Global Cloud Computing Market Size, Share, Industry Analysis Report By Service Type (Software as a Service (SaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (laas), Platform as a Service (PaaS)), By Deployment Mode (Hybrid Cloud, Private Cloud, and Public Cloud), By Enterprise Size (Small & Medium Enterprises and Large Enterprises), By End-Use Industry (IT & Telecommunications, BFSI, Retail & Consumer Goods, Energy & Utilities, Manufacturing, Government & Public Sector, Media & Entertainment, Healthcare, Other End-Use Industries), By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: August 2025
- Report ID: 32302
- Number of Pages: 296
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
- Report Overview
- Key Takeaways
- Cloud Computing Statistics
- Analysts’ Viewpoint
- Consequences of Generative AI
- U.S. Cloud Computing Market Size
- Emerging Trends
- Growth Factors
- Service Type Analysis
- Deployment Mode Analysis
- Enterprise Size Analysis
- End-Use Industry Analysis
- Key Market Segments
- Driving Factor
- Restraining Factor
- Growth Opportunity
- Challenge Analysis
- Top Use Cases
- Business Benefits
- Geopolitical and Recession Impact Analysis
- Regional Analysis
- Key Player Analysis
- Recent Developments
- Report Scope
Report Overview
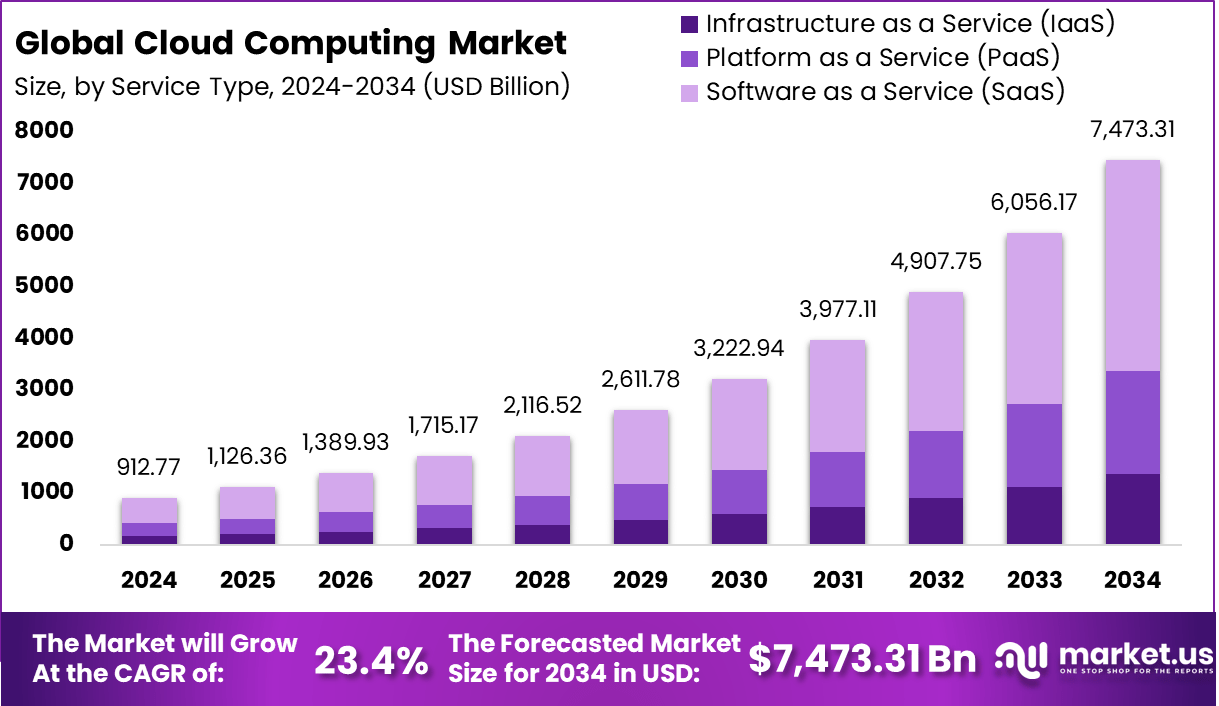
The global Cloud Computing market size accounted for USD 912.77 billion in 2024 and is predicted to increase from USD 1,126.36 billion in 2025 to approximately USD 7,473.05 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 23.40% from 2025 to 2034.
The cloud computing market has experienced robust expansion, driven by enterprises’ desire for scalable infrastructure, operational flexibility, and more efficient technology stacks. This evolution is underpinned by widespread digital transformation initiatives and the integration of advanced computing workloads. Demand for accessible and agile cloud services continues to grow in tandem with rising usage of intelligent systems, data analytics, and distributed computing models.
Top driving factors include the growing demand for advanced AI workloads, increased need for hybrid and multi-cloud infrastructures, and the pressing requirements for scalable digital environments. Businesses seek cloud computing to handle fluctuating workloads, enable faster time to market, and support remote workforces, especially highlighted by the recent acceleration in distributed business models. These factors contribute to heightened adoption as companies prioritize flexibility, cost savings, and rapid innovation.
Organizations are increasingly adopting cloud solutions to enhance cost efficiency and operational agility. The shift toward remote work, data‑driven decision making, and decentralized IT has elevated cloud’s role as a core enabler. Public, private, hybrid, and multi‑cloud models are all gaining traction, reflecting diversified enterprise strategies for balancing control, performance, regulatory compliance, and resilience. This demand is further stimulated by the ability to scale resources dynamically, reduce capital expenditures, and foster innovation.
