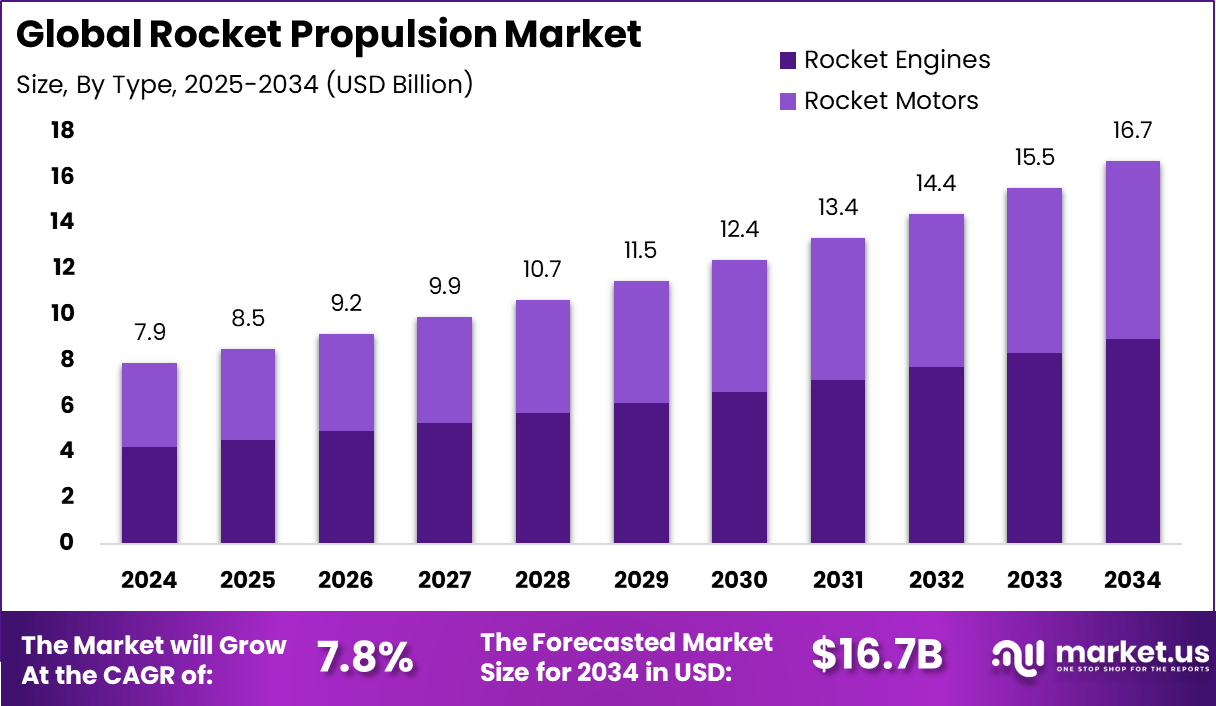
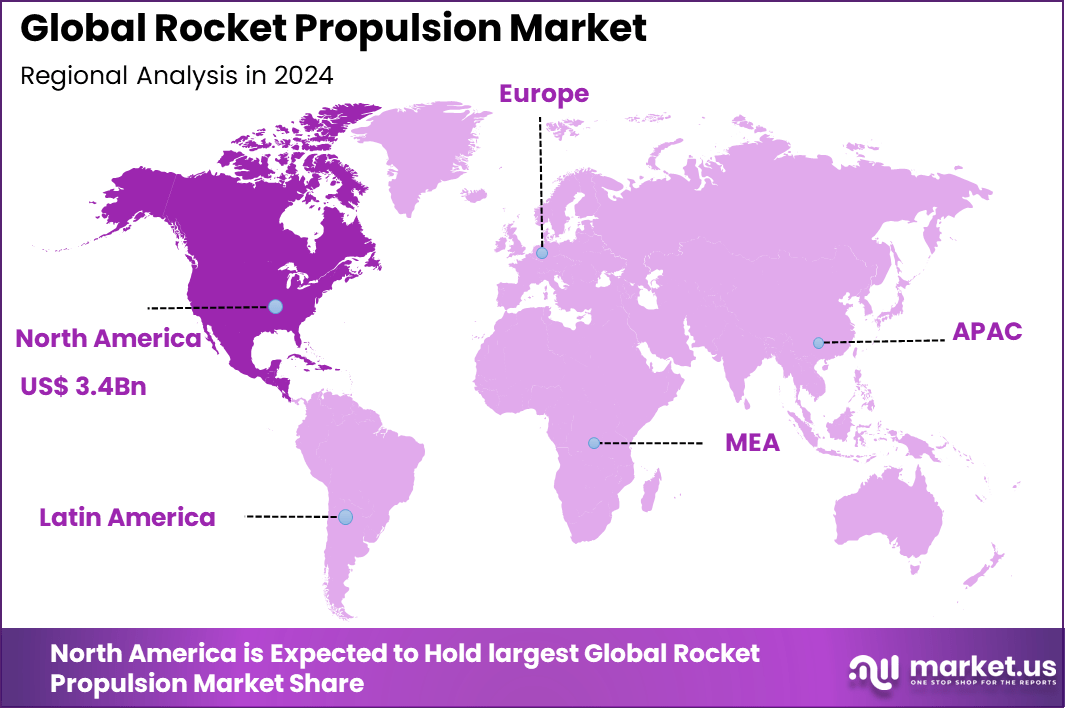
The Global Rocket Propulsion Market size is expected to be worth around USD 16.7 Billion By 2034, from USD 7.9 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 44.7% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North America held a dominan market position, capturing more than a 43.1% share, holding USD 3.4 Billion revenue.
The Rocket Propulsion Market refers to the industry involved in the design, development, production, and supply of propulsion systems that generate thrust to launch rockets, spacecraft, and missiles. These systems use chemical or non-chemical propellants to achieve motion and are critical for space exploration, satellite deployment, defense applications, and commercial spaceflight.
Key Insight Summary
- By type, Rocket Engines led the market with a 53.6% share.
- By fuel type, Liquid Fuel dominated, capturing 47.5% share.
- By orbit type, Low Earth Orbit (LEO) commanded around 42.7% share.
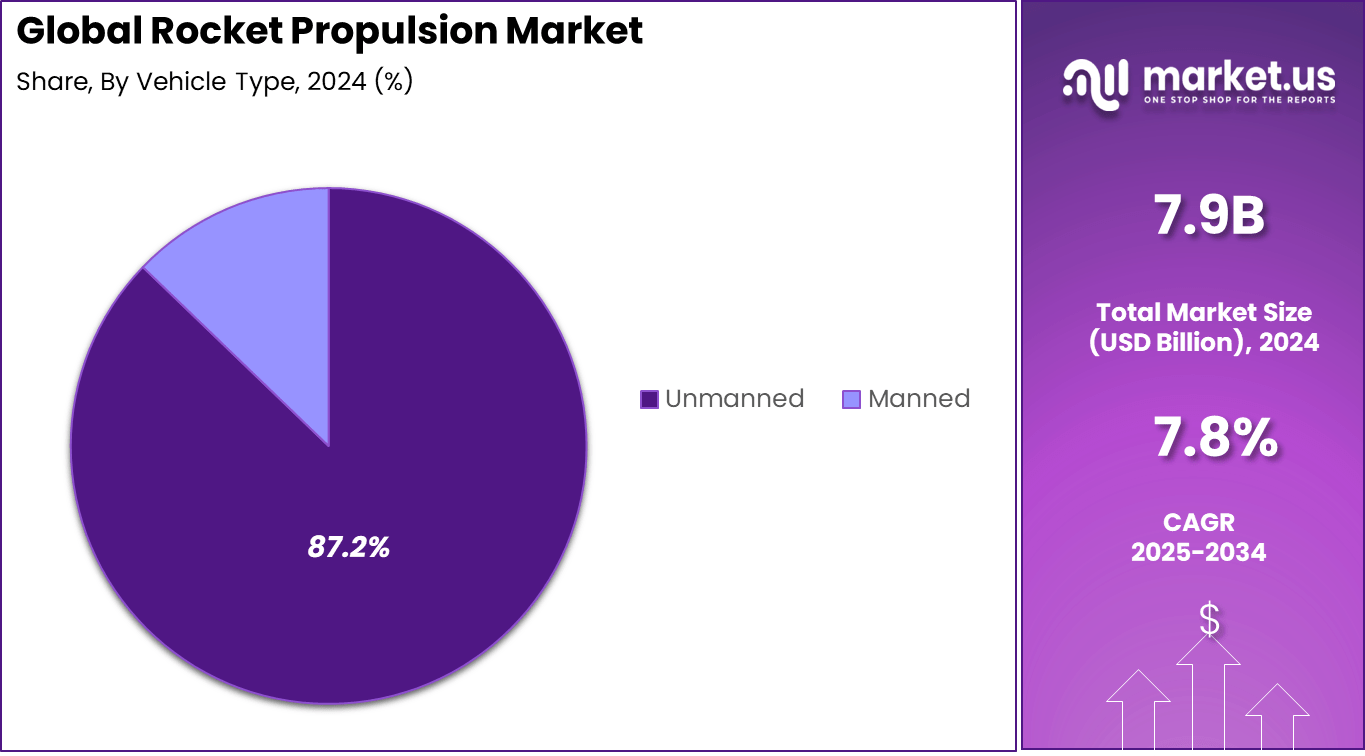
- By vehicle type, the Unmanned segment was the clear leader with 87.2% share.
- By end use, the Commercial segment held the dominant position.
- Regionally, North America accounted for 43.1%, supported by strong space investments and private sector growth.
Market Overview
