Global Plant Based Vitamin D Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Product Type (Vitamin D2, Vitamin D3), By Form (Powder, Liquid, Capsule, Tablet, Others), By Source (Mushroom, Lichen, Algae, Yeast, Others), By Application (Dietary Supplements, Food And Beverages, Pharmaceuticals, Cosmetics And Personal Care, Others), By Distribution Channel (Online Stores, Supermarkets Or Hypermarkets, Specialty Stores, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Dec 2025
- Report ID: 169784
- Number of Pages: 347
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
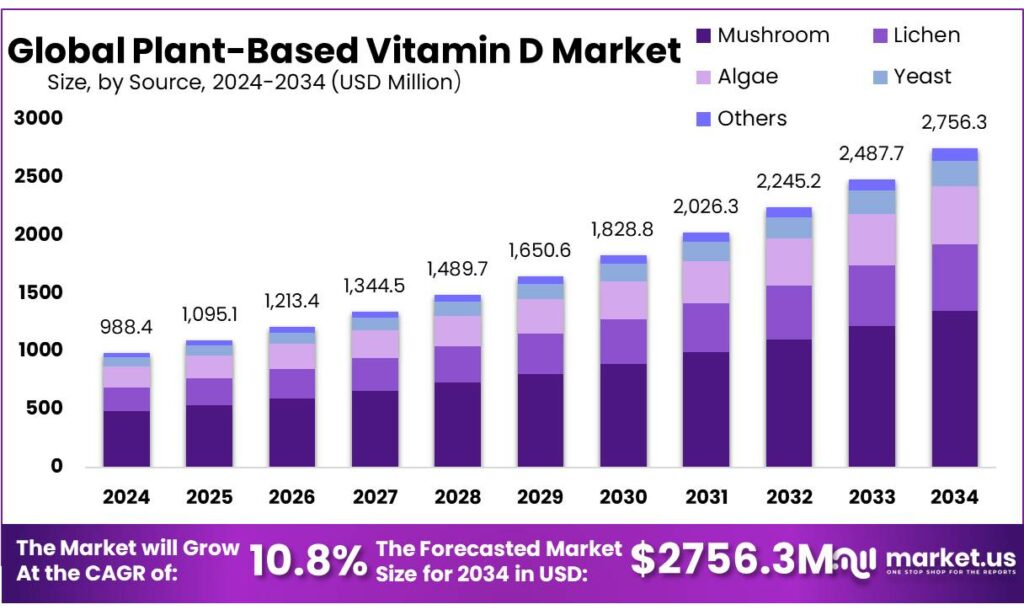
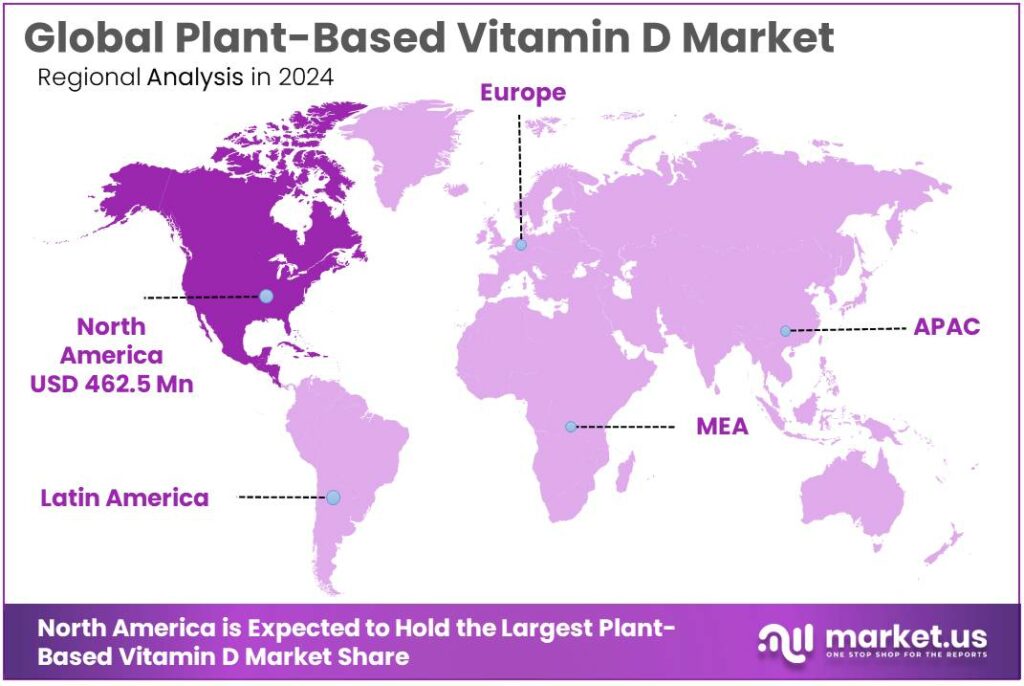
The Global Plant Based Vitamin D Market size is expected to be worth around USD 2756.3 Million by 2034, from USD 988.4 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 10.8% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 46.80% share, holding USD 462.5 Million revenue.
