Global Seed Colorant Market Size, Share, Growth Analysis By Time of Application (Preharvest, Pre and Postharvest), By Formulation (Powder, Liquid), By Сгор Туре (Grains and Cereals, Oil Seeds, Fruits and Vegetables, Turf and Ornamentals, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Sep 2025
- Report ID: 158170
- Number of Pages: 235
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
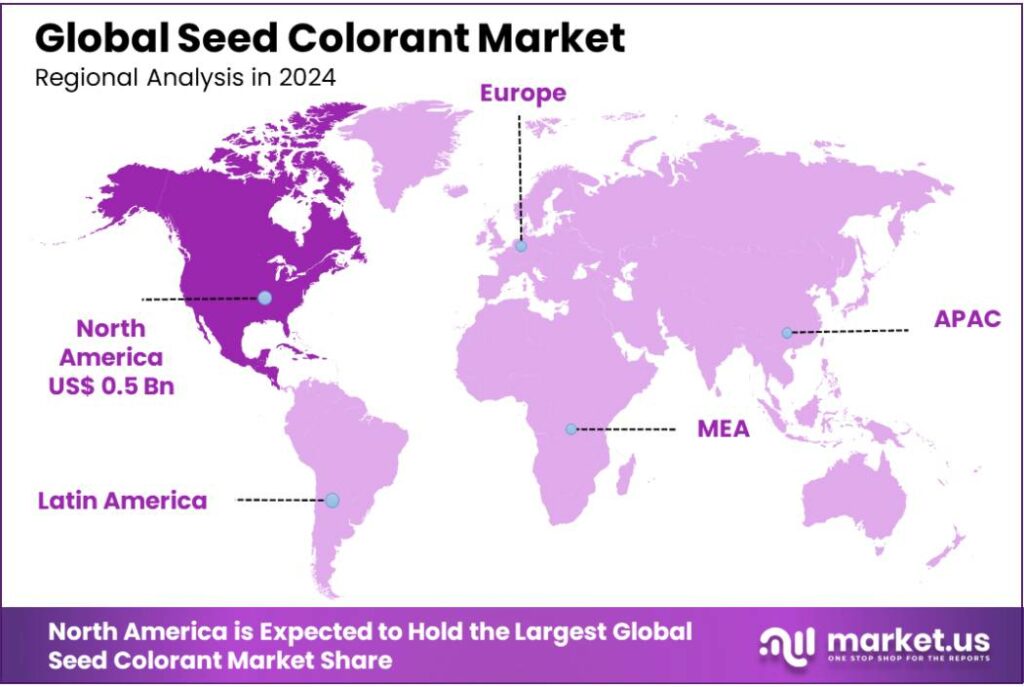
The Global Seed Colorant Market size is expected to be worth around USD 2.8 Billion by 2034, from USD 1.3 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 8.1% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024 North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.9% share, holding USD 0.5 Billion in revenue.
Seed colorants are additives used in seed coatings or treatments primarily for identification (brand, variety, trait), safety (preventing unintentional mixing), handling (improving visibility, seed counter, etc.), and sometimes functional properties (e.g. helping adhesion of other coatings, reducing dust off). The colorant is typically an inert ingredient, often listed in regulatory frameworks, and must comply with safety, environmental, and residue rules.
