Company Overview
NVIDIA Statistics: NVIDIA Corporation is a global leader in accelerated computing and semiconductor innovation. Driving advancements across artificial intelligence (AI), graphics, and high-performance computing. The company operates through 2 key reportable segments: Compute & Networking and Graphics.
The Compute & Networking segment encompasses NVIDIA’s data centre-accelerated computing platforms. AI software solutions, networking technologies, and automotive platforms that support autonomous and electric vehicles. It also includes Jetson systems for robotics and embedded applications. As well as DGX Cloud services that deliver scalable computing power for AI training and inference workloads.
The Graphics segment focuses on GeForce GPUs for gaming and PCs. As well as the GeForce NOW game streaming platform and its supporting infrastructure. It also offers Quadro/NVIDIA RTX GPUs for professional visualization. vGPU software for virtual computing environments, and Omniverse Enterprise, a collaborative platform for industrial AI and digital twin applications.
Market Analysis
NVIDIA’s technologies power 4 major markets: Gaming, Professional Visualization, Data Center, and Automotive. The company powers all 30 of the top autonomous vehicle data centres globally and supports over 40,000 enterprises that use NVIDIA AI technology to build and operate AI factories. Companies using GeForce GPUs have more than 200 million creators and gamers. Over 4 million developers have adopted the MONAI framework for AI-based medical imaging. Additionally, more than 1.7 million developers utilize the Jetson platform for edge AI, and NVIDIA holds over 8,700 granted and pending patents worldwide. The company also fosters innovation through its NVIDIA Developer Program. This includes 6 million developers and its Inception program, supporting over 27,000 startups globally.
NVIDIA maintains a strong global presence with offices in over 50 countries. In North America, operations are located across major technology hubs. Including California (Santa Clara, Sunnyvale, San Dimas), Texas (Austin), Washington (Seattle, Redmond), Colorado (Boulder), New York (New York City), and several others. Internationally, the company operates in regions such as Brazil (São Paulo) and Canada (Toronto, Ontario), underscoring its extensive reach and commitment to supporting customers worldwide.
(Source: Company Website)
Historical Milestones of NVIDIA Corporation
- In 1993, NVIDIA was founded by Jensen Huang, Chris Malachowsky, and Curtis Prym to transform 3D graphics for gaming and multimedia. Setting the stage for a new era in visual computing.
- In 1999, the company introduced the world’s first graphics processing unit (GPU). Redefining computer graphics architecture and establishing the foundation for modern parallel computing.
- In 2006, NVIDIA launched the CUDA architecture, unlocking GPU parallelism for scientific research and high-performance computing. Extending its influence far beyond traditional graphics applications.
- In 2012, NVIDIA’s technology powered the AlexNet neural network. A breakthrough moment that signalled the company’s pivotal role in the development of accelerated AI computing and machine learning.
- In 2018, NVIDIA introduced the RTX platform, the first GPU capable of real-time ray tracing, revolutionizing realistic rendering and immersive gaming experiences.
- In 2022, the company unveiled the Omniverse platform. A digital twin and industrial simulation environment that enables collaborative design and advances the metaverse ecosystem.
