Company Overview
The Boeing Company specializes in the design, development, manufacturing, sale, service, and support of commercial jetliners, military aircraft, satellites, missile defense systems, human space flight, and launch services. As one of the two leading manufacturers of aeroplanes with 100+ seats, Boeing plays a crucial role in the global commercial airline industry, alongside being a prominent defense contractor in the US. The company operates across 3 primary business segments: Defense, Space & Security (BDS), Commercial Airplanes (BCA), and Global Services (BGS).
The Commercial Airplanes division focuses on the development, production, marketing, and maintenance of commercial aircraft. This sector also provides extensive fleet support services to airlines globally. The Defense, Space & Security segment designs, manufactures, and tests both manned and unmanned military aircraft and systems for global security. This includes fighter jets, combat helicopters, missile systems, and mobility platforms such as tankers and tiltrotor aircraft. It also covers airborne surveillance and reconnaissance. The Global Services division provides support services to defense and commercial customers, enhancing operational efficiency.
Moreover
Boeing Capital manages the financial exposure for the company and aids in facilitating the purchase and delivery of Boeing products. As of December 31, 2024, the company employed around 58,000 union workers. Boeing operates globally, serving customers in approximately 150 countries and maintaining a presence in over 65 countries with a network of more than 20,000 suppliers. Its diverse manufacturing, service, and technological partnerships span the globe, with regional offices in regions such as Africa, the Middle East, China, Latin America, Australia, Europe, Israel, India, Japan, South Korea, Southeast Asia, and Turkey, ensuring a local market focus and a global reach.
As of December 31, 2024, and 2023, the company had authorized 1,200,000,000 shares of common stock and 20,000,000 shares of preferred stock. Boeing’s extensive portfolio features renowned aircraft models like the 737, 747, 777, and 787, which are extensively utilized by airlines globally.
Facts About Boeing Company
- The Boeing Company was founded in 1916 by William E. Boeing in Seattle, Washington, originally as an aircraft manufacturing firm named Pacific Aero Products Co.
- Boeing’s headquarters are located in Arlington, Virginia, after moving from Chicago in 2022.
- The company operates through four major business segments: Commercial Airplanes, Defense, Space & Security, Global Services, and Boeing Capital.
- Boeing is one of the largest aerospace and defense manufacturers in the world and a leading exporter for the United States.
- The company produces iconic aircraft models such as the 737, 747, 767, 777, and 787 Dreamliner families.
- Boeing’s Defense, Space & Security division manufactures military aircraft, satellites, and advanced defense systems.
- The company also provides maintenance, modification, and logistics support through its Global Services segment.
- Boeing has major production and engineering facilities in Washington, South Carolina, Missouri, and California.
- The Boeing 737 MAX, introduced in 2017, is one of the company’s best-selling aircraft models.
- Boeing plays a key role in space exploration, including work on the NASA Space Launch System (SLS) and participation in the International Space Station.
History of Boeing Motors
- 1916: Founded by William E. Boeing in Seattle initially specialized in seaplane production.
- 1920: Merged with Pacific Aero Products Co, forming Boeing Airplane and Transport Co.
- 1930: Launched the Boeing 247, the first all-metal, twin-engine commercial aircraft.
- 1940: Became a significant supplier during World War II, developing the B-17 Flying Fortress and B-29 Superfortress
- 1950: Introduced the Boeing 707, marking Boeing’s entry into the jet age as the first commercially successful jetliner.
- 1960: Unveiled the Boeing 727 and 737, solidifying its leadership in the commercial aviation market.
- 1970: Revolutionized air travel with the introduction of the Boeing 747, the first wide-body airliner.
- 1980: Entered the space industry by providing solid rocket boosters for NASA’s Space Shuttle
- 1997: Merged with McDonnell Douglas, expanding its capabilities in the defense and aerospace sectors.
- 2000: Focused on sustainability with the 787 Dreamliner, featuring lightweight composite materials for improved fuel efficiency.
- 2010: Strengthened its defense portfolio with advanced military systems such as the KC-46 tanker and F/A-18 Super Hornet.
- 2020: Addressed challenges from the 737 MAX crisis, emphasizing safety and operational quality improvements.
