Global Insulin Market By Product Type (Rapid-acting, Long-acting, Intermediate-acting, Premixed, Regular/short-acting, Others), By Source (Human Insulin, Insulin Analog), By Diabetes Type (Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Gestational Diabetes), By Delivery Device (Insulin Pens, Jet Injection, Insulin Pumps, Pen Needles & Syringes, Others), By Distribution Channel (Hospital Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies, Online Pharmacies), Region and Companies – Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Aug 2025
- Report ID: 20942
- Number of Pages: 374
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
- Report Overview
- Key Takeaways
- Product Type Analysis
- Source Analysis
- Diabetes Type Analysis
- Delivery Device Analysis
- Distribution Channel Analysis
- Key Market Segments
- Drivers
- Restraints
- Opportunities
- Impact of Macroeconomic / Geopolitical Factors
- Latest Trends
- Regional Analysis
- Key Players Analysis
- Recent Developments
- Report Scope
Report Overview
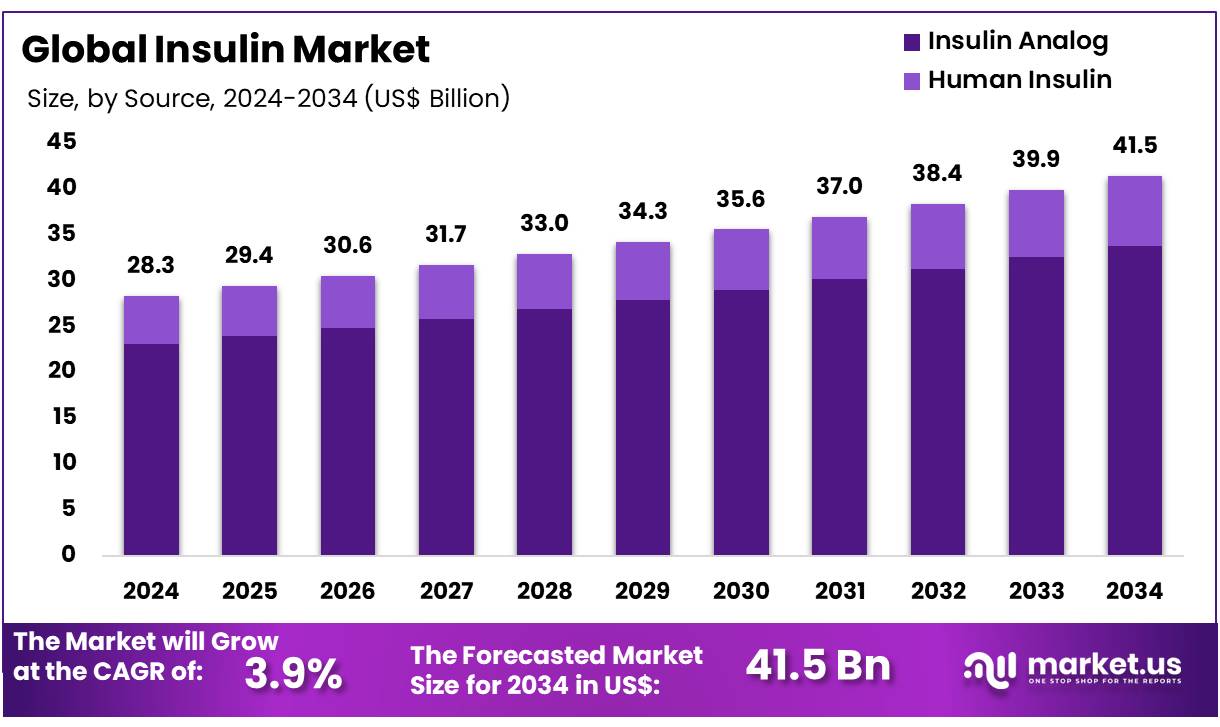
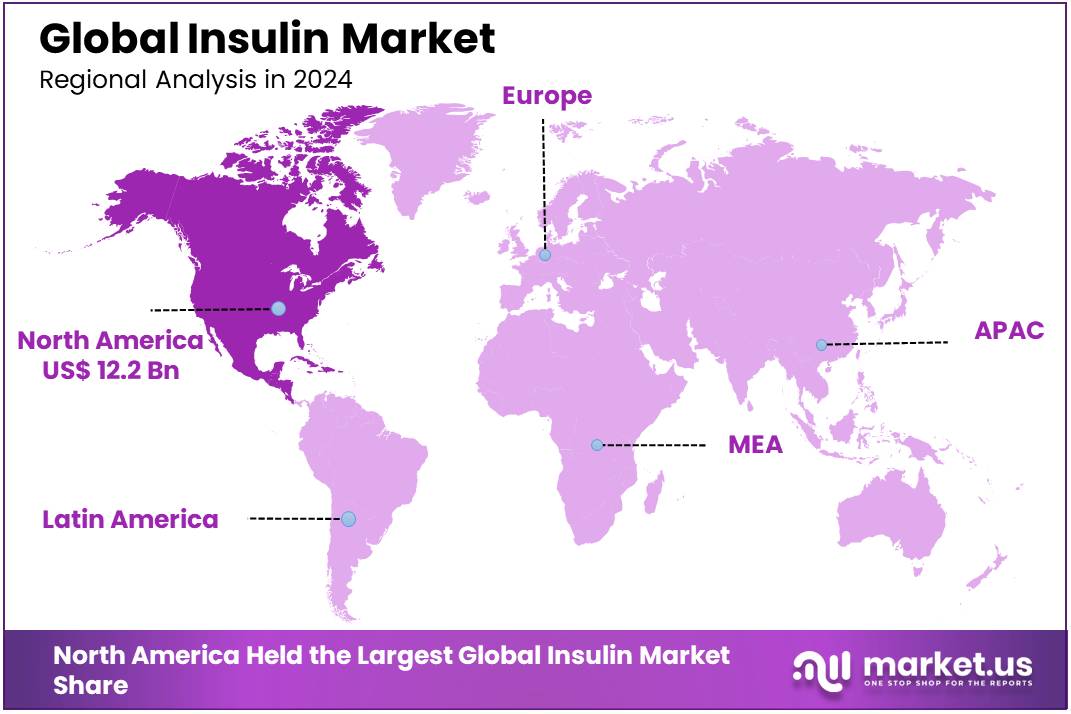
Global Insulin Market size is forecasted to be valued at US$ 41.5 Billion by 2034 from US$ 28.3 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 3.9% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North America led the market, achieving over 43.1% share with a revenue of US$ 12.2 Billion.
The market is growing steadily, primarily due to the increasing number of diabetes cases, advances in insulin formulations, and a greater demand for easier-to-use treatment options. Diabetes, especially type 2, is becoming more common worldwide, with millions of people now living with the condition. The World Health Organization (WHO) projects that by 2030, diabetes will be one of the leading causes of death, highlighting the urgent need for effective treatment options like insulin.
Over the years, insulin therapies have seen significant improvements. Long-acting insulins, such as insulin degludec, offer better control with fewer injections, making diabetes management easier for patients. On the other hand, rapid-acting insulins like insulin aspart are designed for quicker action, particularly useful for controlling blood sugar levels after meals. These advancements are making insulin more effective and convenient for patients, driving demand for better treatment options.