NVIDIA Financial Analysis
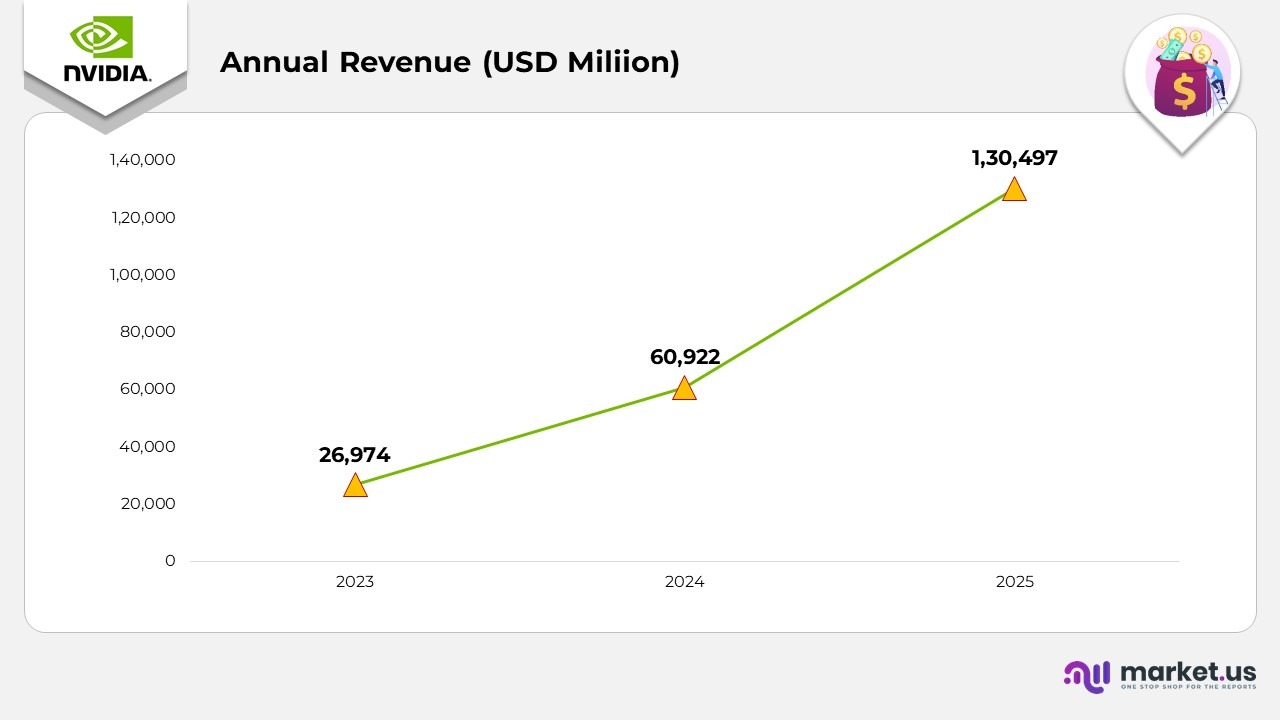
- In 2023, NVIDIA generated $26,974 million in annual revenue, supported by strong demand for gaming GPUs. Expanding cloud infrastructure and the growing use of AI-driven workloads within global data centers.
- In 2024, the company’s revenue climbed to $60,922 million, reflecting an 8% year-over-year growth. This surge was fueled by the rapid adoption of AI training systems. Robust demand for the H100 Tensor Core GPUs, and large-scale investments in enterprise and cloud-based AI infrastructure.
- In 2025, NVIDIA’s revenue reached $130,497 million, an impressive 2% rise from the previous year. The increase was driven by the global expansion of generative AI applications, the widespread deployment of large language models (LLMs), and strategic collaborations with hyperscalers and cloud providers that adopted NVIDIA’s AI computing platforms.
- The company recorded a gross margin of 75.0%, representing a 2.3 percentage point improvement from 72.7% in 2024, reflecting enhanced operational efficiency and a favourable product mix driven by strong demand for high-performance GPUs.
- Operating expenses increased to $16,405 million, a 45% rise from $11,329 million in the previous year, primarily due to higher investments in R&D and workforce expansion to advance AI technologies and infrastructure.
- Operating income grew significantly to $81,453 million, marking a 147% increase from $32,972 million in 2024, supported by robust revenue growth and effective expense management across business divisions.
- Net income reached $72,880 million, up 145% from $29,760 million in the prior year, driven by exceptional profitability in data center operations and AI computing platforms.
- Net income per diluted share rose to $2.94, a 147% jump from $1.19 in 2024, highlighting strong earnings growth and reinforcing NVIDIA’s position as a leading value creator for shareholders.
(Source: NVIDIA Corporation Annual Report)
Segmental Analysis of NVIDIA
- Compute & Networking revenue reached $116,193 million in 2025, up 145% from $47,405 million in 2024, reflecting exceptional demand for NVIDIA’s accelerated computing and AI infrastructure solutions.
- Data Center computing revenue surged 162% year-over-year, driven by widespread adoption of the Hopper computing platform, which supports large language models (LLMs), recommendation engines, and generative AI.