(Source: Company Website)
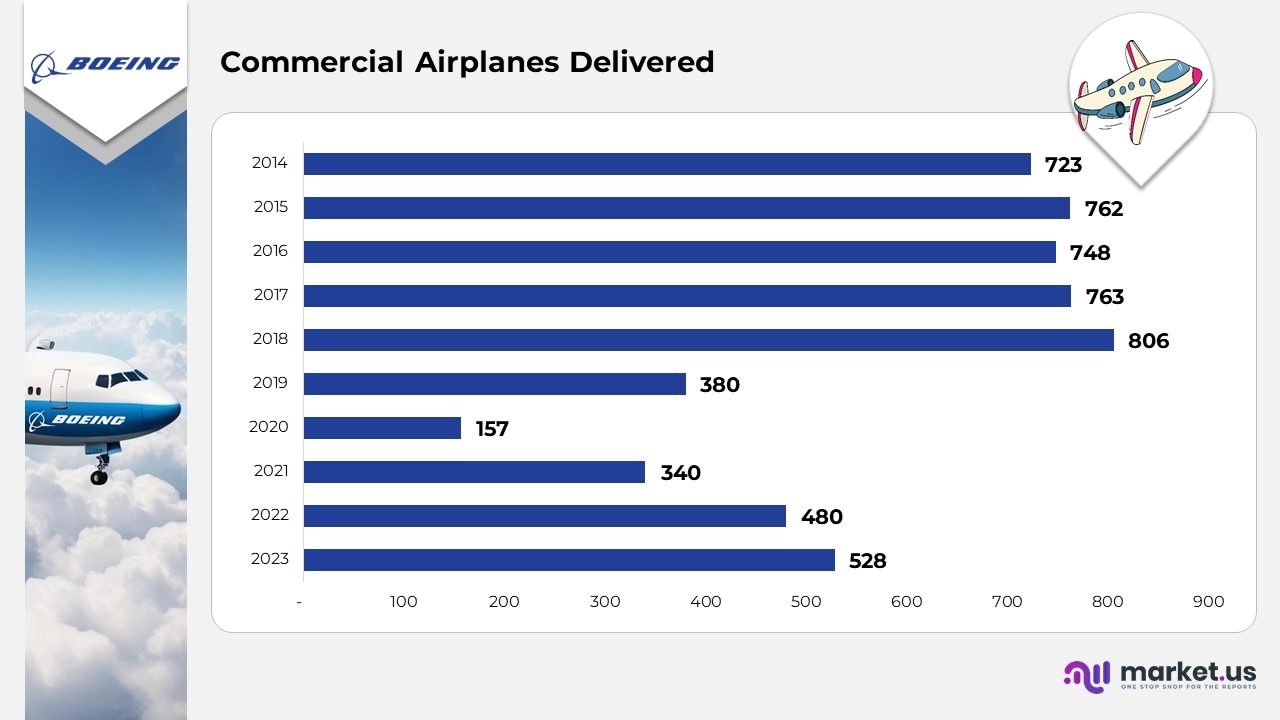
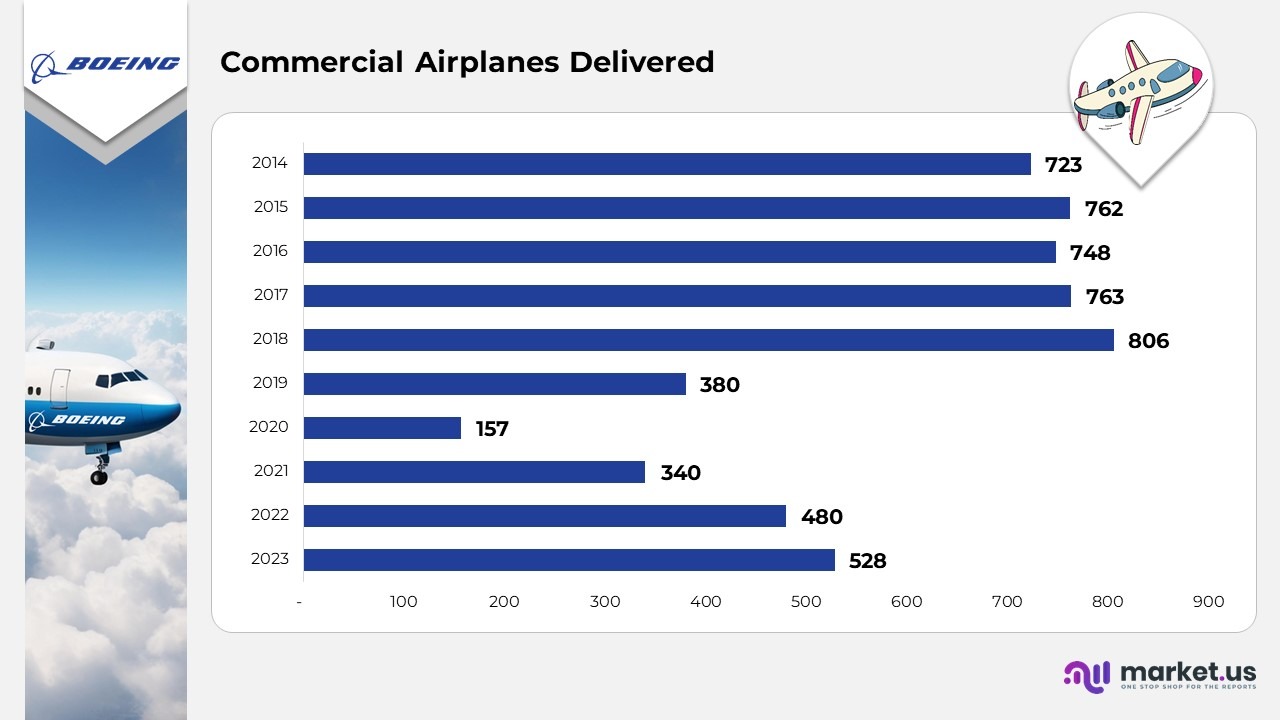
Commercial Airplane Deliveries
- In 2023, Boeing delivered 528 commercial airplanes, signaling a steady resurgence in global aviation activity.