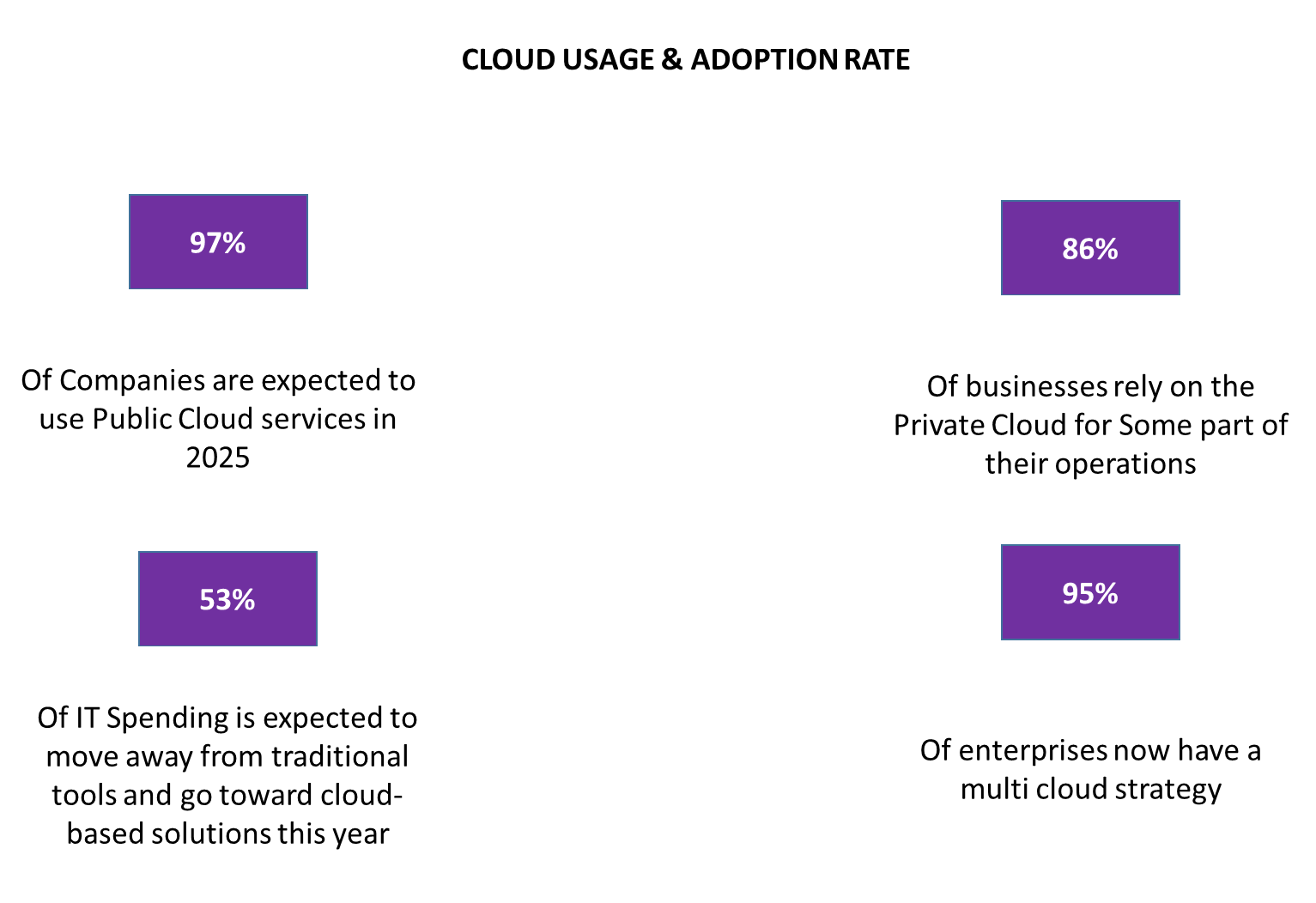
According to a report by Radixweb, it is anticipated that by 2025, 85% of organizations will adopt a cloud-first strategy. Presently, 60% of corporate data is stored in the cloud, underscoring its critical role in modern data management strategies. It is expected that 51% of IT budgets will transition from traditional IT solutions to cloud-based alternatives by 2025, reflecting a significant shift in technology investment priorities.
Cloud security knowledge remains a challenge for many organizations, as 40% of IT decision-makers seek assistance from suppliers in this area. Additionally, there is a strong interest among IT executives, with 59% considering moving private customer data and 52% contemplating the migration of financial data from businesses to the cloud. The complexity of managing cloud assets is also evident, as 40% of IT officials express a need for assistance in overseeing their cloud resources.
Founderjar highlights the extensive adoption of cloud services across various sectors, with Retail (96.9%), Media & Entertainment (94.9%), and Finance & Banking (92.8%) leading in cloud utilization. About 31% of organizations anticipate that more than 75% of their workloads will be cloud-based by the end of 2023. Leading the market in cloud storage solutions are Microsoft Azure and Amazon Web Services, utilized by over 73% of surveyed organizations.
Key Takeaways
- The Software as a Service (SaaS) segment held a leading position, capturing 60.2% share, reflecting the strong demand for subscription-based cloud software solutions.
- Hybrid Cloud accounted for 45.7% share, showing its importance as enterprises balance flexibility, scalability, and security.
- Large Enterprises dominated with 60.5% share, driven by heavy investment in digital transformation and advanced IT infrastructure.
- The Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI) sector led industry adoption, holding 23.5% share, supported by compliance, security, and fintech integration.
- The U.S. Cloud Computing Market reached USD 306.46 Billion in 2024, expanding at a strong 20.2% CAGR, reflecting the country’s leadership in digital innovation.
- North America captured 39.5% share of the global market, highlighting its dominance in enterprise cloud adoption and technology ecosystems.
Governments around the world are playing a crucial role in propelling the adoption of cloud computing technologies. Recognizing the potential for cloud services to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve data accessibility, public sector entities are increasingly implementing cloud-based solutions. This governmental endorsement not only leads to substantial infrastructure investments but also fosters a regulatory environment that supports secure and robust cloud implementations.
Cloud Computing Statistics
- According to spacelift, By 2026, the market is forecast to be worth USD 947.3 billion, reflecting accelerated enterprise adoption.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) leads with a 32% share, followed by Microsoft Azure at 21% and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) at 12%.
- 96% of companies use the public cloud, while 84% use the private cloud, showing widespread hybrid strategies.
- By 2025, global data volumes will reach 200 zettabytes, intensifying demand for scalable cloud infrastructure.
- The biggest challenge for decision-makers is managing cloud spend, with 82% citing cost control as a concern.
- 94% of businesses report improved security after migrating to the cloud, strengthening trust in cloud adoption.
- Based on data from nextwork, Spending on Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) will approach USD 300 billion by 2025, underlining its dominance in enterprise IT.
- Infrastructure services are projected to grow by 25%, while platform services will expand by 22% in 2025.
- By 2025, 51% of IT spending will shift from traditional tools to cloud-based solutions.
- 75% of enterprises are prioritizing cloud-native application development.
- 92% of companies are expected to adopt multi-cloud strategies, reducing vendor lock-in and enhancing flexibility.
Analysts’ Viewpoint
Investment opportunities in the cloud market are expanding, with major cloud providers committing billions to infrastructure development across developed and emerging markets. There is strong interest in regions where demand for digital transformation and AI-powered cloud services is growing rapidly. Investments focus on building regional data centers, scaling cloud capacity, and enhancing AI capabilities.
