Global Liver Cancer Drugs Market By Drug Class (Targeted Therapy, Immunotherapy, Chemotherapy and Others), By Cancer Type (Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC), Cholangiocarcinoma, Hepatoblastoma and Others), By Route of Administration (Oral and Injectable), By Distribution Channel (Hospital Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies, and Online Pharmacies), Region and Companies – Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Aug 2025
- Report ID: 43471
- Number of Pages: 394
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
- Report Overview
- Key Takeaways
- Drug Class Analysis
- Cancer Type Analysis
- Route of Administration Analysis
- Distribution Channel Analysis
- Key Market Segments
- Drivers
- Restraints
- Opportunities
- Impact of Macroeconomic / Geopolitical Factors
- Latest Trends
- Regional Analysis
- Key Players Analysis
- Recent Developments
- Report Scope
Report Overview
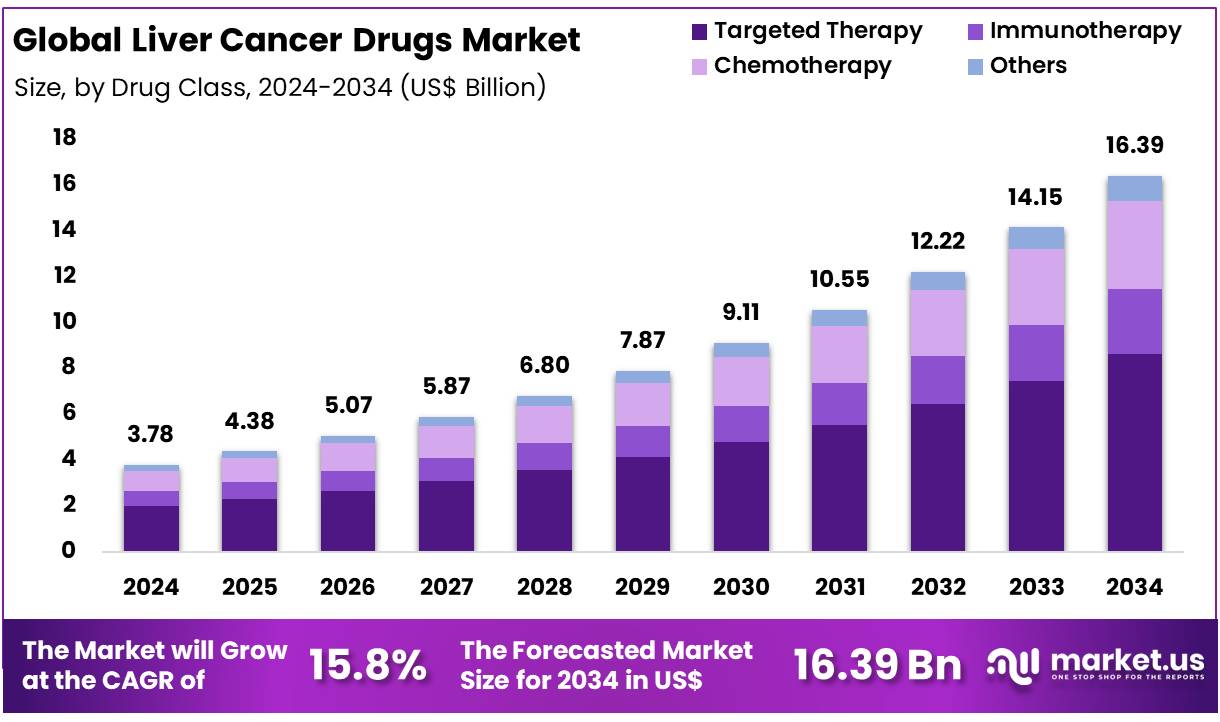
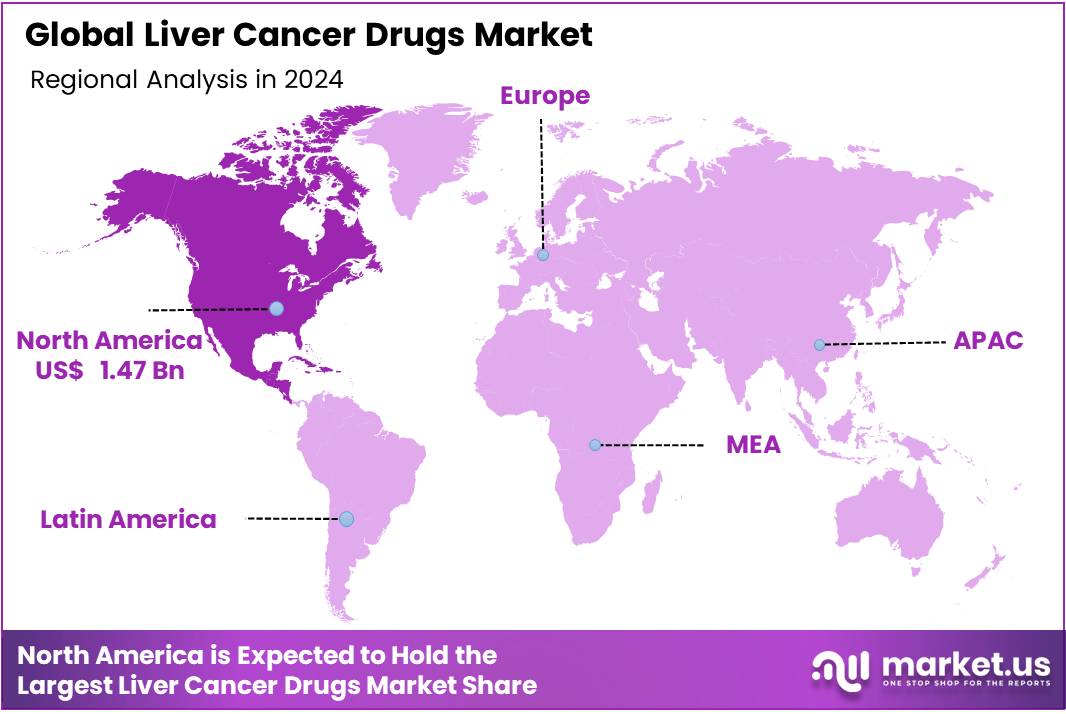
Global Liver Cancer Drugs Market size is expected to be worth around US$ 16.39 Billion by 2034 from US$ 3.78 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 15.8% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North America led the market, achieving over 38.8% share with a revenue of US$ 1.47 Billion.
The liver cancer drugs market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing prevalence of liver cancer worldwide. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common form of liver cancer, is largely caused by risk factors such as chronic hepatitis B and C, alcohol consumption, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
With over 800,000 new cases diagnosed annually, the demand for effective treatments continues to rise. The market is dominated by targeted therapies like sorafenib (Nexavar) and lenvatinib (Lenvima), as well as immunotherapies such as nivolumab (Opdivo) and pembrolizumab (Keytruda), which have significantly improved survival rates for patients with advanced liver cancer. The growth of the market is further supported by ongoing research into innovative drug combinations and novel treatment modalities, such as personalized medicine and combination therapies.
However, the high cost of treatments remains a key challenge, limiting access for patients in low- and middle-income countries. Despite this, the development of biosimilars and generic versions of existing drugs is expected to ease cost burdens in the coming years. As healthcare systems globally improve and more patients gain access to modern therapies, the liver cancer drugs market is projected to continue expanding, with an increasing focus on improving patient outcomes through more targeted and efficient treatment strategies.
Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved a number of drugs for liver cancer, below is the list:
Atezolizumab Used with bevacizumab as a first-line treatment for advanced or unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Atezolizumab and Hyaluronidase-tqjs Subcutaneous formulation used with bevacizumab for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in patients not previously treated systemically. Avastin (Bevacizumab) Given with atezolizumab for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma as initial therapy. Bevacizumab Used in combination with atezolizumab for unresectable or metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma. Cabometyx (Cabozantinib-S-Malate) Approved for second-line treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Cabozantinib-S-Malate Used alone for previously treated advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Cyramza (Ramucirumab) For advanced hepatocellular carcinoma, particularly with high AFP levels. Durvalumab Used alone or with tremelimumab for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Futibatinib For unresectable or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma with FGFR2 fusion/rearrangement. Imfinzi (Durvalumab) Monotherapy or combined with tremelimumab for advanced liver cancer. Imjudo (Tremelimumab-actl) Combined with durvalumab for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Ipilimumab Investigated for use in advanced liver cancer, often with nivolumab. Keytruda (Pembrolizumab) Used for previously treated advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Lenvatinib Mesylate Approved for first-line treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Lenvima (Lenvatinib Mesylate) First-line therapy for advanced/unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Lytgobi (Futibatinib) For FGFR2 fusion-positive intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Nexavar (Sorafenib Tosylate) First oral treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Nivolumab Used for previously treated advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Nivolumab and Hyaluronidase-nvhy Subcutaneous nivolumab formulation for cancer therapy. Opdivo (Nivolumab) Immunotherapy option for previously treated advanced liver cancer. Opdivo Qvantig (Nivolumab and Hyaluronidase-nvhy) Subcutaneous version of nivolumab for liver cancer. Pemazyre (Pemigatinib) For advanced cholangiocarcinoma with FGFR2 fusion/rearrangement. Pembrolizumab Used in advanced or previously treated hepatocellular carcinoma. Pemigatinib Targeted therapy for cholangiocarcinoma with FGFR2 fusion. Ramucirumab For advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with elevated AFP. Regorafenib Second-line oral therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Sorafenib Tosylate Approved for first-line advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Stivarga (Regorafenib) For patients with hepatocellular carcinoma previously treated with sorafenib. Tecentriq (Atezolizumab) Used with bevacizumab for advanced or unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Tecentriq Hybreza (Atezolizumab and Hyaluronidase-tqjs) Subcutaneous combo used with bevacizumab for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Tremelimumab-actl Used with durvalumab for advanced liver cancer. Yervoy (Ipilimumab) Investigated with nivolumab for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. The market for liver cancer treatments has been driven by the development of novel therapies, such as targeted therapies, immunotherapies, chemotherapy, and combination therapies.
These innovations have significantly improved survival rates and enhanced patients’ quality of life. Furthermore, growing awareness of the importance of early detection and diagnosis has encouraged more patients to seek treatment in the earlier stages of the disease.
Key Takeaways
- In 2024, the market for Liver Cancer Drugs generated a revenue of US$ 3.78 Billion, with a CAGR of 15.8%, and is expected to reach US$ 16.39 billion by the year 2034.
- The Drug Class segment is divided into Targeted Therapy, Immunotherapy, Chemotherapy, and Others with Targeted Therapy taking the lead in 2024 with a market share of 52.6%.
