Animal Vaccine Market By Product (Attenuated Vaccines, Inactivated Vaccines, Subunit Vaccines, Toxoid Vaccines, Recombinant Vaccines, DNA Vaccines), By Type of Animal Species (Livestock Animals- Poultry, Swine, Sheep, Goat, Others; Companion Animals- Dogs, Cat, Horse, Birds, Others), By Route of Administration (Subcutaneous, Intramuscular, Oral, Intraocular, Intranasal, Others), By Distribution Channel (Veterinary Hospitals and clinics, Retail Pharmacy, Online Retail Pharmacy), By Region And Companies – Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Trends 2025-2034
- Published date: April 2025
- Report ID: 54840
- Number of Pages: 376
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
- Report Overview
- Key Takeaways
- Product Type Analysis
- Animal Species Type Analysis
- Route of Administration Analysis
- Distribution Channel Analysis
- Key Market Segments
- Drivers
- Restraints
- Opportunities
- Impact of Macroeconomic / Geopolitical Factors
- Latest Trends
- Regional Analysis
- Key Players Analysis
- Recent Developments
- Report Scope
Report Overview
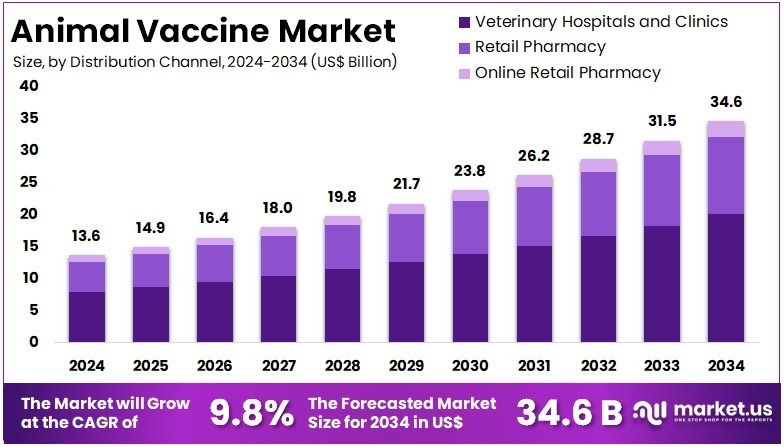
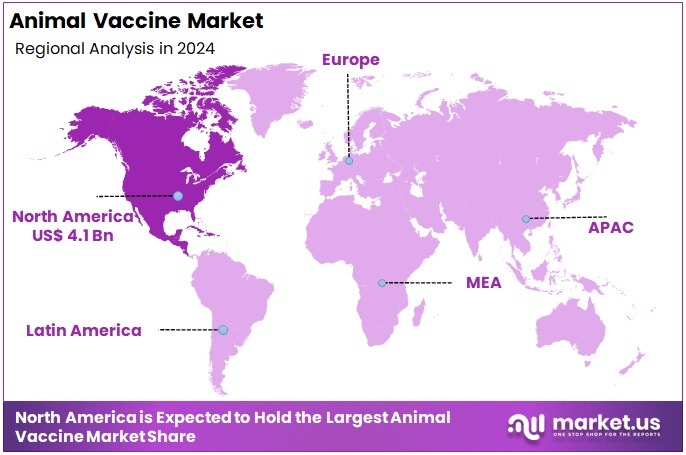
The Global Animal Vaccine Market Size is expected to be worth around US$ 34.6 Billion by 2034, from US$ 13.6 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 9.8% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 30.2% share and holds US$ 4.1 Billion market value for the year.
Vaccination plays a critical role in safeguarding the health of domestic, livestock, and wildlife species against infectious diseases by stimulating the immune system to identify and combat pathogens without causing illness. The market is seeing a significant shift toward advanced vaccine technologies, including DNA-based and recombinant vaccines, in addition to traditional inactivated and live-attenuated vaccines. These vaccines not only protect pets from highly contagious and potentially fatal diseases but also enhance their overall health and well-being.
The rise in cattle disease outbreaks, along with the growing global livestock population, is a major driver for the increasing adoption of vaccines for ruminants, particularly cattle. Furthermore, the expanding global population and rising disposable incomes have heightened the demand for animal-derived products such as meat, milk, and eggs.