- In 2022, the company shipped 480 aircraft as airlines continued their post-pandemic recovery and expanded operations.
- In 2021, Boeing’s deliveries climbed to 340, indicating gradual stabilization in production and supply chains.
- In 2020, the manufacturer handed over 157 airplanes, representing a significant dip due to worldwide aviation disruptions.
- In 2019, Boeing recorded 380 deliveries, affected by ongoing regulatory reviews and production setbacks.
- In 2018, the company achieved a record high of 806 aircraft deliveries, marking its strongest year in recent history.
- In 2017, Boeing maintained robust performance with 763 deliveries, sustaining its leadership in the aerospace sector.
- In 2016, total deliveries reached 748, driven by solid global demand and fleet expansion initiatives.
- In 2015, Boeing successfully delivered 762 airplanes, reflecting consistent production momentum.
- In 2014, the company completed 723 deliveries, establishing a strong foundation ahead of its subsequent peak years.
(Source: DMR)
Employee Analysis
- As of December 2024, the employment figures by location are as follows:
- In Alabama (AL), the workforce totals 3,225
- Arizona (AZ) employs 4,932
- California (CA) has 13,948
- Missouri (MO) employs 17,387
- Oklahoma (OK) reports a workforce of 3,654.
- Pennsylvania (PA) has 3,782
- South Carolina (SC) employs 8,253
- Texas (TX) accounts for 7,304
- Washington (WA) has the largest workforce, with 67,567
- The “Other U.S. States” category contributes 17,311
- Globally, there are 25,086
- In total, the company employs 172,449 individuals across all locations.
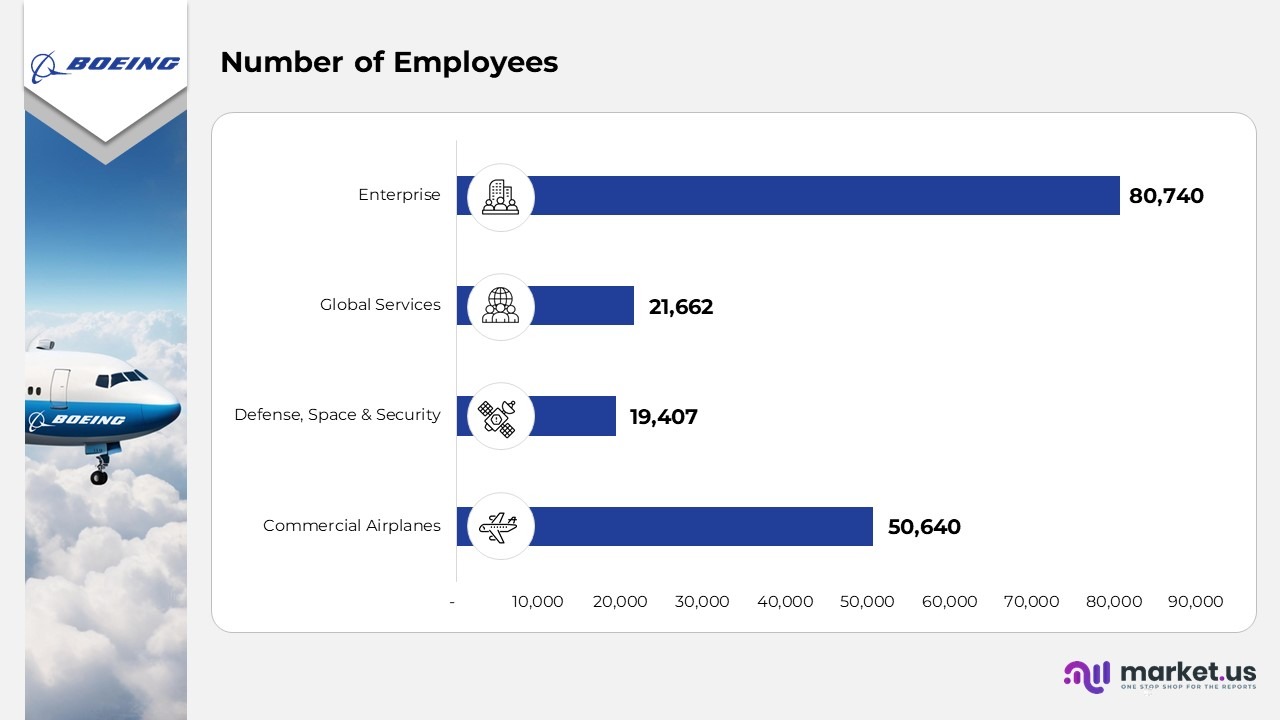
By group, the employment breakdown for December 2024 is as follows:
- The Commercial Airplanes division has 50,640
- The Defense, Space & Security division employs 19,407
- Global Services reports 21,662
- The Enterprise group has a workforce of 80,740.