The introduction of biosimilar insulins has made insulin more affordable. These biosimilars are similar to existing insulin products but are priced lower, making them more accessible to people who might not have been able to afford the brand-name versions. Another change in the insulin market is the move toward non-injectable insulin.
Inhalable insulin products, like Afrezza, offer an alternative for patients who find injections uncomfortable. The demand for insulin is also increasing in developing regions such as Asia-Pacific and Africa, where rising urbanization and lifestyle changes are leading to more cases of diabetes. As these regions grow and improve healthcare access, the demand for insulin therapies is expected to rise even more.
Despite these positive developments, the insulin market still faces challenges. The cost of insulin remains high in many countries, and this can make it difficult for some patients to afford the medication they need. Even though biosimilars are helping to bring prices down, many people in low-income areas still struggle to get the treatment.
Lilly’s Efforts to Improve Insulin Access and Affordability:
Insulin Product New List Price Discount/Price Reduction Effective Date Additional Information Insulin Lispro Injection 100 units/mL (Non-branded) $25 per vial Lowest list-priced mealtime insulin, lower than Humalog® vial price in 1999 May 1, 2023 Non-branded insulin Humalog® (insulin lispro injection) 100 units/mL Reduced by 70% 70% price reduction Q4 2023 Lilly’s most commonly prescribed insulin Humulin® (insulin human) injection 100 units/mL Reduced by 70% 70% price reduction Q4 2023 Insulin for diabetes management Rezvoglar™ (insulin glargine-aglr) injection $92 per five pack of KwikPens® 78% discount to Lantus® April 1, 2023 Biosimilar to Lantus, interchangeable with Lantus Estimated Number of People using Insulin Globally
Year Est. Patient Population (Mn) 2023 125.1 2022 121.5 2021 119.6 2020 92.0 Key Takeaways
- In 2024, the market for fertility supplements generated a revenue of US$ 28.3 billion, with a CAGR of 3.9%, and is expected to reach US$ 41.5 billion by the year 2034.
