Global Kitchen Automation Systems Market Size, Share Report Analysis By Product Type (Automated Appliances & Cookers, Food Preparation Robots, Cooking Robots, Dishwashing & Cleaning Automation, Others), By Level of Automation (Semi-Automated, Fully Automated), By End-User (Residential, Commercial), By Distribution Channel (Online, Offline), By Regional Analysis, Global Trends and Opportunity, Future Outlook By 2025-2034
- Published date: Dec. 2025
- Report ID: 170360
- Number of Pages: 361
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
- Report Overview
- Key Takeaway
- Key Adoption and Impact Insights
- Role of Generative AI
- Investment and Business Benefits
- U.S. Market Size
- Product Type Analysis
- Level of Automation Analysis
- End-User Analysis
- Distribution Channel Analysis
- Emerging trends
- Growth Factors
- Key Market Segments
- Drivers
- Restraint
- Opportunities
- Challenges
- Key Players Analysis
- Recent Developments
- Report Scope
Report Overview
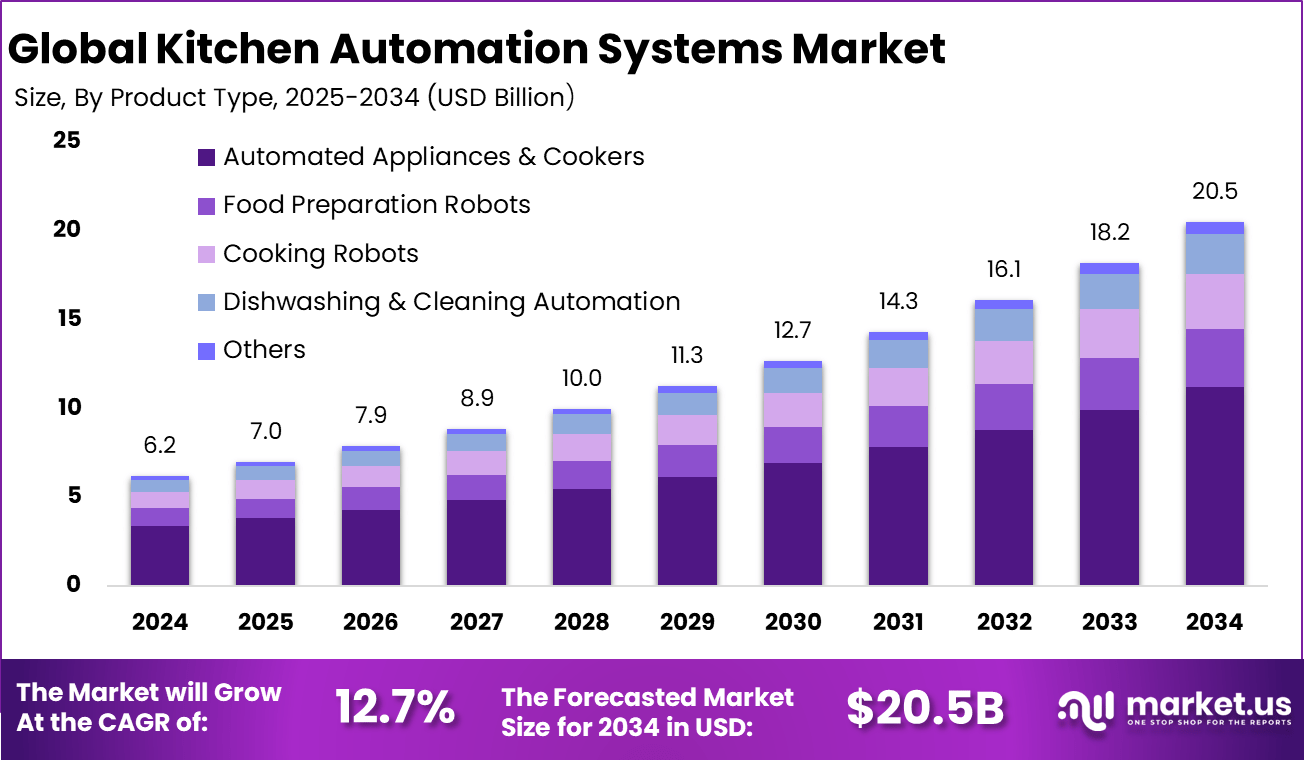
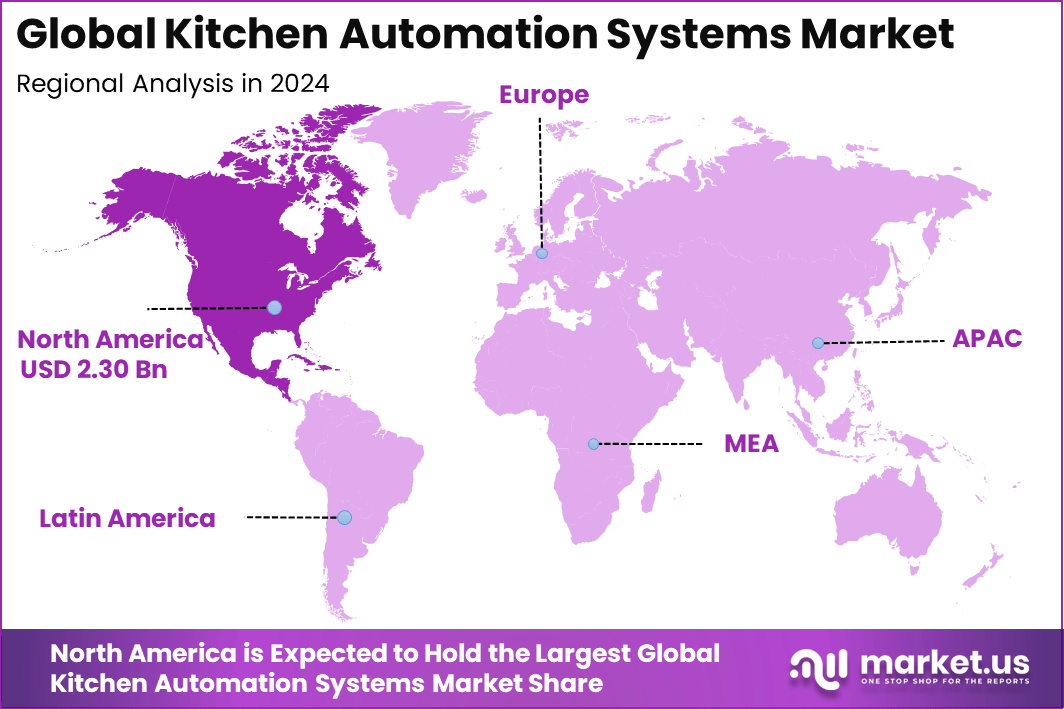
The Global Kitchen Automation Systems Market size is expected to be worth around USD 20.5 billion by 2034, from USD 6.2 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 12.7% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 37.2% share, holding USD 2.30 billion in revenue.
The kitchen automation systems market covers technologies that automate food preparation, cooking, storage, and cleaning processes in both commercial and residential kitchens. These systems include automated cooking equipment, robotic food handlers, smart appliances, and integrated kitchen management software. Adoption has been strongest in commercial kitchens such as quick service restaurants, cloud kitchens, and large institutional food service operations.
The market is driven by the need to improve consistency, hygiene, and operational efficiency while reducing dependence on manual labor. Growth of this market is supported by rising labor shortages and increasing wage pressure in the food service industry. Operators are investing in automation to maintain service levels and manage high order volumes with fewer staff. Demand for consistent food quality and improved food safety standards has also encouraged the use of automated systems.
The expansion of cloud kitchens and food delivery platforms has further strengthened adoption, as automation helps manage peak demand efficiently. Advances in robotics, sensors, and smart kitchen software have made these systems more reliable and easier to integrate into existing kitchen layouts. Demand for kitchen automation is expanding from high-income homes and flagship venues to mid-range households, chain outlets, and institutional kitchens that see clear savings in labour hours and utilities.
Smart appliances already form a visible share of global appliance sales and are among the more widely adopted smart home products, especially in urban regions with strong broadband access. In commercial spaces, interest is strongest where order volumes are high, menus are standardised and safety rules are strict, such as quick service locations, cloud kitchens, and large cafeterias.