- Data Center networking revenue grew 51%, primarily fueled by strong uptake of Ethernet for AI solutions, including the Spectrum-X end-to-end Ethernet platform, which optimizes AI workloads across hyperscale environments.
- Graphics revenue increased 6% to $14,304 million in 2025 from $13,517 million in 2024, supported by higher sales of GeForce RTX 40 Series GPUs, driven by continued demand for advanced gaming and creative applications.
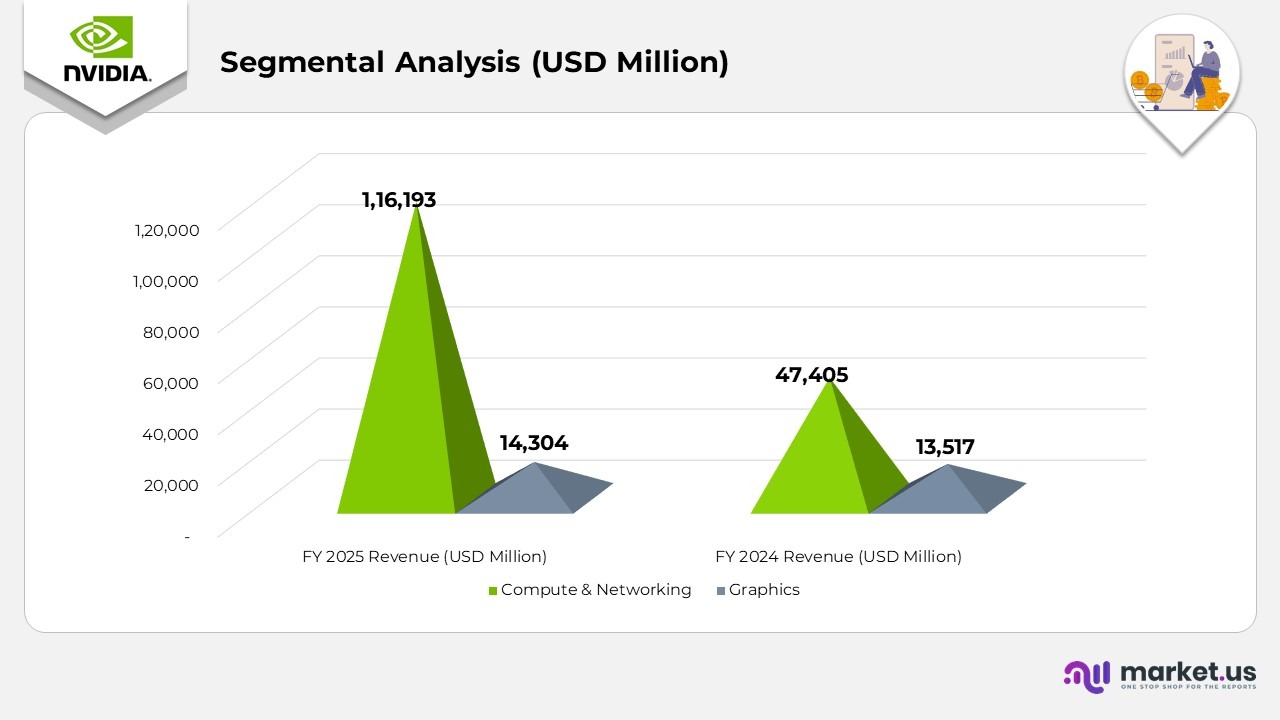
(Source: NVIDIA Corporation Annual Report)
Operating Income Performance by Reportable Segments
- Compute & Networking operating income reached $82,875 million in 2025, marking a 159% increase from $32,016 million in 2024.
- This remarkable growth was primarily driven by exceptional performance in the Data Center and AI computing divisions, fueled by large-scale deployment of NVIDIA’s Hopper platform and accelerating enterprise adoption of generative AI infrastructure.
- Graphics’ operating income totaled $5,085 million, representing a 13% decline from $5,846 million in the previous year.
- The decrease reflects increased production costs, competitive pricing pressures, and a temporary normalization in gaming GPU demand following the post-pandemic hardware surge.