- Among the product type segment, Long-acting insulin dominated the market with 47.3% share in 2024.
- By Source, Insulin Analog contributed to the largest revenue share of 81.5% in 2024.
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus held the largest shares of 58.2% in 2024.
- By Delivery Device, Insulin Pens captured the majority of the market share with 40.6% in 2024.
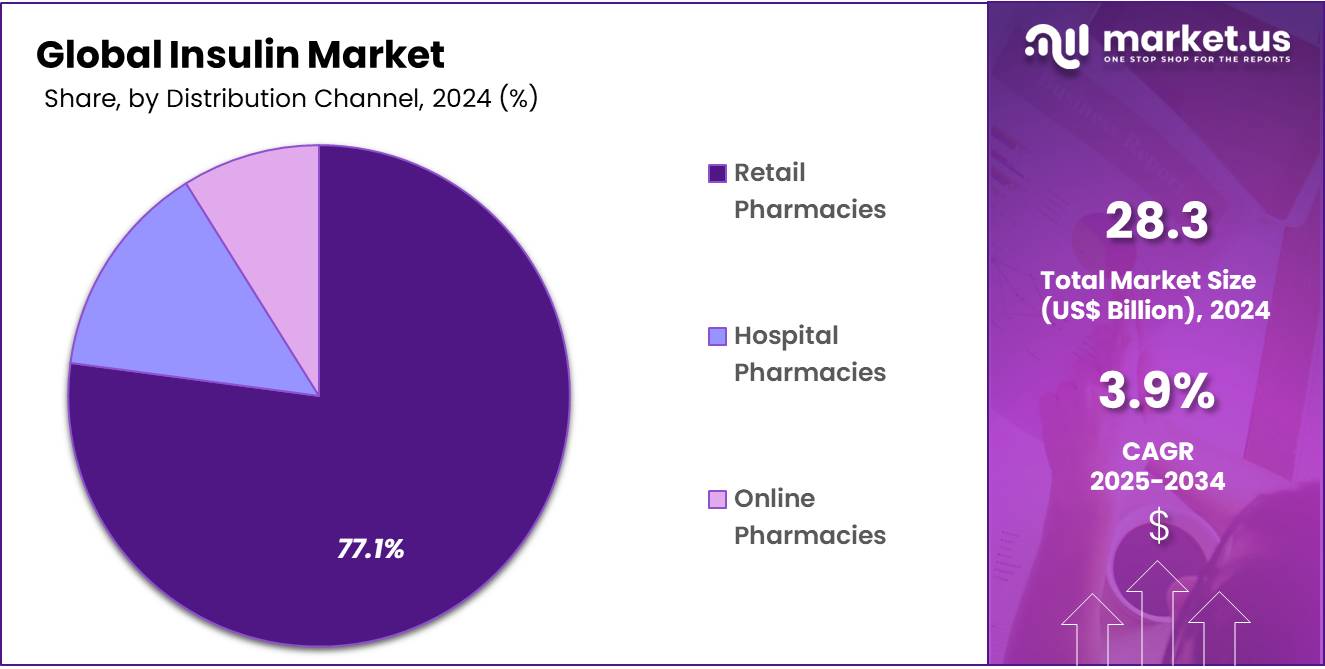
- Among the distribution channel segment, Retail Pharmacies held the largest segment accounting for 77.1% in 2024.
- North America held the maximum share of 43.1% in 2024 in the global market.
Product Type Analysis
Long-acting insulin, with 47.3% share has become the largest segment in the global insulin market in 2024, largely due to its effectiveness in managing diabetes. These insulins, designed to release insulin slowly over an extended period, typically for up to 24 hours or more, help maintain steady blood glucose levels throughout the day and night. The steady release eliminates the need for multiple daily injections, which increases convenience for patients and improves adherence to treatment. This ability to deliver consistent blood sugar control has made long-acting insulins the preferred choice for many diabetes patients.