For instance, in April 2025, Electrolux Professional promoted its SkyLine combi ovens and SkyDuo configuration as a smart‑kitchen backbone, where ovens and blast chillers communicate to automate cook‑chill sequences. With AI‑driven ARTE 2.0 control and eco‑cooking modes, customers report cutting energy costs by up to 20 and significantly reducing food weight loss in large‑scale kitchens.
Key Takeaway
- Automated appliances and cookers led the market with a 54.7% share, driven by demand for consistent cooking quality and reduced manual effort.
- Semi-automated systems dominated with 85.9%, as food service operators prefer gradual automation without fully replacing human control.
- Commercial kitchens accounted for 66.4%, reflecting strong adoption across restaurants, cloud kitchens, and large food service chains.
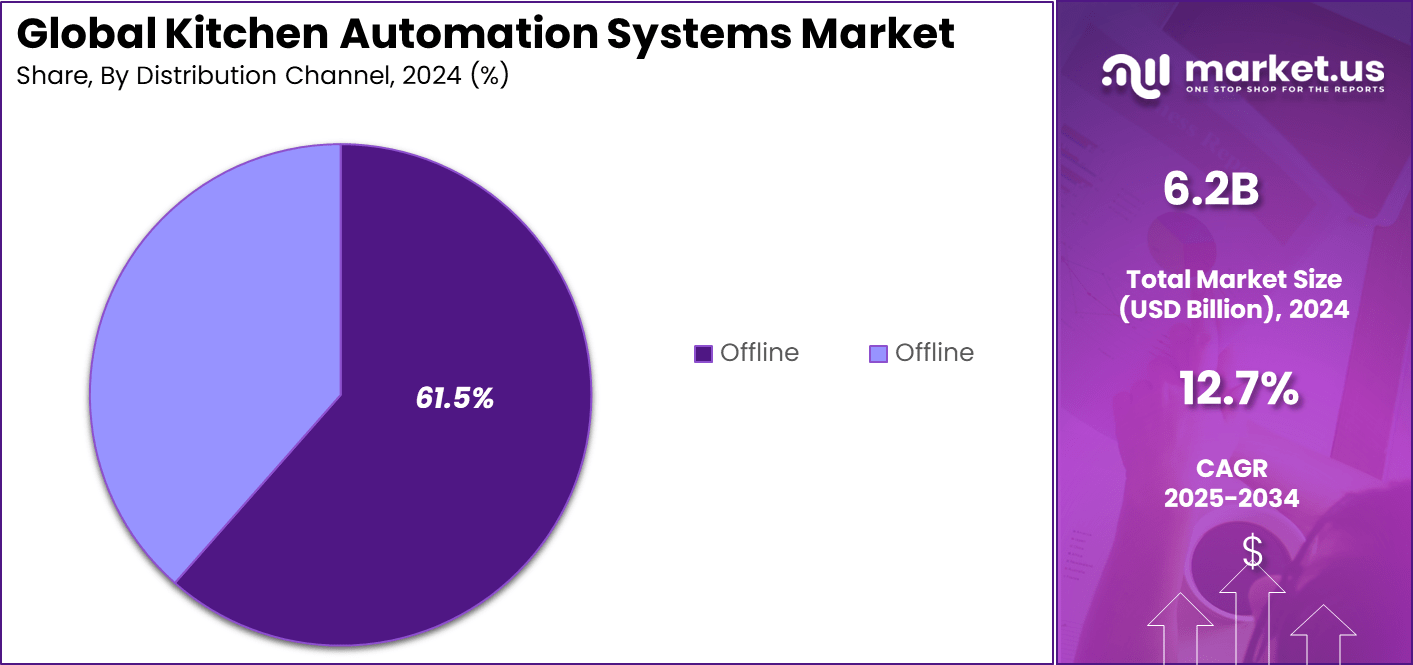
- Offline sales channels held 61.5%, supported by the need for on-site demos, installation support, and after-sales service.
