Global Maritime Freight Transport Market Size, Share, Growth Analysis By Cargo Type (Dry Bulk, Liquid Bulk, Containerized Goods, General Cargo), By Vessel Type (Container Ships, Bulk Carriers, Tankers, Ro-Ro Vessels, LNG/LPG Carriers, Offshore Support Vessels, Cruise Ships), By End-use (Manufacturing, Food and Beverage, Oil and Ores, Electrical and Electronics, Others), By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Statistics, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Dec 2025
- Report ID: 170557
- Number of Pages: 384
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
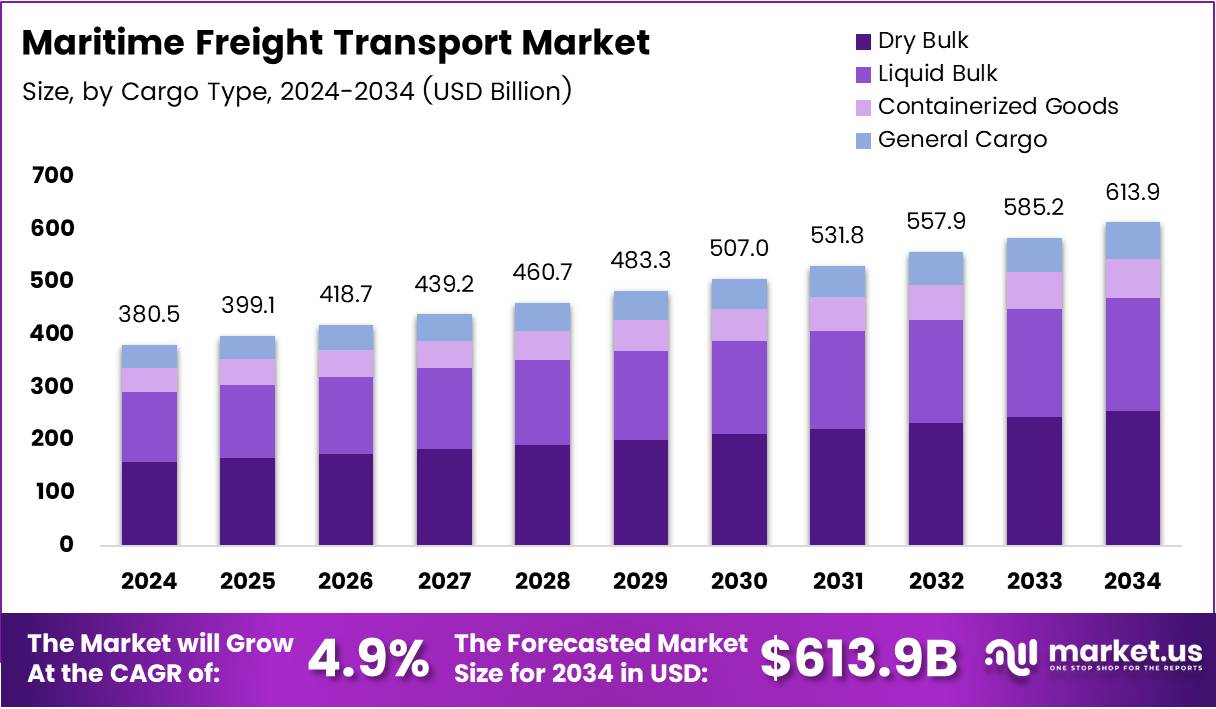
Global Maritime Freight Transport Market size is expected to reach approximately USD 613.9 Billion by 2034 from USD 380.5 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 4.9% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
Maritime freight transport serves as the backbone of international trade and commerce worldwide. This market encompasses ocean-based cargo movement including containerized goods, bulk commodities, energy products, and manufactured items. Maritime shipping handles over 80% of global trade volumes, making it indispensable for economic connectivity.
