Global Ethyl Cellulose Market Size, Share, And Business Benefits By Form (Solid, Liquid), By Viscosity Grade (100-400 mPa.s, 400-1000 mPa.s, Above 1000 mPa.s), By Application (Pharmaceuticals, Adhesives and Sealants, Coatings, Food, Printing Inks, Others), By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends, and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: November 2025
- Report ID: 164900
- Number of Pages: 284
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
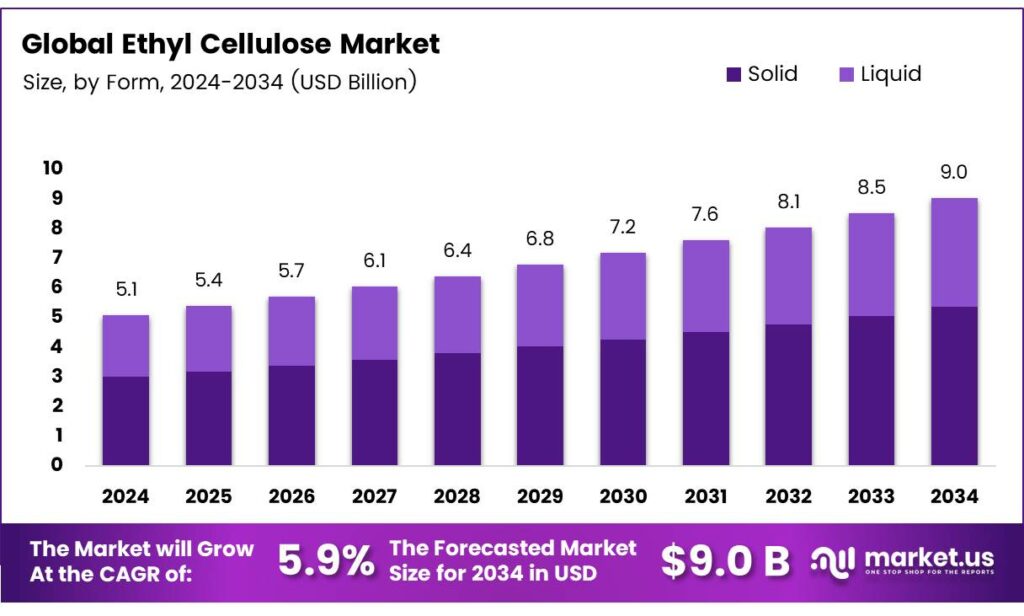
The Global Ethyl Cellulose Market size is expected to be worth around USD 9.0 billion by 2034, from USD 5.1 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 5.9% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
Ethyl cellulose (EC) is a versatile cellulose derivative formed by substituting hydroxyl groups on anhydroglucose units with ethyl ether groups through the reaction of alkali cellulose with ethyl chloride or ethyl iodide. Known for its non-toxic, thermoplastic, hydrophobic, and biodegradable nature. It dissolves readily in organic solvents such as ethanol, toluene, and chloroform, but remains insoluble in water when the degree of substitution exceeds 2.5, typically 47.5–49% ethoxy content in commercial Ethocel grades.
- EC excels in microencapsulation for infant nutrition and functional foods. Ferrous sulfate encapsulated in EC microcapsules prevents unwanted sensory changes and interactions in infant formulae, delivering approximately 33% iron bioavailability. Heat-cured vitamin E-loaded EC microcapsules release the active 10–20% slower in gastric conditions and offer superior storage stability, while folate-loaded EC capsules protect the vitamin from stomach degradation, enhancing bioavailability during pregnancy and early childhood.
In the broader food industry, EC functions as a tackifier, emulsifier, coating agent, and preservative. Electrospun zein-EC nanofibers preserve food quality, EC-based active films provide antioxidant and antibacterial properties, and their use extends to pharmaceutical coatings, cosmetics, printing inks, and specialty packaging. With its combination of safety, functionality, and adaptability across high-performance membranes and sensitive nutritional applications, ethyl cellulose continues to be a cornerstone material in both advanced materials science and everyday consumer products.
Key Takeaways
- The Global Ethyl Cellulose Market is expected to grow from USD 5.1 billion in 2024 to USD 9.0 billion by 2034 at a 5.9% CAGR (2025-2034).