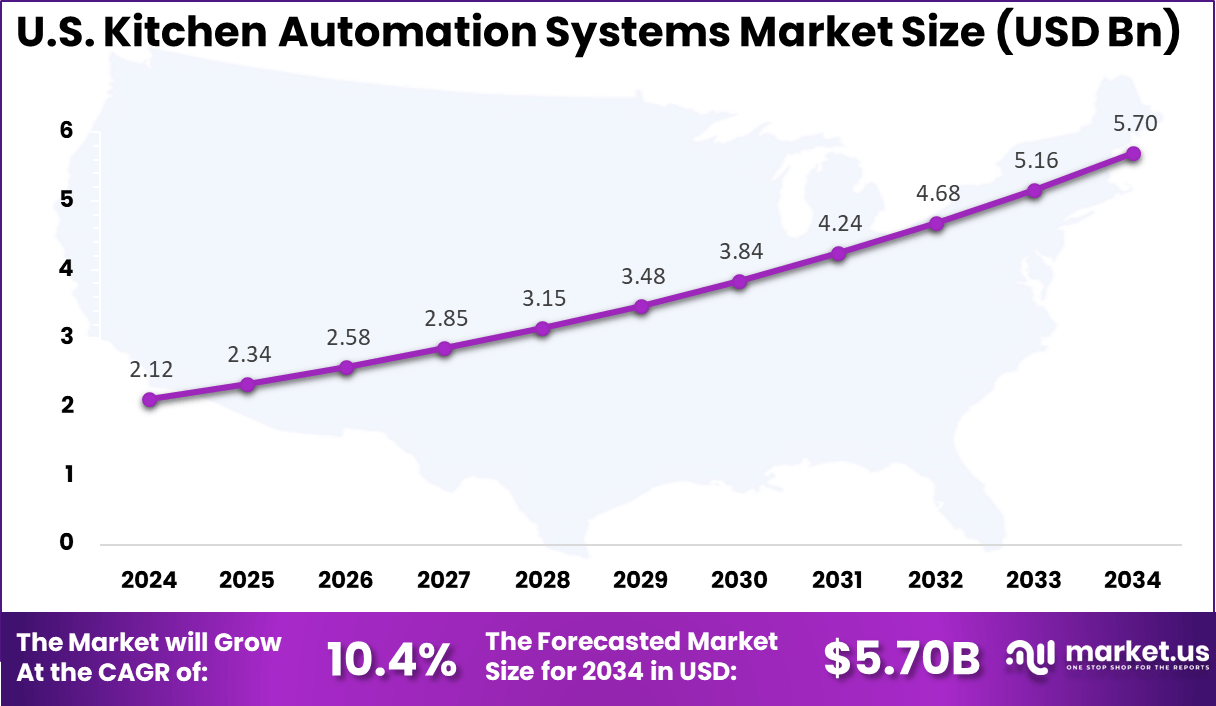
- The U.S. market reached USD 2.12 billion in 2024, expanding at a 10.4% CAGR due to rising labor costs and efficiency needs.
- North America led globally with over 37.2% share, supported by early adoption of smart kitchen technologies and a mature food service industry.
Key Adoption and Impact Insights
- 62% of quick-service restaurants are adopting robotic kitchen equipment to reduce dependence on manual labor.
- 60% of restaurant operators believe automation improves overall operational efficiency.
- 73% report higher productivity after investing in kitchen technology.
- Kitchen display systems reduce average ticket time by 69% and improve order accuracy by 83%.
- Self-ordering kiosks cut labor costs by 25% while increasing revenue by 20% through automated upselling.
- AI-driven kitchen systems lower food waste by 10-15%, supporting cost control and sustainability.
- Highly automated kitchens can reduce total operating costs by 25-35%.
- 60% of diners prefer ordering through mobile apps for convenience and speed.
- 71% of customers say self-service options deliver faster service than traditional ordering.
- Millennials and Gen Z show higher acceptance of AI-prepared food and robot-assisted delivery, supporting long-term adoption trends.
Role of Generative AI
Generative AI in kitchen automation is moving from trial to daily use in quick service chains and institutional kitchens, where managers track every minute and ingredient. It helps plan menus, forecast demand and generate simple instructions for staff, and roughly 65% of companies now report using some form of generative AI, while about 70% of business users rate its output as good quality.
This acceptance matters because staff are more likely to trust AI-generated prep lists, cleaning checklists and training scripts that fit real kitchen workflows. Generative AI is also layered on top of existing connected ovens, fryers, dishwashers and sensors, turning raw data into guidance that feels closer to human coaching.