The market includes liquid, solid, hybrid, and electric propulsion technologies, as well as supporting components such as engines, thrusters, and fuel systems. The growth of the rocket propulsion market is driven by rising private investments in space exploration, more satellite launches, higher defense budgets, advances in propulsion technology, and growing interest in space tourism, supported by government initiatives and public-private collaborations.
Top driving factors in the rocket propulsion market include the surge in satellite launches and space exploration missions. The number of satellites launched globally increased by over 20% in recent years, fueling demand for reliable and efficient propulsion systems. Government spending on defense and space programs, coupled with private sector investments in commercial space ventures, also propels market growth.
Demand is strong in the satellite launch sector, where propulsion systems are essential for placing payloads into orbit. National defense organizations are significant consumers, using rocket propulsion for tactical and strategic missile systems. Space agencies and private companies are increasing demand for propulsion in crewed and uncrewed missions to the moon, Mars, and beyond. Commercial demand is growing in space tourism and private satellite constellations.
Investment and Business Benefits
Investment opportunities abound in the development of next-generation propulsion systems, manufacturing innovations like 3D printing, and partnerships between private companies and government agencies. The private sector’s growing role in space launch services offers venture capital and strategic investment potential.
Emerging economies investing in indigenous space programs also present new markets for propulsion technology providers. Focus areas include reusable engines, electric propulsion, and hybrid green fuel systems, which promise scalability and cost advantages for diverse applications from satellite constellations to interplanetary missions.
Business benefits associated with advanced rocket propulsion include improved operational efficiency, reduced launch costs, enhanced mission success rates, and the ability to support a wide range of applications from defense to commercial space activities. Companies gain competitive advantages by innovating in propulsion materials, fuel efficiency, and engine reusability.
By Type Analysis
In 2024, Rocket engines dominate the rocket propulsion market, commanding a significant 53.6% share. This high share reflects the critical role rocket engines play in providing the thrust necessary for launch vehicles and space missions. Their robust performance, reliability under extreme conditions, and ability to generate high thrust make them essential components in almost all modern propulsion systems.
In addition to their power, rocket engines benefit from continuous technological improvements that enhance fuel efficiency and control. These developments help extend mission capabilities while supporting a wide range of applications, from satellite launches to exploration missions. The dominance of rocket engines signifies their central place in advancing space technology and maintaining reliable access to orbits.