Business benefits derived from cloud adoption include improved profitability and revenue growth, faster deployment of products, enhanced operational efficiency, and better disaster recovery capabilities. Cloud platforms help enterprises reduce costs related to hardware, support remote workforces effectively, and enable more agile responses to market changes.
The regulatory environment surrounding cloud computing is complex and varies across industries and regions. Regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), HIPAA for healthcare data, and FedRAMP for government cloud usage establish standards for data security and privacy. Compliance with these regulations requires businesses and cloud providers to implement robust encryption, access controls, and continuous monitoring practices.
Consequences of Generative AI
The implementation of Generative AI capabilities across cloud infrastructure represents a significant technological advancement with profound implications for industries worldwide. Generative AI, which includes technologies like natural language processing, image generation, and predictive analytics, can be seamlessly integrated into cloud environments due to the scalable and flexible nature of cloud computing.
This integration allows businesses to leverage advanced AI tools without the need for substantial upfront investment in physical hardware. Cloud providers can offer AI as a service, enabling companies to access state-of-the-art models and computing power on demand. This democratizes access to powerful AI technologies, making them available to a wider range of enterprises, including startups and small businesses that may not have the resources to develop such capabilities in-house.
Furthermore, deploying Generative AI in the cloud enhances innovation by facilitating rapid prototyping and experimentation. Companies can quickly test and iterate on AI-driven solutions, reducing development cycles and accelerating time to market for new products and services. This is particularly valuable in sectors like marketing, where AI can generate personalized content at scale, and in product design, where AI algorithms can predict consumer preferences and help design products that meet those needs more effectively.
Moreover, cloud-based Generative AI can improve operational efficiency by automating routine tasks and analyzing large volumes of data to identify optimization opportunities. For example, in supply chain management, AI can predict disruptions and automatically adjust orders and logistics to maintain efficiency.
U.S. Cloud Computing Market Size
The US Cloud Computing Market was valued at USD 306.46 Billion in 2024, with a robust CAGR of 20.2%. The U.S. cloud computing market is a rapidly growing sector, driven by increasing demand for scalable, cost-efficient solutions across industries. Key segments include infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), platform-as-a-service (PaaS), and software-as-a-service (SaaS).
Major players like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud dominate the market. The rise of artificial intelligence, big data analytics, and remote work further fuels cloud adoption.
Security and compliance remain top priorities for businesses adopting cloud solutions.With government initiatives supporting digital transformation, the U.S. is a global leader in cloud innovation. The market’s growth is also supported by expanding internet access and the need for enhanced data storage, driving businesses towards cloud migration and services.
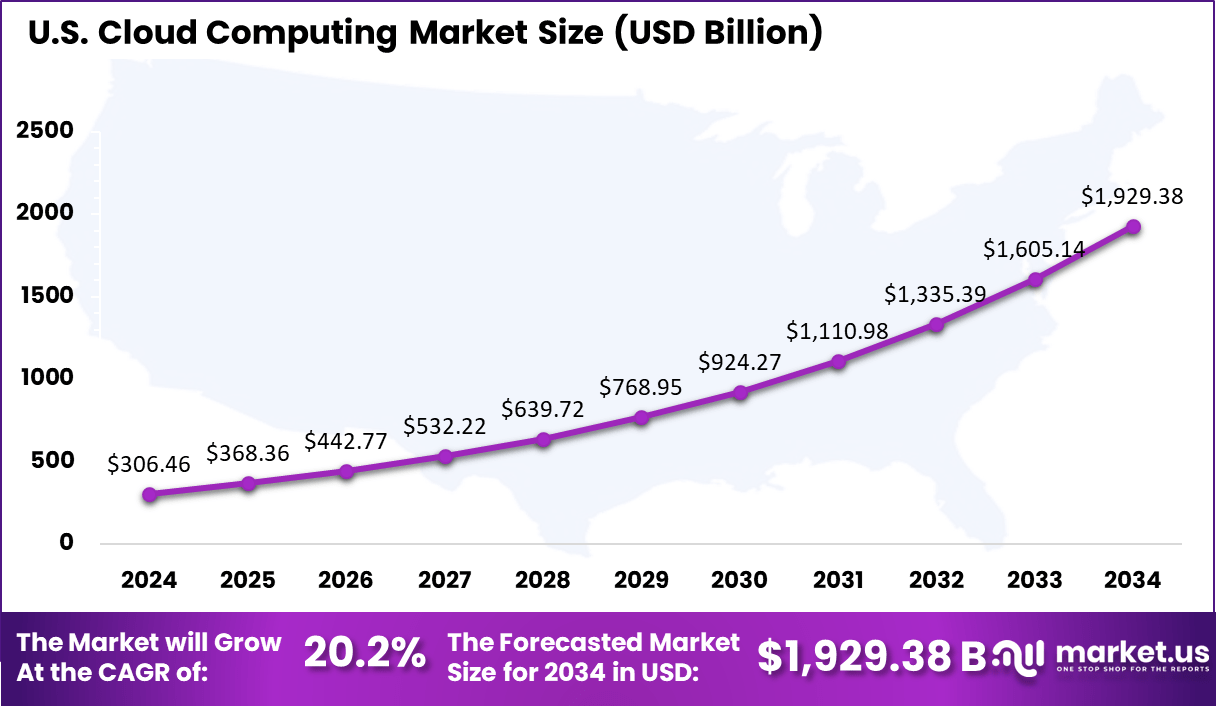
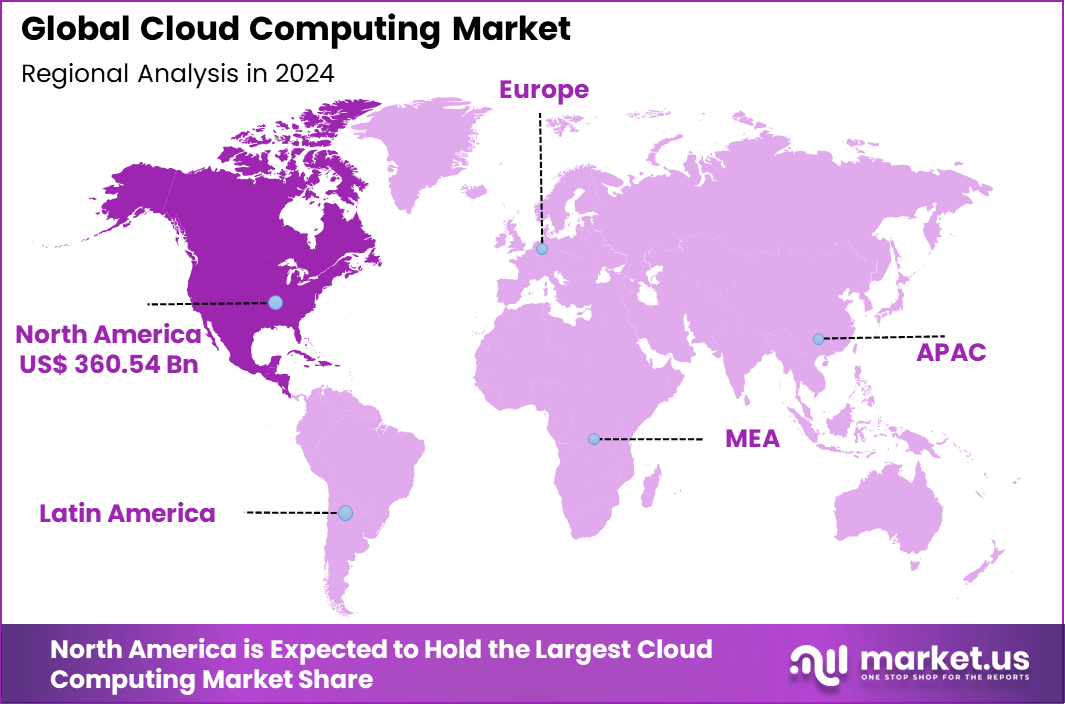
In 2024, North America held a dominant market position in the global Cloud Computing Market, capturing more than a 39.5 % share. This leadership can be attributed to several key factors, including advanced technological infrastructure, substantial investment in cloud technologies, and the presence of major cloud service providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
