Global Steam Turbine Market Capacity(Up to 150 MW, 151 to 300 MW, More than 300 MW), Design(Reaction, Impulse), Fuel Type(Fossil Fuel, Biomass, Geothermal), End-user(Power and Utility, Industrial, Oil and Gas, Others), By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2024-2033
- Published date: Dec 2023
- Report ID: 21035
- Number of Pages: 292
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Market Overview
The Steam Turbine Market size is expected to be worth around USD 23.5 billion by 2033, from USD 17.8 billion in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 2.8% during the forecast period from 2023 to 2033.
Steam turbines, also known as turbine engines, are mechanisms that use steam pressure to generate power. Steam turbines have been used since the late 19th century and have seen a resurgence in recent years due to their ability to produce large amounts of electricity. The steam turbine market covers both industrial and utility-scale applications with a wide range of customer requirements.
The technology behind steam turbines is relatively simple; water is heated until it turns into steam, which then passes through a turbine, turning the blades and creating kinetic energy. This energy can be used directly or converted into electricity depending on the application.
The most common types of steam turbines are condensing, noncondensing and impulse-type turbines; each type has its own set of advantages and limitations. For example, condensing turbines are more efficient than noncondensing ones but require higher temperatures for operation.
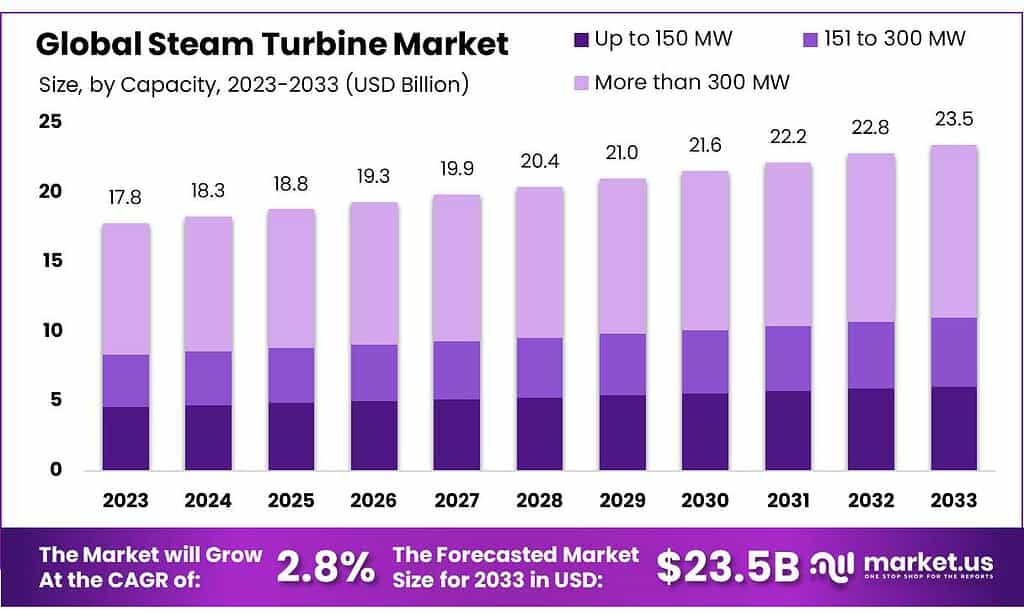
*Actual Numbers Might Vary In The Final Report
Key Takeaways
- Capacity Analysis: More than 300 MW turbines hold over 53.4% share, meeting extensive electricity needs for industries and utilities. Their use in large-scale projects emphasizes their efficiency in addressing rising energy demands.
- Design Preference: Impulse turbines dominated with over 68.2% share, valued for simplicity and reliability in smaller-scale power plants. Their consistency in providing reliable power underscores their importance in diverse industries.
- Fuel Type Impact: Fossil fuels hold a significant share (over 61.1%), reflecting reliance on traditional sources for power generation. Despite interest in renewables, the established infrastructure of fossil fuel-driven turbines remains crucial.