The market demonstrates consistent expansion driven by globalization and cross-border manufacturing networks. E-commerce growth significantly boosts containerized cargo demand across major shipping routes. Additionally, bulk shipping remains essential for transporting raw materials and energy resources cost-effectively. According to Eurostat, 814.3 million tonnes of goods were handled in main EU ports in Q1 2025.
Infrastructure modernization continues to reshape the maritime freight landscape across strategic trade corridors. Consequently, ports worldwide invest in advanced loading systems and digital tracking capabilities. According to the European Technology Platform for Logistics, maritime transport maintains a 67.4% share in freight movement. Furthermore, environmental regulations drive adoption of low-emission vessel technologies and alternative fuels.
Government initiatives worldwide support shipping industry transformation through green corridor development and digitalization programs. Moreover, port authorities collaborate with shipping operators to reduce turnaround times and enhance efficiency. The market faces challenges including fuel price volatility and geopolitical disruptions affecting canal access. However, opportunities emerge through AI-driven optimization, refrigerated transport expansion, and strategic alliance formation. According to UNCTAD data, maritime transport moves over 80% of goods traded worldwide, reinforcing its critical role.
Key Takeaways
- Global Maritime Freight Transport Market projected to reach USD 613.9 Billion by 2034 from USD 380.5 Billion in 2024.
- Market growing at a CAGR of 4.9% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
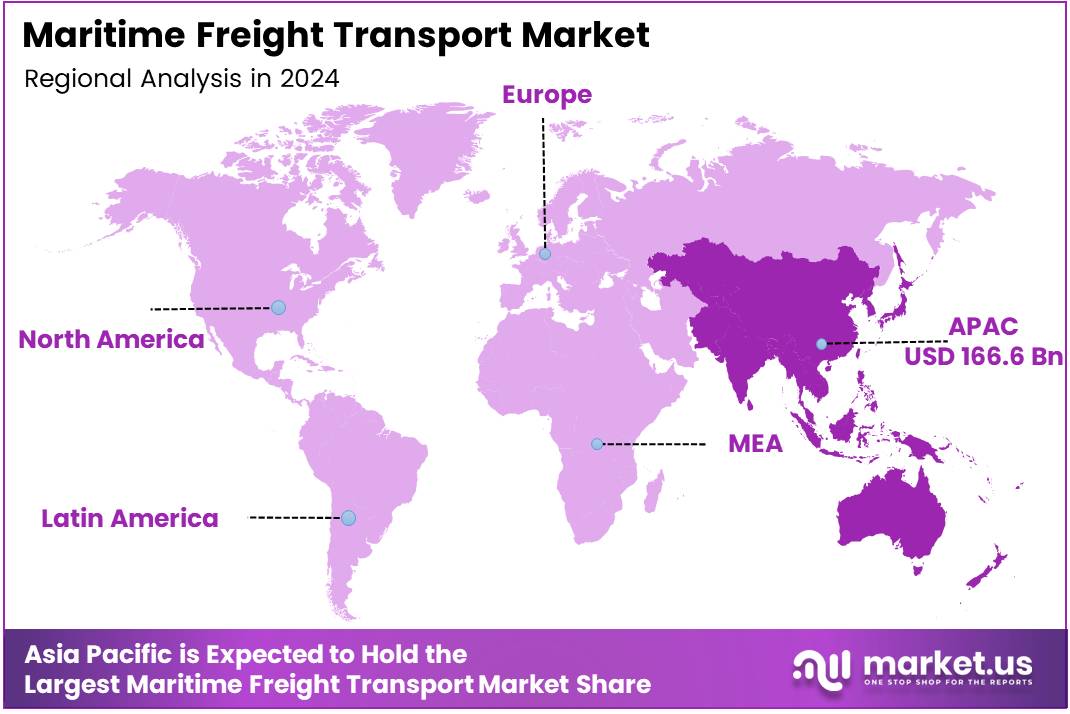
- Asia Pacific dominates with 43.8% market share, valued at USD 166.6 Billion.
- Dry Bulk cargo type leads with 38.1% market share in 2024.