- Overall, the total number of employees across all divisions is 172,449.
(Source: The Boeing Company Annual Report)
Financial Analysis
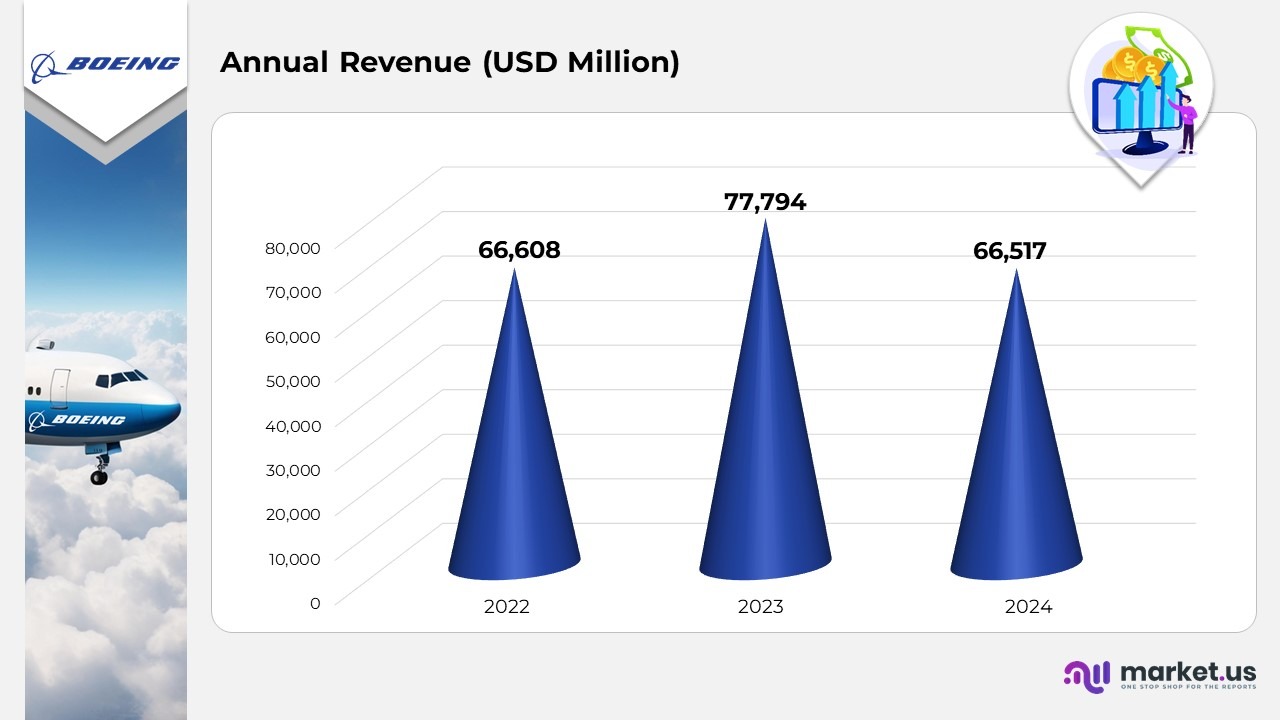
Annual Revenue
- In 2024, revenues decreased by $11,277 million compared to 2023, mainly driven by:
- BCA revenues fell by $11,040 million, primarily due to a reduction in deliveries across all programs and customer considerations for the 737-9 after its grounding in January 2024.
- BDS revenues declined by $1,015 million, mainly due to higher net unfavourable cumulative contract catch-up adjustments on major fixed-price development programs.
- BGS revenues rose by $827 million, largely attributed to increased commercial services revenue.
- In 2023, revenues increased by $11,186 million compared to 2022, with growth across all 3 operating segments:
- BCA revenues grew by $7,875 million, primarily driven by higher deliveries of the 787
- BDS revenues increased by $1,771 million, mainly due to higher revenues from fixed-price development programs.
- BGS revenues expanded by $1,516 million, largely attributed to a boost in commercial services revenue driven by market recovery across the commercial portfolio.