- End-user Significance: The power and utility sector reigns with over 82.1% share, highlighting steam turbines’ vital role in continuous energy supply. Their reliability sustains operations across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors.
- Drivers: Global electricity demand surge is projected due to population growth, emphasizing the need for efficient power generation technologies. Steam turbines stand out for reliability, high energy production, and reduced emissions, aligning with sustainability goals.
- Challenges: Rising competition from gas turbines and renewable energy sources impacts steam turbine demand. Environmental concerns around pollution and stricter regulations pose challenges despite their efficiency.
- Opportunities: Growing natural gas plants and demand for small turbines in sectors like petrochemicals indicate growth prospects. Awareness of their versatility and efficiency drives adoption, especially in Combined Heat and Power systems.
- Regional Insights: APAC holds the largest revenue share (over 39.1%) and anticipates rapid growth due to the construction of power stations. America uses steam turbines for everyday applications, while Russia faces increasing power demands.
Capacity Analysis
In 2023, the More than 300 MW segment emerged as the frontrunner in the steam turbine market, capturing a commanding share of over 53.4%. This segment’s dominance underscores the strong demand and reliance on high-capacity steam turbines within the power generation sector.
These turbines, boasting capacities exceeding 300 MW, play a pivotal role in meeting substantial electricity requirements for industries and utilities. Their ability to generate significant power output positions them as preferred choices for large-scale power generation projects, offering robust solutions for fulfilling the escalating energy needs of various sectors.
The preference for More than 300 MW steam turbines signifies their efficiency and effectiveness in providing substantial power output. Their utilization in diverse applications, including utility-scale power plants and industrial facilities, is instrumental in supporting the electricity demands of a growing population and industries.
Additionally, the market dominance of this segment highlights the continuous emphasis on power generation efficiency and capacity expansion, driving the adoption of high-capacity steam turbines in the energy sector.
By Design
In 2023, the dominance of the Impulse segment characterized the steam turbine market, capturing an extensive share of over 68.2%. This commanding position signals the strong inclination towards Impulse-designed turbines within the realm of power generation.
Impulse turbines stand out due to their simplicity, reliability, and adaptability, particularly in smaller-scale power plants. Their operational efficiency in providing consistent and reliable power output makes them a favored choice across multiple industries for meeting specific power generation requirements.
The significant market share held by Impulse-designed turbines reflects their versatility and effectiveness in various applications. Their suitability for scenarios demanding precise power generation, often found in specific industrial operations, underscores their pivotal role in providing reliable and consistent energy solutions.
Additionally, the dominance of the Impulse segment signifies the continued reliance on this turbine design for targeted power generation needs, emphasizing its relevance and demand in the steam turbine market.
By Fuel Type
In 2023, the Fossil Fuel segment emerged as the dominant force in the steam turbine market, capturing a significant share exceeding 61.1%. This substantial market presence reflects the prevalent use and reliance on steam turbines fueled by traditional fossil fuels like coal, natural gas, and oil in the realm of power generation.
These turbines, powered by fossil fuels, stand out due to their well-established infrastructure and efficiency, serving as primary sources of electricity across diverse industries and large-scale utility applications.
The pronounced market share held by Fossil Fuel-driven steam turbines underscores the continued dependence on conventional energy sources to meet substantial electricity demands globally. Their widespread use in power generation facilities demonstrates their reliability, scalability, and established infrastructure, making them preferred choices for ensuring consistent and substantial energy output.
The dominance of this segment signifies the ongoing reliance on fossil fuels despite the growing interest in renewable energy sources, reflecting the current energy landscape’s complexities and the challenges in transitioning to greener alternatives.
By End-user
The year 2023 witnessed the Power and utility segment reigning supreme in the steam turbine market, capturing an impressive share exceeding 82.1%. This dominance underscores the pivotal role of steam turbines in powering the electricity generation and utility sector.