More than 60% of early adopters apply generative AI to analyze operational data and suggest actions, such as adjusting oven cycles, scheduling maintenance, or flagging food safety risks before they become incidents. Instead of just raising an alarm, the system can propose a simple step-by-step plan that a busy line cook or facility manager can follow, which helps adoption during peak hours.
Investment and Business Benefits
Investment opportunities in kitchen automation span hardware, software, and services that link existing devices into integrated control platforms. There is growing interest in start ups and solutions focused on modular robotics, AI-driven kitchen planning and retrofit kits that add sensors and connectivity to traditional equipment rather than replacing entire lines.
Emerging markets with rising middle-income households and fast smart home adoption also offer room for new brands and service models around installation, maintenance and performance analytics. Business benefits from kitchen automation include higher productivity, lower waste, and better use of staff skills in both small and large operations.
When machines handle repetitive and physically heavy tasks such as lifting pans, cleaning, and constant monitoring, human workers can focus more on customer service, menu innovation and quality control. This shift often results in quicker order turnaround, improved accuracy, fewer workplace injuries and more predictable daily costs, which is vital in a sector that works with low margins.
U.S. Market Size
The market for Kitchen Automation Systems within the U.S. is growing tremendously and is currently valued at USD 2.12 billion, the market has a projected CAGR of 10.4%. The market is growing due to rising adoption of smart cooking appliances in both homes and commercial kitchens, as operators look for ways to manage labor shortages, reduce errors, and speed up food preparation.
Strong demand from quick-service restaurants and cloud kitchens is boosting investment in connected ovens, automated fryers, and semi-automated prep lines. Increasing focus on food safety, energy-efficient equipment, and consistent product quality is also encouraging upgrades. In addition, busy lifestyles and higher disposable incomes are pushing U.S. consumers toward convenient, tech-enabled kitchen solutions.
For instance, in January 2025, ITW Food Equipment Group, parent of Hobart, announced it will showcase advanced dishroom, cooking, and foodservice equipment at The NAFEM Show 2025 in Atlanta, emphasizing technologies that improve labor productivity, uptime, and sustainability, further cementing U.S. dominance in automated warewashing and integrated kitchen systems for institutional and commercial operators.
In 2024, North America held a dominant market position in the Global Kitchen Automation Systems Market, capturing more than a 37.2% share, holding USD 2.30 billion in revenue. This dominance is due to the strong presence of large foodservice chains, early adoption of connected cooking equipment, and a mature infrastructure that supports reliable IoT integration across commercial kitchens.
High labor costs are pushing restaurants and hotels to automate repetitive tasks, from cooking to dishwashing, to keep operations efficient. Consumers in the region are also quick to embrace smart kitchen appliances at home, encouraging manufacturers to launch advanced products here first. Favorable regulations around food safety and energy-efficient equipment further reinforce North America’s leadership.
For instance, in January 2025, Miso Robotics launched a new generation of its AI‑powered Flippy Fry Station, which is half the size, twice as fast, and significantly easier to install, with pilots at major U.S. quick‑service brands like White Castle and plans for broader roll‑outs, underscoring North America’s pioneering role in robotic kitchen automation for fry stations and repetitive back‑of‑house tasks.
Product Type Analysis
In 2024, The Automated Appliances & Cookers segment held a dominant market position, capturing a 54.7% share of the Global Kitchen Automation Systems Market. These devices take over key cooking steps such as exact temperature control and timed operations. They help busy home cooks and food service teams save hours each day.
Reliability stands out as users get even results every time without constant oversight. Most setups blend into existing kitchens easily, needing no major overhauls. Demand grows from folks wanting fresh meals fast amid packed schedules. This segment thrives because it tackles real pain points like uneven cooking in traditional methods.
Appliances now feature simple interfaces that anyone can learn quickly. In commercial spots, they boost output during peak times without extra staff. Home users value how these tools free up time for family moments. Energy savings add another draw as models run efficiently on less power. Overall, the balance of smart features and everyday fit drives this strong market hold.
For Instance, in September 2025, Welbilt showcased next-generation automated cooking solutions at HOST 2025 in Milan. The display featured AI-driven combi ovens and connected systems for precise cooking tasks. These appliances handle steaming, baking, and grilling with minimal input. Operators gain consistent results across busy shifts.