- All Other segments reported a loss of $6,507 million, compared to a $4,890 million loss in 2024, indicating a 33% increase in losses due to higher operating expenditures related to emerging product development and corporate investments.
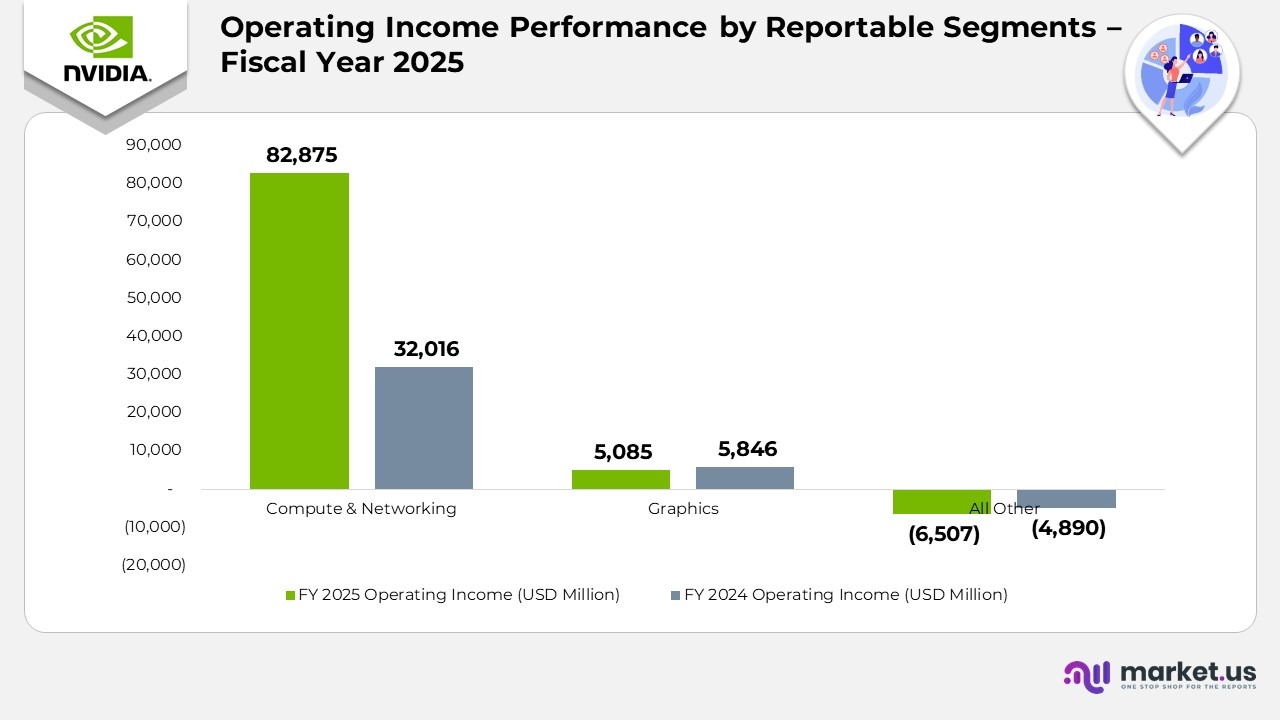
(Source: NVIDIA Corporation Annual Report)
NVIDIA Geographical Revenue Analysis
- In fiscal year 2025, the United States recorded revenue of 61,257 million, up sharply from 26,966 million in 2024 and 8,292 million in 2023, reflecting exceptional demand for NVIDIA’s Compute & Networking solutions, particularly within AI data centers.
- Singapore contributed 23,684 million in 2025, compared with 6,831 million in 2024 and 2,288 million in 2023. This growth was primarily driven by centralized invoicing operations, with most shipments distributed globally rather than within Singapore.
- Taiwan generated 20,573 million in 2025, rising from 13,405 million in 2024 and 6,986 million in 2023, supported by strong demand for semiconductor manufacturing and AI hardware components.