Livestock producers are now adopting more preventive healthcare practices to protect their animals. Vaccinations play a key role in maintaining animal health and boosting productivity. This growing trend is driving the expansion of the animal vaccine market. Vaccines have saved millions of animals from disease over the past century. The first vaccine dose prepares the immune system to recognize threats. Later doses boost antibody production for protection. This preventive approach helps reduce illness, supports food supply chains, and improves the overall welfare of farm animals.
Veterinary vaccines follow similar standards to human vaccines, with animal health as the top priority. However, their development is faster and more cost-effective. Regulatory requirements are less strict, and fewer preclinical trials are needed. These factors lower the costs associated with vaccine development. Another benefit is the ability to test vaccines directly on the target animal species. This leads to more accurate results compared to human vaccines, which often rely on less reliable rodent models during early research stages.
The global population reached 8 billion in 2022 and is expected to rise to 9.7 billion by 2050. This growth creates a higher demand for animal-based food. Meeting this demand will require healthy livestock and increased food production. Animal vaccines are essential to this effort. They reduce disease outbreaks and increase productivity. By supporting the health of livestock, vaccines help stabilize food supply. As the population grows, animal vaccinations will play a vital role in ensuring food security and sustainability worldwide.
Key Takeaways
- In 2024, the animal vaccines market generated a revenue of US$ 13.6 billion, with a CAGR of 9.8% and is expected to reach US$ 34.6 billion by the year 2034.
- The product type segment is attenuated live vaccine, inactivated vaccine, subunit vaccine, toxoid vaccine, recombinant vaccine, DNA vaccine in which attenuated live vaccine taking the lead in 2024 with a market share of 38.2%.
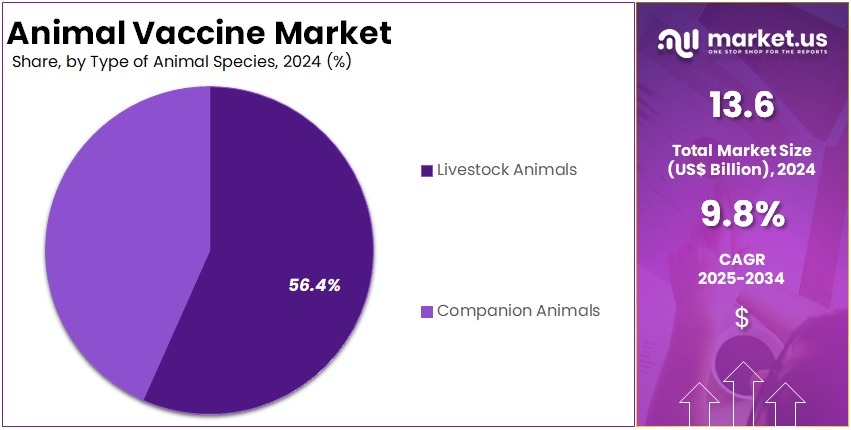
- By type of animal species segmentation is livestock animal and companion animal in which livestock animal held a significant share of 56.4%.
- By route of administration the market is segregated into subcutaneous, intramuscular, oral, intraocular, intranasal, parenteral, others. The subcutaneous segment held a significant share of 42.7% in animal vaccines market.
- In 2024, the veterinary hospital and clinic segment took the lead in the global market, securing 57.8% of the total revenue share.
- North America led the market by securing a market share of 30.2% in 2024.
Product Type Analysis
In 2024, the Attenuated (Live) Vaccines segment held a dominant market position in the product type segment of animal vaccine market, and captured more than a 38.2% share. Live attenuated vaccines are among the fastest-growing segments due to their advantages and the increasing demand for effective disease prevention in livestock. These vaccines are made using pathogens, typically viruses, that have been weakened (attenuated) to replicate sufficiently to trigger an immune response without causing illness. They generally provide long-lasting immunity and help prevent disease outbreaks, supporting both food security and economic stability in the livestock sector.
Live-attenuated vaccines typically require fewer doses compared to other vaccine types, reducing costs and increasing convenience for livestock producers. They generate a strong immune response, including both antibody and cell-mediated immunity, and offer rapid onset protection. However, challenges in production, storage, and transportation exist due to the use of live pathogens.