These turbines serve as backbone sources for producing electricity in power plants and utility companies, ensuring a reliable and continuous supply of energy to meet the diverse needs of residential, commercial, and industrial users worldwide. Their prevalence and dominance in this segment highlight their indispensable contribution to fulfilling the global electricity demand, facilitating essential infrastructure and every day operations across various sectors.
The substantial market share held by the Power and utility segment emphasizes the critical nature of steam turbines in supporting the backbone of power generation and utility services. Their reliability, efficiency, and scalability make them indispensable for ensuring a steady and uninterrupted power supply, vital for sustaining modern societies and industries.
Furthermore, the dominance of this segment signifies the enduring importance of steam turbines in the energy landscape, reinforcing their position as key components in the global power generation infrastructure.
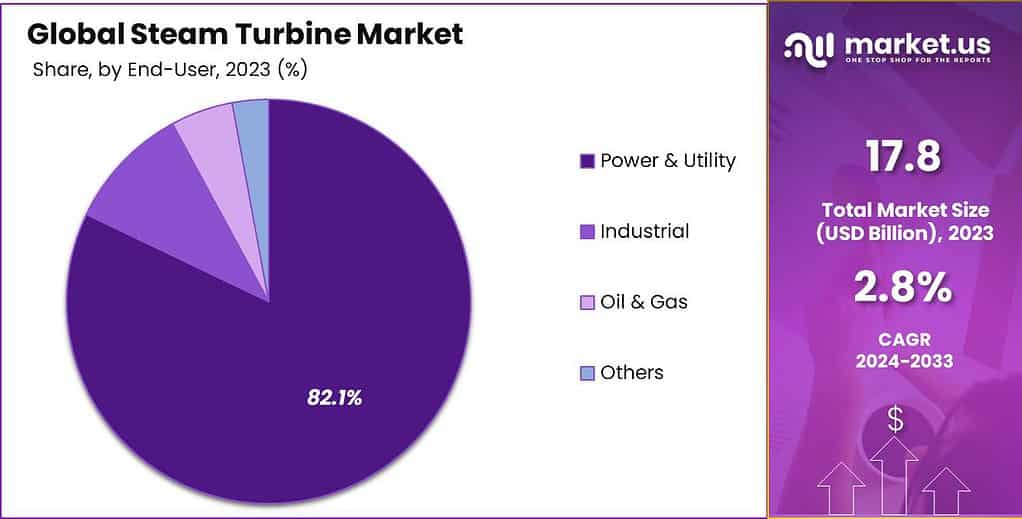
*Actual Numbers Might Vary In The Final Report
Кеу Маrkеt Ѕеgmеntѕ
Capacity
- Up to 150 MW
- 151 to 300 MW
- More than 300 MW
Design
- Reaction
- Impulse
Fuel Type
- Fossil Fuel
- Biomass
- Geothermal
End-user
- Power & Utility
- Industrial
- Oil & Gas
- Others
Drivers
The escalating global demand for electricity has become a focal point due to the considerable population growth and the current unmet need for electricity among approximately 1 billion people globally, as highlighted by the United Nations. Projections estimating a global population of 8.6 billion by 2030 indicate a surge in energy requirements.
Forecasts show that worldwide electricity demand will increase by nearly two-thirds by 2030 from its current levels and that manufacturing companies have begun relying on natural gas more for producing electricity, due to an increasing awareness of sustainable energy sources.
Efforts towards more efficient power generation technologies are propelling the growth of the steam turbine market. Steam turbines stand out for their reliability, often serving as consistent power sources for extended durations. They boast high energy production with minimal operating expenses, relying on the turbine’s rotor speed for output.
Their high efficiency not only reduces operational costs but also minimizes emissions, which aligns with the escalating emphasis on sustainability. This becomes particularly relevant as heat source prices rise, urging industries to prioritize efficient and sustainable energy solutions.