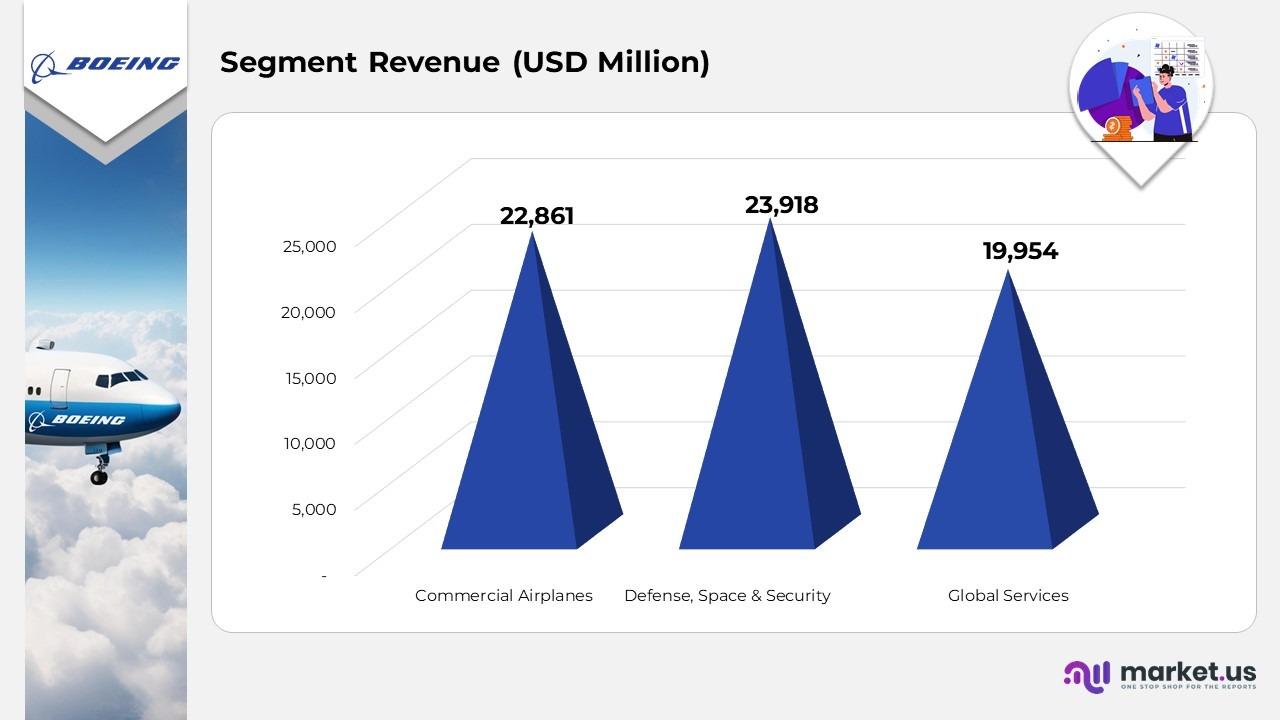
Segment Revenue
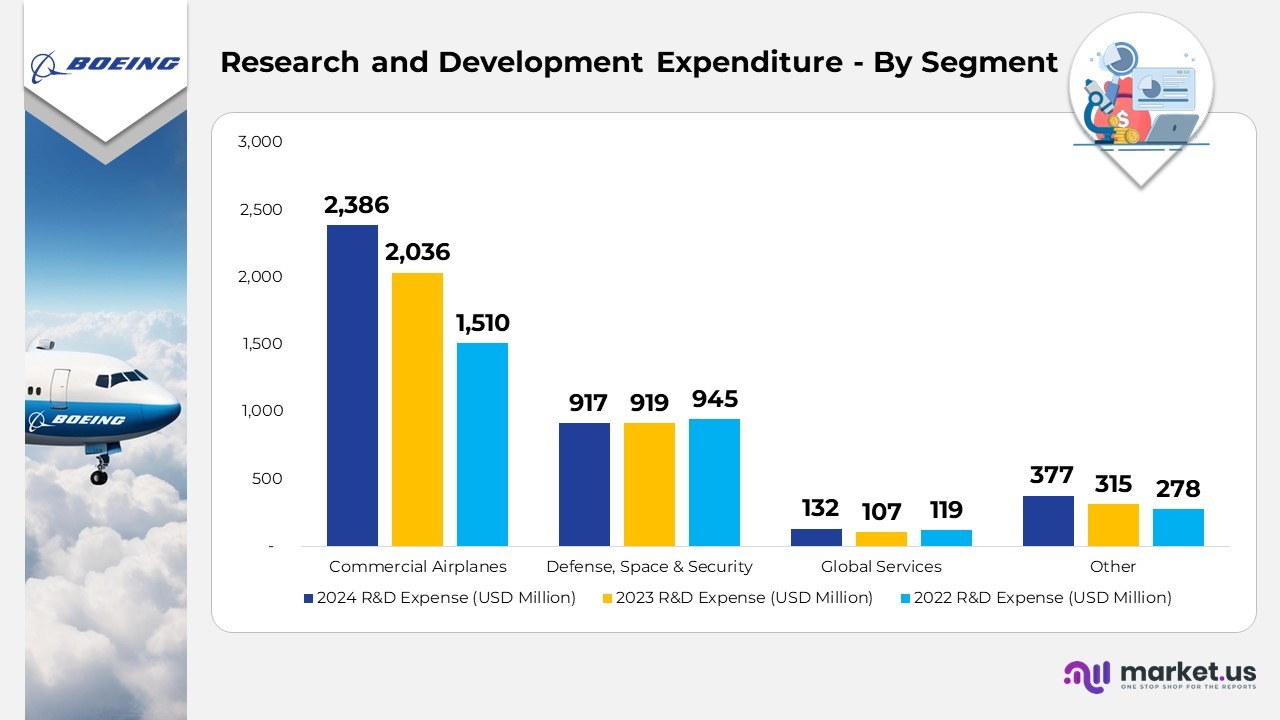
Research and Development Expenditure – By Segment
- In 2024, Commercial Airplanes allocated $2,386 million towards research and development, a rise from $2,036 million in 2023 and $1,510 million in 2022.