Level of Automation Analysis
In 2024, the Semi-Automated segment held a dominant market position, capturing an 85.9% share of the Global Kitchen Automation Systems Market. Users set recipes while devices handle repetitive tasks like mixing or portioning. This approach cuts mistakes in busy environments such as cafes or large households. Flexibility lets operators tweak on the fly for custom needs. Setup costs stay lower than full automation, making it accessible for small operations. Adoption surges as it builds confidence through familiar controls.
The appeal lies in its practical middle ground between manual work and total machine takeover. In restaurants, it speeds service without losing the chef’s creative edge. Home kitchens benefit from reduced fatigue on long cooking days. Maintenance proves straightforward, keeping downtime minimal. As tech improves, these systems learn user habits for even smoother runs. This mix of ease and control explains the dominant position in kitchen automation today.
For instance, in January 2025, Miso Robotics refined its Flippy Fry Station with AI vision from NVIDIA partners. The semi-automated arm fries foods like fries and rings at twice human speed. Users oversee output while it handles baskets nonstop. Quick installs fit existing counters overnight.
End-User Analysis
In 2024, The Commercial segment held a dominant market position, capturing a 66.4% share of the Global Kitchen Automation Systems Market. Restaurants, hotels, and catering firms rely on these to handle high volumes during rush hours. Consistency in food quality becomes key to customer loyalty in competitive spots. Labor shortages push operators toward tools that ease staff workloads.
Safety standards improve with less manual handling of hot items. Scalability matches growing order demands seen in fast-paced food chains. These users prioritize systems that deliver quick returns through faster prep times. In large kitchens, automation standardizes dishes across shifts for uniform taste. Energy-efficient designs lower ongoing costs in high-use settings. Training staff takes little time, fitting tight hiring cycles.
For Instance, in September 2025, Rational AG hit 100,000 networked cooking systems for commercial digital management. ConnectedCooking platform pushes updates and alerts to cut downtime. Caterers handle peak demands with remote oversight. Error fixes happen via linked service techs.
Distribution Channel Analysis
In 2024, The Offline segment held a dominant market position, capturing a 61.5% share of the Global Kitchen Automation Systems Market. Buyers prefer physical stores to inspect devices up close before committing. Major retailers and specialty shops offer live demos that build instant trust.
Staff advice helps match gear to specific kitchen layouts. For high-value items, touching and testing eases purchase decisions. Local availability speeds delivery and setup support. This hands-on path suits cautious shoppers in the market.
Traditional outlets excel at showcasing full system integrations rarely seen online. In-store events let users see real cooking demos in action. Return policies feel more secure when buying face-to-face. Rural areas gain easier access without shipping waits. Relationships with sales teams aid ongoing service needs. Offline strength comes from bridging the gap between tech specs and daily use realities.
For Instance, in March 2025, Middleby set up MIK showrooms for hands-on testing of kitchen gear. Customers try connected cooking appliances before buying. Live demos show automation in real workflows. Sales teams guide fits for specific layouts onsite.
Emerging trends
Emerging trends in kitchen automation show a clear shift toward deeper integration between robotics, smart appliances and cloud software, with the software layer capturing the largest share of value in many automation platforms. Smart kitchen appliances are expanding quickly in regions with strong smart home uptake, and this is changing how designers think about layouts, with more focus on connected ovens, hoods and refrigerators that share data and respond to remote updates.
Kitchens are becoming more like controlled production cells where data ties together prep, cooking and cleaning. Another strong trend is the rise of fully or semi-automated cooking and cleaning zones using robotic arms, automated fryers, and dishwashing lines that run with limited human supervision.
Studies highlight that cooking, baking and automated cleaning are among the fastest adopters of kitchen automation, supported by growth in dedicated “robot kitchen” solutions for repetitive frying, grilling, and salad preparation. This encourages operators to reconfigure space around conveyor systems, ingredient dispensers, and overhead cameras that feed real-time data into AI systems tracking quality, safety, and throughput.