The region’s strong emphasis on digital transformation across various sectors, such as healthcare, finance, and retail, has also played a crucial role in propelling the cloud computing market forward. The North American market benefits from a highly developed IT ecosystem and a favorable regulatory environment that encourages innovation and adoption of cloud services.
Government initiatives and policies supporting cloud technology integration further boost the market. Additionally, the region’s large enterprises and SMEs are increasingly leveraging cloud solutions to enhance operational efficiency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. The rapid adoption of advanced technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT), has further fueled the demand for cloud services, solidifying North America’s leading position in the market.
Emerging Trends
Key Trends Description AI and Machine Learning in Cloud Integration of AI and ML boosts automation, analytics, and intelligent cloud services. Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Organizations increasingly adopt multi-cloud strategies for flexibility, optimization, and risk management. Edge Computing Growth Rising need for real-time data processing drives expansion in edge computing alongside cloud usage. Serverless Computing Serverless architectures gain popularity for scalable, cost-efficient application deployment. Cloud Security Advancements Enhanced security protocols and compliance frameworks address growing concerns around data protection. Growth Factors
Key Factors Description Digital Transformation Businesses shifting operations to cloud to enable agility, remote work, and digital services. Expanding IoT Adoption Proliferation of connected devices generates huge data volumes requiring cloud platform support. Cost Efficiency Pay-as-you-go pricing and reduced upfront infrastructure costs attract enterprises. Regulatory Support Governments promote cloud usage through policies and incentives with focus on data sovereignty. Increasing SaaS Usage Widespread adoption of software-as-a-service solutions boosts cloud platform demand. Service Type Analysis
In 2024, the Software as a Service (SaaS) segment held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 60.2% share of the Global Cloud Computing Market. This segment’s leadership can be attributed to its straightforward deployment model and cost-effectiveness, which make it accessible for businesses of all sizes.
SaaS solutions provide applications hosted on remote servers, offering businesses the advantage of low upfront costs, minimal maintenance requirements, and scalable options that can grow with their needs. This model eliminates the need for organizations to install, update, and manage software on their local computers, which not only reduces IT labor costs but also decreases the potential for software-related issues.
Additionally, the widespread adoption of SaaS is driven by its flexibility and the broad range of applications it covers, from customer relationship management (CRM) and human resources to specialized project management tools. Businesses benefit from the ability to access services from anywhere, fostering collaboration among teams that are geographically dispersed.
Moreover, SaaS models are continually enhanced with the latest features without requiring user intervention, ensuring that all clients have access to the most up-to-date technology without additional upgrade costs or downtime. The leading position of the SaaS segment underscores its integral role in the digital transformation strategies of modern enterprises.
By providing versatile and user-friendly solutions, SaaS not only supports a wide array of business processes but also accelerates innovation and operational efficiency. This makes it a pivotal element of the cloud computing ecosystem, likely to maintain its dominance as more businesses migrate to cloud-based operations.