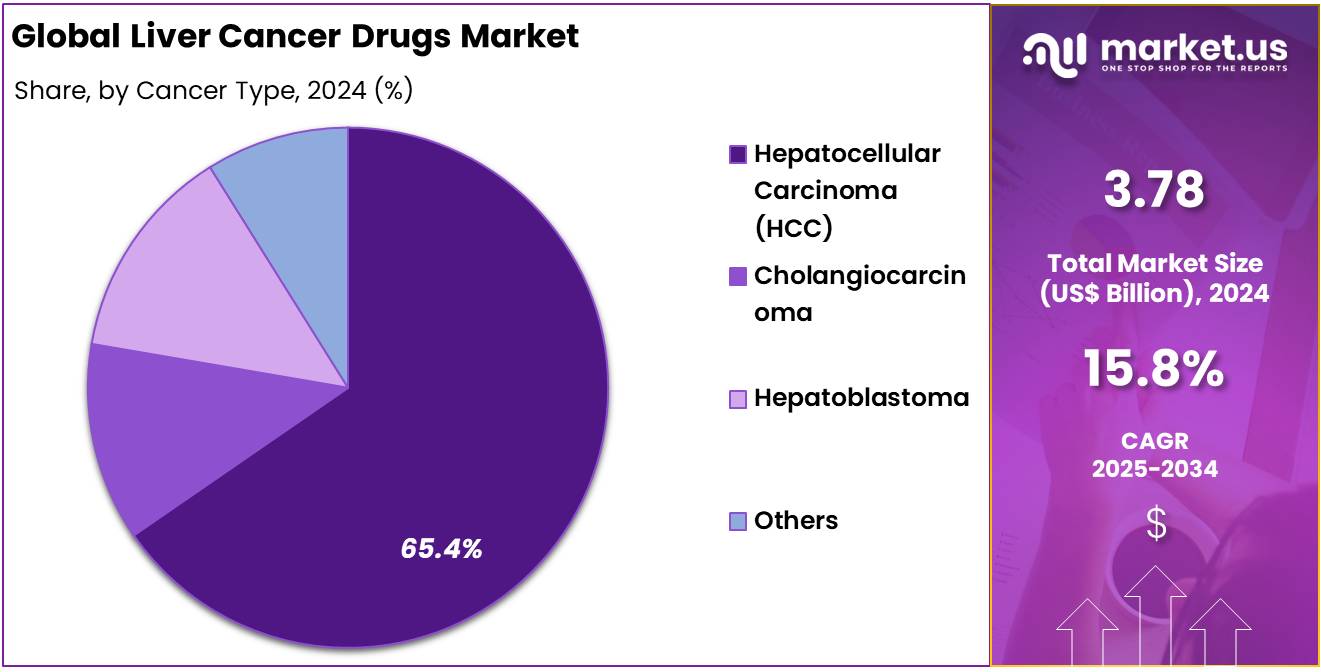
- By Cancer Type, the market is bifurcated into Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC), Cholangiocarcinoma, Hepatoblastoma, and Others, with Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) leading the market with 65.4% of market share in 2024.
- Considering the Route of Administration segment, the market is bifurcated into Oral and Injectable, with Oral taking the lead in 2024 with 63.3% market share.
- By Distribution Channel, the market is classified into Hospital Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies, and Online Pharmacies with Hospital Pharmacies taking the lead in 2024 with 58.2% market share.
- North America led the market by securing a market share of 38.8% in 2024.
Drug Class Analysis
In the liver cancer drugs market, Targeted Therapy is the dominating segment accounting for 52.6% makret share in 2024. Targeted therapies have revolutionized liver cancer treatment by specifically targeting cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissue. This precision in treatment has led to significant improvements in survival rates, especially in advanced stages of liver cancer. Drugs like Sorafenib (Nexavar), Regorafenib (Stivarga), and Lenvatinib (Lenvima) are prime examples of targeted therapies that block the growth and spread of cancer cells by inhibiting specific molecules involved in tumor growth.
These therapies are often the first line of treatment for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). For instance, in October 2022, AstraZeneca’s Imjudo (tremelimumab) in combination with Imfinzi (durvalumab) has received approval in the US for treating adult patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common form of liver cancer. The combination therapy follows a novel dosing and scheduling regimen called STRIDE (Single Tremelimumab Regular Interval Durvalumab). This regimen involves a single 300mg dose of the anti-CTLA-4 antibody Imjudo, paired with a 1500mg dose of the anti-PD-L1 antibody Imfinzi, followed by continued Imfinzi administration every four weeks.
While Immunotherapy and Chemotherapy also play vital roles in treatment, they are less widely used as first-line options compared to targeted therapy. Immunotherapies like Nivolumab (Opdivo) and Pembrolizumab (Keytruda) work by boosting the body’s immune system to fight cancer, while Chemotherapy drugs like Cisplatin and Gemcitabine are often employed for liver cancer in combination therapies or when targeted therapies are ineffective. The targeted therapy segment is expected to maintain its dominance due to its efficacy and focus on personalized medicine, offering improved clinical outcomes for liver cancer patients.