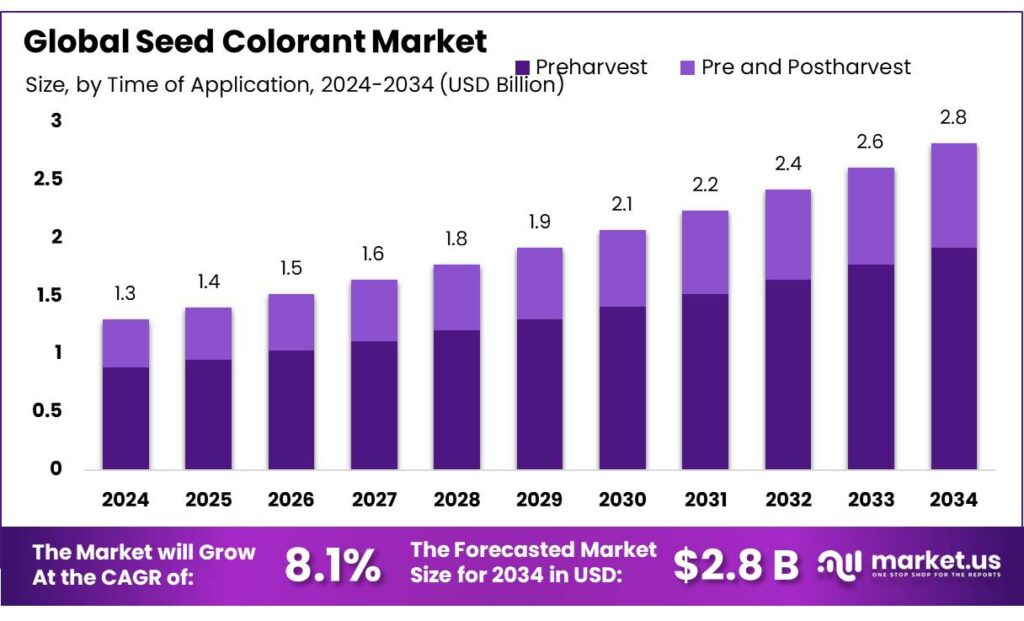
The industrial scenario is buoyed by very large sowing baselines that pull through demand for coatings and colorants. FAO reports 1,600 million hectares of global cropland in 2023 within 4,800 million hectares of agricultural land, underscoring the breadth of seed use worldwide. In the US, where treated seed adoption is mature, NASS estimated 95.2 million acres of corn planted in 2025 and 83.4 million acres of soybeans—acreage that directly translates into high-volume coating campaigns before spring planting.
Driving factors include regulatory stewardship, dust-off reduction targets, and traceability. Euroseeds’ ESTA framework ties market access to dust reference values that many plants now design coatings to meet or beat, directly increasing the use of polymeric binders and purpose-made pigments. Peer-reviewed protocols quantify abrasion in g dust/100 kg or per 100,000 seeds, giving buyers objective specifications for tendering colorant systems. In North America, EPA-listed inert colorants under 40 CFR §180.910–§180.960 and REACH-registered pigments in the EU provide clear chemistries for seed applications, supporting faster qualification and multi-region sourcing.
Key Takeaways
- Seed Colorant Market size is expected to be worth around USD 2.8 Billion by 2034, from USD 1.3 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 8.1%.
- Preharvest held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 67.9% share in the Seed Colorant Market.
- Liquid held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 63.2% share in the Seed Colorant Market.
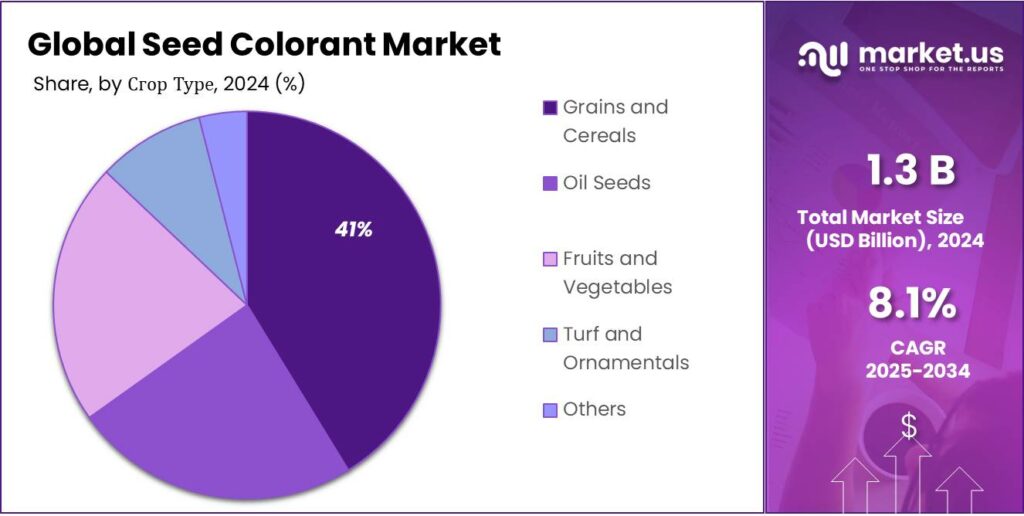
- Grains and Cereals held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 41.4% share in the Seed Colorant Market.