Deployment Mode Analysis
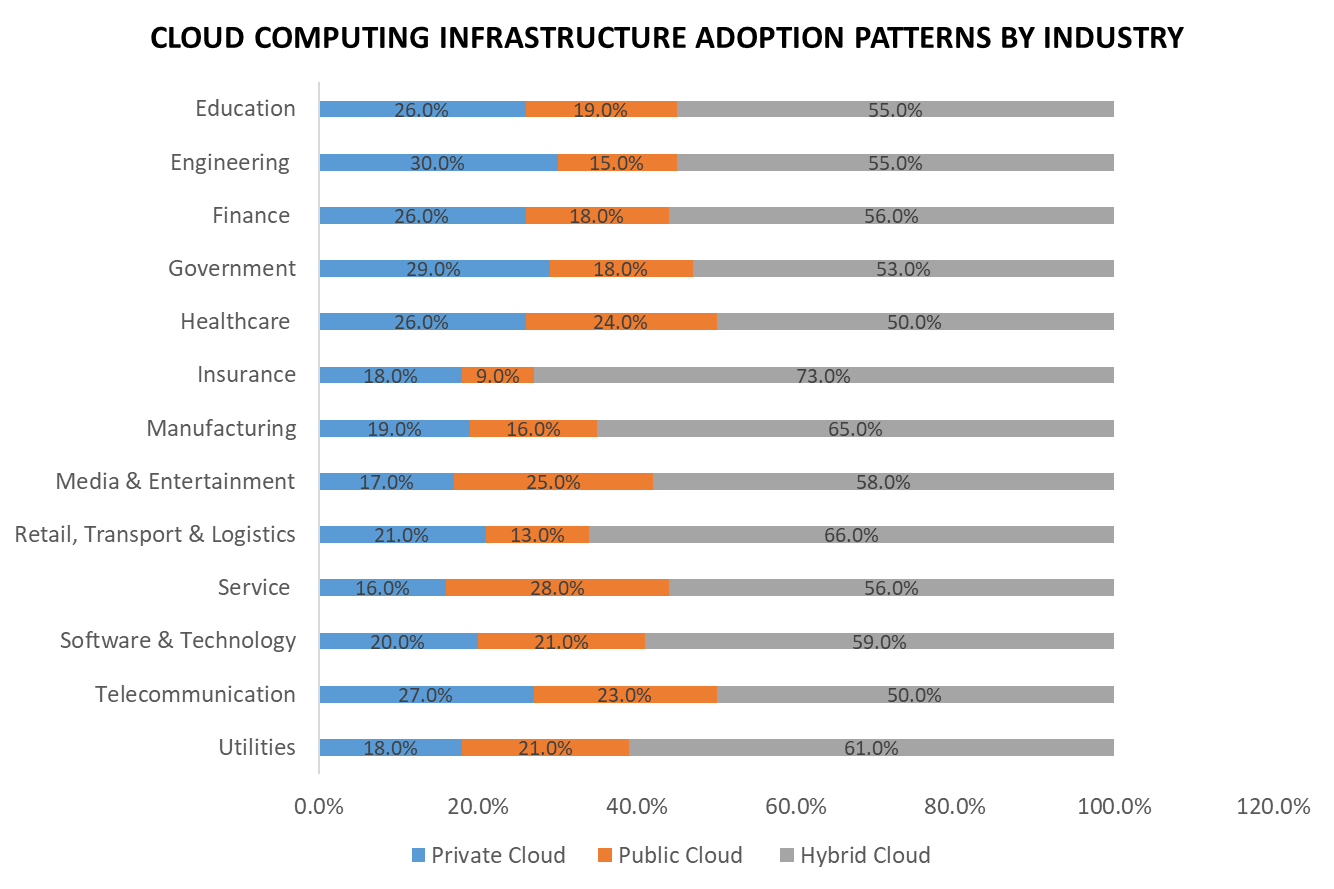
In 2024, the Hybrid Cloud segment held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 45.7% share of the Global Cloud Computing Market. This segment’s prominence is largely due to its enhanced security features and control, which are crucial for organizations handling sensitive data or requiring strict data governance.
Private clouds offer a dedicated environment where resources are not shared with other organizations, providing businesses with the ability to configure and manage it according to their specific compliance requirements and security standards. This exclusivity makes private cloud an attractive option for sectors such as finance, healthcare, and government, where data privacy is paramount.
Moreover, the private cloud model offers organizations predictable performance and reliable resources, which are essential for critical operations. The ability to customize its infrastructure and keep it within a controlled environment allows businesses to optimize their IT performance without the potential variability associated with public cloud resources. This control also extends to data sovereignty, as companies can choose the exact location of their data centers, further enhancing their compliance with regional regulations.
The leading position of the Private Cloud segment reflects its continued relevance to businesses prioritizing security and control over their IT environments. As more companies become data-driven and cloud adoption increases across all sectors, private clouds provide a tailored solution that aligns with stringent operational, regulatory, and security requirements, ensuring that this segment remains a cornerstone of the cloud computing landscape.
Enterprise Size Analysis
In 2024, the Large Enterprises segment held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 60.5% share of the Global Cloud Computing Market. This leadership is primarily due to the extensive IT infrastructure needs and robust budget capacities of large enterprises, which enable them to invest significantly in comprehensive cloud solutions.
Large enterprises often operate across multiple geographic locations, necessitating cloud services that can seamlessly integrate vast amounts of data, provide high-level security, and ensure consistent service availability. Cloud computing offers these organizations the scalability to efficiently manage big data analytics, enterprise resource planning (ERP), and customer relationship management (CRM) systems on a global scale.
Furthermore, large enterprises are increasingly adopting cloud services to foster innovation and improve operational efficiencies. By leveraging cloud technologies, these organizations can quickly deploy and scale new applications, respond more agilely to market changes, and reduce the time to market for new products or services. Cloud solutions also facilitate enhanced collaboration among dispersed teams, making it easier for large businesses to manage projects and share information securely and efficiently across different regions.
The dominance of the Large Enterprises segment reflects their ongoing need to manage complex operations and large volumes of data effectively. Cloud computing not only meets these demands but also offers a competitive edge by enabling large enterprises to innovate faster and operate more dynamically in today’s digital economy. This segment’s substantial investment in cloud infrastructure is likely to continue as businesses seek to capitalize on the advantages of cloud technology to drive growth and maintain market leadership.
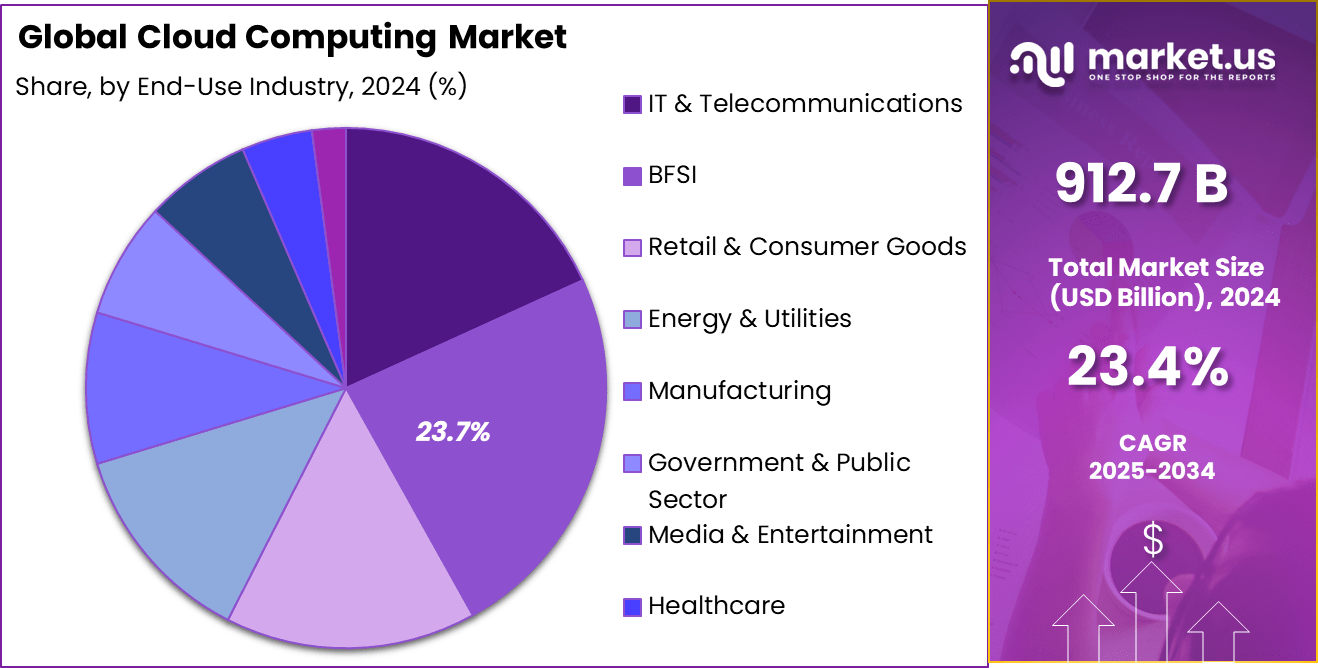
End-Use Industry Analysis
In 2024, the Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI) segment held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 23.7% share of the Global Cloud Computing Market. This prominence is primarily attributed to the digital transformation initiatives that have become a strategic necessity in the BFSI sector.