Cancer Type Analysis
Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) is the dominant cancer type which accounted for 65.4% market share. HCC accounts for approximately 75-85% of all liver cancer cases and is the most common form of liver cancer globally. The high prevalence of HCC, driven by risk factors such as chronic hepatitis B and C, alcohol consumption, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), makes it the primary focus of liver cancer drug development. Drugs like Sorafenib (Nexavar), Lenvatinib (Lenvima), and Atezolizumab (Tecentriq), often used in combination with other therapies, are widely used for treating advanced HCC, leading the market in terms of sales and clinical adoption.
According to NCBI, Hepatocellular carcinoma constitutes more than 90% of the primary tumor of the liver. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is currently the fifth most prevalent cancer globally. In 2018, nearly 841,000 new cases of HCC were diagnosed. It ranks as the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in men, following lung cancer, with 780,000 deaths attributed to HCC in 2018. The incidence of HCC is three times higher in men compared to women. Over 80% of new HCC cases are reported in developing regions, including Sub-Saharan Africa, Southeast Asia, and China, where hepatitis B virus infections are widespread and contribute to the high burden of the disease.
While Cholangiocarcinoma, a cancer of the bile ducts, and Hepatoblastoma, a rare liver cancer primarily affecting children, contribute to the overall market, they have a smaller share compared to HCC. Cholangiocarcinoma has a more limited treatment landscape with fewer FDA-approved drugs, while Hepatoblastoma treatments are typically focused on chemotherapy and surgical options. However, ongoing research and clinical trials are working to expand treatment options for these less common liver cancers.
Route of Administration Analysis
In the liver cancer drugs market, Oral administration is the dominant route of delivery with 63.3% market share. Oral drugs offer significant advantages, including ease of use, convenience for patients, and the ability to be taken at home, which improves patient compliance and overall treatment experience. Drugs like Sorafenib (Nexavar) and Lenvatinib (Lenvima) are commonly prescribed in oral form for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), making them the preferred choice for many patients with advanced liver cancer. The growing preference for oral therapies is expected to continue as they reduce the need for hospital visits and intravenous injections, thus lowering the overall cost of treatment.
Injectable drugs, on the other hand, also play a vital role, especially for immunotherapies and combination therapies. Drugs like Nivolumab (Opdivo) and Pembrolizumab (Keytruda) are administered via intravenous injections and are used in the treatment of advanced liver cancer, particularly when oral therapies are ineffective. While injectables generally offer potent effects, they require administration in a clinical setting, which can limit patient convenience. Despite this, the injectable segment remains essential for certain types of treatment and advanced stages of liver cancer.
Distribution Channel Analysis
In the liver cancer drugs market, Hospital Pharmacies dominated the distribution channel segment with 58.2% market share. These pharmacies are typically the primary point of access for liver cancer drugs due to the specialized nature of the treatments and the need for professional medical oversight. Many of the drugs used in liver cancer treatment, such as Sorafenib (Nexavar) and Lenvatinib (Lenvima), require close monitoring due to potential side effects and the complexity of the disease. Hospital pharmacies provide a controlled environment for drug administration, making them a crucial distribution channel for both oral and injectable therapies. Additionally, hospitals are the primary setting for patients undergoing intensive treatments, including chemotherapy and immunotherapy.
Retail Pharmacies also play a significant role, especially for patients who require long-term medication or follow-up treatments. Oral drugs like Sorafenib (Nexavar), which can be taken at home, are often available in retail pharmacies, offering greater convenience to patients who do not need immediate clinical supervision.
In February 2025, Pharmac announced funding for medicines targeting liver, ovarian, and neuroendocrine cancers. Starting 1 March 2025, individuals with these cancers will have access to additional treatment options. Pharmac will fund the following medications:
- Atezolizumab and bevacizumab for unresectable liver cancer.
- Bevacizumab for advanced ovarian cancer.
- Lanreotide for neuroendocrine cancers, bowel blockages caused by cancer, and the growth disorder acromegaly.