By Fuel Type Analysis
In 2024, Liquid fuel propulsion leads the market with a 47.5% share. Liquid fuel engines offer advantages in efficiency, thrust control, and restart capability, which are crucial for complex space missions. Their specific impulse tends to be higher, meaning they can deliver more thrust per unit of fuel, making them suitable for both orbital and deep-space applications.
Liquid fuel systems also provide flexibility in mission design, enabling maneuvers and adjustments during flight. These engines are widely used in launch vehicles and upper stages, as they offer precise control that solid fuels cannot. Their important role in commercial, military, and scientific missions underscores their market leadership.
By Orbit Type Analysis
In 2024, Low Earth Orbit (LEO) holds approximately 42.7% of the market share in orbit types. LEO is favored due to its accessibility and relevance for a variety of satellite missions, including Earth observation, communication, and scientific research. The relatively lower energy required to reach LEO compared to higher orbits makes it the primary target for many satellite launches.
The high demand for constellations of small satellites for internet coverage and data collection is expanding LEO’s share further. Additionally, missions focused on quick data relay or those requiring frequent revisit times typically operate in LEO, reinforcing its dominance. The orbit’s strategic importance reflects ongoing trends in satellite deployment and space utility.
By Vehicle Type Analysis
In 2024, the unmanned vehicle segment overwhelmingly leads with an 87.2% share. Unmanned rockets and spacecraft dominate the market as they drive the majority of satellite launches, cargo delivery missions, and exploratory missions. The ability to operate without crew reduces risks and costs, making unmanned vehicles the preferred choice for most current space activities.
Automation and remote operation advances have made unmanned vehicles more reliable and capable, enabling longer missions and complex operations without human intervention. This dominance also ties closely to expanding satellite networks and commercial space activities, which primarily use unmanned launch systems to deploy payloads efficiently.
By End-Use Analysis
In 2024, the commercial segment leads demand for rocket propulsion across markets. Commercial activities such as satellite deployment for communications, broadcasting, and internet services drive the need for advanced propulsion technologies. Growing investments from private space companies are creating a broader market outlook focused on cost efficiency and reliable launch solutions.
Commercial propulsion applications benefit from innovations aimed at reusability and faster turnaround times. These trends support the increasing frequency of launches, especially for satellite constellations meant to enhance global connectivity. The expanding commercial sector is pushing the rocket propulsion industry toward new performance and economic benchmarks.
Emerging Trends
Emerging trends in rocket propulsion include the rise of reusable engines, hybrid propulsion systems, and the integration of electric propulsion for satellite and deep-space missions. The adoption of 3D printing technology is accelerating manufacturing cycles while reducing costs of rocket components. There is growing interest in eco-friendly “green” propellants as part of efforts to improve environmental sustainability.
Additionally, AI-based autonomous control systems are becoming more common for in-flight adjustments, enhancing mission reliability and precision. Expansion toward lunar and Mars exploration is driving demand for propulsion systems capable of prolonged and adaptive thrust in space. These trends highlight a broader shift toward systems designed for multi-mission flexibility and operational efficiency.
Growth Factors
Growth factors supporting the rocket propulsion market include increased satellite launch frequency, expanded government space exploration budgets, and commercial demand for rapid and reliable space access. Defense modernization programs are another major driver, with investments aimed at enhancing tactical missile propulsion and precision strike capabilities.
The global push for reusable rocket technologies is also significant, lowering operational costs and increasing launch cadence. Moreover, improvements in liquid fuel technology such as cryogenic and methane-based propellants are enabling safer and more efficient long-duration missions. The overall growth is underpinned by better materials, advanced manufacturing techniques, and broader adoption of AI in design and operations.
Regional Trends
North America Market Trends
In 2024, North America holds a commanding 43.1% market share, driven by high government spending, a strong aerospace industry, and significant commercial space activity. The presence of numerous space agencies and private enterprises fosters innovation and steady demand for advanced propulsion systems.