Restraints
Renewable Energy Focus is a People are turning more to solar and wind power, so the demand for traditional steam-based power, like from steam turbines, is getting lower. Expensive Setup: Setting up a steam turbine power plant costs a lot of money. Because of this high cost, some companies might choose other, cheaper ways to make electricity.
Environment Impact is a Steam turbine that uses fossil fuels that can cause pollution. Because of rules about pollution and worries about climate change, companies might want to use cleaner energy sources instead of steam turbines. Lots of Competition Steam turbines have to compete with other ways to make power, like gas turbines and renewable energy. These other ways keep improving, so it’s harder for steam turbines to stay popular.
Limited Fuel Choices is Steam turbines need specific fuels or special setups for fuel, which can make them less flexible than other ways to make power, like renewable energy sources that can use different things to make electricity.
Opportunities
The global steam turbine market is poised for significant growth opportunities driven by the increasing presence of natural gas combined cycle plants and thermal coal power plants. This expansion is chiefly influenced by the surging electricity demand in emerging economies.
Additionally, there’s a growing requirement for small steam turbines in the petrochemical and oil and gas industries. These sectors represent major end-users of steam turbines, paving the way for substantial revenue prospects for market participants.
A rising awareness regarding the advantages offered by steam turbines is anticipated to unlock significant growth avenues. One of the primary benefits of steam turbines, in comparison to gas turbines, is their proficiency in generating electricity. Steam turbines typically operate with a boiler as the heat source for steam production, enabling their use with various fuels like natural gas, coal, and biomass such as sugar cane bagasse or rice hulls.
This adaptability allows their integration into a comprehensive CHP system, known as a Combined Heat and Power system, renowned for its high efficiency in energy production. This growing awareness of their versatile applications and efficiency is expected to drive their adoption, presenting promising opportunities for market expansion.
Challenges
In the steam turbine market, some challenges can make things tricky: Rising Competition is Steam turbines have to compete with other types of power generators like gas turbines and renewable energy. This competition gets tougher because these other options keep getting better.
Environmental Concerns is a Steam turbines that run on fossil fuels can cause pollution. Due to regulations on pollution levels, companies are subject to limits regarding how much pollution they can emit. Finding ways to decrease this level can be a significant challenge for them.
Change in Energy Trends More people are considering alternative forms of power such as wind and solar, meaning less demand for traditional steam turbines to generate steam-based electricity. High Initial Costs is expensive to set up a steam turbine power plant. Because of this big cost at the start, some companies might choose other, cheaper ways to make electricity.
Limited Fuel Options is Steam turbines usually need specific kinds of fuel, which can limit their flexibility compared to other ways to generate power. Handling these challenges means finding ways to make steam turbines more efficient, environmentally friendly, and adaptable to the changing energy landscape.
Regional Analysis
APAC had the largest revenue share at over 39.1% in 2023. This region is expected to experience the fastest growth rate over the forecast period. As many fossil and biomass power stations are constructed in countries like Indonesia, South Korea, Thailand, Bangladesh, and Japan, the Asia Pacific region will continue to be the dominant market in volume and value.
This will help support the market growth during the forecast period. Due to rapid industrialization and a growing population, the demand for electricity in the region is increasing. This is driving the development of clean coal technology, thereby increasing the demand for steam turbines.
CHP applications in America are an everyday use of steam turbines. Steam turbine-based generators generate electricity using heat, unlike reciprocating engine CHP systems and gas turbines. Because separate heat sources power steam turbines, they do not convert fuel to electricity. High-pressure steam powers generators and turbines and transfers the energy from boilers to turbines.
Due to rapid industrialization, Russia’s demand for power is increasing rapidly, pushing down the current production limits. In addition, the country’s high-energy industrial users consider the key benefits of both onsite and self-generation due to rising electricity prices and concerns about the uninterrupted and secure power supply.
*Actual Numbers Might Vary In The Final Report
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Germany
- UK
- France
- Italy
- Russia
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of South America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Israel
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Key Players Analysis
Globalization is key to market competition, with international trade being an important part of sustainable growth. Many of these players have formed joint ventures with multiple customers and suppliers worldwide that increase their market share, lower costs, and allow them to access new markets.