Financial institutions are leveraging cloud computing to enhance their operational efficiencies, improve customer experiences, and introduce innovative financial products quickly. The scalability and flexibility offered by cloud services enable these institutions to manage large volumes of transactions and data securely and efficiently, which is crucial in maintaining competitiveness in a rapidly evolving financial landscape.
Moreover, cloud technology in the BFSI sector supports the deployment of advanced technologies such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, and big data analytics, facilitating more personalized and secure customer services. Regulatory compliance also plays a critical role in this adoption; cloud providers are increasingly offering solutions that comply with stringent financial regulations, helping institutions navigate the complexities of data governance and cybersecurity.
The leading position of the BFSI segment underscores its push towards more agile and customer-centric business models. As financial institutions continue to face pressure from fintech disruptors and heightened customer expectations, the adoption of cloud computing remains integral to their strategic operations. This ensures not only operational resilience but also positions these institutions to capitalize on new opportunities for growth and innovation in the financial sector.
Key Market Segments
Service Type
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Infrastructure as a Service(laas)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Deployment Mode
- Hybrid Cloud
- Private Cloud
- Public Cloud
Enterprise Size
- Small & Medium Enterprises
- Large Enterprises
End-Use Industry
- IT & Telecommunications
- BFSI
- Retail & Consumer Goods
- Energy & Utilities
- Manufacturing
- Government & Public Sector
- Media & Entertainment
- Healthcare
- Other End-Use Industries
Driving Factor
Increasing Need for Business Agility
One of the strongest drivers pushing organizations toward cloud computing is the need for greater business agility. Companies today operate in a fast-changing environment where the ability to quickly scale resources or deploy new applications can provide a critical competitive edge.
Cloud computing enables businesses to rapidly adjust their IT resources to meet fluctuating demands without the delays and costs associated with traditional hardware investments. This flexibility means companies can innovate faster, respond promptly to market shifts, and optimize operations for better efficiency.
Moreover, cloud solutions provide seamless access to advanced digital tools such as real-time analytics and collaboration platforms, facilitating quicker decision-making and enhanced productivity. By adopting cloud technologies, businesses become more resilient and prepared to meet evolving challenges, which is why agility stands out as a foundational factor driving cloud adoption across industries.
Restraining Factor
Data Security and Privacy Concerns
Despite its benefits, a major restraint slowing cloud computing adoption is concerns about data security and privacy. Storing sensitive information on remote servers managed by third parties raises fears about unauthorized access, data breaches, and compliance risks.
Organizations remain cautious because when data moves outside the company’s direct control, safeguarding it becomes more complex. Issues like misconfigurations, insider threats, and the lack of visibility into cloud environments intensify these worries.
This restraint is especially significant for highly regulated sectors or businesses dealing with confidential customer data. Companies often face challenges ensuring that customer privacy regulations and internal policies are fully met in cloud environments. Until there is greater assurance around secure cloud operations and transparent control, some organizations remain hesitant to fully embrace the cloud.
Growth Opportunity
Expansion of Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies
The rise of hybrid and multi-cloud architectures presents a significant opportunity for businesses leveraging cloud computing. Hybrid clouds combine private and public cloud resources, allowing organizations to keep sensitive workloads on-premises while using public clouds for less critical applications.
Multi-cloud strategies involve using multiple cloud service providers simultaneously to optimize costs, avoid vendor lock-in, and enhance resilience. These approaches provide businesses the flexibility to tailor their cloud use to specific operational needs and risk profiles.
This opportunity supports more customized, efficient IT environments that can evolve with business demands. Companies are investing in tools and expertise to manage hybrid and multi-cloud complexities, which opens new avenues for innovation and competitive advantage. As more sectors recognize the strategic benefits of combining different cloud options, the overall cloud ecosystem becomes richer and more diverse.
Challenge Analysis
Managing Cloud Complexity and Integration
One of the toughest challenges in cloud computing today is handling the complexity involved in managing and integrating diverse cloud services. With many organizations using multiple cloud platforms and a mix of on-premises and cloud infrastructure, coordinating across these environments is technically demanding.
This complexity can lead to increased operational overhead, difficulties in ensuring consistent security policies, and troubles with data management across siloed systems. Integrating cloud services with existing applications and workflows requires specialized skills and tools, which are often in short supply. Without proper governance and alignment between IT teams, businesses can face inefficiencies or increased risk of errors.
Top Use Cases
- AI as a Service (AIaaS): With AI integration into cloud solutions, businesses can access advanced AI tools and models, such as large language models like ChatGPT, without the need for extensive infrastructure. This service allows enterprises to leverage AI for enhancing business processes and creating new value propositions while avoiding the high costs of setting up and maintaining AI systems.
- Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies: These strategies provide businesses with the flexibility to distribute their workloads across various cloud environments from different providers, reducing dependency on any single vendor and enhancing business continuity planning. This setup supports regulatory compliance and enables more robust disaster recovery protocols.
- Edge Computing: This technology pushes computational tasks to the edge of the network, closer to the data sources, which reduces latency and allows for real-time data processing and decision-making. This is increasingly crucial for IoT devices and mobile applications where immediate data processing is necessary.
- Serverless Computing: This model allows businesses to run applications without managing underlying infrastructure, significantly reducing overhead and speeding up the deployment process. It supports rapid scaling and improves cost efficiency by charging only for the resources used during the execution of applications.