- Container Ships vessel type holds dominant position with 34.9% share.
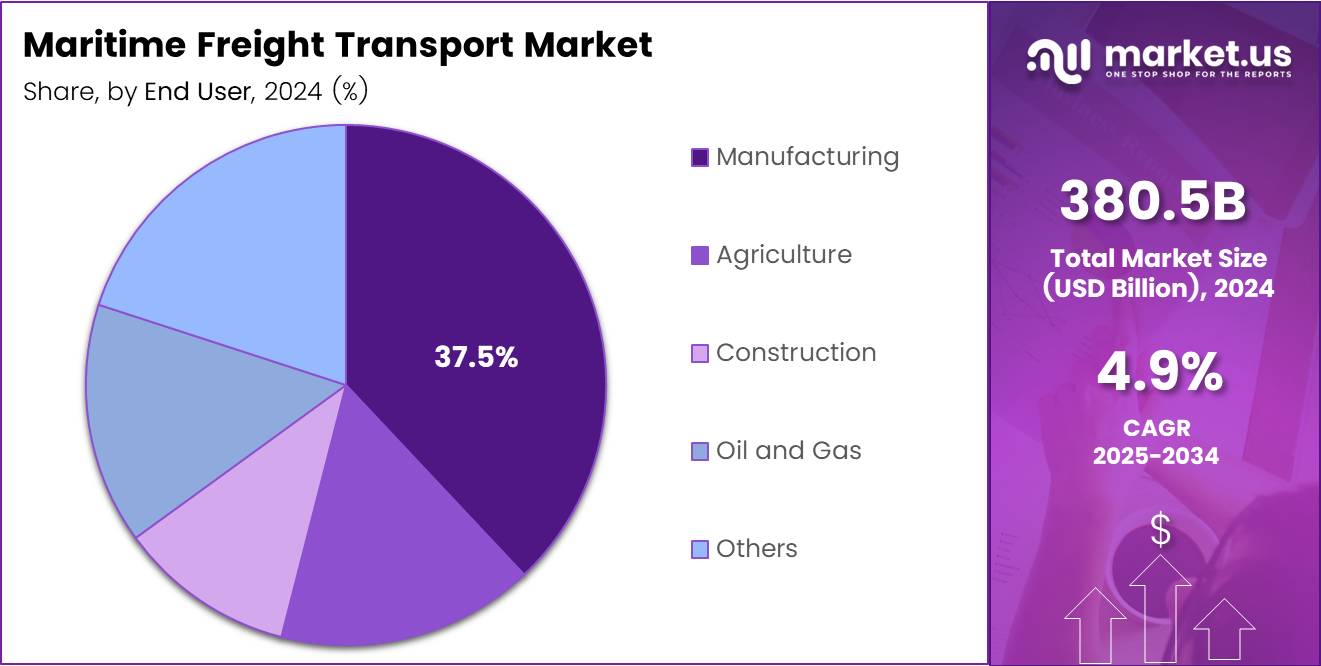
- Manufacturing end-use segment captures 37.5% market share.
Cargo Type Analysis
Dry Bulk dominates with 38.1% due to sustained demand for raw materials and commodities transport.
In 2024, Dry Bulk held a dominant market position in the By Cargo Type segment, capturing 38.1% share. This segment transports essential commodities including coal, iron ore, grains, and industrial minerals globally. Consequently, manufacturing expansion and infrastructure development drive continuous demand for dry bulk shipping. Moreover, cost-effectiveness makes it the preferred mode for transporting large volumes across long distances.
Liquid Bulk represents a significant cargo category focused on petroleum products, chemicals, and liquefied gases. This segment benefits from sustained global energy consumption and chemical industry growth. Additionally, specialized tanker vessels ensure safe transport of hazardous and temperature-sensitive liquid materials. Furthermore, emerging economies drive increased demand for refined petroleum and industrial chemicals.