An important example of long-acting insulin is insulin glargine, a product that has been a cornerstone in the treatment of diabetes. Insulin glargine is available under several brand names, including Lantus and Basaglar, and is used primarily to manage type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Insulin degludec, marketed as Tresiba, is another long-acting insulin that has gained popularity due to its extended duration of action, offering patients the flexibility to administer their doses at different times without compromising efficacy. These long-acting insulins have transformed the way diabetes is managed by providing greater flexibility and improved control for patients.
Source Analysis
Insulin analogs have become the leading segment holding 81.5% share in 2024 due to their enhanced ability to control blood sugar levels and improve patient outcomes. These insulins, including insulin lispro, insulin aspart, and insulin glargine, are designed to more closely mimic the body’s natural insulin response. Unlike traditional human insulin, which is a more straightforward formulation, insulin analogs offer greater precision in how they interact with the body, leading to more stable blood glucose levels and reduced instances of hypoglycemia.
These provide a steady release of insulin over a 24-hour period, eliminating the need for multiple injections each day. For patients, this means fewer injections and more consistent control of their blood sugar, which has made treatment easier and more effective. These benefits have made insulin analogs the preferred choice for many patients living with diabetes.
In recent years, the development of ultra-long-acting insulin analogs has further advanced diabetes care. Insulin degludec, for example, offers up to 42 hours of insulin action, which gives patients greater flexibility in their dosing schedules. This flexibility can be especially important for individuals with busy lifestyles or those who experience difficulty sticking to strict routines. Another breakthrough is insulin icodec, which has a half-life of more than eight days, allowing for a once-weekly injection. This convenience is a game-changer for many people who struggle with daily insulin injections, making it easier to stay on top of their treatment plans.
Despite the higher cost of insulin analogs compared to traditional human insulin, their benefits in terms of more stable blood sugar control and fewer side effects have led to widespread adoption, particularly in high-income countries.
Diabetes Type Analysis
In 2024, Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM) represented the largest segment of the global insulin market, accounting for 58.2% of the share, largely due to the crucial role insulin plays in managing the condition. T1DM is a chronic autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Consequently, individuals with T1DM cannot produce insulin naturally and rely on insulin therapy for survival.
According to ScienceDirect, approximately 9.50 million people were living with type 1 diabetes in 2025, with 1.85 million of them being under 20 years old. Around 30,000 children and youth may die undiagnosed at the clinical onset of T1D in 2025. The increasing trend in diagnoses, especially among younger populations, is noteworthy.
A study published in The Lancet revealed that the number of new T1D cases among youth rose by nearly 30% from 2020, highlighting the disease’s growing prevalence and the escalating demand for insulin. Additionally, the American Diabetes Association reports a significant rise in insulin pump use, with around 30% of people with T1DM in the U.S. now utilizing insulin pumps for disease management.
For people with type 1 diabetes, insulin is indispensable. Unlike those with type 2 diabetes, who may still produce some insulin, individuals with T1DM rely entirely on external insulin sources. The high demand for insulin is a direct result of the necessity for continuous insulin therapy. The development of insulin analogs, such as rapid-acting and long-acting formulations, has been instrumental in improving the management of T1DM, allowing for better control of blood glucose levels and greater flexibility in treatment.
Delivery Device Analysis
Insulin pens have emerged as the most widely used insulin delivery method, surpassing traditional syringes and vials in terms of both patient preference and market share. This segment held 40.6% share in 2024. This shift can be largely attributed to the increased convenience and ease of use that insulin pens offer.
Studies have consistently shown that a majority of patients with diabetes prefer insulin pens over syringes due to their user-friendly design, reduced injection pain, and the discretion they provide for administering insulin in public spaces. According to a survey by T1International, 82% of respondents favored insulin pens over traditional syringes, highlighting their advantages in terms of comfort and practicality.
Insulin pens are available in two main types: reusable and disposable. Reusable pens, which allow for the replacement of insulin cartridges, have become popular for their cost-effectiveness and environmental benefits. Dr. Vincent Simpson, a doctor and honorary researcher at the University of Exeter, is spearheading a campaign to establish reusable insulin pens as the standard for diabetes treatment. His goal is to reduce plastic waste and save the NHS money by promoting the switch from single-use pens to reusable alternatives.