Plant-based vitamin D refers mainly to vitamin D₂ from UV-exposed fungi and yeast, and vitamin D₃ derived from lichen, offering a non-animal alternative to conventional lanolin-based D₃. This niche has emerged at the intersection of escalating global vitamin D deficiency and accelerating adoption of vegetarian and vegan diets. Meta-analyses estimate that around 15.7% of the world’s population has serum 25(OH)D levels below 30 nmol/L, a threshold associated with deficiency, over the 2000–2022 period. Other reviews suggest roughly 1 billion people are deficient and about 50% have vitamin D insufficiency, underscoring the scale of unmet need that plant-based solutions can address.
The industrial scenario for plant-based vitamin D is closely aligned with wider plant-based food trends. Global retail sales of plant-based foods reached about USD 28.6 billion in 2024, with U.S. retail alone contributing USD 8.1 billion, according to industry data compiled by the Good Food Institute. Fortified beverages are a primary delivery format. Studies show that around 21% of plant-based milks in some markets are fortified with vitamin D, while many dairy and plant-based milks supply roughly 100 IU per serving.
Government initiatives and nutrition policy are strong structural drivers. Finland’s long-running fortification programme recommends up to 20 μg/100 g vitamin D in fat spreads and around 1 μg/100 g in fluid milk products, a measure that has measurably improved national vitamin D status and is frequently cited as a policy benchmark. In 2025, WHO issued guidelines on fortifying edible oils and fats with vitamins A and D, broadening the global policy push for vitamin D enrichment of staple foods.
Regulators are tightening nutritional guidance, reinforcing this demand. The U.S. National Academies and NIH recommend 15–20 μg/day (about 600–800 IU) of vitamin D for most adults, while Europe’s EFSA sets an adequate intake of 15 μg/day, signalling broad consensus on baseline requirements. Yet recent European modelling work indicates that in some populations, up to 100% of individuals fail to meet even 10 μg/day, highlighting the need for fortification strategies and supplemental products. Parallel to this, dietary shifts are significant: India, for example, reports around 38% of its population following a vegetarian diet, a structurally attractive base for plant-only supplements and fortified foods.
Future growth opportunities in plant-based vitamin D span ingredients, formats, and sustainability positioning. On the ingredient side, UV-exposed mushrooms can deliver approximately 20–160 μg of vitamin D₂ per 100 g, and portabella mushrooms treated with UV for seconds can reach around 11.2 μg (446 IU) per 100 g, creating scope for whole-food ingredients and mushroom-derived concentrates.
Key Takeaways
- Plant Based Vitamin D Market size is expected to be worth around USD 2756.3 Million by 2034, from USD 988.4 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 10.8%.
- Vitamin D2 held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 59.3% share.
- Powder held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 39.8% share.
- Mushroom held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 49.4% share.
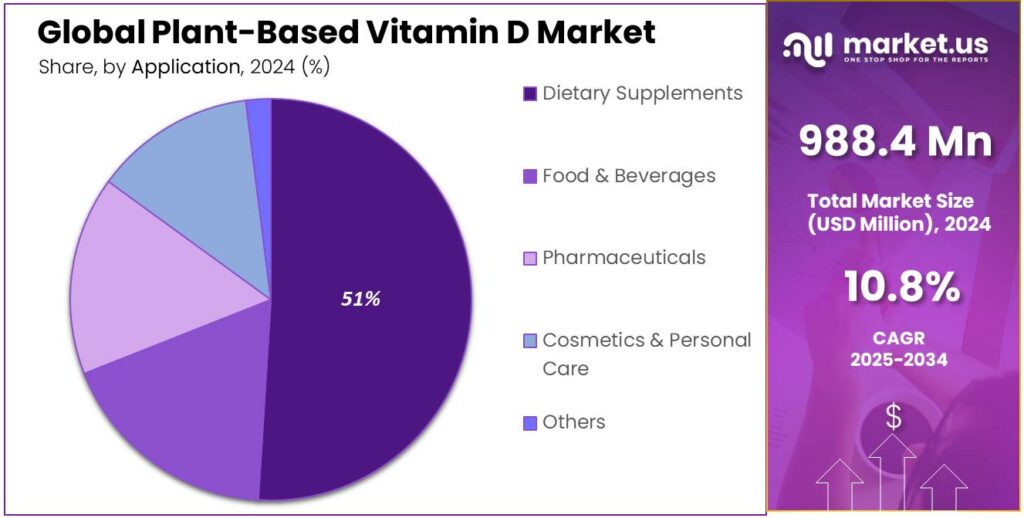
- Dietary Supplements held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 51.7% share.