Containerized Goods segment experiences robust growth fueled by e-commerce expansion and consumer goods trade. Standardized container units enable efficient multimodal transport and streamlined port operations. Moreover, digitalization enhances cargo tracking and documentation processes throughout the supply chain. This segment adapts quickly to changing consumer demands and retail fulfillment requirements.
General Cargo includes non-containerized manufactured goods, machinery, and project equipment requiring specialized handling. This segment serves construction, heavy machinery, and oversized equipment transport needs. Additionally, breakbulk shipping provides flexibility for unique cargo dimensions and specialized loading requirements. Furthermore, project cargo logistics support infrastructure development in emerging markets.
Vessel Type Analysis
Container Ships dominate with 34.9% driven by containerized trade growth and supply chain integration.
In 2024, Container Ships held a dominant market position in the By Vessel Type segment, accounting for 34.9% share. These vessels transport standardized containers efficiently across major international trade routes. Consequently, economies of scale through larger vessel sizes reduce per-unit transportation costs significantly. Moreover, alliance formations optimize route networks and enhance schedule reliability for shippers.
Bulk Carriers serve the dry bulk cargo segment transporting commodities like grain, coal, and ore worldwide. These vessels feature specialized cargo holds designed for efficient loading and unloading operations. Additionally, varying sizes from Handysize to Capesize accommodate different port capabilities and cargo volumes. Furthermore, demand correlates directly with industrial production and construction activity levels.
Tankers transport liquid bulk cargo including crude oil, refined products, and chemicals across global markets. This vessel type employs specialized tank configurations ensuring safe carriage of hazardous materials. Moreover, double-hull designs enhance environmental protection against accidental spills. Additionally, product tankers serve regional distribution while crude carriers operate on long-haul routes.
Ro-Ro Vessels facilitate wheeled cargo transport including automobiles, trucks, and heavy machinery efficiently. This vessel type enables drive-on/drive-off operations reducing port dwell time significantly. Furthermore, automotive industry expansion drives sustained demand for specialized car carrier services. Additionally, these vessels support military logistics and construction equipment deployment.
LNG/LPG Carriers transport liquefied natural gas and petroleum gas using specialized cryogenic containment systems. Growing natural gas trade and energy transition initiatives drive this segment’s expansion. Moreover, these vessels require advanced technology for safe low-temperature cargo handling. Furthermore, new trade routes emerge as countries diversify energy supply sources.
Offshore Support Vessels serve oil and gas exploration, production, and renewable energy installation activities. These vessels provide essential logistics, maintenance, and emergency response capabilities. Additionally, offshore wind farm development creates new demand for specialized support services. Furthermore, vessel versatility enables adaptation to changing energy sector requirements.
Cruise Ships represent the passenger segment within maritime transport focused on leisure travel experiences. This category faces distinct operational challenges compared to cargo-focused vessel types. Moreover, environmental regulations drive adoption of cleaner propulsion systems and waste management technologies. Additionally, itinerary diversity and onboard amenities differentiate competitive offerings.
End-use Analysis
Manufacturing leads with 37.5% supported by global production networks and component trade flows.
In 2024, Manufacturing held a dominant market position in the By End-use segment, representing 37.5% share. This sector relies heavily on maritime freight for raw material imports and finished product exports. Consequently, globalized supply chains and offshore production facilities drive sustained shipping demand. Moreover, just-in-time manufacturing practices require reliable and frequent shipping services.
Food and Beverage segment depends on maritime transport for agricultural commodities, processed foods, and beverages distribution. Refrigerated container services enable perishable goods trade across continents efficiently. Additionally, growing middle-class populations in developing markets increase imported food product demand. Furthermore, specialty cargo handling ensures product quality throughout the transportation journey.
Oil and Ores category encompasses energy resources and mineral commodities essential for industrial production. This segment utilizes bulk carriers and tankers for large-volume, cost-effective transport solutions. Moreover, resource-rich regions export to manufacturing hubs creating consistent trade flows. Additionally, strategic stockpiling by importing nations supports steady demand patterns.