Dr. Simpson highlighted that four million single-use insulin pens are prescribed annually, generating 79 tonnes of plastic waste and over 1,000 tonnes of carbon dioxide emissions. Disposable pens, on the other hand, come pre-filled with insulin and are particularly convenient for patients who want a hassle-free option without the need for refilling cartridges. These pens have made daily insulin delivery easier for many people with diabetes. The ease of use and convenience of disposable pens make them an attractive option for patients who prioritize simplicity in their treatment regimen
Distribution Channel Analysis
Retail pharmacies have become the dominant distribution channel for insulin, accounting for 77.1% share in 2024 of the insulin market. The widespread use of insulin in diabetes management has made retail pharmacies an essential source for obtaining insulin and related supplies. One of the main reasons for this is the convenience and accessibility these pharmacies provide.
With extended hours of operation and locations available in nearly every community, retail pharmacies make it easy for patients to access their insulin medications without the need for specialized appointments or hospital visits. This is especially valuable for individuals who need insulin frequently and want to avoid waiting for prescriptions or dealing with complex healthcare processes.
In countries like the US, major retail pharmacy chains such as CVS, Walgreens, and Rite Aid play a significant role in the distribution of insulin. CVS, with over 9,000 locations across the country, ensures that insulin is widely available, making it easy for patients to find a nearby pharmacy to pick up their insulin prescriptions. Similarly, Walgreens operates nearly 8,500 stores, providing convenient access to insulin and other diabetes-related products. These pharmacy chains have become trusted sources for individuals managing diabetes, contributing to their substantial share in the insulin distribution.
Key Market Segments
By Product Type
- Rapid-acting
- Long-acting
- Intermediate-acting
- Premixed
- Regular/short-acting
- Others
By Source
- Human Insulin
- Insulin Analog
By Diabetes Type
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Gestational Diabetes
By Delivery Device
- Insulin Pens
- Jet Injection
- Insulin Pumps
- Pen Needles & Syringes
- Others
By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies
Drivers
Rising Diabetes Prevalence
The global insulin market is experiencing significant growth, largely driven by the rising prevalence of diabetes worldwide. According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), approximately 589 million adults aged 20–79 were living with diabetes in 2024, and this number is projected to increase to 853 million by 2050 . This surge in diabetes cases is contributing to a higher demand for insulin and related therapies. The World Health Organization (WHO) reports that the number of people living with diabetes has risen from 200 million in 1990 to 830 million in 2022, with a global prevalence of 14% among adults aged 18 years and older.
The rising diabetes prevalence is influenced by several factors, including aging populations, urbanization, and lifestyle changes. Increased consumption of high-calorie diets, sedentary lifestyles, and higher obesity rates are contributing to the higher incidence of type 2 diabetes. Additionally, genetic predispositions and environmental factors play significant roles in the development of the disease.
As the number of individuals diagnosed with diabetes continues to grow, the demand for insulin and other diabetes management products is expected to rise correspondingly. This trend underscores the importance of addressing the underlying causes of diabetes through public health initiatives, promoting healthy lifestyles, and ensuring equitable access to medical care. By focusing on prevention and early intervention, it is possible to mitigate the impact of the diabetes epidemic and reduce the strain on healthcare systems globally.
Number of Adult Population (20–79 years) with Diabetes (Mn), by Region, 2024 & 2050:
Region 2024 2050 North America and Caribbean 56.2 68.1 South and Central America 35.4 51.5 Europe 65.6 72.4 South-East Asia 106.9 184.5 Western Pacific 215.4 253.8 Africa 24.6 59.5 Middle East and North Africa 84.7 162.6 Restraints
High insulin Cost
The rising cost of insulin has become a significant challenge for people with diabetes, especially in the US. The price of insulin has surged far beyond inflation, creating a financial burden for many individuals who depend on this life-saving medication. The sharp increase in cost is making it difficult for many people with diabetes to afford their medications, leading to dangerous practices such as rationing insulin or delaying doses, which can result in severe health consequences.
Cost of Insulin, by Top 10 Countries:
Country Insulin Cost Human Analog United States $98.70 $85.21 $99.94 Chile $21.48 $17.77 $21.99 Mexico $16.48 $9.45 $18.91 Japan $14.40 $14.30 $14.41 Switzerland $12.36 $6.86 $12.60 Canada $12.00 $7.11 $12.99 Germany $11.00 $7.13 $12.60 Luxembourg $10.15 $4.93 $10.40 Italy $10.03 $6.88 $10.07 Netherlands $9.98 $5.86 $10.24 One of the primary factors contributing to the high cost of insulin is the limited competition within the insulin market. The market is dominated by just a few manufacturers, which reduces the ability of the patients to shop around for lower prices. As a result, these companies can set prices that are not necessarily reflective of production costs. The financial strain caused by high insulin prices is not limited to people without health insurance.