Key Market Segments
By Drug Class
- Targeted Therapy
- Immunotherapy
- Chemotherapy
- Others
By Cancer Type
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
- Cholangiocarcinoma
- Hepatoblastoma
- Others
By Route of Administration
- Oral
- Injectable
By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies
Drivers
Increasing Incidence of Liver Cancer
The rising global incidence of liver cancer is a significant driver for the liver cancer drugs market. As the prevalence of risk factors such as hepatitis B and C, alcohol consumption, and obesity continues to grow, liver cancer cases are on the rise, particularly in regions like Asia-Pacific. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), liver cancer is the sixth most common cancer worldwide, with over 800,000 new cases annually. This increased incidence boosts the demand for effective treatments, creating substantial growth opportunities for pharmaceutical companies.
For example, drugs like sorafenib (Nexavar) and lenvatinib (Lenvima) are currently leading treatments, and their market success is driven by the growing number of liver cancer patients seeking innovative therapies. According to World Cancer Research Fund, there were 866,136 new cases of liver cancer in 2022.
Liver cancer incidence (cases), 2022
Rank Country New cases Age-standardised rates (ASR) /100,000 World 8,66,136 8.6 1 China 3,67,657 15 2 US 43,492 6.8 3 Japan 41,388 9.2 4 India 38,703 2.7 5 Egypt 27,946 32 6 Thailand 27,936 22.7 7 Vietnam 24,502 20.2 8 Indonesia 23,805 8 9 South Korea 14,791 13.7 10 Brazil 13,599 4.5 Restraints
High Treatment Costs
Despite advancements in liver cancer drug development, the high cost of treatment remains a major restraint. New therapies, particularly immunotherapies and targeted treatments, can cost tens of thousands of dollars per treatment cycle, which may be prohibitive for patients in lower-income regions or countries with less developed healthcare systems. For instance, sorafenib, a standard treatment, can cost up to USD 10,000 per month in some markets. These high treatment costs limit patient access to essential medications, affecting market growth and widening healthcare inequality.
For instance, below are the key components of a patient going through different liver cancer treatment regimes and their estimated costs:
Type/Staging Typical Cost Range (USD) Diagnosis (CT, blood) $500–$5,000 Minimally invasive Tx $30,000 Stage I $30,000–$50,000 Stage II $50,000–$100,000 Stage IV $200,000+ Annual average care ~$134,000–$150,000 Liver transplant $579,000–$800,000 Chemotherapy drugs $579–$100,000 (varies greatly) Diagnosis (CT, blood) $500–$5,000 Opportunities
Advancements in Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy presents a promising opportunity for growth in the liver cancer drugs market. With the approval of immuno-oncology drugs like nivolumab (Opdivo) and pembrolizumab (Keytruda) for liver cancer, immunotherapy has revolutionized treatment by harnessing the body’s immune system to target cancer cells. This class of drugs offers significant potential to improve survival rates for patients with advanced liver cancer. As research continues, novel immunotherapy combinations, such as combining immune checkpoint inhibitors with other therapies, are expected to further expand the treatment landscape and provide new avenues for market growth.
In January 2025, researchers at Mount Sinai made a significant breakthrough in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Their Phase 3 study, titled “LEAP-012: Transarterial Chemoembolization Combined with Lenvatinib Plus Pembrolizumab Versus Dual Placebo for Unresectable, Non-Metastatic Hepatocellular Carcinoma,” was published in The Lancet. This study presents promising results in improving the treatment outcomes for patients with unresectable, non-metastatic HCC.
Impact of Macroeconomic / Geopolitical Factors
Economic downturns can lead to reduced healthcare spending, impacting the affordability and availability of liver cancer treatments. For instance, during the 2008 financial crisis, many countries faced budget cuts in healthcare, leading to delays in the procurement of essential cancer medications. Variations in currency exchange rates can affect the cost of importing raw materials and exporting finished drugs. A stronger domestic currency can make exports more expensive, potentially reducing the competitiveness of liver cancer drugs in international markets.