Electrical and Electronics industry requires maritime freight for components, finished products, and consumer devices globally. This segment values schedule reliability and cargo security for high-value shipments. Furthermore, rapid product innovation cycles demand flexible and responsive logistics solutions. Additionally, Asia-Pacific manufacturing dominance drives extensive intra-regional and export shipping volumes.
Others category includes diverse sectors such as automotive parts, pharmaceuticals, construction materials, and consumer goods. This segment demonstrates varied shipping requirements from specialized handling to temperature-controlled transport. Moreover, project cargo and oversized equipment necessitate customized maritime logistics solutions. Additionally, emerging industries create new shipping demand patterns continuously.
Key Market Segments
By Cargo Type
- Dry Bulk
- Liquid Bulk
- Containerized Goods
- General Cargo
By Vessel Type
- Container Ships
- Bulk Carriers
- Tankers
- Ro-Ro Vessels
- LNG/LPG Carriers
- Offshore Support Vessels
- Cruise Ships
By End-use
- Manufacturing
- Food and Beverage
- Oil and Ores
- Electrical and Electronics
- Others
Drivers
Rapid Expansion of Cross-Border Trade Drives Maritime Freight Growth
Globalized manufacturing networks fundamentally transform international trade patterns and shipping demand. Companies establish production facilities across multiple countries to optimize costs and market access. Consequently, intermediate goods movement between manufacturing sites generates substantial maritime freight volumes. Moreover, free trade agreements reduce barriers and encourage cross-border commerce expansion.
E-commerce growth dramatically increases containerized cargo volumes through retail fulfillment requirements worldwide. Online retailers depend on efficient maritime logistics to maintain competitive delivery timeframes. Additionally, cross-border e-commerce enables consumers to access products from international suppliers directly. Furthermore, this trend drives smaller shipment sizes and increased frequency of maritime services.
Cost-efficient bulk shipping remains essential for transporting energy resources and raw materials globally. Maritime transport offers unmatched economies of scale for commodities like coal, oil, and iron ore. Moreover, developing nations depend on imported energy and materials to support economic development. Additionally, established trade routes connect resource-rich regions with manufacturing hubs efficiently.
Restraints
Fuel Price Volatility Challenges Maritime Freight Cost Predictability
Marine fuel prices fluctuate significantly due to crude oil market dynamics and refining capacity variations. Shipping companies struggle to maintain stable rate structures when bunker costs change rapidly. Consequently, freight rate volatility affects shipper budgets and supply chain planning processes. Moreover, long-haul routes become particularly vulnerable to fuel price spikes impacting profitability.
Geopolitical tensions and canal congestion create capacity disruptions affecting global shipping networks critically. Conflicts in strategic maritime regions force route diversions increasing voyage times and costs. Additionally, canal closures or restrictions limit vessel transit options through key waterways. Furthermore, port congestion during peak periods delays cargo delivery and reduces supply chain efficiency.
Environmental regulations impose additional compliance costs through emission reduction requirements and monitoring systems. Shipping companies invest in cleaner fuels, scrubbers, or vessel modifications to meet standards. Moreover, regulatory complexity varies across jurisdictions creating compliance challenges for international operators. Additionally, carbon taxation proposals could further increase operational expenses industry-wide.
Growth Factors
Green Shipping Corridors Create New Opportunities for Sustainable Maritime Operations
Low-emission vessel development accelerates through alternative fuel adoption including LNG, methanol, and hydrogen. Shipping companies invest in green technologies to meet environmental targets and customer expectations. Consequently, green corridor initiatives connect major ports committed to zero-emission shipping support. Moreover, government incentives encourage fleet modernization and infrastructure development for cleaner fuels.
Short-sea shipping expansion reduces dependence on congested inland road and rail transportation networks. Coastal shipping routes offer environmentally friendly alternatives for regional cargo movement. Additionally, port infrastructure improvements enable efficient intermodal connections and faster cargo transfers. Furthermore, this approach alleviates highway congestion and reduces overall supply chain carbon footprints.