Even those with insurance often find themselves facing significant out-of-pocket costs, particularly if their insurance plans have high deductibles or co-pays for insulin. This financial burden can lead to people skipping doses, adjusting their insulin intake, or even going without insulin entirely, all of which can result in dangerous health complications. Studies have shown that nearly one in four people with diabetes in the US have skipped or delayed insulin doses due to cost, a trend that has led to a range of serious medical issues, including diabetic ketoacidosis, which can be life-threatening if left untreated.
In response to the rising cost of insulin, some pharmaceutical companies have begun to make changes in an attempt to address the issue. For example, Eli Lilly, one of the major insulin producers, announced in 2024 that it would lower the list price of its insulin products in the US and cap out-of-pocket costs for patients at $35 per month. The price of insulin continues to be a critical issue, and there is a growing call for broader policy reforms to make insulin more affordable for everyone who needs it, regardless of their income or insurance status.
Opportunities
AI-Powered Insulin Dosing
Artificial intelligence (AI)-powered insulin dosing represents a transformative opportunity in diabetes management, offering the potential to enhance precision, reduce the burden of daily decision-making, and improve overall glycemic control. Traditional methods of insulin dosing often rely on manual calculations and estimations, which can lead to errors and inconsistent results. AI introduces a data-driven approach that can analyze vast amounts of information to provide personalized insulin recommendations.
For instance, the integration of AI with continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems and insulin pumps, creating automated insulin delivery systems. These systems use real-time glucose data to adjust insulin delivery automatically, mimicking the function of a healthy pancreas. For instance, the Tandem Diabetes Care’s Control-IQ technology, when combined with the Dexcom G6 CGM, predicts glucose levels and adjusts insulin delivery accordingly, aiming to keep blood glucose levels within a target range. Research has demonstrated the efficacy of AI in insulin dosing.
A study published in JAMA has shown that a real-time AI-based insulin clinical decision support system (iNCDSS) can safely and effectively guide insulin dosing, performing at a level comparable to senior physicians in managing patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) during hospitalization. The study involved 149 participants (mean age 64.2 years; 56.4% male). Patients managed with the AI tool spent an average of 76.4% (SD: 16.4%) of their time within the target glucose range, while the physician group spent 73.6% (SD: 16.8%) in the target range. The estimated treatment difference was 2.7% (95% CI: −2.7%–8.0%), demonstrating the AI system’s noninferiority.
Furthermore, AI’s role extends beyond automated systems. Applications like the Buzud app, developed in collaboration with Tan Tock Seng Hospital, utilize AI-driven image recognition to analyze meals and calculate the appropriate insulin dosage. Users take a photo of their meal, and the app, in conjunction with CGM data, determines the necessary insulin dose, reducing the guesswork involved in meal-time insulin administration.
The potential benefits of AI in insulin dosing are substantial. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, these systems can adapt to individual patient needs, learning from patterns in glucose levels, activity, and diet to optimize insulin delivery. This personalized approach can lead to more stable blood glucose levels, reduced risk of complications, and an improved quality of life for individuals with diabetes.
Impact of Macroeconomic / Geopolitical Factors
One of the major challenges is the rising cost of insulin, which has been a global concern. Over the years, insulin prices have increased far beyond inflation, creating financial strain for individuals who rely on it for managing diabetes. This high cost often results in patients rationing their insulin, which can lead to severe health complications.
Despite recent efforts such as the Inflation Reduction Act in the U.S., which aims to cap insulin costs for Medicare patients, those without insurance or with inadequate coverage still face high out-of-pocket costs. The total estimated cost of diagnosed diabetes in the U.S. for 2022 was $412.9 billion, comprising $306.6 billion in direct medical expenses and $106.3 billion in indirect costs related to the condition.
Trade policies, tariffs, and international relations can disrupt the supply chains for insulin and its raw materials, resulting in shortages and price increases. For example, in some developing countries, insulin may be difficult to obtain due to high import taxes or unstable political environments that disrupt the distribution of healthcare products. These issues are exacerbated in regions facing economic challenges, where the cost of insulin remains prohibitively high for many individuals.