- Sustainable Cloud Computing: Driven by increasing awareness of environmental impacts, cloud providers are focusing on reducing carbon emissions and energy consumption. This includes optimizing data center operations and using renewable energy sources, thus contributing to a more sustainable technology ecosystem.
Business Benefits
- Cost Efficiency: Cloud computing can significantly reduce costs related to IT infrastructure by leveraging economies of scale. Pay-as-you-go models, prevalent in cloud services, ensure that businesses pay only for what they use, reducing wasted resources.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud environments allow businesses to quickly adjust their resource usage based on current demand without the need for significant upfront capital investments. This agility is crucial for businesses to respond effectively to market changes and opportunities.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Cloud platforms enable better collaboration across teams by providing centralized data access and tools that can be used simultaneously by multiple users, irrespective of their location. This is particularly beneficial for organizations with geographically dispersed teams.
- Improved Security and Compliance: Many cloud providers offer robust security features that comply with various regulatory standards, helping businesses protect data and meet compliance requirements more efficiently than traditional IT setups could.
- Innovation Facilitation: By removing many of the traditional barriers to technology adoption, such as initial cost and complexity, cloud computing allows businesses to experiment with new ideas and technologies more freely, accelerating innovation cycles.
Geopolitical and Recession Impact Analysis
Geopolitical Impact Analysis
Geopolitical tensions and policy shifts significantly impact the Global Cloud Computing Market. Regulations and data security laws emerging from these tensions compel cloud service providers to adapt to diverse national standards, affecting market entry strategies and operational models.
For instance, policies mandating local data storage can lead to increased costs for providers needing to establish regional data centers. Moreover, geopolitical conflicts can disrupt global supply chains, affecting the availability and cost of hardware essential for cloud infrastructure. Such dynamics can lead to market fragmentation and influence investment decisions, potentially limiting the market’s growth in certain regions while creating opportunities in others.
Recession Impact Analysis
In times of economic downturn, the Cloud Computing Market exhibits a degree of elasticity, primarily due to its cost-efficiency and scalability. During recessions, businesses often seek to reduce operational costs, and cloud services offer a viable solution by eliminating the need for significant capital investments in IT infrastructure.
However, a prolonged recession could lead to reduced IT spending and delayed decision-making regarding new technology adoption, potentially slowing market growth. However, the inherent flexibility of cloud services, allowing businesses to scale resources according to their changing needs, positions cloud computing as a relatively stable sector even in challenging economic conditions.
Regional Analysis
The cloud computing market exhibits significant differences in adoption rates, technological advancements, and regulatory environments across various regions and countries. Below is a countrywise breakdown of key trends and insights within the cloud computing sector:
North America
- The United States: The U.S. is a global leader in the cloud computing market, driven by the presence of major technology giants such as Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud. These companies continue to innovate and expand their infrastructure, resulting in widespread adoption across enterprises of all sizes.
- Canada: Canada’s cloud computing market is growing due to increased government spending on digital infrastructure and the adoption of cloud-based solutions by small and medium-sized enterprises. The focus on data privacy and security is particularly strong, influenced by national policies and regulations.
Europe
- Germany: Germany shows robust growth in cloud computing, fueled by the country’s strong industrial base and initiatives like Industrie 4.0, which promote the use of smart manufacturing technologies.
- France: In France, cloud adoption is encouraged by government-led digital transformation projects and the growing startup ecosystem, which relies heavily on scalable cloud solutions.
- The UK: Post-Brexit, the UK continues to show strong cloud adoption with an emphasis on maintaining data sovereignty and building local data centers to comply with legal and regulatory requirements.
- Spain and Italy: Both countries have seen a rapid increase in cloud computing utilization due to the need for digital transformation and economic recovery strategies post-pandemic.
- Netherlands: Known for its robust internet infrastructure, the Netherlands serves as a significant data center hub in Europe, facilitating cloud services across the region.
- Russia: Russia is gradually expanding its cloud computing market with a focus on developing local providers to comply with national data handling laws.
Asia-Pacific (APAC)
- China: China’s cloud market is dominated by local giants such as Alibaba Cloud and Tencent Cloud, which are expanding their services globally. The government’s push for digitalization in all sectors fuels cloud adoption.
- Japan: Japan’s cloud market is growing due to its aging population and the need for accessible computing resources, driving innovation in healthcare and public services.
- South Korea and India: These countries are rapidly adopting cloud solutions, driven by government policies supporting digital economies and a booming IT workforce.
- Australia and New Zealand: Both countries are advanced in their use of cloud services, emphasizing data security and robust regulatory frameworks.
Latin America
- Brazil and Mexico: In Latin America, Brazil and Mexico lead in cloud adoption, supported by a need for business scalability and digital transformation in response to economic pressures and a young, tech-savvy population.
Middle East and Africa (MEA)
- South Africa, Saudi Arabia, and UAE: These regions are witnessing a transformation in cloud adoption, with significant investments in IT infrastructure and smart city projects. Data sovereignty and local data center developments are key concerns.