- China (including Hong Kong) reported revenue of 17,108 million in 2025, up from 10,306 million in 2024 and 5,785 million in 2023, reflecting steady adoption of NVIDIA’s AI and computing platforms despite regulatory challenges.
- Other regions accounted for 7,875 million in 2025, compared to 3,414 million in 2024 and 3,623 million in 2023, showing consistent global diversification in NVIDIA’s customer base.
- Singapore accounted for 18% of NVIDIA’s total revenue in fiscal year 2025, based on customer billing location. However, this primarily reflects centralized invoicing practices, as actual shipments to Singapore represented less than 2% of total revenue.
- Revenue from customers outside the United States accounted for 53% of total revenue in 2025, compared to 56% in 2024 and 69% in 2023, indicating a steady decline in U.S.-based contributions.
- The increase in U.S. revenue during 2025 and 2024 was largely driven by strong demand in the Compute & Networking segment, particularly for AI infrastructure and data center expansion.
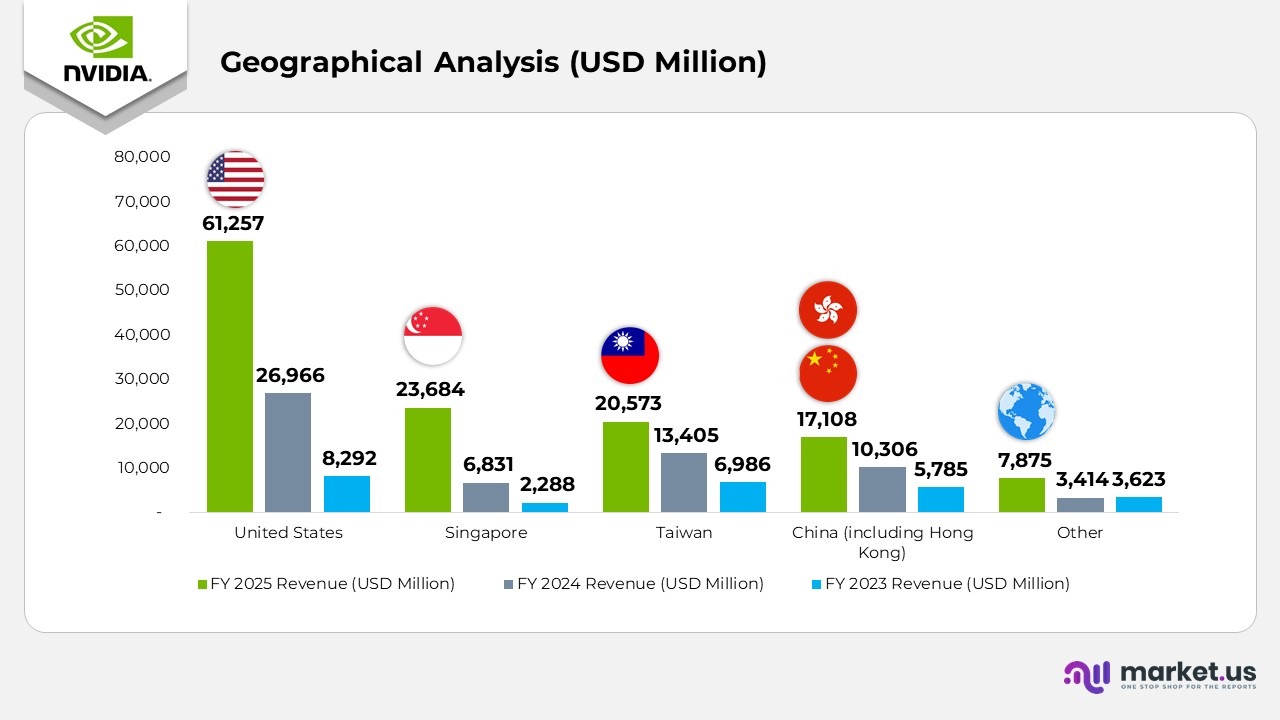
(Source: NVIDIA Corporation Annual Report)
NVIDIA Revenue Breakdown by End Market Statistics
- Data Center revenue reached 115,186 million in 2025, up from 47,525 million in 2024 and 15,005 million in 2023, reflecting exponential growth driven by AI infrastructure, accelerated computing, and cloud deployments.