- Solid form dominated in 2024 with a 59.4% share due to excellent storage life and ease in dry-mix blending.
- 100-400 mPa.s viscosity grade led in 2024 with 42.7% share, ideal for tablet coatings and sustained-release drugs.
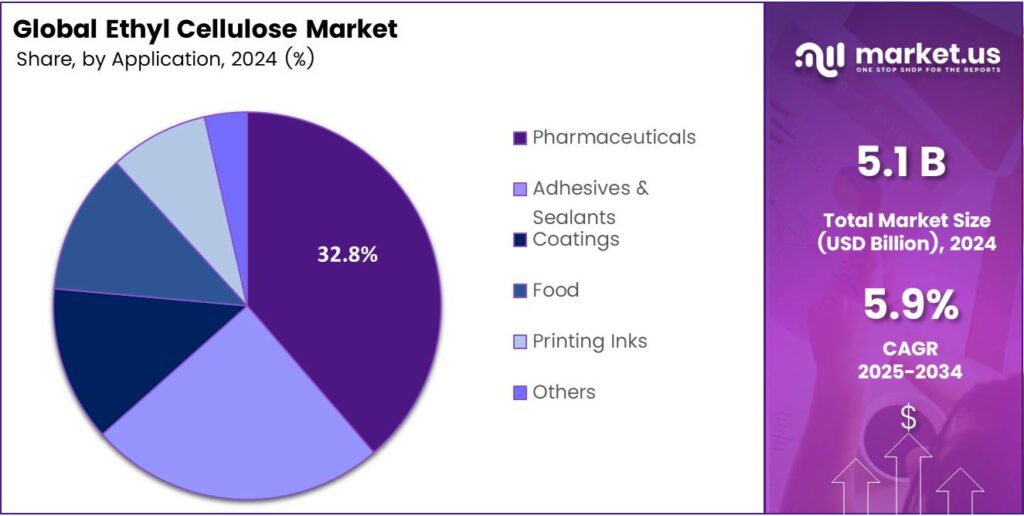
- The pharmaceuticals segment held the largest share at 32.8% in 2024, driven by taste-masking and extended-release needs.
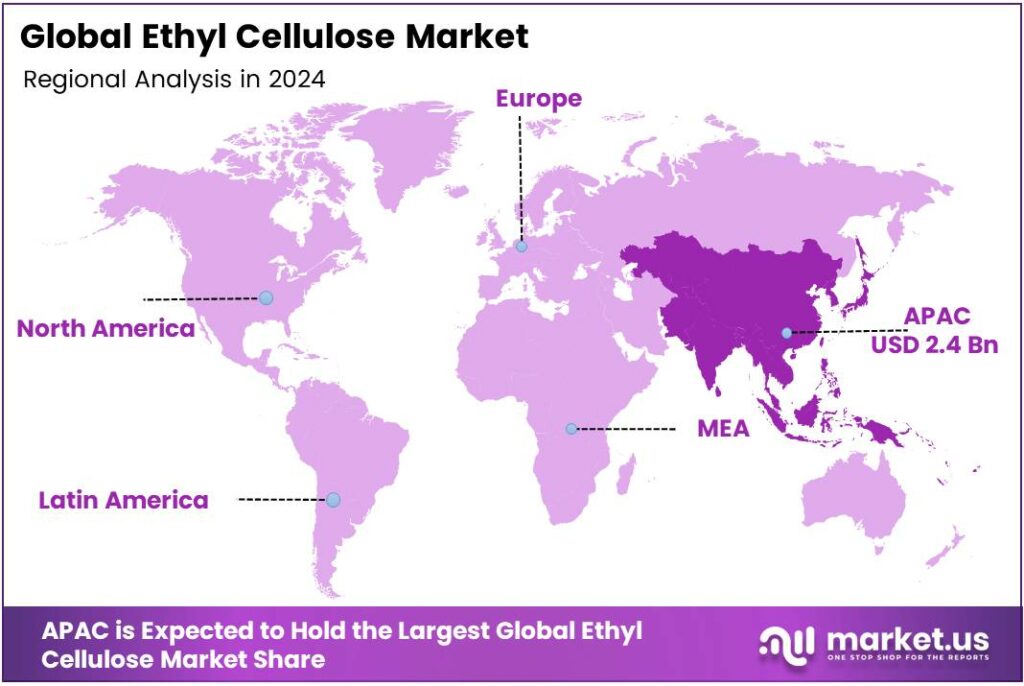
- Asia-Pacific commanded 47.9% of the global market in 2024 USD 2.4 billion, led by China, India, Japan, and South Korea.