- Online Stores held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 37.9% share.
- North America accounted for a commanding regional share of the plant-based vitamin D market, representing 46.80% of revenues and approximately USD 462.5 million.
By Product Type Analysis
Vitamin D2 leads with 59.3% as the preferred plant-based option for fortification and supplements.
In 2024, Vitamin D2 held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 59.3% share. The segment’s strength was driven by its plant-derived sourcing, vegan suitability, and broad acceptance for food fortification and dietary supplements. Manufacturers favoured D2 for its supply-chain resilience and ease of incorporation into powdered and liquid formats, which supported strong retail and industrial uptake. Quality control and standardised dosing were emphasised to meet label claims and regulatory expectations, while product development focused on improving stability and bioavailability in diverse matrices.
Retail and e-commerce channels expanded shelf space for D2-based SKUs, and formulation improvements helped reduce variability between batches. By 2025, the Vitamin D2 segment remained the primary contributor to plant-based vitamin D volumes, with ongoing efforts targeted at enhancing efficacy, reducing production costs, and widening use in fortified foods to sustain market leadership.
By Form Analysis
Powder leads with 39.8% as the go-to form for fortification and supplement blends.
In 2024, Powder held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 39.8% share. The powder form was favoured because it is easy to dose, stable in storage, and simple to incorporate into dry mixes, beverages and food-fortification processes; accordingly, manufacturers scaled production of powdered D-rich premixes and optimized encapsulation techniques to preserve potency. Quality control and batch standardization were prioritised to meet label claims and regulatory requirements, while supply-chain efficiencies lowered cost per serving for large-volume customers.
Processing advantages—such as compatibility with spray-drying and microencapsulation—were leveraged to improve bioavailability and reduce degradation during shelf life. By 2025, the powder segment remained the primary format for plant-based vitamin D applications, with continued focus on stability improvements, process standardization, and wider adoption in fortified food and beverage formulations.
By Source Analysis
Mushroom dominates with 49.4% as demand for natural vitamin-rich sources accelerates.
In 2024, Mushroom held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 49.4% share. The segment benefitted from rising consumer preference for naturally derived vitamin sources, as UV-exposed mushrooms provide a clean and plant-based option for Vitamin D production. The growth of vegan and vegetarian populations further supported demand, while manufacturers focused on controlled cultivation, UV-treatment optimisation, and improved extraction processes to enhance yield and potency.
In 2025, the segment continued to advance as food and nutraceutical companies increased the use of mushroom-derived Vitamin D in fortified foods, beverage mixes, and supplements, supported by steady supply chains and broader regulatory acceptance of mushroom-based inputs across global markets.
By Application Analysis
Dietary Supplements dominate with 51.7% as consumers increasingly seek plant-based nutrition.
In 2024, Dietary Supplements held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 51.7% share. The segment benefitted from the rising demand for clean-label and plant-derived nutrients, as more consumers shifted toward vegan and natural health products. Plant-based Vitamin D supplements gained strong traction due to growing awareness of vitamin deficiencies and the preference for non-synthetic sources.
The expansion of e-commerce channels and the availability of mushroom- and lichen-based formulations further supported adoption. By 2025, steady growth was observed as manufacturers focused on higher bioavailability, improved extraction methods, and broader product formats such as capsules, powders, and gummies. The emphasis on preventive healthcare and immunity support also continued to strengthen demand across global markets.
By Distribution Channel Analysis
Online Stores dominate with 37.9% as consumers prefer convenient access to plant-based nutrition.
In 2024, Online Stores held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 37.9% share. The growth of this channel was supported by the rapid shift toward digital purchasing, with consumers seeking convenient access to plant-based Vitamin D products in diverse formats. The availability of detailed product information, transparent ingredient lists, and user reviews encouraged higher adoption, particularly among health-conscious buyers comparing natural and vegan formulations.