The region leads in the development of liquid fuel rocket engines, electric propulsion systems, and hybrid solutions. Focus on deep-space missions and satellite constellations continues to support growth, with a well-established supply chain and advanced manufacturing infrastructure further reinforcing North America’s dominance.
Europe Market Trends
Europe is experiencing consistent growth in rocket propulsion, with a CAGR around 10% projected for the upcoming years. Governments across the region are investing in satellite launches, exploration missions, and defense applications, expanding the propulsion market steadily.
European propulsion development emphasizes sustainability and efficiency, with electric propulsion and green fuels gaining attention. Collaborative projects across countries strengthen technological advances, while initiatives supporting the private space sector add momentum.
Asia Pacific Market Trends
Asia Pacific is a rapidly growing market, with an estimated CAGR of 13.5%. Increasing governmental space budgets, especially in China, India, Japan, and South Korea, are driving demand for propulsion technologies. These countries are launching more satellites for communication, defense, and research purposes.
The region benefits from scaling manufacturing capabilities and expanding commercial space activities. Close government-industry collaboration accelerates innovation, and the focus on satellite constellation deployments enhances the need for reliable, efficient rocket propulsion systems.
Latin America Market Trends
Latin America holds a smaller but growing share, with growth projected at a CAGR of about 10.9%. Brazil, Argentina, and Mexico lead government-led space program investments, primarily focused on Earth observation and satellite communication.
Emerging commercial interest in space technologies and regional collaborations adds to the market potential. The push for domestic propulsion technology development and increasing satellite projects within the region are important factors shaping growth.
Key Market Segments
By Type
- Rocket Motors
- Rocket Engines
By Fuel Type
- Solid Fuel
- Liquid Fuel
- Hybrid Fuel
By Orbit Type
- Low Earth Or Medium Earth Orbit
- Geostationary Earth Orbit
- Beyond Geosynchronous Earth Orbit
By Vehicle Type
- Unmanned
- Manned
By End-use
- Defense & Civil
- Commercial
Regional Analysis and Coverage
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherlands
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of Latin America
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Driver Analysis
Rising Demand for Satellite Launches and Space Missions
The increasing number of satellite launches and space exploration missions is a key factor driving growth in the rocket propulsion market. Governments and private companies are investing heavily to support communications, Earth observation, and deep space exploration.
For instance, expanding deployment of low-earth orbit satellite constellations requires reliable propulsion systems to maintain orbits and enable maneuvering, which elevates demand for advanced propulsion technologies. This growing launch activity enhances the need for both liquid and solid propulsion engines tailored to diverse mission profiles.
Such increased activity is also reflected in rising government budgets and commercial investments in space ventures. The trend toward reusable rocket systems adds another boost by reducing costs and encouraging more frequent launches. In my view, this driver will continue to push market expansion as new space initiatives emerge globally, highlighting rocket propulsion as fundamental to satellite deployment and exploration progress.
Restraint Analysis
High Development and Operational Costs
The considerable financial investment required to develop and operate rocket propulsion systems acts as a major market restraint. Designing reliable engines, especially for reusable launch systems, involves advanced materials, precision engineering, and rigorous testing that translates into high upfront costs.
For example, the cost of launching using reusable rockets can still be significant despite reductions compared to older models, affecting the barriers to entry for smaller players and some national programs. Additionally, political factors and supply chain disruptions can inflate costs further, complicating market growth.
The complexity and safety demands of propulsion technology mean ongoing maintenance and innovation expenses also weigh heavily. Hence, despite rising demand, these economic and technical costs slow wider adoption, especially in emerging space nations or startups without robust funding.
Opportunity Analysis
Expansion of Commercial Space Ventures
The rise of private space companies and commercial space tourism opens significant opportunities for the rocket propulsion market. New business models centered on lunar missions, asteroid mining, and satellite internet constellations require scalable and efficient propulsion systems.
For instance, advances in reusable liquid propulsion and hybrid engines support more affordable, rapid launch cycles that cater to this growing sector. Emerging economies investing in local space capabilities also present fresh opportunities for propulsion technology providers through partnerships and technology transfers.