By Form Analysis
Solid form dominates with 59.4% due to its superior stability and ease of handling in industrial applications.
In 2024, Solid held a dominant market position in the By Form Analysis segment of the Ethyl Cellulose Market, with a 59.4% share. This form is widely preferred in pharmaceuticals and coatings because it offers excellent storage life, precise dosing, and seamless blending into dry mixes. Manufacturers favor solid ethyl cellulose for its non-hygroscopic nature, reducing production complications and ensuring consistent quality across batches.
Liquid form, meanwhile, captured the remaining share and continues to grow steadily. It excels in applications requiring instant dispersion, such as liquid coatings and adhesives. The pre-dissolved nature eliminates additional solvent steps, saving time and enhancing process efficiency, particularly in high-speed manufacturing lines where uniformity is critical.
By Viscosity Grade Analysis
100-400 mPa.s leads with 42.7% thanks to its perfect balance of flow and film-forming properties.
In 2024, 100-400 mPa.s held a dominant market position in the By Viscosity Grade segment of the Ethyl Cellulose Market, with a 42.7% share. This mid-range viscosity delivers optimal thickness control in tablet coatings and inks, providing smooth application without excessive drag. Pharmaceutical giants rely on it for sustained-release formulations where precise barrier layers ensure predictable drug delivery.
400-1000 mPa.s follows closely, offering stronger film strength for heavy-duty industrial coatings. Its higher viscosity creates tougher barriers against moisture and chemicals, making it ideal for protective sealants in construction and automotive sectors where durability trumps speedy application.
Above 1000 mPa.s serves niche high-performance needs, forming ultra-thick, robust films. Though smaller in volume, it commands premium pricing in specialized food packaging and advanced electronics coatings that demand maximum resistance to environmental stress.
By Application Analysis
Pharmaceuticals rule with 32.8% driven by booming demand for controlled-release medications.
In 2024, Pharmaceuticals held a dominant market position in the By Application segment of the Ethyl Cellulose Market, with a 32.8% share. It remains the cornerstone for taste-masking, moisture protection, and extended-release tablets. Rising chronic disease prevalence worldwide keeps pushing demand higher as formulators seek safe, biodegradable polymers that meet stringent FDA and EMA standards.
Adhesives and Sealants rank second, leveraging ethyl cellulose’s quick-drying and strong bonding traits. From woodworking to packaging, it enhances tack and flexibility, helping manufacturers achieve faster production cycles while maintaining bond integrity under temperature fluctuations. The coatings segment thrives in inks, paints, and varnishes, where ethyl cellulose imparts gloss, adhesion, and scratch resistance.
The shift toward eco-friendly solvent systems has accelerated its adoption in architectural and automotive finishes that need both beauty and long-lasting protection. Food application, though smaller, grows fastest with clean-label trends. Used as a thickener, stabilizer, and glazing agent, it meets vegan and gluten-free requirements, appearing in everything from confectionery coatings to encapsulated flavors that preserve taste during shelf life.
Key Market Segments
By Form
- Solid
- Liquid
By Viscosity Grade
- 100-400 mPa.s
- 400-1000 mPa.s
- Above 1000 mPa.s
By Application
- Pharmaceuticals
- Adhesives and Sealants
- Coatings
- Food
- Printing Inks
- Others
Emerging Trends
Growing Demand for Eco-friendly Coatings Using Ethyl Cellulose
One major emerging trend for ethyl cellulose (EC) is its increasing adoption in sustainable coatings and packaging applications. As industries seek greener alternatives, EC stands out because it is derived from cellulose, a renewable, naturally abundant polymer, and can form durable films, binders, or thickening agents.