Growth Factors
The first strong growth driver is the pressure on labor availability and cost in both restaurants and institutional kitchens. In many hospitality and foodservice surveys, operators report chronic staff shortages and rising wage bills, and AI-powered kitchen automation offers a way to keep output stable while reducing reliance on manual prep and cleaning tasks, which is especially important in markets where urbanization and eating out frequency are rising each year.
At the same time, automation helps standardize quality, which matters as brands expand across regions and seek consistent taste and safety across dozens or hundreds of outlets. The second major factor is the push for energy efficiency, food safety and waste reduction. Smart kitchen appliances and automated systems use connected sensors and AI to optimize oven cycles, refrigeration loads, and inventory rotation, and energy agencies link smart device adoption with national goals on lower electricity use in buildings, including foodservice.
Key Market Segments
By Product Type
- Automated Appliances & Cookers
- Food Preparation Robots
- Cooking Robots
- Dishwashing & Cleaning Automation
- Others
By Level of Automation
- Semi-Automated
- Fully Automated
By End-User
- Residential
- Commercial
- Full-Service Restaurants (FSR)
- Quick Service Restaurants (QSR) & Fast Casual
- Cloud/Kitchenless Kitchens & Dark Kitchens
- Hospitality
- Others
By Distribution Channel
- Online
- Offline
Regional Analysis and Coverage
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherlands
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of Latin America
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Drivers
Labor Shortages Push Adoption
Widespread staffing challenges across restaurants and commercial kitchens are accelerating automation adoption. Robots and smart kitchen systems now take over repetitive tasks such as chopping, grilling, and cleaning, helping businesses sustain output even with fewer workers. This shift ensures consistent service during high-demand hours and reduces reliance on seasonal or temporary hires.
Managers report smoother operations and quicker service during rush periods, improving both efficiency and customer satisfaction. The reliability of automated systems attracts growing investment, especially in regions facing chronic labor gaps. As more businesses witness the benefits, adoption spreads steadily across large chains and independent establishments alike.
For instance, in January 2025, Miso Robotics introduced a new generation of its Flippy Fry Station, powered by proprietary Kitchen AI to automate high-volume frying tasks in quick service restaurants. The system handles items like fries, chicken, and tacos with high precision and consistent quality while freeing staff from repetitive and hazardous work. Trials show strong uptime and reduced waste, helping operators offset ongoing labor gaps. These deployments act as practical proof of automation’s value in busy kitchens.
Restraint
High Upfront Costs Limit Reach
The steep initial cost of installing robotic systems and advanced kitchen software remains a major barrier. Many small and mid-sized restaurants hesitate to commit large sums to equipment, setup, and integration. Even though long-term labor savings are appealing, the heavy starting outlay makes full automation unrealistic for businesses with tight margins.
Maintenance and regular upgrades further add to expenses, forcing operators to weigh whether technology truly offsets labor costs. In developing regions, small-scale producers face additional hurdles like unclear pricing, limited supplier options, and trust issues with untested tech. These challenges slow broad adoption beyond well-funded enterprises.
For instance, in January 2024, Welbilt reportedly expanded an R&D hub in Asia to accelerate development of advanced, connected cooking systems that integrate automation for professional kitchens. The company targets high‑end chains first, as these buyers can justify the higher capital cost of smart combi ovens and connected fryers. Smaller independent operators still struggle with the price of such equipment and the added cost of installation and training.
Opportunities
Tech Advances Open Doors
Rapid progress in AI and IoT is transforming kitchen automation into user-friendly, adaptable systems. Smart devices can learn cooking routines, adjust recipes, and respond to voice commands, removing friction for users at both professional and household levels. Energy-efficient designs and connected features also attract sustainability-minded and tech-savvy consumers.
Collaborations between robotics firms and appliance brands are accelerating innovation and expanding product availability. Ghost kitchens and the delivery economy stand out as major beneficiaries, where scalable automation reduces waste and boosts output. As technology costs continue to fall, household kitchens increasingly embrace automation for everyday convenience.
For instance, in January 2024, Panasonic expanded its partnership with smart kitchen platform Fresco to bring an AI-based cooking assistant to its HomeCHEF multi-oven line. The integration allows users to adapt recipes, manage cooking modes, and personalize meals through a connected app experience.