The maturing space tourism industry exemplifies an additional growth area, where propulsion innovation can reduce operational costs and increase safety for commercial orbital flights. Overall, this expanding commercial space economy diversifies demand beyond traditional government programs, driving long-term market growth.
Challenge Analysis
Stringent Safety and Regulatory Requirements
trict safety standards and regulatory oversight form a significant challenge for the rocket propulsion market. Given the high risks associated with rocket launches, propulsion systems must undergo exhaustive testing, certification, and compliance processes to meet national and international guidelines. This complexity adds time delays and cost pressures to development and deployment.
For example, technologies such as new propellants or reusable engines face rigorous evaluation to ensure mission and environmental safety before commercial use. These challenges can limit the pace of innovation and raise entry barriers, particularly for newcomers lacking experience or resources to navigate complex regulatory landscapes.
Competitive Analysis
In the rocket propulsion market, SpaceX and Blue Origin are key disruptors, driving innovation with reusable rocket technologies and cost-efficient propulsion systems. Their advancements have reshaped the commercial space sector by lowering launch costs and enabling more frequent missions.
Traditional aerospace giants such as Lockheed Martin, The Boeing Company, and Airbus Defence and Space remain influential with their extensive expertise in propulsion technologies for defense and commercial applications. Their strong relationships with government agencies and space programs allow them to secure long-term contracts.
Asian players including Korea Aerospace Industries and Hanwha Aerospace add to the competitive landscape with growing investments in domestic space programs. Their focus on developing indigenous propulsion technologies aligns with regional ambitions to strengthen space capabilities.
Top Key Players in the Market
- SpaceX.
- Blue Origin
- Lockheed Martin
- Airbus Defence and Space
- Korea Aerospace Industries.
- Hanwha Aerospace
- The Boeing Company
- Others
Recent Developments
- In August 2025, SpaceX successfully launched its Super Heavy-Starship rocket (Flight 10), marking a critical test flight for the fully reusable launch system. This launch used the latest generation of Raptor engines fueled by sub-cooled liquid methane and liquid oxygen, underscoring ongoing propulsion innovation.
- In January 2025, Blue Origin achieved orbit with its New Glenn rocket’s first launch, powered by BE-4 engines, a liquid oxygen/liquefied natural gas rocket engine delivering 2,400 kN thrust. This was a milestone after over a decade of development effort.
- In January 2024, RocketStar, Inc. raised USD 2 million in seed funding to acquire Miles Space, Inc., a spacecraft and propulsion manufacturer developing an advanced electric thruster and a nuclear-fusion enhanced version. The deal expands RocketStar’s focus on fusion propulsion, aeronautics, and deep space communications through Miles Space’s digital signal processing software and passive radar expertise.
- In 2024, L3Harris Technologies launched a modernization program for Aerojet Rocketdyne’s propulsion facilities under a U.S. Department of Defense contract awarded in April. The upgrades targeted production sites in Arkansas, Alabama, and Virginia, enhancing efficiency and advancing rocket propulsion manufacturing in line with Pentagon defense goals.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 7.9 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 16.7 Bn CAGR(2025-2034) 7.8% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue forecast, AI impact on Market trends, Share Insights, Company ranking, competitive landscape, Recent Developments, Market Dynamics and Emerging Trends Segments Covered By Type (Rocket Motors, Rocket Engines), By Fuel Type (Solid Fuel, Liquid Fuel, Hybrid Fuel), By Orbit Type (Low Earth Orbit, Medium Earth Orbit, Geostationary Earth Orbit, Beyond Geosynchronous Earth Orbit), By Vehicle Type (Unmanned, Manned), By End-use (Defense & Civil, Commercial) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of Latin America; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape SpaceX, Blue Origin, Lockheed Martin, Airbus Defence and Space, Korea Aerospace Industries, Hanwha Aerospace, The Boeing Company, Others Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three license to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- SpaceX.
- Blue Origin
- Lockheed Martin
- Airbus Defence and Space
- Korea Aerospace Industries.
- Hanwha Aerospace
- The Boeing Company
- Others