Latest Trends
Shift towards Biosimilars
The shift towards biosimilar insulins is becoming a significant trend in the global insulin market, driven by the rising demand for more affordable diabetes treatment options. As the prevalence of diabetes continues to increase worldwide, the cost of insulin remains a major concern. Biosimilars, which are highly similar to branded insulins but offered at a lower cost, are emerging as an attractive alternative for patients and healthcare systems looking to reduce expenditures. The approval of biosimilar insulin products has opened the door to more competition in the market, providing opportunities for both patients and healthcare providers to manage treatment costs more effectively.
For instance, the growing adoption of biosimilar insulin glargine, which has been approved as a more affordable alternative to the original branded version. Semglee is a biosimilar version of insulin glargine that has been introduced to the market as a way to reduce the financial burden on patients.
In November 2021, Biocon and Viatris launched this product in the US as the first interchangeable biosimilar insulin, allowing pharmacists to dispense it in place of the reference product without the need for the prescribing physician’s approval. This interchangeability has significantly increased its accessibility, helping more patients gain access to affordable insulin. In addition, in February 2025, the US FDA also approved Merilog (insulin-aspart-szjj) as biosimilar to Novolog (insulin aspart) for the improvement of glycemic control in adults and pediatric patients with diabetes mellitus.
The uptake of biosimilars has varied by region, with countries in Europe leading the way in terms of biosimilar adoption. In Europe, biosimilars have become an integral part of diabetes care, helping to increase competition and lower prices. The availability of biosimilar insulin glargine has allowed European patients to access more affordable insulin, improving overall access to treatment. In these regions, the adoption of biosimilars has led to greater market efficiency, benefiting both healthcare providers and patients by offering lower-cost alternatives without sacrificing the quality or effectiveness of treatment.
Regional Analysis
North America is leading the Insulin Market
In the insulin market, North America dominated among the regions holding a significant share of 43.1% in 2024. North America, particularly the US, continues to lead the global insulin market due to a combination of high diabetes prevalence and well-established healthcare infrastructure. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), more than 38 million Americans have diabetes, and around 98 million have prediabetes.
The demand for insulin in the U.S. has grown steadily as a result, with diabetes being one of the most prevalent chronic diseases in the country. The high concentration of major insulin manufacturers, such as Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, and Sanofi, has contributed to meeting the growing demand for insulin and diabetes care products. The U.S. market’s size is further supported by the widespread adoption of advanced insulin delivery devices, including insulin pens, pumps, and CGM systems, which enhance blood glucose control.
The availability of these technologies has helped improve patient outcomes and contributed to better adherence to insulin therapies. For almost 50 years, the CDC’s Division of Diabetes Translation (DDT) has been leading efforts to combat diabetes. As part of its goal to reverse the epidemic, the CDC is targeting a 1% annual reduction in diabetes incidence by the end of 2030.
The CDC funds initiatives aimed at preventing or delaying type 2 diabetes in high-risk individuals, as well as broader population-based strategies to address social determinants of health. Additionally, the CDC monitors progress toward national objectives, such as those outlined in Healthy People 2030, and supports the development of policies and programs.
However, despite the advanced healthcare systems and insurance programs in place, the U.S. insulin market faces challenges due to the high cost of insulin. According to the American Diabetes Association, the price of insulin has increased dramatically over the last few decades, making it unaffordable for many patients. This has led to concerns over insulin accessibility, with some individuals resorting to rationing their insulin doses due to financial constraints.
The U.S. government has started addressing these issues, with new policies aimed at capping out-of-pocket insulin costs for patients on Medicare, but the challenge of affordability continues to impact the broader population. In December 2024, Novo Nordisk announced that it would cut the U.S. list prices of two insulin products by over 70%, starting in January 2026.
The Asia Pacific region is expected to experience the highest CAGR during the forecast period
Asia Pacific has become the fastest-growing region in the global insulin market, driven by the increasing prevalence of diabetes and rapid urbanization in countries like China, India, and Japan. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that around 110 million adults in China are living with diabetes, and this number is expected to rise significantly due to changing lifestyles, dietary habits, and an aging population. Similarly, India, which has one of the highest diabetes rates in the world, has seen its diabetic population surge, with IDF reporting that around 89.8 million people aged 20–79 years in India were living with diabetes in 2024. This sharp increase in cases has fueled the demand for insulin and diabetes-related treatments in the region.
Biosimilars are playing a key role in driving market growth in Asia Pacific. These cost-effective alternatives to traditional insulin products are particularly beneficial in countries with large diabetic populations but limited healthcare resources. The Indian market, for example, has embraced biosimilar insulins as an affordable option to address the growing diabetes burden. In January 2024, Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd. introduced a biosimilar of the widely used anti-diabetic drug Liraglutide in India.