- North America captured around 43.90% of the global Seed Colorant Market, amounting to approximately USD 0.5 billion.
By Time of Application Analysis
Preharvest Seed Colorant dominates with 67.9% share due to regulatory needs and seed safety marking.
In 2024, Preharvest held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 67.9% share in the Seed Colorant Market by Time of Application segment. This strong lead is mainly because most commercial seeds undergo treatment and coloring before sowing to meet safety and regulatory standards. Farmers and seed companies rely on preharvest colorants to mark treated seeds clearly, making them easy to identify and ensuring they are not mistaken for food or feed.
The practice is particularly widespread in crops like corn, wheat, and soybeans where treated seeds are the norm. With global awareness growing around treated seed handling, 2025 is likely to continue this trend, as policymakers and regulatory bodies enforce pre-sowing colorant usage more strictly. This segment remains the most standardized and widely adopted in commercial agriculture.
By Formulation Analysis
Liquid Seed Colorant leads with 63.2% share thanks to easy application and smooth seed coating.
In 2024, Liquid held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 63.2% share in the Seed Colorant Market by Formulation segment. The liquid form is widely preferred because it blends easily with other seed treatment chemicals, ensuring even coverage and bright, lasting color. Seed companies favor liquid formulations for their smooth flow, precise dosing, and compatibility with modern seed treatment machinery. Unlike powders, liquid colorants reduce dust and improve handling safety. Their efficiency in large-scale operations makes them ideal for treating high volumes of seeds like maize, canola, and pulses. Looking ahead to 2025, demand for liquid formulations is expected to grow further as seed treatment standards tighten and mechanized application becomes the norm.
By Сгор Туре Analysis
Grains and Cereals lead with 41.4% share due to large-scale seed treatment across staple crops.
In 2024, Grains and Cereals held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 41.4% share in the Seed Colorant Market by Crop Type segment. This leadership is mainly driven by the widespread cultivation and high seed treatment rates in staple crops like wheat, corn, and rice. These crops are often treated with fungicides and insecticides before planting, and colored seed coatings are essential for safety, compliance, and identification. Farmers and seed processors rely on colorants to distinguish treated seeds and ensure safe use in food systems. In 2025, with growing awareness around seed quality and stricter farming protocols, the dominance of grains and cereals is expected to hold strong, especially in high-output farming regions.
Key Market Segments
By Time of Application
- Preharvest
- Pre and Postharvest
By Formulation
- Powder
- Liquid
By Сгор Туре
- Grains and Cereals
- Oil Seeds
- Fruits and Vegetables
- Turf and Ornamentals
- Others
Emerging Trends
Digital Traceability and Sustainability-Linked Seed Colorants
A major trend reshaping the seed colorant market today is the integration of digital traceability with sustainability-focused seed treatment practices. This development is being driven by both government regulations and industry stewardship programs that want to make seeds safer, more transparent, and environmentally responsible. Seed colorants are no longer just about making seeds visible—they are becoming part of the larger ecosystem of digital labeling, sustainable farming, and responsible use of crop protection products.
In Europe, the European Commission is in the process of introducing digital labelling for plant protection products under Regulation (EU) No 547/2011, a step that also affects treated seeds. This regulation aims to provide harmonised and accessible information to farmers through scannable QR codes, linking packaging and even seed batches to online databases. Seed colorants tie directly into this shift because color is often used as the first visible identifier of treatment, and now that identification is being connected to digital platforms for full traceability.
This trend is reinforced by environmental policies. The European Green Deal’s Farm to Fork Strategy is targeting a 50% reduction in the use and risk of chemical pesticides by 2030. For seed colorants, this means more demand for eco-friendly pigments and coating materials that meet sustainability criteria while still delivering visibility and safety. As chemical pesticide intensity is reduced, better seed stewardship, with visible and durable treatments, becomes even more critical.
Drivers
Dust Reduction & Environmental Safety from Seed Coatings
One of the major drivers pushing the use of colourants in seed coating is reducing harmful dust and enhancing environmental safety during sowing operations. Governments and international bodies have identified that treated seeds often generate dust or abrasion particles during planting; these particles can carry pesticide residues or chemical treatments, which may drift into the air, fall onto soil, or be picked up by pollinators (bees, etc.). Colourants help build a coating that reduces abrasion, ensures better adhesion, makes drift visible, and often is required by regulation.