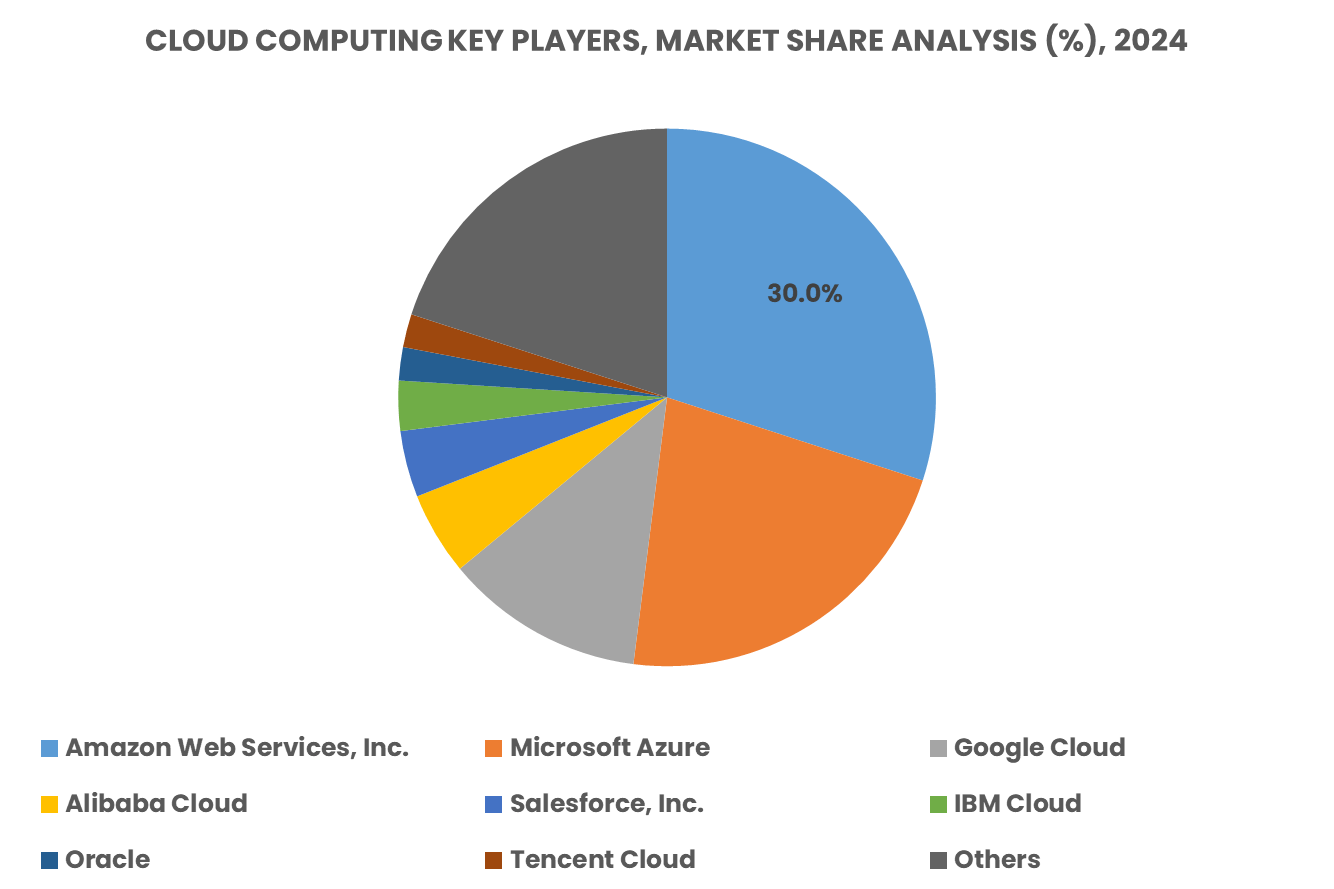
Key Player Analysis
The Global Cloud Computing Market is shaped by the dominance of Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform, with additional competition from IBM Cloud, Oracle Cloud, and a growing number of niche providers. This competitive structure drives continuous innovation and diversification, as specialized players target industry-specific needs and service gaps.
Amazon Web Services remains a leader with its comprehensive suite of cloud offerings. Its emphasis on hybrid cloud models and enterprise services has strengthened its role across industries. The scalability of AWS, combined with its wide range of services, continues to attract enterprises seeking flexibility and cost optimization.
Microsoft Azure has gained a strong position due to its seamless integration with the Microsoft ecosystem, including Windows Server, Active Directory, and Office 365. Its hybrid cloud features, AI integration, and enterprise-grade solutions appeal strongly to businesses already reliant on Microsoft platforms. Azure’s commitment to security, compliance, and developer support has expanded its adoption across startups and global enterprises.
Google Cloud has established itself with a focus on artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics. Its leadership in handling large-scale data sets and providing cloud-native tools such as Kubernetes makes it a preferred platform for technology-driven and digital-first businesses. Continuous investments in infrastructure, edge computing, and open-source frameworks reinforce Google Cloud’s positioning as a transformative player in data-driven industries.
Top Key Players in the Cloud Computing Market
- Adobe Inc.
- Google LLC
- Alibaba Group Holding Limited
- IBM Corporation
- Oracle Corporation
- Salesforce, Inc.
- Microsoft Corporation
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- VMware LLC
- SAP SE
- Other Key Players
Recent Developments
- In September 2024, Oracle and Amazon Web Services, Inc. (AWS) announced the launch of Oracle Database@AWS, a new offering that allows customers to access Oracle Autonomous Database on dedicated infrastructure and Oracle Exadata Database Service within AWS. Oracle Database@AWS provide customers with a unified experience between Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) and AWS, offering simplified database administration, billing, and unified customer support.
- In November 2024, Microsoft has launched cloud-connected software that lets companies run Azure computing, networking, storage and application services in an edge location or hybrid cloud environment.
- In March 2025, Kyndryl, the largest IT infrastructure services provider, announced an expanded partnership with Google Cloud to leverage generative AI to help streamline and accelerate the modernization of mainframe applications and data. As part of the partnership, Kyndryl has been certified as a specialized partner for Google Cloud’s AI and Gemini models.
- In February 2025, Fujitsu announced the launch of the Fujitsu Cloud Service Generative AI Platform. The new service, which combines data confidentiality with the ease of use of the cloud, with a global rollout planned for the future. The company offers Fujitsu Cloud Service Generative AI Platform for secure and flexible enterprise data management
- In September 2024, Oracle announced the launch of a new version of the Oracle Cloud Native SCCA Landing Zone for centralized IT teams, or their partners, to manage SCCA-compliant implementations for multiple customers and systems. Using a framework of cloud native services, the landing zone automates the process of building an SCCA-compliant architecture for the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) Impact Level 2, 4, and 5 (IL2, IL4, IL5) workloads, saving significant time building secure systems in the cloud.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 912.7Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 7,473.3 Bn CAGR(2025-2034) 23.4% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue forecast, AI impact on Market trends, Share Insights, Company ranking, competitive landscape, Recent Developments, Market Dynamics and Emerging Trends Segments Covered By Service Type (Software as a Service (SaaS), Infrastructure as a Service(laas), and Platform as a Service (PaaS)), By Deployment Mode (Hybrid Cloud, Private Cloud, and Public Cloud), By Enterprise Size (Small & Medium Enterprises and Large Enterprises), By End-Use Industry Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of Latin America; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Adobe Inc., Google LLC, Alibaba Group Holding Limited, IBM Corporation, Oracle Corporation, Salesforce Inc., Microsoft Corporation, Cisco Systems Inc., VMware LLC, SAP SE, Other Key Players Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three license to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)

-
-
- Adobe Inc.
- Google LLC
- Alibaba Group Holding Limited
- IBM Corporation
- Oracle Corporation
- Salesforce, Inc.
- Microsoft Corporation
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- VMware LLC
- SAP SE
- Other Key Players