- Within the Data Center segment, Compute revenue increased sharply to 102,196 million in 2025 from 38,950 million in 2024, fueled by strong demand for large-scale AI model training and inference workloads using Hopper GPUs.
- Networking revenue climbed to 12,990 million in 2025, compared with 8,575 million in 2024. Supported by the rising adoption of NVIDIA’s Spectrum-X and InfiniBand solutions for AI data center connectivity.
- Gaming revenue rose modestly to 11,350 million in 2025 from 10,447 million in 2024, driven by sustained demand for GeForce RTX 40 Series GPUs and gaming innovations powered by ray tracing and DLSS technologies.
- Further, Professional Visualization revenue grew to 1,878 million in 2025 from 1,553 million in 2024. Reflecting increased enterprise demand for Omniverse-based 3D design, simulation, and digital twin applications.
- Automotive revenue increased to $ 1,694 million in 2025, up from $ 1,091 million in 2024, driven by the expansion of NVIDIA DRIVE platforms in autonomous vehicle and electric mobility ecosystems.
- OEM and Other revenue reached 389 million in 2025, up slightly from 306 million in 2024, primarily driven by higher demand for embedded and AI edge computing solutions.
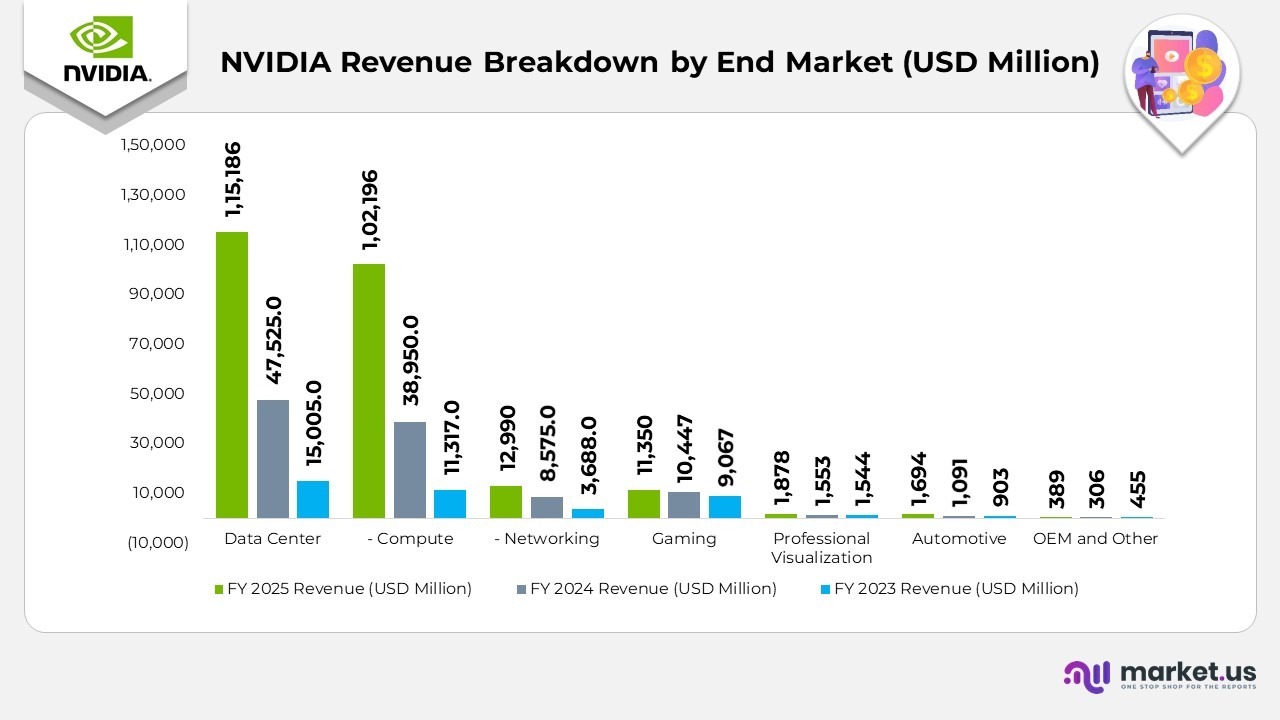
(Source: NVIDIA Corporation Annual Report)
NVIDIA Long-Lived Assets by Country Statistics
- In 2025, long-lived assets in the United States totaled $3,626 million, up from $2,595 million in 2024. Reflecting continued investment in domestic manufacturing and R&D infrastructure.