Refrigerated maritime transport grows rapidly supporting international trade in perishable foods and pharmaceutical products. Cold chain logistics ensures product quality throughout long-distance ocean voyages. Moreover, emerging market consumers demand diverse imported fresh and frozen food products. Additionally, pharmaceutical supply chains require temperature-controlled shipping for vaccines and biologics distribution.
Emerging Trends
LNG-Powered Vessels Lead Alternative Fuel Adoption in Maritime Industry
LNG and methanol-ready cargo vessels gain market share as shipping companies pursue emission reduction goals. These alternative fuels significantly lower sulfur oxide and particulate emissions compared to conventional marine fuel. Consequently, regulatory compliance becomes easier while demonstrating environmental leadership. Moreover, bunkering infrastructure expands at major ports supporting alternative fuel vessel operations.
AI-driven route optimization enhances operational efficiency through real-time weather analysis and fuel consumption modeling. Predictive maintenance technologies reduce unplanned downtime and extend vessel equipment lifespan. Additionally, digital platforms provide end-to-end cargo visibility improving supply chain coordination. Furthermore, automation in navigation and engine management optimizes vessel performance continuously.
Smart port operations integrate automated cranes, autonomous vehicles, and digital documentation systems comprehensively. These investments reduce cargo handling times and minimize human error in port operations. Moreover, blockchain technology enhances transparency and security in shipping documentation processes. Additionally, port authorities collaborate with shipping lines to implement interoperable digital standards.
Regional Analysis
Asia Pacific Dominates Maritime Freight Transport Market with 43.8% Share, Valued at USD 166.6 Billion
Asia Pacific leads the global maritime freight transport market, commanding 43.8% share valued at USD 166.6 Billion. This region hosts major manufacturing hubs and the world’s busiest container ports. Consequently, intra-regional trade and export shipping generate substantial maritime freight volumes. Moreover, China, Japan, South Korea, and Southeast Asian nations drive continuous shipping demand growth. Additionally, port infrastructure investments enhance cargo handling capacity across the region.
North America Maritime Freight Transport Market Trends
North America maintains significant maritime freight activity through Atlantic and Pacific coast ports. The region imports consumer goods, automotive products, and raw materials from global suppliers. Moreover, agricultural exports including grains and soybeans generate substantial bulk shipping volumes. Additionally, Panama Canal access facilitates efficient trade between East and West coasts. Furthermore, nearshoring trends increase maritime freight between North American countries.
Europe Maritime Freight Transport Market Trends
Europe demonstrates robust maritime freight activity through Mediterranean and North Sea port networks. The region balances intra-European short-sea shipping with intercontinental deep-sea routes. Moreover, environmental regulations drive adoption of cleaner vessel technologies ahead of global standards. Additionally, Brexit impacts trade patterns and customs procedures affecting shipping operations. Furthermore, port digitalization initiatives enhance operational efficiency across European facilities.
Middle East and Africa Maritime Freight Transport Market Trends
Middle East serves as a strategic transshipment hub connecting Asia, Europe, and Africa. The region exports petroleum products while importing manufactured goods and consumer products. Moreover, Suez Canal provides critical connectivity for vessels transiting between Mediterranean and Red Sea. Additionally, African ports undergo modernization to support growing intra-African trade initiatives. Furthermore, logistics free zones attract distribution operations serving regional markets.
Latin America Maritime Freight Transport Market Trends
Latin America relies on maritime freight for commodity exports including agricultural products and minerals. The region imports manufactured goods, machinery, and consumer products from global suppliers. Moreover, Pacific coast ports serve Asia trade while Atlantic facilities connect with North America and Europe. Additionally, Panama Canal expansion accommodates larger vessels improving regional connectivity. Furthermore, infrastructure investments address port capacity constraints in major economies.