Trade tensions can lead to the imposition of tariffs on pharmaceutical products. For example, the U.S.-China trade war resulted in China imposing tariffs up to 125% on U.S.-made drugs, including cancer medications. This increased the cost of these drugs in China, affecting their accessibility to patients. Geopolitical conflicts can lead to sanctions that hinder the approval and distribution of liver cancer drugs. For instance, sanctions on countries like Iran have delayed the availability of certain cancer therapies, impacting patient outcomes.
These macroeconomic and geopolitical factors underscore the complexities in the global liver cancer drug market, highlighting the need for strategic planning and international cooperation to ensure equitable access to treatments.
Latest Trends
Growing Adoption of Combination Therapies
Combination therapies are an emerging trend in the liver cancer drug market. Researchers and oncologists are increasingly focusing on combining different treatment modalities, such as targeted therapies with immunotherapy or chemotherapy, to improve treatment outcomes. For example, the combination of atezolizumab (Tecentriq) and bevacizumab (Avastin) has shown promising results in clinical trials for advanced liver cancer, leading to its approval. This trend reflects a shift towards more personalized and effective treatment strategies, providing better response rates and prolonging survival. The focus on combination therapies is likely to drive market growth as they offer hope for patients with refractory liver cancer, who have limited treatment options.
In June 2025, a research team from the School of Clinical Medicine at the LKS Faculty of Medicine, University of Hong Kong (HKUMed), pioneered the use of a “dual immunotherapy” combination nivolumab and ipilimumab (NIVO+IPI) in treating liver cancer patients since 2016. This groundbreaking treatment has shown significant improvements in survival rates and tumor control when compared to existing first-line therapies, such as lenvatinib and sorafenib. Recently, it received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and China’s National Medical Products Administration (NMPA), making it available for global use and offering new hope to liver cancer patients worldwide.
Regional Analysis
North America is leading the Liver Cancer Drugs Market
The United States reports over 41,000 new cases of liver cancer annually, with incidence rates more than tripling since 1980 . This high prevalence necessitates advanced treatment options, fueling market demand. North America boasts state-of-the-art medical facilities and cutting-edge diagnostic technologies, enabling early detection and effective treatment of liver cancer, hence the region dominated the market in 2024 with 38.8% market share. Moreover, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved several innovative therapies for liver cancer, such as sorafenib (Nexavar) and lenvatinib (Lenvima), enhancing treatment options and patient outcomes in the region.
Key Regions and Countries
North America
- US
- Canada
Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherland
- Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Key players in the Liver Cancer Drugs market includes Bayer AG, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck & Co., Inc., Pfizer Inc., Exelixis, Inc., Eisai Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly and Company, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Novartis AG, AstraZeneca, Ipsen, Sirtex Medical, Gilead Sciences, BeiGene, Innovent Biologics, Sumitomo Pharma, Hepion Pharmaceuticals, and Others.
Pfizer is a leading global biopharmaceutical company involved in liver cancer drug development. They focus on targeted therapies, particularly in immuno-oncology. Pfizer’s collaboration with Merck in clinical trials for liver cancer treatments has expanded the use of Atezolizumab (Tecentriq), a prominent immunotherapy for liver cancer.
Exelixis is known for developing Cabometyx (cabozantinib), a key targeted therapy for liver cancer. Cabometyx is used to treat advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), particularly for patients who have previously been treated with sorafenib. Exelixis is actively involved in clinical trials to expand its liver cancer drug portfolio.
Eisai, a Japanese pharmaceutical company, manufactures Lenvima (lenvatinib), a highly effective targeted therapy for advanced liver cancer. Lenvima has shown positive results in clinical trials and is approved for first-line treatment in combination with immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), demonstrating improved patient survival outcomes.
Top Key Players
- Bayer AG
- Bristol-Myers Squibb
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- Pfizer Inc.
- Exelixis, Inc.
- Eisai Co., Ltd.