In Europe, for example, the European Seed Treatment Assurance (ESTA) scheme sets dust reference values using the Heubach test method. Some examples: corn treated seed must have no more than 0.75 grams of dust per 100,000 seeds, oilseed rape no more than 0.50 g per 700,000 seeds, sugar beet no more than 0.25 g per 100,000 seed pellets, sunflower no more than 0.40 g per 75,000 seeds. These numbers are standards seed-treatment firms must often meet to market in EU countries. The existence of such quantitative caps forces innovation in coatings, including the use of better colourants and binders.
The United Nations’ FAO also emphasizes “high quality seed coatings” as part of risk mitigation for treated seeds. In its Pesticide Registration Toolkit, FAO states that where coatings are of good quality, dust dispersion during sowing can be reduced by up to 90% through a combination of suitable coating quality and drilling equipment. This magnitude of reduction is substantial: it shows that improvements in seed coatings directly translate to environmental safety gains.
Governments are increasingly enshrining these requirements into regulation. The EU has proposed new rules under its Plant Reproductive Material (PRM) legislation that are aimed at more standardized labelling, technical innovations, and harmonising seed treatment regulation across member states. Under PRM proposals, seed-treated material will need to comply not just with safety thresholds, but also with sustainability standards, traceability, and environmental impact.
Restraints
Tightening microplastics rules are forcing expensive reformulation of seed colorants
Across seed treatment plants, the biggest brake on colorant adoption and product changeovers right now is the new wave of rules on intentionally-added microplastics. In the EU, the microplastics restriction under REACH took effect on 17 October 2023. It covers synthetic polymer microparticles intentionally added to mixtures—this captures many seed-coating systems, including colorant-binder packages. The European Commission’s summary notes the measure applies to mixtures (not articles) and sets phased deadlines so industry can adapt.
The legal text (Commission Regulation (EU) 2023/2055) explains why the phase-in is long: regulators judged that up to eight years are necessary for agricultural and horticultural uses “such as seeds coated with colorants or lubricants” to reformulate and obtain authorisations, without abruptly removing existing encapsulation technologies. That eight-year figure has become the planning anchor for many seed treatment lines.
The numbers behind the rule are large. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) estimated that the restriction would prevent about 500,000 tonnes of microplastics from entering the environment over 20 years. That high-level benefit target—half a million tonnes—explains why compliance pressure is intense and sustained. For colorant suppliers and seed companies, this translates into reformulating away from polymer particles that count as microplastics, validating alternatives, requalifying pigments, and proving performance under the new constraints.
This is not a narrow, niche issue. FAO’s latest land accounting shows 4,800 million hectares of global agricultural land in 2023, with about 1,600 million hectares of cropland. Even a small fraction of this area passing through modern seed-coating programs implies very large volumes of coatings and pigment systems to reassess under microplastics rules. The scale of the seeded area magnifies the cost and complexity of reformulation.
Opportunity
Expansion of Seed Colorants in Sustainable Agriculture and Food Security Programs
One of the biggest growth opportunities for seed colorants lies in their role in sustainable agriculture and global food security initiatives. Around the world, governments and food organizations are stressing the need to improve seed quality and productivity to meet the demands of a rising population. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), the global population is projected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, requiring food production to increase by about 60% compared to 2007 levels.
The opportunity also extends from the sheer volume of cropland that depends on treated seed. FAO data shows that in 2023, there were 1,600 million hectares of cropland globally out of a total 4,800 million hectares of agricultural land. Even if a fraction of this cropland uses treated seed coatings with colorants, the scale of demand is massive. Regions like North America and Europe already have mature seed treatment adoption, but emerging economies in Africa and Asia—where governments are investing in modern seed systems—offer significant room for expansion.
For example, the African Development Bank’s “Feed Africa” strategy targets doubling crop yields in Africa by providing improved seeds and inputs, aiming to lift 400 million people out of poverty by 2025. Seed colorants, through their role in certified seed programs, can directly benefit from such initiatives because they are part of quality control and branding of improved seed varieties. In India, the government’s National Food Security Mission (NFSM) has emphasized improved seed distribution as a pillar of its program, supplying over 2.1 million quintals of certified seeds in 2022–23.