Key Regions and Countries
North America
- US
- Canada
Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Maritime Freight Transport Company Insights
Mediterranean Shipping Company (MSC) operates as the world’s largest container shipping line by capacity. The company maintains an extensive global network serving major trade routes across six continents. Moreover, MSC continuously expands its fleet through newbuild orders and vessel acquisitions. Additionally, the company invests in terminal operations and logistics infrastructure to support integrated services.
A.P. Moller-Maersk stands as an integrated container logistics company offering end-to-end supply chain solutions. The company pioneered large container vessel deployment and alliance-based network operations. Furthermore, Maersk leads industry sustainability initiatives through alternative fuel adoption and emission reduction targets. Additionally, digital transformation remains a strategic priority enhancing customer experience and operational efficiency.
COSCO Shipping Lines represents China’s flagship container shipping operator with significant global market presence. The company benefits from strong domestic market position and government support for maritime industry development. Moreover, COSCO participates in strategic alliances optimizing route networks and vessel utilization. Additionally, the company expands terminal investments securing port capacity at key locations worldwide.
Hapag-Lloyd operates as a major German container shipping company serving global trade lanes comprehensively. The company maintains modern fleet composition with focus on fuel-efficient vessel technologies. Furthermore, strategic mergers and acquisitions strengthen market position and route coverage. Additionally, Hapag-Lloyd emphasizes quality service and schedule reliability differentiating its market offering.
Key Companies
- Mediterranean Shipping Company (MSC)
- A.P. Moller-Maersk
- COSCO Shipping Lines
- Hapag-Lloyd
- Ocean Network Express (ONE)
- Evergreen Marine Corp.
- HMM Co., Ltd.
- Yang Ming Marine Transport
- ZIM Integrated Shipping
- Pacific International Lines (PIL)
- SITC International
Recent Developments
- In September 2024, Maritime Transport was acquired by Swiss logistics giant MEDLOG, strengthening integrated supply chain capabilities. This strategic acquisition expands MEDLOG’s maritime freight portfolio and enhances service offerings. Moreover, the transaction reflects industry consolidation trends as companies pursue operational synergies. Additionally, combined operations enable improved customer service through integrated logistics solutions.
- In January 2025, Maersk Halifax was retrofitted to become the world’s first methanol dual-fuel conversion container ship. This pioneering project demonstrates technical feasibility of converting existing vessels to alternative fuels. Consequently, the industry gains confidence in fleet decarbonization pathways beyond newbuild programs. Moreover, the conversion reduces vessel emissions significantly while maintaining operational performance standards.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 380.5 Billion Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 613.9 Billion CAGR (2025-2034) 4.9% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Cargo Type (Dry Bulk, Liquid Bulk, Containerized Goods, General Cargo), By Vessel Type (Container Ships, Bulk Carriers, Tankers, Ro-Ro Vessels, LNG/LPG Carriers, Offshore Support Vessels, Cruise Ships), By End-use (Manufacturing, Food and Beverage, Oil and Ores, Electrical and Electronics, Others) Regional Analysis North America (US and Canada), Europe (Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, and Rest of Europe), Asia Pacific (China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, and Rest of APAC), Latin America (Brazil, Mexico, and Rest of Latin America), Middle East & Africa (GCC, South Africa, and Rest of MEA) Competitive Landscape Mediterranean Shipping Company (MSC), A.P. Moller-Maersk, COSCO Shipping Lines, Hapag-Lloyd, Ocean Network Express (ONE), Evergreen Marine Corp., HMM Co., Ltd., Yang Ming Marine Transport, ZIM Integrated Shipping, Pacific International Lines (PIL), SITC International Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Maritime Freight Transport MarketPublished date: Dec 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Maritime Freight Transport MarketPublished date: Dec 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Mediterranean Shipping Company (MSC)
- A.P. Moller-Maersk
- COSCO Shipping Lines
- Hapag-Lloyd
- Ocean Network Express (ONE)
- Evergreen Marine Corp.
- HMM Co., Ltd.
- Yang Ming Marine Transport
- ZIM Integrated Shipping
- Pacific International Lines (PIL)
- SITC International