By 2025, steady expansion was observed as brands strengthened their online presence through direct-to-consumer platforms and subscription models. Promotional campaigns, wider product assortment, and faster delivery options further improved customer engagement. The rising preference for clean-label supplements and the growing popularity of e-commerce in emerging markets continued to reinforce the strong position of online distribution in the plant-based Vitamin D market.
Key Market Segments
By Product Type
- Vitamin D2
- Vitamin D3
By Form
- Powder
- Liquid
- Capsule
- Tablet
- Others
By Source
- Mushroom
- Lichen
- Algae
- Yeast
- Others
By Application
- Dietary Supplements
- Food & Beverages
- Pharmaceuticals
- Cosmetics & Personal Care
- Others
By Distribution Channel
- Online Stores
- Supermarkets Or Hypermarkets
- Specialty Stores
- Others
Emerging Trends
Plant-Based Drinks Moving to “D-Standard” Nutritional Equivalence
A clear trend in plant-based vitamin D is the quiet shift from “nice-to-have” fortification to something much closer to a standard, especially in plant-based drinks. The UK government’s Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition (SACN) and the Committee on Toxicity (COT) recently reviewed almond, oat and soy drinks and explicitly stated that a good formulation should fortify plant-based drinks with vitamin D and aim for nutritional equivalence to semi-skimmed cow’s milk for key nutrients. Their 2025 report notes that vitamin D in these drinks is usually added as fungal vitamin D₂ or lichen-derived vegan D3.
At the same time, global plant-based food volumes are big enough now that a change in how these products are fortified really matters for vitamin D intake. The Good Food Institute reports that worldwide retail sales of plant-based meat, seafood, milk, yoghurt, ice cream and cheese reached about US$28.6 billion in 2024, while U.S. plant-based food retail alone was worth US$8.1 billion that year. When brands decide to switch from animal-derived D₃ to plant-based D₂ or lichen D₃ across such high-volume categories, it quietly expands the footprint of vegan vitamin D without asking consumers to swallow extra pills.
Foodservice is following a similar path. GFI’s 2024 foodservice snapshot shows that plant-based protein dollar sales through U.S. broadline distributors reached US$289 million in 2024, growing at about 4% CAGR since 2020, while plant-based milk and creamer also gained share; plant-based creamer reached 31% of total creamer distributor sales. Every time a café or chain reformulates its oat latte base or dairy-free creamer to include plant-based vitamin D, that trend becomes part of everyday behaviour rather than a specialist nutrition choice.
- You can already see this normalisation in country-level markets. GFI Europe notes that in Germany, retail sales across six core plant-based categories reached €1.68 billion in 2024, up 1.5% versus 2023 and 6.8% versus 2022. In such mature markets, the next competitive edge is not just taste but nutritional profile. Brands increasingly talk about matching cow’s milk for calcium, B12 and vitamin D, and doing so with “100% plant-based sources.” That framing naturally favours UV-treated fungal vitamin D3 and lichen-based D3 over lanolin-derived D3.
Drivers
Widespread Global Vitamin D Deficiency — Creating Demand for Plant-Based Vitamin D
Other authoritative sources underscore the scale: globally about 1 billion individuals are estimated to have “low” vitamin D levels across all age groups. In some regions, especially in lower-income countries or among women and the elderly, deficiencies are more severe — which makes the problem not only widespread but also deep, with serious implications for bone health, immune function, and chronic disease risk.
- One of the strongest forces fueling growth in the plant-based vitamin D segment is the sheer scale of global vitamin D deficiency. According to a comprehensive meta-analysis covering studies from 2000 to 2022 (with around 7.9 million participants), 15.7% of people worldwide had serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels below 30 nmol/L (a threshold many experts consider as deficiency). Additionally, the same analysis found that 47.9% had levels below 50 nmol/L (insufficiency) and 76.6% had levels below 75 nmol/L.
Governments and public health bodies increasingly recognize food fortification as the most feasible way to raise vitamin D levels across entire populations. In fact, fortifying staple foods (like milks, flours, oils) with vitamin D has been recommended by nutrition experts as an effective, low-risk, population-wide strategy.
For people who avoid animal-based foods — vegetarians, vegans, or those concerned with sustainability — the uptake of plant-based vitamin D is especially attractive because it fills the nutritional gap without compromising dietary choices. In many countries, dietary habits already lean toward plant-based staples; combining such diets with plant-based vitamin D fortification or supplementation offers a humane, inclusive, and practical route to address deficiency.