Government and institutional policies further bolster the trend. Green-chemistry frameworks emphasise the use of bio-based polymers and derivatives, and in India and other regions, there is growing attention on cellulose-based materials in sustainable packaging and coatings. While a direct government statistic for EC is scarce, one linked commentary indicates India’s cellulose market to see double-digit growth rising demand for eco-friendly packaging.
The shift of ethyl cellulose into eco-coatings and sustainable packaging is a credible emerging trend. At the same time, this trend carries implications for supply chains (availability of cellulose feedstock, purity of EC grades), cost structures (premium pricing relative to commodity resins), and performance requirements. Industries that recognise and invest in the sustainable-polymer angle of EC now may capture longer-term value as regulation and consumer preferences move in that direction.
Drivers
Oral-Solid Dose (OSD) expansion is pulling Ethyl Cellulose forward
A clear, single driver for ethyl cellulose (EC) today is the steady expansion of oral solid-dose (OSD) medicines tablets and capsules that rely on EC as a binder, film former, and release-control polymer. When more OSDs are developed and manufactured, excipients like EC ride the same wave. The U.S. FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation, underscoring an active pipeline that feeds downstream formulation work.
- North America accounted for 54.8% of estimated world pharmaceutical sales in 2024, with Europe at 22.7%. These are not abstract percentages; they signal where OSD development, tech-transfer, and commercial runs are concentrated—precisely the environments where EC demand is anchored.
India, one of the world’s key OSD manufacturing hubs, has earmarked ₹15,000 crore under its Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for pharmaceuticals, explicitly to boost domestic manufacturing depth. That funding helps expand capacity in APIs and formulations, which, in turn, supports stable offtake for critical excipients such as EC across coatings and controlled-release systems.
Restraints
Feedstock volatility and compliance costs are squeezing Ethyl Cellulose
A big restraint on ethyl cellulose (EC) today is simple but stubborn: the cost and steadiness of its cellulose feedstock, plus the compliance burden around chlorinated reagents and solvents used in production and coating. Global wood-pulp supply has not been growing smoothly. FAO reports that world wood-pulp output fell 2% to 193 million tonnes, even as pulp trade hit a record 71 million tonnes, a combo that keeps supply tight and pricing sensitive to shocks.
At the mill gate, U.S. wholesale pricing for wood pulp still sits elevated by historical standards; in 2025, the index has hovered in the 220–230 range, underscoring that input costs remain structurally high even after recent easing. Europe’s pulp and paper trade balance stayed positive in 2024, but the sector’s own association (CEPI) notes shifting flows and export swings as signals of a market that remains tight and reactive to logistics and energy conditions.
- EC manufacturing and downstream coating often involve volatile or chlorinated substances that raise environmental, safety, and regulatory costs. For example, ethyl chloride, relevant as a chlorinating agent in EC production, carries an OSHA permissible exposure limit of 1,000 ppm (2,600 mg/m³) TWA, while ACGIH’s guidance is far stricter at 100 ppm. Designing ventilation, capture, and monitoring to live within these limits is not optional, and it adds real operating expense.
Opportunity
Rise of Bio-based Chemicals and Polymers Supports Ethyl Cellulose
One compelling growth factor for ethyl cellulose (EC) lies in its alignment with the global push toward bio-based chemicals and polymers, and the clear policy backing that’s now in place. In the BioE3 Policy, the government highlights bio-based chemicals and biopolymers as a thematic sector prioritized for development. This indicates that materials derived from renewable cellulose—such as EC—are likely to benefit from the broader strategic push.
- Globally, the report by the International Energy Agency-Bioenergy Task 42 estimates that total bio-based chemical and polymer production is around 90 million tonnes. EC is one among many cellulose-derivative polymers gaining relevance, but the total available platform is large and growing. In other words, EC is positioned to capture a share of that expanding renewable‐materials pie as industries look to transition away from purely fossil-based polymers.
The fact that EC is derived from cellulose sets it apart in formulation choices. Because cellulose is renewable and bio‐derived, it aligns with sustainability mandates—another lever pushing demand. While the exact volume of EC used in bio-applications is not always disclosed, the policy direction and feedstock trend clearly favour materials like EC. In India, the BioE3 policy is explicitly meant to accelerate the commercialization of bio-based products, including polymers.
