Global Remote Patient Monitoring Market By Product Type (Services and Software & Devices), By Application (Cardiovascular Diseases, Diabetes, Respiratory Diseases, Musculoskeletal Diseases and Others), By End-User (Hospitals, Home Healthcare Settings, Long Term Care Centers and Ambulatory Care Settings), Region and Companies – Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Jan 2026
- Report ID: 175008
- Number of Pages: 234
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
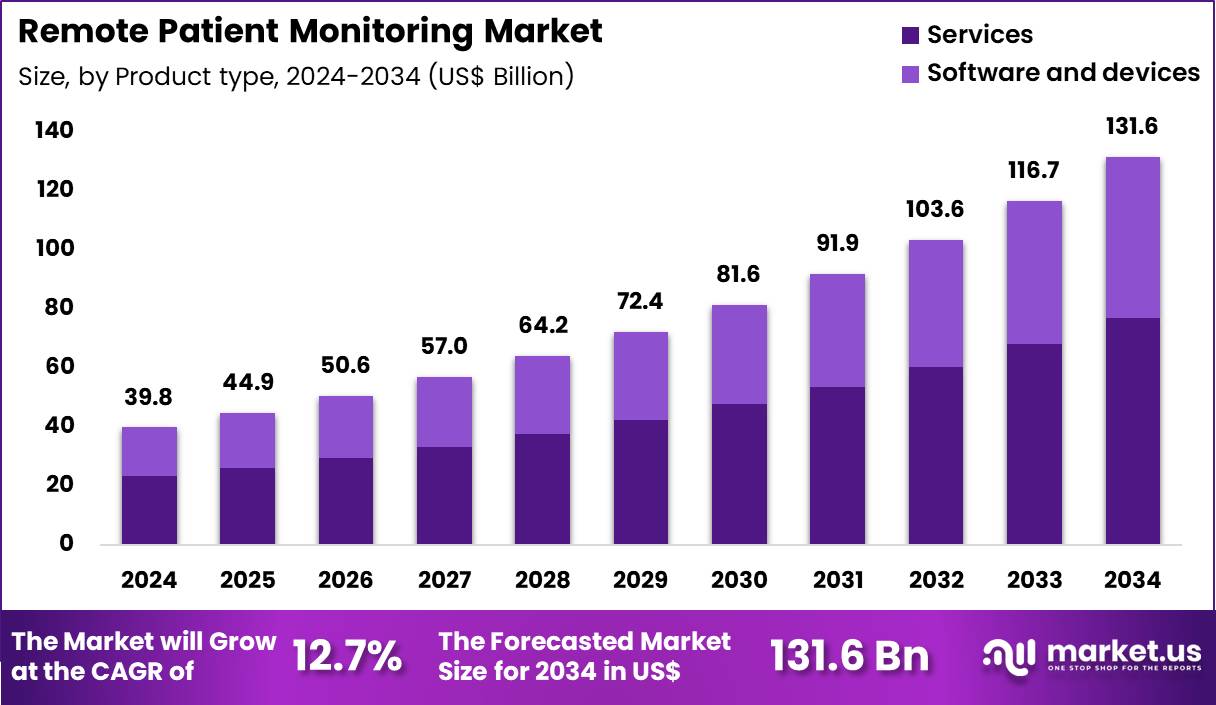
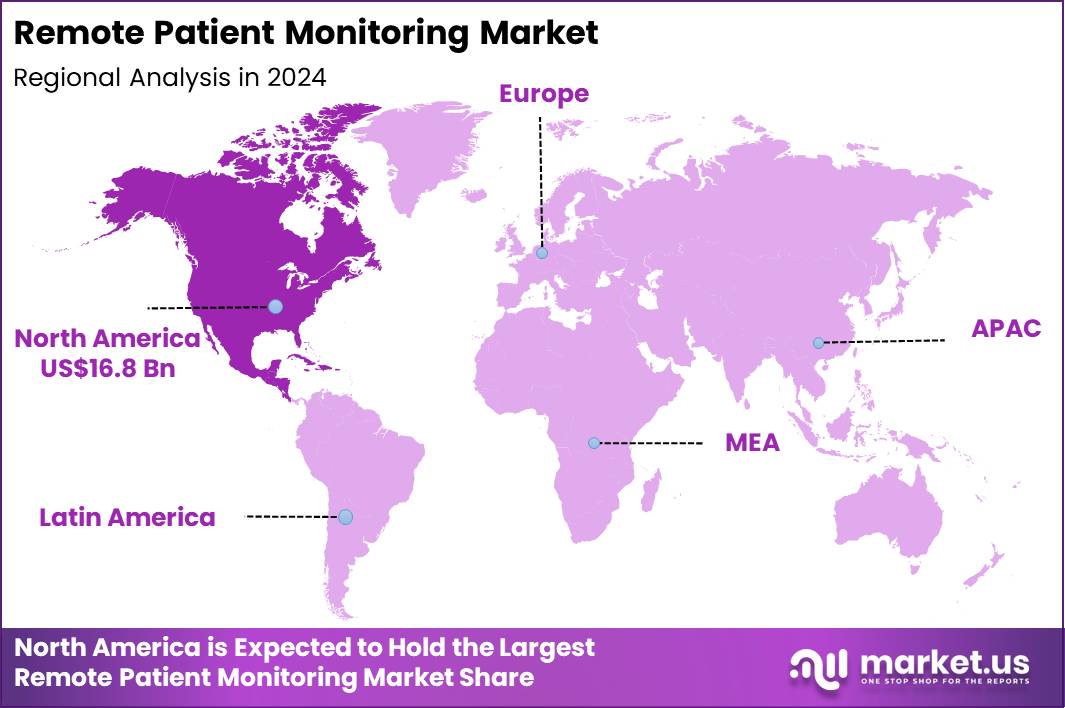
The Global Remote Patient Monitoring Market size is expected to be worth around US$ 131.6 Billion by 2034 from US$ 39.8 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 12.7% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North America led the market, achieving over 42.2% share with a revenue of US$ 16.8 Billion.
Rising prevalence of chronic diseases and an aging population accelerate the adoption of remote patient monitoring systems that enable continuous health tracking outside traditional clinical settings. Cardiologists increasingly deploy connected devices to monitor heart failure patients, capturing daily weight, blood pressure, and heart rate data to detect early decompensation and prevent hospital readmissions.
These systems support diabetes management by transmitting real-time glucose readings from continuous monitors to clinicians, facilitating timely insulin adjustments and reducing hypoglycemic events. Pulmonologists utilize remote spirometry and pulse oximetry devices to track chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations, guiding medication changes and oxygen therapy adjustments from afar.