Additionally, because these vaccines contain live organisms, they may pose risks to immunocompromised individuals. For example, live vaccines are often more effective than inactivated ones in stimulating cell-mediated immune responses. Nonetheless, the safety of these vaccines requires careful attenuation to ensure the pathogen can replicate without causing disease. While there are a variety of live-attenuated vaccines available, administering them to food-producing animals can pose a risk of human exposure to vaccine strains, potentially affecting human health.
For example, recombinant vaccines using fowlpox virus in the poultry industry incorporate Newcastle disease virus HA and F genes, providing immunity against both fowlpox and Newcastle diseases. Similarly, modified live virus vaccines, such as those involving streptomycin-dependent Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida, use bacterial mutants that require streptomycin for growth and are killed once the absence of streptomycin triggers a protective immune response.
- In September 2024, the U.S. FDA approved FluMist (Influenza Vaccine Live, Intranasal) for administration by individuals or their caregivers, marking an important step in live vaccine approval.
- In India, the animal vaccine market is expanding rapidly, largely driven by the country’s leadership in livestock population, with approximately 535.8 million animals according to census data. The Indian animal healthcare sector contributes around 3% of the global market’s value and approximately 10% of its volume.
- Additionally, government initiatives focusing on livestock health and disease control, such as the National Animal Disease Control Programme, have further accelerated industry growth. The program aims to vaccinate 303.3 million animals by 2024, with over 170 million already vaccinated and nearly 180 million animals tagged.
Animal Species Type Analysis
In 2024, the Livestock Animals segment held a dominant market position in the Animal Species type segment of animal vaccine market, and captured more than a 56.4% share.
Livestock animals, which include poultry, swine, sheep, goats, and other species, are primarily raised for food production and are essential to the global food supply. Poultry, for example, represents one of the largest sectors, with billions of chickens raised annually for meat and eggs, making them highly susceptible to diseases that can impact both animal welfare and food safety.
Swine and cattle are also major contributors to meat production, with vaccination programs focused on diseases such as African swine fever and foot-and-mouth disease, which can cause significant losses in the meat industry. The vaccination of livestock is vital in preventing these diseases and ensuring a stable and productive agricultural system. Therefore, this segment held significant shares in the animal species type category.
Companion animals, including dogs, cats, horses, and birds, are also an essential part of the animal care landscape, though their role differs significantly from livestock. These animals are often kept for companionship, therapy, and other non-food-related purposes. Dogs and cats, as the most common companion animals, require vaccinations for diseases such as rabies, parvovirus, and distemper to ensure their health and prevent the transmission of zoonotic diseases. Over 90% of dog owners took their pets to the vet for at least one visit.
The rise in dog ownership, along with more people spending time at home with their pets, has led to an increase in the need for veterinary care. Horses, often used for sport, work, and recreation, also have specific vaccination needs, with equine influenza and tetanus being among the most common. Birds, particularly pet species such as parrots, require vaccines to prevent diseases like avian influenza and Newcastle disease, which can affect both the animals and the broader avian population.
Route of Administration Analysis
In 2024, the subcutaneous segment held a dominant market position in the route of administration segment of animal vaccine market, and captured more than a 42.7% share. This method is preferred for animal vaccination because it is simple and effective in inducing a strong immune response. Subcutaneous administration involves injecting the vaccine just beneath the skin, which is less invasive than intramuscular injections and reduces the risk of damaging deeper tissues, making it a safer option for animals.
Additionally, the gradual absorption of the vaccine into the body enhances its efficacy and provides controlled delivery, ensuring consistent results. This route is practical for veterinarians and farmers, especially in field settings, where ease of use and quick application are essential for managing large groups of animals. Subcutaneous injections are also easier to teach to veterinary professionals, streamlining training processes.
Both subcutaneous and intramuscular routes are the most commonly used methods for administering vaccines in animals, but the SC route is particularly suited for large-scale vaccination programs due to its practicality, safety, and reliability. It is recommended for administering various attenuated live vaccines and certain non-live vaccines, as it allows for slow absorption, delivering vaccines into fatty tissues with limited blood flow. The SC route’s ability to support sustained immunity makes it ideal for long-term health management in both livestock and pets.