Regional Analysis
Asia-Pacific leads with a 47.9% share and a USD 2.4 Billion market value.
In 2024, Asia-Pacific emerged as the leading region in the global ethyl cellulose market, accounting for 47.9% of the total share, equivalent to around USD 2.4 billion in market value. The dominance of this region is driven by its expanding pharmaceutical, food, and coatings industries, particularly in China, India, Japan, and South Korea.
Ethyl cellulose plays a key role in drug formulation as a binder and coating agent, aligning with the region’s booming pharmaceutical manufacturing base. The packaging and construction industries are also major contributors to growth, where ethyl cellulose is utilized in adhesives, coatings, and specialty inks.
Rapid urbanization across Southeast Asia has elevated the consumption of construction coatings and protective materials. Additionally, the growing focus on bio-based and sustainable polymers in Japan and South Korea is fostering innovation in cellulose derivatives to reduce environmental footprints. Plant-based materials, such as ethyl cellulose for industrial applications.
Asia-Pacific’s dominance is expected to continue, supported by rising R&D spending, robust manufacturing capacity, and government-backed sustainability programs that promote cellulose-based solutions across the pharmaceutical, food, and coatings sectors. The region’s large consumer base and strong export orientation make it the core growth engine of the global ethyl cellulose market.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Ashland is a leading global specialty chemicals company, renowned for its high-quality ethyl cellulose products marketed under the AQUALON brand. Its strength lies in deep application expertise and strong technical support, particularly in pharmaceuticals, coatings, and personal care. Ashland focuses on providing customized solutions that enhance drug delivery systems and formulation stability.
Dow is a materials science powerhouse, leveraging its immense scale and integrated manufacturing to be a dominant force in the ethyl cellulose market. Its CELLOSIZE products are industry standards. Dow excels in supplying large-volume, consistent-quality material, primarily for construction and industrial coatings. It’s a significant investment in R&D that drives the development of new applications and sustainable solutions.
Shin-Etsu is a global chemical giant and a leading producer of ethyl cellulose, known for its exceptional product purity and consistency. The company benefits from a vertically integrated supply chain, controlling key raw materials. This allows for superior quality control and reliable supply, making them a preferred partner for the stringent pharmaceutical and specialty food industries.
Top Key Players in the Market
- Ashland Global Holdings Inc.
- The Dow Chemical Company
- Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd.
- NIPPON PAPER CHEMICALS Co., Ltd.
- Lamberti S.p.A.
- Eastman Chemical Company
- Daicel Corporation
- J. Rettenmaier and Söhne GmbH + Co. KG
Recent Developments
- In 2025, Ashland appointed Tilley Distribution as the exclusive U.S. distributor for its food and beverage ingredients, including cellulosic hydrocolloids used in nutraceuticals and beverages. This enhances distribution for cellulose-based thickeners and stabilizers, potentially including EC applications in food coatings.
- In 2024, Dow received ISCC PLUS certification for its propylene oxide/propylene glycol (PO/PG) and polyols facility in Freeport, Texas, emphasizing sustainable practices—but this is not directly linked to cellulose production. Dow produces ETHOCEL ethyl cellulose, widely used in pharmaceuticals, food, and industrial coatings.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 5.1 Billion Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 9.0 Billion CAGR (2025-2034) 5.9% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Form (Solid, Liquid), By Viscosity Grade (100-400 mPa.s, 400-1000 mPa.s, Above 1000 mPa.s), By Application (Pharmaceuticals, Adhesives and Sealants, Coatings, Food, Printing Inks, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Ashland Global Holdings Inc., The Dow Chemical Company, Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd., NIPPON PAPER CHEMICALS Co., Ltd., Lamberti S.p.A., Eastman Chemical Company, Daicel Corporation, J. Rettenmaier and Söhne GmbH + Co. KG Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited Users and Printable PDF)  Ethyl Cellulose MarketPublished date: November 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Ethyl Cellulose MarketPublished date: November 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Ashland Global Holdings Inc.
- The Dow Chemical Company
- Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd.
- NIPPON PAPER CHEMICALS Co., Ltd.
- Lamberti S.p.A.
- Eastman Chemical Company
- Daicel Corporation
- J. Rettenmaier and Söhne GmbH + Co. KG