Restraints
Limited Fortification Reach and Low Supplement Use Restrain Plant-Based Vitamin D
One of the biggest brakes on plant-based vitamin D is not demand, but how little of the world is actually reached by vitamin D fortification and supplementation in practice. The World Health Organization notes that 39 countries currently mandate or allow fortification of edible oils with vitamin A only, and just 13 countries mandate or allow co-fortification with both vitamins A and D. That means most countries still have no systematic way to put vitamin D, let alone plant-based vitamin D, into everyday foods. In these markets, even motivated brands often face weak policy support, unclear standards, and fragmented guidance on which vitamin D forms (D₂, lanolin-D₃, lichen-D₃) regulators prefer.
India is a good example of how regulation can both help and limit this space. The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) encourages fortification of edible oils and fats with vitamins A and D, and states that fortified oil can supply about 25–30% of the recommended dietary allowance for these vitamins. Yet, a recent policy brief on vitamin D fortification in India notes that, despite these efforts, only edible oil and milk are currently permitted vehicles for vitamin D.
On the intake side, numbers from major public-health datasets show how far we still are from adequate vitamin D consumption, and how small a role supplements play for many people. In the United States, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data analysed by the National Institutes of Health show that 92% of men, more than 97% of women, and 94% of people aged 1 year and older consume less than the Estimated Average Requirement of 10 µg/day (400 IU) from food and beverages. That gap is huge, yet supplement use is uneven. A European analysis reported vitamin D supplement use as low as 1.4% in one large cohort, so low that the authors did not even stratify results by supplement use.
Regulators are also careful about upper limits, which can make companies conservative about dosing, especially with new plant-based forms. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) set a tolerable upper intake level of 100 µg/day of vitamin D for adults and adolescents, and 50 µg/day for children aged 1–10 years. These limits are important for safety, but they also push formulators to stay modest with vitamin D content in fortified foods and supplements. When you combine these upper limits with low baseline intake, complex labelling rules, and the extra cost of vegan sources like lichen-derived D₃, many mass-market players default to cheaper, established animal-derived ingredients or skip vitamin D fortification altogether.
Opportunity
Fortifying Fast-Growing Plant-Based Foods with Vitamin D
A big growth opportunity for plant-based vitamin D sits exactly where two trends meet: the rapid rise of plant-based foods and the push from public-health bodies to use everyday foods as carriers for vitamin D. Global retail sales of plant-based meat, seafood, milk, yoghurt, ice cream and cheese reached about $28.6 billion in 2024, with the United States alone accounting for roughly $8.1 billion. These figures come from analysis shared by the Good Food Institute and reported by The Food Institute.
Within that universe, plant-based milk is the workhorse category, and that matters a lot for vitamin D. Data from the Plant Based Foods Association show that 40.6% of U.S. households bought plant-based milk in 2022, and an impressive 75.7% of those consumers purchased it again, confirming it as a staple rather than a trial product. Good Food Institute’s State of the Industry work also notes that nearly half of U.S. households bought plant-based milk at least once in 2023, with almost 80% of those households being repeat shoppers.
Regulators and scientific committees are now explicitly looking at plant-based drinks as vehicles for vitamin D. A 2025 report for the UK government by SACN and the Committee on Toxicity points out that plant-based drinks are “often fortified with vitamin D,” whereas cow’s milk naturally contains only trace amounts. It also explains that vitamin D₂ is typically derived from fungi and UV-irradiated yeast, while vegan vitamin D₃ can be obtained from lichen.
Consumer demographics add another layer of opportunity. The Vegan Society, summarising multiple datasets, notes that in India around 9% of the population identify as vegan and almost 25% as vegetarian.Another survey cited by vegconomist suggests roughly 38% of Indians follow a vegetarian diet. Europe and North America also show steady growth in people choosing plant-based eating, whether for health, ethics or the climate. For these consumers, lanolin-derived vitamin D₃ from sheep’s wool feels inconsistent with their values, so lichen-based D₃ and fungal D₂ can command a clear preference, especially when clearly labelled as “100% plant-based.”
Regional Insights
North America leads with 46.80% (≈ USD 462.5 Mn) as the principal regional market for plant-based vitamin D.
In 2024, North America accounted for a commanding regional share of the plant-based vitamin D market, representing 46.80% of revenues and approximately USD 462.5 million in sales. This leadership was supported by strong consumer demand for vegan and clean-label supplements, widespread retailer and e-commerce adoption, and earlier regulatory acceptance of mushroom- and lichen-derived vitamin ingredients, which together increased product availability across mainstream and specialty channels.