Distribution Channel Analysis
In 2024, the veterinary hospital and clinic segment held a dominant market position in the distribution channel segment of animal vaccine market, and captured more than a 57.8% share. Veterinary clinics and animal hospitals play a vital role in ensuring the health of animals by providing comprehensive care, including surgeries, treatments, and nursing for various health concerns. Veterinarians offer expert advice on diet, exercise, medications, and vaccinations, which are essential for protecting pets and livestock from infectious diseases, thereby enhancing their overall health and immunity.
Routine veterinary visits not only aid in the early detection of illnesses but also ensure timely vaccinations, promoting longer, healthier lives for animals. The controlled environment of veterinary clinics allows for the monitoring and management of any adverse reactions, thereby improving the safety and effectiveness of vaccination programs. As the number of veterinary professionals continues to rise, it is expected that more animals will visit clinics, further driving the growth of this distribution channel.
The importance of veterinary hospitals and clinics in animal health care emphasizes their dominant role in vaccination efforts, especially as they increasingly focus on the treatment of chronic and targeted diseases. This highlights the confidence pet owners place in professional veterinary services and the crucial role veterinarians play in supporting and improving animal health.
Key Market Segments
By Product Type
- Attenuated (Live) Vaccines
- Inactivated Vaccines
- Subunit Vaccines
- Toxoid Vaccines
- Recombinant Vaccines
- DNA Vaccines
By Type of Animal Species
- Livestock Animals
- Poultry
- Swine
- Sheep
- Goat
- Others
- Companion Animals
- Dogs
- Cat
- Horse
- Birds
- Others
By Route of Administration
- Subcutaneous
- Intramuscular
- Oral
- Intraocular
- Intranasal
- Others
By Distribution Channel
- Veterinary Hospitals and clinics
- Retail Pharmacy
- Online Retail Pharmacy
Drivers
Increasing prevalence of Diseases
The animal vaccine market is experiencing rapid growth due to the increasing prevalence of diseases among animals. The rising incidence of zoonotic diseases and livestock infections has intensified the demand for effective vaccination programs aimed at preventing outbreaks and ensuring animal health. Several factors contribute to this growth, including the growing global demand for food, heightened awareness of zoonotic diseases, and significant advances in vaccine technology.
Governments and organizations are investing in vaccination initiatives to address these challenges, while innovations in vaccine development, such as DNA and recombinant vaccines, are enhancing efficacy and safety. Additionally, the rising awareness of biosecurity and the importance of disease prevention in livestock and pets is further driving market expansion. As the global population increases and the demand for animal-derived products rises, ensuring the health of livestock becomes crucial to maintaining a stable food supply.
Livestock diseases like blackleg can devastate herds, severely affecting food production. The growing prevalence of infectious diseases such as foot-and-mouth disease, rabies, and avian influenza has created an urgent need for robust vaccination programs. Technological advancements in vaccine development, including DNA and recombinant vaccines, have significantly improved vaccine effectiveness.
Vaccination not only safeguards animal health but also helps reduce veterinary costs, prevent production losses, and support food security, contributing to overall public health. Despite these efforts, challenges remain in the prevention and control of zoonotic diseases, including inadequate surveillance and reporting systems, limited diagnostic capacity for emerging diseases, and insufficient coordination between sectors.
The lack of awareness, limited resources, and weak data collection further hinder progress. However, successful vaccine initiatives, such as the eradication of canine-mediated rabies in the U.S. and the use of Salmonella Enteritidis vaccines in poultry, showcase the effectiveness of vaccines in controlling zoonotic diseases. Veterinarians play a key role in promoting comprehensive vaccination strategies and collaborating with producers to evaluate the public health benefits of vaccine use.
In addition, initiatives like PREZODE, supported by the French government during the G7 summit in 2022, aim to enhance understanding of emerging zoonotic diseases and improve prevention and early detection capabilities. Through these efforts, the animal vaccine market is positioned to continue growing and addressing critical global health challenges.
The World Health Organization (WHO) highlights that approximately 60% of human infectious diseases originate from animals, and 75% of emerging infectious diseases have an animal source. This presents a significant risk, making animal vaccination programs essential in preventing disease transmission and protecting both animal and human health.