- Defense, Space & Security spent $917 million on research and development in 2024, a slight decrease from $919 million in 2023 and $945 million in 2022.
- For Global Services, research and development expenses totaled $132 million in 2024, higher than the $107 million spent in 2023 and $119 million in 2022.
- The Other category saw research and development costs of $377 million in 2024, compared to $315 million in 2023 and $278 million in 2022.
- In 2024, research and development expenses rose by $435 million compared to 2023, mainly driven by the 777X program at BCA and increased enterprise investments in product development.
- In 2023, research and development expenses increased by $525 million compared to 2022, primarily due to higher expenditures on the 777X program and enterprise investments in product development.
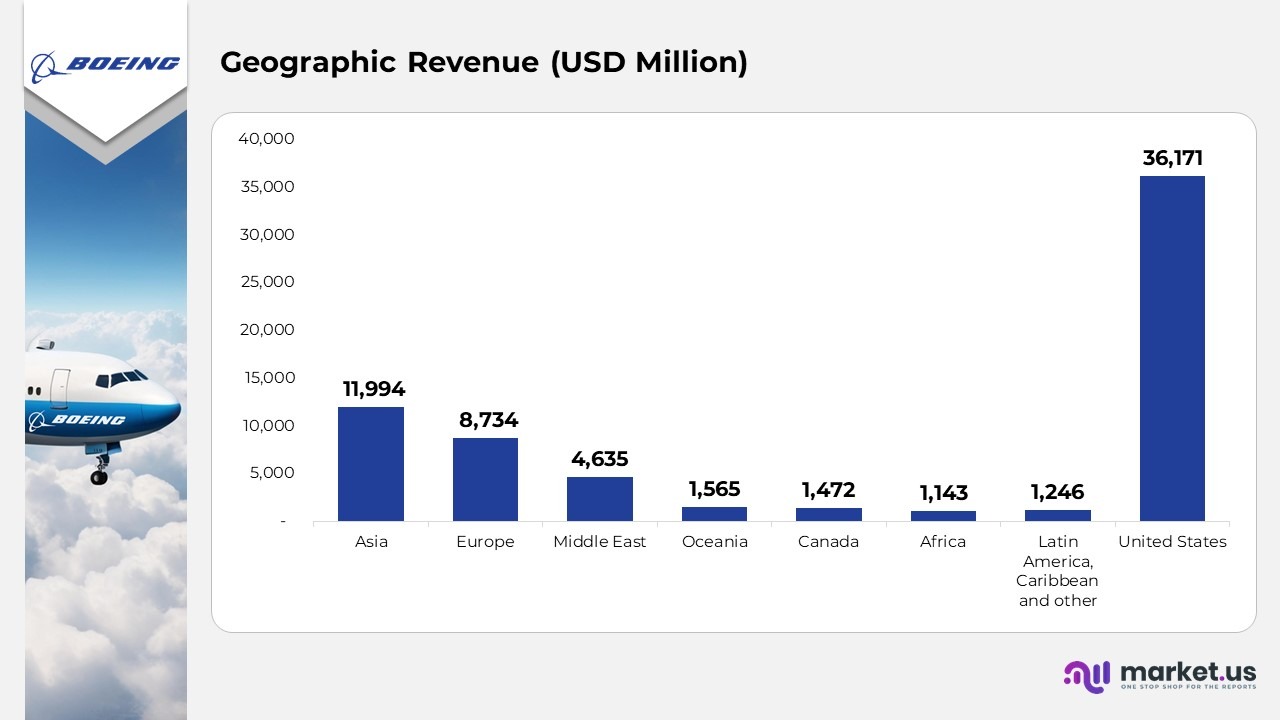
Geographic Revenue
- Revenues from the U.S. government, including foreign military sales through the U.S. government, accounted for 42% of consolidated revenues in 2024, 37% in 2023, and 40% in 2022, primarily recorded at BDS and BGS.