Remote monitoring platforms also assist post-surgical recovery by logging vital signs and activity levels, allowing early identification of complications such as infections or arrhythmias in orthopedic and cardiac patients. Primary care providers apply wearable sensors to oversee hypertension and atrial fibrillation, ensuring adherence to treatment plans and alerting teams to irregular rhythms or uncontrolled pressures.
Manufacturers pursue opportunities to integrate artificial intelligence algorithms that analyze multi-parameter data streams, predicting adverse events and personalizing care plans for complex chronic conditions. Developers advance hybrid platforms that combine implantable cardiac monitors with external wearables, expanding applications in arrhythmia detection and stroke prevention.
These innovations facilitate virtual care models that reduce in-person visits for stable patients while maintaining close oversight in high-risk populations. Opportunities emerge in pediatric remote monitoring for asthma and epilepsy, where connected inhalers and seizure detection devices empower families and providers to respond swiftly to triggers.
Companies invest in secure, interoperable ecosystems that link monitoring data to electronic health records, supporting seamless collaboration across multidisciplinary teams. Recent trends emphasize patient engagement features such as mobile apps with educational content and gamified adherence tools, driving sustained use and improved outcomes in long-term chronic disease management.
Key Takeaways
- In 2024, the market generated a revenue of US$ 39.8 billion, with a CAGR of 12.7%, and is expected to reach US$ 131.6 billion by the year 2034.
- The product type segment is divided into services and software & devices, with services taking the lead with a market share of 58.4%.