Challenges
Maintenance Demands Expertise
Despite their benefits, automated kitchen systems require specialized maintenance to stay reliable. Breakdowns from hardware or software issues can disrupt workflows and service speed, particularly during peak times. Finding skilled technicians is difficult and often leads to extended downtimes, raising operational stress for restaurant owners.
Regular cleaning and calibration to meet food safety standards add to daily workloads. In regions lacking strong technical support networks, repairs and spare parts become significant obstacles. Manufacturers are responding with simplified designs and remote monitoring tools, but the need for technical know-how still limits smooth operations for many users.
For instance, in June 2025, Miso Robotics partnered with Roboworx, a specialist in robot field services, to deliver nationwide installation, preventive maintenance, and on-demand repairs for Flippy Fry Stations. Restaurants adopting these systems often lack in-house technical expertise, facing downtime risks during peak hours that disrupt operations. This collaboration boosts uptime through a dedicated network but underscores ongoing hurdles in maintenance, spare parts, and technician availability for kitchen automation.
Key Players Analysis
One of the leading players in June 2025, Miso Robotics signed a partnership with Roboworx to handle installation, maintenance, and ongoing support for its Flippy Fry Station restaurant automation systems across North America. Roboworx’s nationwide technician network is intended to keep uptime high and ensure “day one ROI” for operators, while also highlighting that reliable service, spare parts, and technical expertise remain critical operational considerations for automated kitchens.
Top Key Players in the Market
- Welbilt, Inc.
- Middleby Corporation
- Rational AG
- Miso Robotics
- Chowbotics (acquired by DoorDash)
- Hobart (ITW Food Equipment Group)
- Electrolux Professional
- Ali Group S.r.l.
- Hestan Commercial Corporation
- Fujitsu Limited
- Panasonic Corporation
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
- Haier Group Corporation
- Bosch (BSH Hausgeräte GmbH)
- Whirlpool Corporation
- Siemens AG
- Others
Recent Developments
- In January 2025, Miso Robotics launched its next‑generation Flippy fry‑station robot, a smaller unit that installs overnight into existing hoods and runs at roughly twice the throughput of the prior version. Developed with partners such as NVIDIA and Ecolab and piloted at White Castle, the new Flippy is aimed squarely at chains facing labor shortages but needing tightly automated, data‑rich fry operations.
- In February 2024, Hestan Commercial Corporation returned to KBIS, showcasing its Smart Gas Dual Fuel Range and connected oven technologies, which set and maintain exact burner temperatures automatically. Paired with the Campania Pizza Oven and PureVection controls, Hestan is pushing precision, sensor‑driven cooking from restaurants into premium residential and show kitchens.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 6.2 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 20.5 Bn CAGR(2025-2034) 12.7% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue forecast, AI impact on Market trends, Share Insights, Company ranking, competitive landscape, Recent Developments, Market Dynamics and Emerging Trends Segments Covered By Product Type (Automated Appliances & Cookers, Food Preparation Robots, Cooking Robots, Dishwashing & Cleaning Automation, Others), By Level of Automation (Semi-Automated, Fully Automated), By End-User (Residential, Commercial), By Distribution Channel (Online, Offline) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of Latin America; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Welbilt, Inc., Middleby Corporation, Rational AG, Miso Robotics, Chowbotics (acquired by DoorDash), Hobart (ITW Food Equipment Group), Electrolux Professional, Ali Group S.r.l., Hestan Commercial Corporation, Fujitsu Limited, Panasonic Corporation, Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., Haier Group Corporation, Bosch (BSH Hausgeräte GmbH), Whirlpool Corporation, Siemens AG, Others Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three license to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Kitchen Automation Systems MarketPublished date: Dec. 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Kitchen Automation Systems MarketPublished date: Dec. 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Welbilt, Inc.
- Middleby Corporation
- Rational AG
- Miso Robotics
- Chowbotics (acquired by DoorDash)
- Hobart (ITW Food Equipment Group)
- Electrolux Professional
- Ali Group S.r.l.
- Hestan Commercial Corporation
- Fujitsu Limited
- Panasonic Corporation
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
- Haier Group Corporation
- Bosch (BSH Hausgeräte GmbH)
- Whirlpool Corporation
- Siemens AG
- Others