The market’s most prominent players are focusing their efforts on critical assets such as product customization, the development of new product ranges, and inorganic growth ventures. Market players also offer services for maintenance and up-gradation to help them gain competitive advantages over their competitors. The following are some of the most prominent players in the global steam turbine market:
Маrkеt Кеу Рlауеrѕ
- Ansaldo Energia S.p.A
- Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited
- Doosan Skoda Power
- Elliot Group
- Siemens AG
- Fuji Electric Co., Ltd.
- Harbin Electric Corporation
- General Electric
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- MAN Energy Solutions
- Mitsubishi Hitachi power systems.
- Siemens Energy
- Toshiba Corporation
- Arani Power Systems
- Other Key Players
Recent Development
In January 2023, Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL) signed a contract for the renovation and modernization (R&M) of steam turbines at Ukai Thermal Power Station(TPS) in GujaratIn February 2022, EDF and GE announced an exclusive agreement for EDF to acquire a portion of GE Steam Power’s nuclear power activities. The proposed transaction would combine GE’s nuclear steam turbine technology and services expertise with EDF’s commitment to the nuclear power sector, resulting in the formation of an industry-leading global steam turbine equipment and services provider within the EDF Group.In April 2023, Doosan Koda Power was awarded a contract to supply a steam turbine to the South Clyde Energy Centre, a Scottish energy-from-waste (EfW) facility. When completed, this new facility will likely power 70,000 homes. Commercial operations will begin in 2025, with Scotland’s ban on landfilling biodegradable municipal garbage.Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2023) USD 1.13 Billion Forecast Revenue (2033) USD 1.81 Billion CAGR (2023-2032) 4.8% Base Year for Estimation 2023 Historic Period 2017-2022 Forecast Period 2024-2033 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered Capacity(Up to 150 MW, 151 to 300 MW, More than 300 MW), Design(Reaction, Impulse), Fuel Type(Fossil Fuel, Biomass, Geothermal), End-user(Power & Utility, Industrial, Oil & Gas, Others) Regional Analysis North America – The US, Canada, & Mexico; Western Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Portugal, Ireland, Austria, Switzerland, Benelux, Nordic, & Rest of Western Europe; Eastern Europe – Russia, Poland, The Czech Republic, Greece, & Rest of Eastern Europe; APAC – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia & New Zealand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, & Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Colombia, Chile, Argentina, Costa Rica, & Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – Algeria, Egypt, Israel, Kuwait, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, & Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Ansaldo Energia S.p.A, Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited, Doosan Skoda Power, Elliot Group, Siemens AG, Fuji Electric Co., Ltd., Harbin Electric Corporation, General Electric, Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd., MAN Energy Solutions, Mitsubishi Hitachi power systems., Siemens Energy, Toshiba Corporation, Arani Power Systems, Other Key Players Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What Is a Steam Turbine?A steam turbine is a device that converts thermal energy from pressurized steam into mechanical work or electricity. It's a crucial component in power generation and various industrial processes.
How Do Steam Turbines Work?Steam turbines work on the principle of converting the energy of high-pressure steam into rotational mechanical energy. Steam is directed onto blades mounted on a rotor, causing the rotor to spin. The kinetic energy from this rotation is then used to drive generators or machinery.
Where Are Steam Turbines Used?Steam turbines are primarily used in power plants to generate electricity. They are also employed in various industries such as petrochemicals, refineries, pulp and paper, and sugar mills for mechanical drive applications.

-
-
- Ansaldo Energia S.p.A
- Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited
- Doosan Skoda Power
- Elliot Group
- Siemens AG
- Fuji Electric Co., Ltd.
- Harbin Electric Corporation
- General Electric
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- MAN Energy Solutions
- Mitsubishi Hitachi power systems.
- Siemens Energy
- Toshiba Corporation
- Arani Power Systems
- Other Key Players