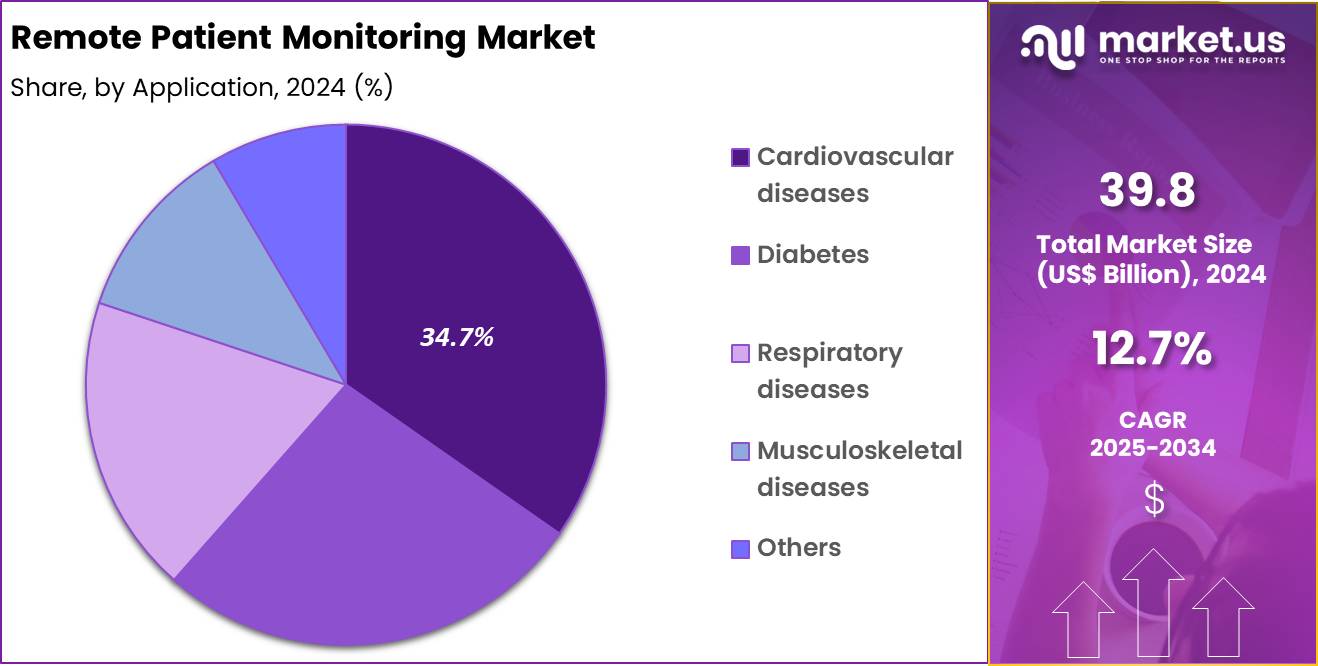
- Considering application, the market is divided into cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, respiratory diseases, musculoskeletal diseases and others. Among these, cardiovascular diseases held a significant share of 34.7%.
- Furthermore, concerning the end-user segment, the market is segregated into hospitals, home healthcare settings, long term care centers and ambulatory care settings. The hospitals sector stands out as the dominant player, holding the largest revenue share of 42.9% in the market.
- North America led the market by securing a market share of 42.2%.
Product Type Analysis
Services contributed 58.4% of growth within product type and drive the remote patient monitoring market through operational delivery rather than standalone hardware ownership. Healthcare providers increasingly choose service-led models because monitoring success depends on enrollment, education, device setup, and continuous patient follow-up. Care teams rely on data review, alerts triage, and clinical escalation services to convert readings into actionable intervention.
Service providers also support workflow integration by coordinating scheduling, patient adherence reminders, and technical troubleshooting. These components reduce drop-off rates and improve daily measurement compliance, which strengthens overall RPM outcomes. Hospitals prefer managed services when staffing constraints limit the capacity to run monitoring programs internally.
Vendors offer bundled programs that include devices, software, logistics, and clinical support under predictable contracts. This structure appeals to health systems aiming to scale programs quickly without expanding headcount.
Service layers also improve risk stratification and personalized care pathways through regular feedback and care coordination. Many programs combine nurse outreach with protocol-based response plans to reduce emergency episodes. Analytics reporting supports quality improvement goals and population health dashboards. Payers increasingly favor programs with clear service frameworks because outcomes depend on consistent follow-up.
Service-led delivery also supports faster expansion into rural and home-based settings where patient training matters most. Continuous improvements in onboarding workflows raise patient satisfaction and long-term participation. The segment is projected to remain dominant due to recurring revenue structure, measurable clinical impact, and scalability across large patient populations.
Application Analysis
Cardiovascular diseases accounted for 34.7% of growth within application and lead remote patient monitoring adoption due to high hospitalization risk and the need for continuous tracking. Hypertension, heart failure, and arrhythmia management require frequent measurement of blood pressure, heart rate, weight trends, and symptom flags. Clinicians prioritize cardiovascular monitoring because early detection of deterioration supports timely medication adjustment and reduces unplanned admissions.
Many hospitals enroll cardiac patients immediately after discharge, since this period carries elevated risk for readmission. Connected blood pressure cuffs and weight scales support home-based monitoring that fits cardiovascular care routines. Risk-based care models increase adoption because cardiovascular episodes carry high costs for providers and payers.