As a result, the global demand for animal vaccines has increased, driven by efforts to prevent zoonotic outbreaks. Lyme disease, typically spread by ticks, is now expanding beyond its traditional regions, underscoring the growing need for effective vaccines. In 2023, the Companion Animal Parasite Council reported that the risk of Lyme disease reached unprecedented levels, emphasizing the importance of proactive disease prevention and management.
Restraints
High cost associated with vaccines
The high costs associated with animal vaccines and the challenges of vaccine storage represent significant restraints on the growth of the animal vaccine market. The expenses tied to vaccine devices and consumables can create financial burdens, limiting access to vaccination programs and placing strain on veterinary resources. These costs arise from several factors, including vaccine development, clinical trials, regulatory approvals, and manufacturing, all of which require advanced technologies and extensive research.
Additionally, the production of vaccines demands specialized systems and strict quality control measures, further driving up costs. Regulatory compliance adds complexity, as meeting international standards and securing approvals involve considerable investment. Moreover, the relatively small market for certain vaccines, particularly those for high-risk animals, often leads to higher production costs due to limited economies of scale.
These factors contribute to the elevated price of vaccines, which can limit their availability, particularly in lower-income regions or for pet owners. Storage issues also represent a major challenge in the supply chain for veterinary vaccines. The limited financial investment available for animal vaccine research and development further compounds this issue.
The cost of basic dog vaccinations, such as the DHLPP vaccine, typically ranges from $20 to $60 per dose, while the rabies vaccine generally costs between $20 and $30. Prices for non-core vaccines can vary but are usually under $100 per shot. For dogs, the overall vaccination cost typically falls between $20 and $60 per dose, with rabies vaccines ranging from $20 to $70. For cats, core vaccines, including those for Feline Leukemia Virus (FeLV) and rabies, usually cost between $25 and $45 per dose.
Opportunities
Shift toward Preventive Healthcare
The shift toward preventive healthcare presents significant opportunities in the animal vaccine market. This proactive approach focuses on disease prevention rather than treatment, increasing demand for effective vaccination programs. It opens avenues for innovation, especially in response to emerging diseases and zoonotic threats.
Additionally, preventive healthcare aligns with the “One Health” concept, which highlights the interconnected health of animals, humans, and the environment. By prioritizing prevention, stakeholders can enhance animal welfare, ensure food security, and reduce the risk of disease outbreaks, thereby contributing to global public health and sustainability. There are numerous opportunities to improve animal care, particularly with the large number of unvaccinated or inadequately treated pets, as well as those lacking permanent identification and proper worm or flea control.
Preventive measures, such as early disease detection and management, can significantly improve animal health. For pets, focusing on prevention helps maintain long-term well-being by identifying potential health issues early and preventing them from becoming severe or costly to treat. Key components of preventive care include regular veterinary visits, vaccinations, balanced nutrition, and consistent health monitoring.
The increasing focus on the One Health approach which highlights the interconnection between human, animal, and environmental health is fueling investments in vaccines aimed at preventing zoonotic diseases such as rabies and avian influenza. At the same time, breakthroughs in biotechnology, including mRNA and recombinant vaccines, are revolutionizing healthcare for both humans and animals.
In the livestock and poultry industries, preventing diseases in cattle, pigs, and poultry helps mitigate food shortages and economic losses. The increasing focus on preventive healthcare and animal vaccination creates significant business and investment opportunities. Veterinary services are expanding, especially in rural areas, through mobile vaccination units and specialized clinics. As awareness of preventive healthcare grows, the animal vaccine market is poised to play a vital role in ensuring global health security and food sustainability.
The shift toward preventive healthcare in animal vaccination is driven by the need to control infectious diseases, reduce transmission risks, and enhance overall animal welfare. With around 60% of human infectious diseases being zoonotic, preventive vaccination plays a vital role in minimizing outbreaks that impact both animals and humans. Advances in vaccine technology, such as AI-driven diagnostics and early disease detection, have led to more effective immunization strategies.
Governments globally are adopting initiatives to expand vaccination coverage, ensuring widespread disease prevention and improved public health. Furthermore, a focus on preventive healthcare supports food security by maintaining livestock health and preventing disruptions in global supply chains. As demand for animal vaccines continues to grow, industry leaders are investing in innovative solutions to improve efficiency and accessibility, reinforcing the importance of proactive disease management in veterinary medicine.