- As of December 31, 2024, and 2023, approximately 3% and 4% of operating assets, respectively, were located outside the United States.
- Asia generated $11,994 million in 2024, reflecting an increase from $10,013 million in 2023 and $8,393 million in 2022.
- Europe earned $8,734 million in 2024, a decrease from $10,520 million in 2023, but an increase compared to $7,916 million in 2022.
- The Middle East recorded $4,635 million in 2024, a decline from $6,594 million in 2023, yet higher than $5,047 million in 2022.
- Oceania contributed $1,565 million in 2024, slightly lower than $1,655 million in 2023, and comparable to $1,576 million in 2022.
- Canada contributed $1,472 million in 2024, an increase from $1,256 million in 2023, but lower than $1,612 million in 2022.
- Africa saw revenues of $1,143 million in 2024, a significant increase from $825 million in 2023 and $418 million in 2022.
- Latin America, the Caribbean, and other regions generated $1,246 million in 2024, a decrease from $1,524 million in 2023 and $2,412 million in 2022.
- In 2024, the United States accounted for $36,171 million in revenue, a decline from $45,380 million in 2023, but higher than $39,218 million in 2022.
(Source: The Boeing Annual Report)
Segmental Analysis
Commercial Airplanes
- This segment focuses on the development, production, and marketing of commercial jet aircraft primarily for the global airline industry.
- It is a leading manufacturer of commercial aircraft, offering a range of jetliners to meet the passenger and cargo needs of airlines worldwide.
- Current aircraft in production include the 737 narrow-body model and the 767, 777, and 787 wide-body models.
- Ongoing development includes the 777X program and derivatives of the 737-7 and 737-10
Defense, Space & Security
- This segment specializes in the research, development, production, and modification of both crewed and unmanned military aircraft and weapons systems, focusing on strike, surveillance, and mobility.
- It includes fighter and trainer aircraft, vertical lift systems (such as rotorcraft and tiltrotor aircraft), and commercial derivative aircraft (e.g., anti-submarine and tanker aircraft).
- The segment also covers the research, development, production, and modification of strategic defense and intelligence systems. Including missile defense systems, C4ISR solutions, cyber and information systems, satellite systems, and space exploration technologies.
Global Services
- This segment delivers a broad range of services to both commercial and defense customers worldwide.
- It sustains aerospace platforms and systems with services such as supply chain and logistics management, engineering, maintenance, modifications, upgrades, and conversions.
- It also provides spare parts, pilot and maintenance training, technical documents, and data analytics and digital services.
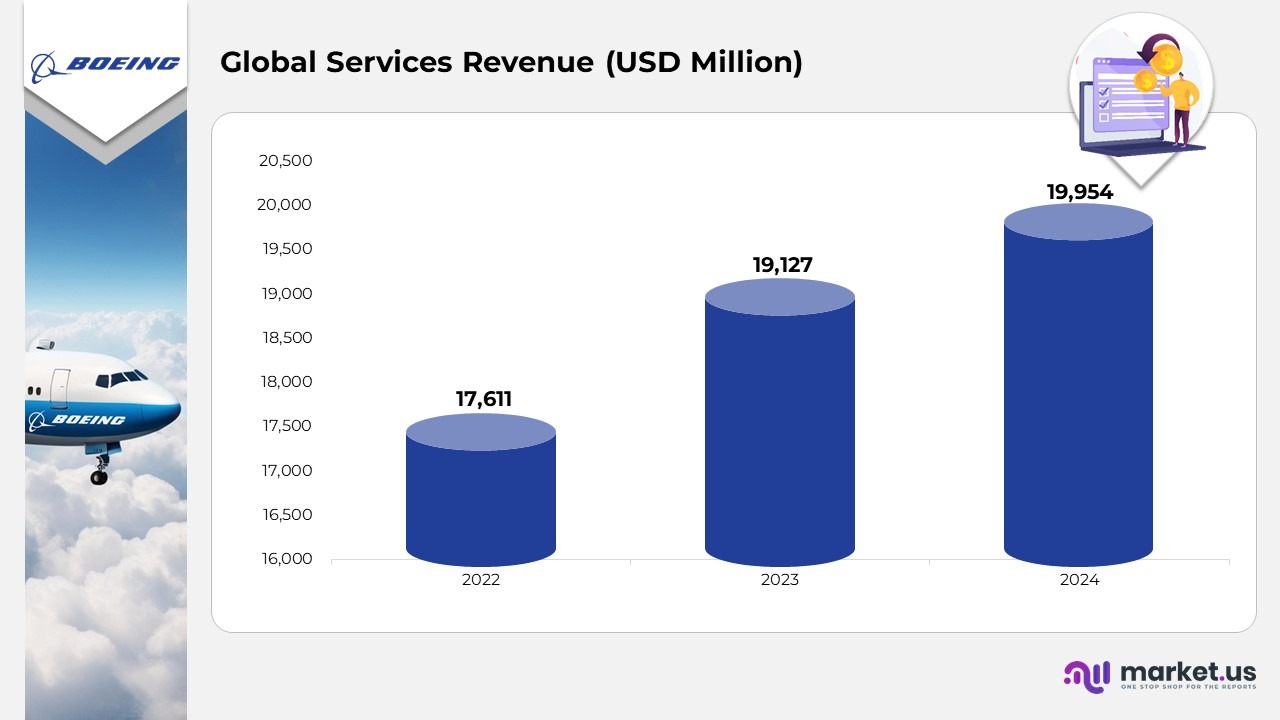
(Source: The Boeing Annual Report)
Fun Facts
- The first Boeing airplane, the B&W Seaplane, was made of wood and linen and first flew in 1916.