Cardiac programs also rely on RPM to improve adherence to lifestyle and medication plans through regular feedback loops. Clinicians use trends rather than single readings to guide decision-making, which supports long-term monitoring enrollment. Demand increases further as aging populations expand the number of patients living with chronic cardiovascular conditions.
Remote monitoring also improves access to cardiology oversight for patients in underserved areas. Integration with telehealth visits strengthens continuity of care for long-term cardiac management. The segment is anticipated to remain a top growth engine due to high disease prevalence, strong clinical justification, and direct impact on preventable hospital utilization.
End-User Analysis
Hospitals generated 42.9% of growth within end-users and remain the primary adopters of remote patient monitoring programs due to their focus on readmission reduction and care coordination. Hospital systems use RPM to extend care beyond discharge and maintain visibility into patient status at home. Clinical leaders prioritize RPM because it supports early intervention before complications escalate into emergency visits.
Hospitals also benefit from centralized teams that monitor large patient cohorts through structured protocols. Multispecialty hospitals deploy RPM across cardiology, endocrinology, and pulmonary programs to standardize chronic disease pathways. Procurement strength supports rapid scaling through enterprise contracts and integrated vendor partnerships.
Hospital-based RPM programs also align with value-based care initiatives that reward outcomes and penalize avoidable readmissions. Clinical documentation and reporting infrastructure support program evaluation and reimbursement workflows. Hospitals maintain the clinical authority needed to adjust therapy quickly based on remote data trends.
Care coordination teams also manage patient onboarding and education, improving adherence and participation. Hospitals increasingly connect RPM dashboards with electronic health records to streamline physician review. Expansion of hospital-at-home models increases the need for continuous monitoring outside the ward. The segment is expected to retain dominance due to budget capacity, patient volume concentration, and strong incentives to prevent costly acute events.
Key Market Segments
By Product Type
- Services
- Software & Devices
By Application
- Cardiovascular Diseases
- Diabetes
- Respiratory Diseases
- Musculoskeletal Diseases
- Others
By End-user
- Hospitals
- Home Healthcare Settings
- Long Term Care Centers
- Ambulatory Care Settings
Drivers
The surging demand for chronic disease management is driving the market
The escalating global burden of chronic diseases, such as diabetes and cardiovascular disorders, is the primary driver for the remote patient monitoring (RPM) market. Healthcare systems are increasingly adopting RPM to manage long-term conditions outside traditional clinical settings to improve outcomes and reduce costs.
In the US, the National Cancer Institute estimated that 2,001,140 new cancer cases were recorded in 2024, many of which require continuous monitoring of vital signs during outpatient care. Key industry players have reported substantial financial growth linked to this demand; for instance, Dexcom reported that its total revenue for the full year 2024 reached US$ 4.033 billion, representing an 11% increase over 2023.
Dexcom’s U.S. revenue alone grew by 10% in 2024, driven by the expanding adoption of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems. Furthermore, Medtronic reported that its Diabetes segment saw organic revenue growth of 12.1% in the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2024, fueled by the global rollout of the MiniMed 780G system.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) also supports this growth, having approved 133 “Hospital-at-Home” programs across 37 states by April 2024. These programs utilize RPM to provide hospital-level care in a home setting, which studies show can be 30% less expensive than traditional inpatient stays. Consequently, the integration of RPM into standard protocols for chronic care management is a critical factor sustaining market expansion.
Restraints
Data privacy concerns and cybersecurity risks are restraining the market
The remote patient monitoring market faces significant restraints due to heightened concerns over data privacy and the increasing frequency of cybersecurity threats. RPM systems continuously collect and transmit highly sensitive physiological data such as heart rhythms and glucose levels—via cloud-based platforms, making them prime targets for cyberattacks. Any breach of this personal health information can lead to severe legal consequences for providers and a permanent loss of patient trust.
Regulatory bodies like the FDA have issued stricter guidelines regarding the cybersecurity of medical devices, which has increased development costs and time-to-market for manufacturers. In 2024, the American Hospital Association (AHA) noted that total hospital expenses grew by 5.1%, with a portion of these costs attributed to upgrading IT security infrastructure to protect remote data.