Biosecurity measures are becoming increasingly crucial for farmers aiming to maintain disease-free environments for their livestock. Effective biosecurity practices can reduce disease outbreaks by up to 60%, significantly improving animal health. Modern livestock operations now integrate enhanced sanitation protocols, restricted access to farming areas, and routine vaccinations to ensure stronger disease prevention, with biosecurity remaining a cornerstone of sustainable livestock management.
Impact of Macroeconomic / Geopolitical Factors
Macroeconomic and geopolitical trends have a strong impact on the animal vaccine market. Increasing global investment in animal health is boosting demand for advanced vaccines. Awareness of disease prevention is also rising, especially in emerging regions. These regions are benefiting from improved access to veterinary care and government-backed initiatives. This growth reflects a shift toward preventive health in livestock and companion animals. Demand is especially strong where outbreaks threaten food security or public health. Innovation is now central to market growth and competitive positioning.
Despite the growth, economic slowdowns can pose challenges. Budget cuts during downturns may delay or reduce vaccination programs, especially in rural and underserved areas. Limited funding affects both public and private veterinary services. Smaller farms and animal shelters are often hit hardest. Cost-sensitive buyers may prioritize short-term needs over preventive care. As a result, animal health outcomes may suffer. This slows market momentum and increases reliance on curative treatments. It also hinders the rollout of new vaccine technologies in cost-constrained regions.
Geopolitical tensions further complicate the market. Trade restrictions and political instability disrupt vaccine supply chains. These disruptions raise the cost of raw materials and delay distribution. Large animal veterinarians are particularly exposed to these risks. They often buy medications and vaccines in bulk. A 10–25% price hike on cattle vaccines can raise annual health program costs for ranchers. These added expenses may be passed to clients or absorbed by the practice. Either option can affect profitability and long-term market sustainability.
Latest Trends
Advancements in Needle-Free Vaccines
A growing trend in the recombinant veterinary vaccine market is the adoption of needle-free delivery systems, which provide a safer, more efficient, and less stressful method of administering vaccines, particularly in large-scale livestock operations. Technologies like jet injectors and oral vaccines reduce the risk of needle-stick injuries, addressing a significant safety concern for veterinary workers.
However, needle-free injections face a clinical challenge: the high-pressure delivery mechanism can potentially damage delicate molecules beneath the skin, especially when administering sensitive substances such as monoclonal antibodies. Recent advancements in pressure mechanisms have shown promise in addressing this issue.
Researchers are exploring ways to develop long-lasting vaccines that reduce the frequency of needle injections, improving vaccine accessibility and efficiency, particularly in large farming environments. This trend is gaining momentum in the poultry and swine industries, where rapid vaccination of large groups of animals is essential. Needle-free systems also ensure consistent vaccine distribution, which enhances efficacy and boosts herd immunity.
As a result, this technology is expected to drive market growth by improving the economic feasibility and accessibility of recombinant veterinary vaccines. While advancements in vaccine technology have proven crucial in addressing global health challenges like COVID-19, the storage requirements for low or ultra-low temperatures remain a challenge. However, progress in needle-free delivery methods, including intradermal and oral vaccines, has contributed significantly to improving animal welfare and enhancing the effectiveness of vaccination programs.
Regional Analysis
North America is leading the animal vaccine Market
North America leads the animal vaccine market and remains one of the fastest-growing regions, driven by several key factors. The high incidence of livestock and zoonotic diseases in the region fuels the demand for effective vaccination programs. The presence of major pharmaceutical companies involved in vaccine development and commercialization further supports market expansion.
Additionally, the rising pet population and increasing awareness of animal health have contributed to greater vaccine adoption. In particular, the US stands out due to its advanced infrastructure and strong research capabilities, which foster continuous innovation in vaccine technologies. The country is home to leading pharmaceutical firms that drive progress in the sector.
Moreover, the high prevalence of zoonotic diseases and the growing number of pets contribute to robust demand for vaccines. Government-supported initiatives and awareness programs play a crucial role in promoting vaccination efforts, ensuring the health and well-being of both livestock and companion animals. With ongoing advancements in vaccine technology and a growing emphasis on preventive care, the U.S. market is positioned for sustained growth.