- Boeing’s logo, known as the “Boeing Totem,” originally reflected its early connection to Seattle’s Pacific Northwest culture.
- The Boeing 747, introduced in 1969, was nicknamed the “Queen of the Skies” and revolutionized long-haul air travel.
- Boeing once owned a company that produced boats and even furniture during World War I to stay afloat financially.
- The Boeing 787 Dreamliner uses lightweight composite materials, making it about 20% more fuel-efficient than previous models.
- Boeing aircraft have carried more than 75% of the world’s air passengers at some point in history.
- The company helped pioneer jet-powered commercial flight with the Boeing 707 in the late 1950s.
- Boeing is a key sponsor of STEM education programs worldwide to inspire the next generation of aerospace engineers.
- Boeing’s production of satellites and rockets makes it one of the few companies active in both the aviation and space industries.
- The company’s name became so iconic that “Boeing” is now used as a generic term for airplanes in several languages.
Recent Developments
- In October 2025, Boeing teamed up with Leonardo to pursue the S. Army’s Flight School Next contractor-owned, contractor-operated (COCO) service contract. This collaboration combines Boeing’s expertise in Army rotary-wing training and program delivery with Leonardo’s AW119T training helicopter, providing an efficient and scalable solution for the next generation of aviators.
- In October 2025, Boeing joined forces with Southwest Airlines (SWA) and Aeroxchange Ltd. to enhance supply chain security by preventing unauthorized spare parts from entering the aerospace aftermarket.
- In September 2025, Boeing partnered with Space & Security and Palantir to accelerate the adoption of artificial intelligence across defense and classified programs.
- In September 2025, Boeing expanded its Boeing Engineering Center within the Cici & Hyatt Brown Epicenter for Aerospace Technology at Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University’s Research Park. The expansion aims to support engineering and advanced technology work for Boeing’s Defense, Space & Security Air Dominance
- In September 2025, the Boeing Engineering Center at Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University’s Research Park became fully operational. This expansion reaffirms Boeing’s commitment to the region.
- In August 2025, Boeing launched the X-37B Orbital Test Vehicle, further solidifying the spaceplane as a reliable testbed for future space missions.
Further
- In July 2025, Boeing successfully launched a satellite, transmitting signals from space after being lifted aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at 5:12 p.m. EDT. This initiative is designed to dynamically address evolving communication needs across diverse geographies and customer bases.
- In July 2025, Boeing donated $200,000 to support recovery efforts following flooding in Texas.
- In July 2025, Boeing secured a $2.8 billion contract for the Evolved Strategic Satellite Communications (ESS) program, part of the U.S. nuclear command, control, and communications (NC3) architecture. The initial contract covers two satellites, with options for two additional satellites in the future.
- In June 2025, Boeing signed an agreement with the Ministry of Transport of the Republic of Angola to explore initiatives aimed at advancing the country’s aviation sector, in partnership with TAAG Angola Airlines.
- In May 2025, Boeing expanded its third distribution center in Germany, bolstering its regional service footprint and customer support capacity. This expansion aligns with Boeing’s ongoing investment in regional distribution centers to optimize parts delivery and enhance supply chain reliability.
- In March 2025, Boeing donated $100,000 from the Boeing Charitable Trust to The Salvation Army to aid in recovery efforts in the greater Louisville area.
- In March 2025, Boeing partnered with BOC Aviation to support global airlines in their operations and growth.
- In January 2025, Boeing collaborated with Norsk e-Fuel to advance the production of Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF), aiming to reduce aviation emissions.
(Source: Boeing Press Releases)