The product, branded as Lirafit™, received approval from the Drug Controller General of India (DCGI). Priced at approximately INR 100 for a 1.2 mg daily dose, it will reduce therapy costs by around 70% and will be available exclusively through a prescription. According to the Indian Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, the introduction of biosimilar insulin has significantly expanded access to diabetes treatment, providing a more cost-effective solution for patients.
Key Regions and Countries
North America
- US
- Canada
Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherland
- Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
The global insulin market is dominated by major players like Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, and Eli Lilly, which hold a significant share due to their extensive product portfolios and innovations in insulin delivery methods. Novo Nordisk leads with products like insulin glargine (Lantus) and insulin degludec (Tresiba), while Sanofi is known for Lantus and expanding its biosimilars. Eli Lilly, with products like Humalog, has also focused on addressing insulin affordability.
The rise of biosimilars, such as Biocon’s Semglee, has introduced more affordable alternatives, especially in emerging markets, intensifying competition. Regional players like Gan & Lee and Tonghua Dongbao are gaining ground by offering cost-effective insulin options. As the demand for affordable insulin increases, these companies are adapting through price reductions, biosimilars, and digital health solutions to maintain their market positions.
Top Key Players
- Novo Nordisk A/S
- Sanofi
- Eli Lilly and Company
- Biocon Ltd
- Pfizer Inc.
- Wockhardt
- Julphar
- Sedico
- Insulet Corporation
- Tonghua Dongbao Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd.
- Adocia
- Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
- United Laboratories International
- Gan & Lee Pharmaceuticals
- MannKind Corporation
Recent Developments
- In June 2025, Indian pharmaceutical companies Biocon, Eris Lifesciences, and Wockhardt announced that they are increasing their insulin production to capitalize on the expanding global market, while industry leader Novo Nordisk is reducing its focus on human insulin to prioritize high-margin GLP-1 therapies and insulin analogues.
- In April 2025, it was stated by Novo Nordisk that its flagship insulin brand, Mixtard, will continue to be available in India in vial form, even as other delivery formats, such as Penfill cartridges, are being phased out. The announcement was made amid widespread concern over the discontinuation of some of the country’s most-used insulin products. In response to reports suggesting the withdrawal of Mixtard India’s top-selling insulin brand with annual sales of over Rs 800 crore a statement was issued by Novo Nordisk. The company explained that, to meet increasing patient demand and ensure a stable supply of its medicines, its insulin portfolio is being consolidated. This consolidation is expected to create the necessary space within the global manufacturing network. As part of this process, the Penfill delivery format is being phased out. While the company acknowledged that this shift will be disruptive for people with diabetes who rely on its treatments, it emphasized that this move would allow for the expansion of its insulin portfolio, ultimately reaching many millions of patients in the next decade.
- In March 2025, Eli Lilly, which recently introduced its blockbuster anti-obesity drug Mounjaro (tirzepatide) in India, revealed plans to increase insulin production, partner on therapies for non-communicable diseases, and advance biomanufacturing within the country.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) US$ 28.3 Billion Forecast Revenue (2034) US$ 41.5 Billion CAGR (2025-2034) 3.9% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, COVID-19 Impact, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Product Type (Rapid-acting, Long-acting, Intermediate-acting, Premixed, Regular/short-acting, Others), By Source (Human Insulin, Insulin Analog), By Diabetes Type (Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Gestational Diabetes), By Delivery Device (Insulin Pens, Jet Injection, Insulin Pumps, Pen Needles & Syringes, Others), By Distribution Channel (Hospital Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies, Online Pharmacies) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Novo Nordisk A/S, Sanofi, Eli Lilly and Company, Biocon Ltd, Pfizer Inc. Wockhardt, Julphar, Sedico, Insulet Corporation, Tonghua Dongbao Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Adocia, Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH, United Laboratories International, Gan & Lee Pharmaceuticals, MannKind Corporation Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Novo Nordisk A/S
- Sanofi
- Eli Lilly and Company
- Biocon Ltd
- Pfizer Inc.
- Wockhardt
- Julphar
- Sedico
- Insulet Corporation
- Tonghua Dongbao Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd.
- Adocia
- Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
- United Laboratories International
- Gan & Lee Pharmaceuticals
- MannKind Corporation