Canada’s industrialized animal agriculture system creates conditions that are conducive to the spread of zoonotic diseases. Factors such as high animal density, frequent antibiotic use, and stressful environments contribute to disease proliferation. The close proximity of genetically similar animals facilitates the easy transmission of viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi, not only among livestock but also between animals and humans, increasing the risk of zoonotic infections. In the United States, rabies in humans is extremely rare, with only 1 to 3 cases reported annually. However, the virus remains widespread in wildlife, with around 4,000 documented cases each year, primarily affecting species such as raccoons, skunks, bats, and foxes.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherland
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Leading companies in the animal vaccine market are focused on developing advanced, highly effective solutions to enhance disease prevention and improve overall animal health outcomes. Significant investments are being directed toward research and development to create innovative vaccines, precision delivery systems, and cutting-edge monitoring technologies that enhance the efficacy of vaccination programs. Partnerships with veterinary clinics, agricultural organizations, and regulatory authorities play a crucial role in improving vaccine accessibility and raising global awareness.
Expansion into emerging markets, where there is growing investment in animal healthcare and an increasing prevalence of diseases, further drives market penetration. Additionally, many companies prioritize offering cost-effective vaccine solutions while adhering to international standards, ensuring widespread adoption and trust in their products. For example, in September 2022, Merck Animal Health introduced Nobivac Intra-Trac Oral BbPi, a vaccine designed to provide dual protection against two key canine respiratory pathogens.
Top Key Players in the Animal Vaccine Market
- Zoetis
- Virbac
- Elanco
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- Calier
- Ceva
- Bimeda Biologicals
- Neogen Corporation
- Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
- Phibro Animal Health Corporation
- HIPRA
- HESTER BIOSCIENCES LIMITED
- Biogénesis Bagó
- Vaxxinova® Autogenous Vaccines GmbH
Recent Developments
- In February 2025: It was announced that Zoetis received a conditional license from the United States Department of Agriculture’s Center for Veterinary Biologics (USDA CVB) for its Avian Influenza Vaccine. The vaccine, which targets the H5N2 subtype and is a killed virus formulation, has been approved specifically for use in chickens.
- In February 2025: Elanco Animal Health Inc. formed a partnership with Medgene, a South Dakota-based company, to utilize its vaccine platform technology. The agreement covers the commercialization of a highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) vaccine for use in dairy cattle.
- In April 2024: Virbac successfully acquired Sasaeah, strengthening its position in the Japanese farm animal vaccines market, particularly within the cattle segment, and expanding its portfolio of pharmaceutical products for all major species. Sasaeah, with a strong presence in Japan, develops, manufactures, and markets a broad range of veterinary products for both farm and companion animals. Through this acquisition, Virbac gains access to Sasaeah’s manufacturing facilities in Japan and Vietnam, its R&D capabilities, and a talented team of over 500 dedicated employees.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) US$ 13.6 billion Forecast Revenue (2034) US$ 34.6 billion CAGR (2025-2034) 9.8% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Product (Attenuated Vaccines, Inactivated Vaccines, Subunit Vaccines, Toxoid Vaccines, Recombinant Vaccines, DNA Vaccines), By Type of Animal Species (Livestock Animals- Poultry, Swine, Sheep, Goat, Others; Companion Animals- Dogs, Cat, Horse, Birds, Others), By Route of Administration (Subcutaneous, Intramuscular, Oral, Intraocular, Intranasal, Others), By Distribution Channel (Veterinary Hospitals and clinics, Retail Pharmacy, Online Retail Pharmacy) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Zoetis, Virbac, Elanco, Merck & Co., Inc., Calier, Ceva, Bimeda Biologicals, Neogen Corporation, Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH, Phibro Animal Health Corporation, HIPRA, HESTER BIOSCIENCES LIMITED, Biogénesis Bagó, and Vaxxinova® Autogenous Vaccines GmbH Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Zoetis
- Virbac
- Elanco
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- Calier
- Ceva
- Bimeda Biologicals
- Neogen Corporation
- Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
- Phibro Animal Health Corporation
- HIPRA
- HESTER BIOSCIENCES LIMITED
- Biogénesis Bagó
- Vaxxinova® Autogenous Vaccines GmbH