Furthermore, behavioral barriers among patients, particularly the elderly, regarding the use of complex digital tools can lead to low engagement and higher discontinuation rates. The requirement for a minimum of 16 days of data collection in a 30-day period to bill certain CMS codes also presents a logistical challenge for providers. High initial investment costs for setting up integrated monitoring hubs further deter smaller clinics with limited capital. These safety-related and financial barriers collectively slow the adoption of RPM, especially in regions with less robust digital infrastructure.
Opportunities
The expansion into underserved and rural populations is creating growth opportunities
The push for health equity and improved access to care in rural and underserved areas provides a major growth opportunity for remote patient monitoring providers. RPM technology bridges the gap for patients living in “medical deserts” where access to specialized clinics is limited by geography or transportation barriers. In 2024, the Bipartisan Policy Center highlighted that while the percentage of patients using RPM remains relatively low, the potential for improving rural health outcomes is vast.
Government initiatives are increasingly targeting these gaps; for example, the Consolidated Appropriations Act mandated reports on how expanded telehealth and RPM coverage impact access in rural communities. Manufacturers are responding by developing low-cost, easy-to-use devices that function on cellular networks, reducing the reliance on high-speed home internet.
The shift toward value-based care also incentivizes providers to use RPM to prevent emergency department visits among high-risk populations. According to a study cited in the Journal of Medical Economics, remote monitoring can reduce healthcare costs by 53%, resulting in savings of approximately US$ 8,375 per patient over six months.
This cost-effectiveness makes RPM an attractive solution for state-funded programs like Medicaid that serve low-income demographics. As reimbursement codes continue to evolve to include more non-physiologic data, the opportunity for RPM to manage a wider array of social and clinical health factors will expand.
Impact of Macroeconomic / Geopolitical Factors
Global economic advancements channel resources into digital health solutions, propelling the remote patient monitoring market as providers expand connected devices for chronic disease management in aging populations. Executives capitalize on favorable reimbursement policies in mature economies, which broadens adoption of wearable sensors and telehealth integrations to improve outcomes efficiently.
Nevertheless, ongoing inflationary pressures worldwide elevate component and connectivity costs, constraining scalability for startups in emerging markets with limited budgets. Geopolitical tensions in electronics supply chains disrupt access to semiconductors and sensors from key regions, compelling firms to manage procurement delays and inventory risks.
Leaders counter these challenges by diversifying manufacturing partnerships toward stable territories, which strengthens operational continuity and encourages collaborative technology advancements. Current US tariffs impose substantial duties on imported medical devices and electronics from major suppliers like China, often ranging from 10% baselines to higher rates under trade measures, which heightens expenses for overseas-reliant systems entering the American market.
Domestic manufacturers seize this environment to accelerate U.S.-based assembly and innovation, which fosters job creation and enhances supply chain resilience. Progressive developments in AI-powered analytics and seamless data interoperability steadily reinforce the market’s momentum, promising greater efficiency, cost savings, and widespread patient benefits across healthcare systems.
Latest Trends
The integration of AI-driven predictive analytics is a recent trend
A defining trend in late 2024 and early 2025 is the transition from reactive monitoring to AI-driven predictive intervention in the RPM sector. Modern RPM platforms are no longer just collecting data; they are using machine learning algorithms to identify subtle patterns that signal clinical deterioration before a crisis occurs. For instance, AI-integrated continuous glucose monitors can now predict hypoglycemic events several hours in advance, allowing for preemptive adjustments to insulin or diet.
The global market for AI in remote patient monitoring reached approximately US$ 1.96 billion in 2024, reflecting its rapid adoption across major health systems. In early 2025, several leading providers launched “smart” cardiac monitors that can automatically detect and prioritize atrial fibrillation alerts for clinical review. This trend addresses the problem of “alert fatigue” among healthcare workers by filtering out noise and highlighting only the most critical patient data.
Furthermore, the 2024 CMS Physician Fee Schedule included updates that facilitate the billing of more sophisticated monitoring services, encouraging the use of advanced analytics. Digital health firms are also partnering with major hospital groups to create centralized virtual care departments that manage outpatient problems through these AI hubs. This shift toward intelligent, automated oversight is setting a new standard for patient safety and operational efficiency in modern healthcare.
Regional Analysis
North America is leading the Remote Patient Monitoring Market
North America held a 42.2% share of the Remote Patient Monitoring market in 2024, reflecting accelerated uptake across hospitals, physician groups, and home care providers. Health systems expanded virtual care models to manage chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and heart failure outside traditional clinical settings. Persistent workforce shortages pushed providers to rely on connected devices and automated alerts to extend care capacity without increasing staff burden.