- Eli Lilly and Company
- Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd
- Novartis AG
- AstraZeneca
- Ipsen
- Sirtex Medical
- Gilead Sciences
- BeiGene
- Innovent Biologics
- Sumitomo Pharma
- Hepion Pharmaceuticals
- Others
Key Opinion Leaders:
Leaders Opinion Bayer AG
Dr. Mark Johnson, Senior Oncologist at Memorial Hospital, USA“Bayer’s Sorafenib (Nexavar) has been a cornerstone in the treatment of advanced liver cancer for years, and the company’s ongoing investment in targeted therapies demonstrates their commitment to improving patient outcomes. The recent combination therapies being explored by Bayer show great promise, potentially providing a broader spectrum of efficacy for patients with more advanced stages of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In my practice, Sorafenib continues to be an essential option, and Bayer’s continuous R&D efforts only strengthen its role in liver cancer treatment.” Exelixis, Inc.
Dr. Laura Adams, Clinical Investigator and Hepatology Specialist, UK“Exelixis has made a significant impact in the liver cancer space with Cabometyx (cabozantinib). As a second-line therapy after Sorafenib, Cabometyx has shown substantial efficacy, particularly for patients with advanced HCC who have failed first-line treatment. The clinical data supporting its use in combination with other immunotherapies is compelling, and Exelixis is undoubtedly setting the stage for innovative treatment regimens that could improve survival rates for a wider patient population.” Eisai Co., Ltd.
Dr. Richard Lee, Medical Director, Oncology Research Group, Germany“Eisai’s Lenvima (lenvatinib) has become a key player in the treatment landscape for advanced liver cancer. It offers a potent option for patients, particularly when used in combination with immunotherapy. The combination of Lenvima with Pembrolizumab (Keytruda) has shown exceptional results in clinical trials, positioning Eisai as a leader in combination therapies. Lenvima’s approval as a first-line treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma has made it a first-choice drug in many oncology centers, and the data supporting its efficacy continues to grow.” Recent Developments
- In December 2024, Medivir AB, a pharmaceutical company dedicated to developing innovative cancer treatments for high unmet medical needs, today announced the approval of its US Investigational New Drug (IND) application. This approval allows the evaluation of fostrox in combination with Lenvima, versus Lenvima alone, in a Phase 2b study for second-line advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
- In September 2024, updated results from the HIMALAYA Phase III trial revealed that AstraZeneca’s Imfinzi (durvalumab) combined with Imjudo (tremelimumab) showed a sustained and clinically meaningful overall survival (OS) benefit at five years for patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who had not previously received systemic therapy and were ineligible for localized treatment. These significant findings from the HIMALAYA trial will be presented today at the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Congress 2024 in Barcelona, Spain (presentation 947MO).
- In October 2022, the FDA approved the combination of tremelimumab (Imjudo, AstraZeneca) and durvalumab (Imfinzi, AstraZeneca) for the treatment of adult patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common form of liver cancer.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) US$ 3.78 Billion Forecast Revenue (2034) US$ 16.39 Billion CAGR (2025-2034) 15.8% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, COVID-19 Impact, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Drug Class (Targeted Therapy, Immunotherapy, Chemotherapy and Others), By Cancer Type (Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC), Cholangiocarcinoma, Hepatoblastoma and Others), By Route of Administration (Oral and Injectable), By Distribution Channel (Hospital Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies, and Online Pharmacies) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Bayer AG, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck & Co., Inc., Pfizer Inc., Exelixis, Inc., Eisai Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly and Company, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Novartis AG, AstraZeneca, Ipsen, Sirtex Medical, Gilead Sciences, BeiGene, Innovent Biologics, Sumitomo Pharma, Hepion Pharmaceuticals, and Others Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Bayer AG
- Bristol-Myers Squibb
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- Pfizer Inc.
- Exelixis, Inc.
- Eisai Co., Ltd.
- Eli Lilly and Company
- Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd
- Novartis AG
- AstraZeneca
- Ipsen
- Sirtex Medical
- Gilead Sciences
- BeiGene
- Innovent Biologics
- Sumitomo Pharma
- Hepion Pharmaceuticals
- Others