Local R&D and ingredient suppliers strengthened supply-chain resilience, while manufacturers scaled production and optimization of UV-exposure and extraction processes to improve yield and potency for mushroom-derived D2 and other plant sources. Market concentration among experienced nutraceutical players enabled rapid route-to-market for new SKUs and fortified foods, and promotional activity—especially digital marketing and subscription models—drove higher conversion and repeat purchase rates in key U.S. and Canadian markets.
Investment in formulation work reduced degradation in powdered and liquid matrices, improving shelf life and enabling broader food-fortification applications. Logistics and regulatory alignment across North American jurisdictions facilitated faster product launches and multi-channel distribution. Looking ahead into 2025, the region’s dominance is expected to persist as brands and ingredient suppliers continue to prioritise product efficacy, bioavailability improvements, and targeted consumer education to convert mainstream buyers to plant-based alternatives.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
DSM remains an ingredient and solutions leader supplying vegan and plant-based vitamin ingredients and technical support for fortified foods and supplements. In 2024 the group reported strong operational improvement with adjusted EBITDA rising ~19% year-on-year, reflecting favourable demand for nutritional ingredients and continued investment in plant-based portfolios. DSM’s ingredient platforms support stabilization, encapsulation, and premix services for plant-based vitamin D applications, enabling fast route-to-market for customers.
Divi’s is a major contract manufacturer and API supplier that supports vitamin and nutraceutical ingredient supply chains, including vitamin D intermediates and formulation services for global customers. Subsidiary financials show net sales of about USD 31.77 million for a reported FY period in 2024, underlining Divi’s export-led manufacturing scale. The firm’s technical capabilities (custom synthesis, stability testing, and bulk supply) enable formulators to source high-quality inputs for plant-based vitamin D premixes and finished SKUs.
Nordic Naturals, known for marine and algae oils, expanded into plant-based vitamin solutions and consumer formats; the brand dates to 1995 and focuses on premium formulations and third-party testing. In 2024 the company offered consumer plant-based vitamin D liquid SKUs (e.g., 1,000 IU liquid priced at about USD 21.95), highlighting a premium, evidence-oriented positioning for health-conscious buyers. Nordic’s retail and practitioner channels support penetration into premium supplement segments seeking vegan alternatives.
Top Key Players Outlook
- DSM NV
- Divi’s Laboratories Limited
- Now Foods
- Swanson Health Products Inc.
- Zhejiang Garden
- Nordic Naturals Inc.
- Vitabiotics Limited
- Fermenta Biotech Limited
- Pure Encapsulations LLC
- MaryRuth Organics LLC
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024 DSM-Firmenich reported sales of €12,799 million and adjusted EBITDA of €2,118 million, reflecting improved performance in its Nutrition and Health platforms and the completion of initial integration synergies.
In 2024 Divi’s Laboratories reported consolidated revenue of approximately INR 8,184 crore (≈ ₹81,840 million), signalling stable top-line scale for its nutraceutical and API businesses. Subsidiary net sales: USD 31,767,802 (2024), reflecting active export and B2B ingredient trade.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 988.4 Mn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 2756.3 Mn CAGR (2025-2034) 10.8% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Product Type (Vitamin D2, Vitamin D3), By Form (Powder, Liquid, Capsule, Tablet, Others), By Source (Mushroom, Lichen, Algae, Yeast, Others), By Application (Dietary Supplements, Food And Beverages, Pharmaceuticals, Cosmetics And Personal Care, Others), By Distribution Channel (Online Stores, Supermarkets Or Hypermarkets, Specialty Stores, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape DSM NV, Divi’s Laboratories Limited, Now Foods, Swanson Health Products Inc., Zhejiang Garden, Nordic Naturals Inc., Vitabiotics Limited, Fermenta Biotech Limited, Pure Encapsulations LLC, MaryRuth Organics LLC Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Plant Based Vitamin D MarketPublished date: Dec 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Plant Based Vitamin D MarketPublished date: Dec 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- DSM NV
- Divi's Laboratories Limited
- Now Foods
- Swanson Health Products Inc.
- Zhejiang Garden
- Nordic Naturals Inc.
- Vitabiotics Limited
- Fermenta Biotech Limited
- Pure Encapsulations LLC
- MaryRuth Organics LLC