- Moreover, Taiwan reported $1,481 million in long-lived assets in 2025, increasing from $773 million in 2024. Driven by enhanced semiconductor production and supply chain expansion.
- Israel saw its long-lived assets rise to $840 million in 2025 compared to $325 million in 2024. Indicating a strong focus on AI research and chip design facilities.
- Assets classified under Other regions reached $336 million in 2025, up from $221 million in 2024. Demonstrating the ongoing global diversification of operational resources.
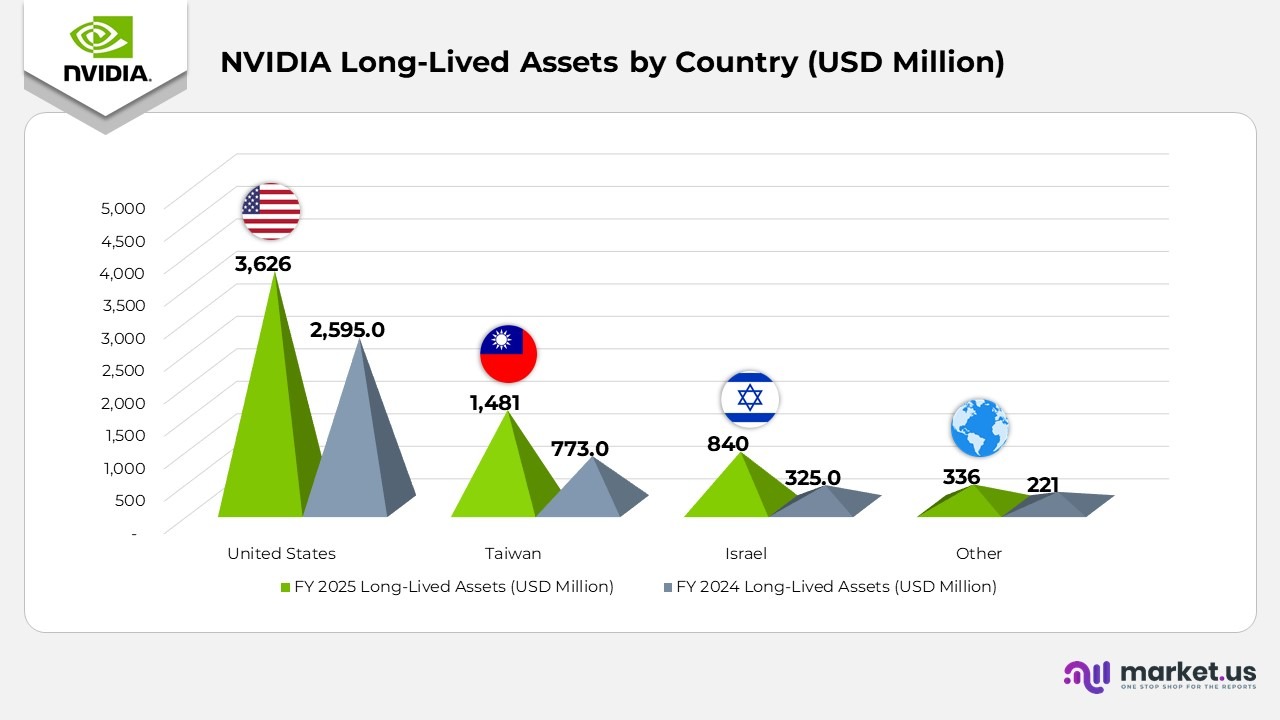
(Source: NVIDIA Corporation Annual Report)
Patents of NVIDIA Corporation
| Patent / Publication Title | Type | Filed | Publication / Grant Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Virtualizing hardware processing resources in a processor | Grant | Mar 10, 2022 | Oct 21, 2025 |
| Asynchronous device of phase shift, employing an injection-locked-oscillator-created phase rotator | Grant | Feb 22, 2024 | Oct 21, 2025 |
| An application programming interface to offer information | Grant | Dec 14, 2022 | Oct 21, 2025 |
| Segmentation is a consuming and unsupervised neural network training technique | Grant | Jul 18, 2023 | Oct 21, 2025 |
| Depth approximation using a neural network | Grant | Dec 13, 2019 | Oct 21, 2025 |
| Pruning neural networks that comprise element-wise operations | Grant | Nov 21, 2018 | Oct 21, 2025 |
| Unified virtual memory management in heterogeneous computing systems | Grant | Mar 19, 2024 | Oct 21, 2025 |
| Sensor calibration for space translation | Grant | May 4, 2021 | Oct 21, 2025 |
| Bare-metal snapshots | Grant | Oct 30, 2023 | Oct 21, 2025 |
| Application programming interface to prevent deselection of storage | Grant | Apr 13, 2022 | Oct 14, 2025 |
| Pattern-enabled aluminium nitride thermal test vehicle for datacenter cooling systems | Grant | Jun 6, 2022 | Oct 14, 2025 |
| Kernel fusion for machine learning | Grant | Oct 2, 2019 | Oct 14, 2025 |
| Frame alignment recovery for a high-speed signaling interconnect | Grant | Dec 13, 2023 | Oct 14, 2025 |
| Application programming interface using node dependencies | Grant | Feb 27, 2023 | Oct 14, 2025 |
| Video synthesis using one or more neural networks | Grant | Jan 16, 2024 | Oct 14, 2025 |
| Dynamic directional rounding | Grant | Feb 1, 2021 | Oct 14, 2025 |
| Parallelization of Hadamard transforms of wireless signals | Grant | Apr 13, 2023 | Oct 14, 2025 |