Value-based care programs encouraged continuous patient monitoring to reduce avoidable hospitalizations and readmissions. Widespread smartphone penetration and broadband access supported seamless integration of connected health devices into daily care routines. Payers continued to reimburse monitoring services, strengthening provider confidence in long-term adoption.
Integration of RPM data into electronic health records improved clinical decision-making and care coordination. As a verifiable indicator, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services reported that more than 570,000 Medicare beneficiaries used RPM services in 2022, highlighting rapid scaling of monitored care models that sustained growth through 2024.
The Asia Pacific region is expected to experience the highest CAGR during the forecast period
Asia Pacific is expected to record strong expansion during the forecast period as healthcare systems adapt to aging populations and rising chronic disease prevalence. Governments actively promote digital health programs to improve access to care in rural and underserved regions. Providers increasingly deploy connected monitoring tools to reduce hospital congestion and manage long-term conditions at lower cost.
Growing smartphone adoption enables patients to participate in continuous health tracking with minimal training. Regional technology firms collaborate with hospitals to localize devices and analytics platforms. Public health agencies support telehealth integration as part of broader healthcare modernization strategies. Insurance coverage for digital care services continues to widen across select markets.
Supporting this outlook, Japan’s Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare reported that people aged 65 and above accounted for over 29% of the national population in 2023, underscoring demographic pressures that are accelerating adoption of continuous, home-based monitoring solutions across the region.
Key Regions and Countries
North America
- US
- Canada
Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherland
- Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Key players in the Remote Patient Monitoring market drive growth by building integrated platforms that capture vitals, symptoms, and adherence data to reduce readmissions and support chronic disease management at scale. Companies expand adoption by partnering with hospitals, payers, and physician groups to embed monitoring into value-based care pathways and reimbursement-backed programs.
Commercial strategies emphasize device-plus-software bundles, analytics dashboards, and care-team workflows that enable actionable interventions rather than raw data collection. Innovation priorities include AI-driven risk stratification, seamless EHR connectivity, and improved device usability that increases patient compliance over long periods.
Market expansion targets regions scaling telehealth infrastructure and home-based care delivery for aging populations. Philips operates as a leading participant through its connected care portfolio, global healthcare relationships, and strong capabilities in clinical monitoring and data platforms that support enterprise-level remote patient programs.
Top Key Players
- Medtronic
- Koninklijke Philips N.V.
- GE HealthCare
- Boston Scientific Corporation
- Abbott
- Dexcom, Inc.
- Masimo
- iRhythm Technologies, Inc.
- ResMed
- Omron Healthcare
Recent Developments
- In July 2024, Boston Scientific introduced a digital platform aimed at extending specialist cardiac support to remote and hard to reach regions, including underserved areas of South Africa and isolated island communities such as the Azores. The solution enables clinicians to connect with global experts for real time guidance, even under unstable infrastructure conditions such as power interruptions. By improving access to clinical expertise and decision support outside major hospitals, this launch strengthens continuity of cardiac care and supports faster, higher confidence interventions in geographically constrained settings.
- In April 2024, Royal Philips announced a strategic collaboration to integrate SmartQare’s viQtor technology with Philips’ clinical patient monitoring systems. The partnership focuses on advancing continuous monitoring across both hospital wards and home care environments, with an initial rollout planned in Europe. By combining wearable enabled monitoring with established clinical platforms, the initiative supports earlier detection of patient deterioration, improved workflow efficiency for care teams, and stronger continuity of care beyond traditional inpatient settings.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) US$ 39.8 Billion Forecast Revenue (2034) US$ 131.6 Billion CAGR (2025-2034) 12.7% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, COVID-19 Impact, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Product Type (Services and Software & Devices), By Application (Cardiovascular Diseases, Diabetes, Respiratory Diseases, Musculoskeletal Diseases and Others), By End-User (Hospitals, Home Healthcare Settings, Long Term Care Centers and Ambulatory Care Settings) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Medtronic, Koninklijke Philips N.V., GE HealthCare, Boston Scientific Corporation, Abbott, Dexcom, Inc., Masimo, iRhythm Technologies, Inc., ResMed, Omron Healthcare Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Remote Patient Monitoring MarketPublished date: Jan 2026add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Remote Patient Monitoring MarketPublished date: Jan 2026add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Medtronic
- Koninklijke Philips N.V.
- GE HealthCare
- Boston Scientific Corporation
- Abbott
- Dexcom, Inc.
- Masimo
- iRhythm Technologies, Inc.
- ResMed
- Omron Healthcare