Sustainability adds another growth layer. Consumers and governments are pushing for environmentally safe practices. The European Commission’s Green Deal aims to reduce pesticide use by 50% by 2030, pushing for safer formulations and better stewardship practices. Seed colorants that integrate into low-dust, sustainable coatings become part of that solution. Since ESTA requires strict dust limits for seeds, more advanced colorant systems are entering demand pipelines to meet compliance and sustainability expectations.
Regional Insights
North America dominates with 43.90% share / USD 0.5 Billion in Seed Colorant Market
In 2024, North America captured around 43.90% of the global Seed Colorant Market, amounting to approximately USD 0.5 billion, making it the dominant region in this sector. This strong position is underpinned by several factors: mature agricultural infrastructure, stringent regulatory frameworks that often mandate coloring of treated seeds, and widespread usage of seed treatment practices among large-scale commercial farmers, particularly in the U.S. and Canada.
The United States contributes the bulk of this regional value. Most seed companies in the U.S. have standardized seed treatment and seed colorant usage to ensure compliance with safety and environmental laws, and to safeguard against misuse of treated seeds. For example, treated corn and soybean seeds, which account for a significant portion of U.S. planted acres, virtually always include a colorant to identify treatment status. Canada, likewise, especially in its prairie provinces, uses seed colorants extensively in wheat, canola, and pulse crops to meet local seed certification and traceability standards.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
BASF SE is a leading player in seed treatment technologies and offers specialized seed colorants through its Agricultural Solutions segment. The company focuses on safety, durability, and regulatory compliance in seed coatings. BASF’s products are widely used in grains and vegetables across North America and Europe. Its R&D efforts aim to develop bio-based and low-toxicity colorants that align with growing sustainability demands. BASF’s global reach and innovation capacity position it strongly in the seed colorant industry.
Milliken & Company operates in advanced materials and chemical colorants, offering innovative seed coatings that combine function with color. Their seed colorants are designed to improve visibility, reduce dust-off, and enhance seed handling safety. Milliken’s focus on sustainability has led to the development of low-VOC and eco-friendly seed dyes. With strong U.S. manufacturing capabilities and a track record of industry partnerships, Milliken is a key contributor to the next generation of agricultural colorant technologies.
Bayer CropScience AG is a major global seed and crop protection firm that integrates colorants into its seed treatment solutions. Its treated seed offerings for crops like corn, soybeans, and canola often feature bright, durable colors for identification and regulatory compliance. Bayer emphasizes product stewardship, ensuring its colorants meet EPA and EU guidelines. Its global distribution network, in-house seed brands, and continuous investment in safe seed technologies support Bayer’s leadership in the seed colorant market.
Top Key Players Outlook
- BASF SE
- Sensient Technologies Corporation
- Milliken & Company
- Bayer CropScience AG
- Chromatech Incorporated
- Lanxess AG
- Heubach GmbH
- Sun Chemical Corporation
- Dystar Group
- Germains Seed Technology
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024, BASF’s agriculture unit generated about €9.8 billion (≈ USD 11.1 billion) in global sales, with seed & trait sales forming close to 22% of that.
In 2024, Bayer CropScience reported €22.3 billion in revenue for the Crop Science division, down about 2.0% (currency‑ and portfolio‑adjusted) from the prior year.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 1.3 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 2.8 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 8.1% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Time of Application (Preharvest, Pre and Postharvest), By Formulation (Powder, Liquid), By Сгор Туре (Grains and Cereals, Oil Seeds, Fruits and Vegetables, Turf and Ornamentals, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape BASF SE, Sensient Technologies Corporation, Milliken & Company, Bayer CropScience AG, Chromatech Incorporated, Lanxess AG, Heubach GmbH, Sun Chemical Corporation, Dystar Group, Germains Seed Technology Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- BASF SE
- Sensient Technologies Corporation
- Milliken & Company
- Bayer CropScience AG
- Chromatech Incorporated
- Lanxess AG
- Heubach GmbH
- Sun Chemical Corporation
- Dystar Group
- Germains Seed Technology