| Denoising with dynamism in ray-traced scenes by consuming historical pixel values | Grant | Jul 21, 2023 | Oct 14, 2025 |
| Synthetic bracketing for experience correction | Grant | Aug 21, 2023 | Oct 14, 2025 |
| Adding greater practicality to a computer-made image by leveling jagged edges within the image in an effectual manner | Grant | Mar 25, 2019 | Oct 14, 2025 |
(Source: Justia Patents)
Recent Developments
- In November 2025, the company partnered with Telekom to launch the Industrial AI Cloud. A sovereign enterprise-grade platform designed for industrial digitalization, scheduled to go live in early 2026.
- In October 2025, NVIDIA introduced Open Models and Data, an initiative aimed at accelerating AI innovation across language, biology, and robotics, thereby fostering an open ecosystem that strengthens U.S. AI leadership.
- In October 2025, the company launched Omniverse DSX Blueprint, a digital framework for designing and managing gigawatt-scale AI factories. This was validated at Digital Realty’s AI Factory Research Centre in Manassas, Virginia.
- In October 2025, NVIDIA unveiled BlueField-4, a next-generation processor engineered to power AI factory operating systems. Enhancing data storage acceleration and performance scalability across global AI infrastructures.
- In October 2025, the company collaborated with the U.S. Department of Energy’s national laboratories and leading industry players to develop America’s AI infrastructure, supporting scientific advancement and industrial transformation.
- In October 2025, NVIDIA entered a partnership with Nokia to accelerate the development and deployment of AI-native mobile networks and next-generation AI networking architectures.
- In September 2025, NVIDIA joined forces with OpenAI to construct and deploy over 10 gigawatts of AI data centers. Leveraging millions of NVIDIA GPUs to support next-generation AI systems.
- In September 2025, the company collaborated with Intel Corporation to co-develop multiple generations of custom data center and PC solutions. Optimizing performance for hyperscale, enterprise, and consumer workloads.
- In September 2025, NVIDIA partnered with organizations in the United Kingdom to advance Physical and Agentic AI, robotics, and life sciences, strengthening cross-industry innovation and applied AI research.
(Source: NVIDIA Press Release)