Global Immunomodulators Market By Product (Immunosuppressants- Corticosteroids, Calcineurin Inhibitors, mTOR Inhibitors, Antimetabolites, Monoclonal Antibodies, Others, Immunostimulants- Cytokines & Interleukins, Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors, Vaccine Adjuvants, Others), By Route of Administration (Parenteral, Oral, Topical), By Application (Cancer, Autoimmune Disorders- Lupus, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Multiple Sclerosis, Psoriasis, Others, Respiratory Diseases, Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Others), By Distribution Channel (Hospital Pharmacy, Retail Pharmacy, Online Pharmacy), Region and Companies – Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: June 2025
- Report ID: 151285
- Number of Pages: 387
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
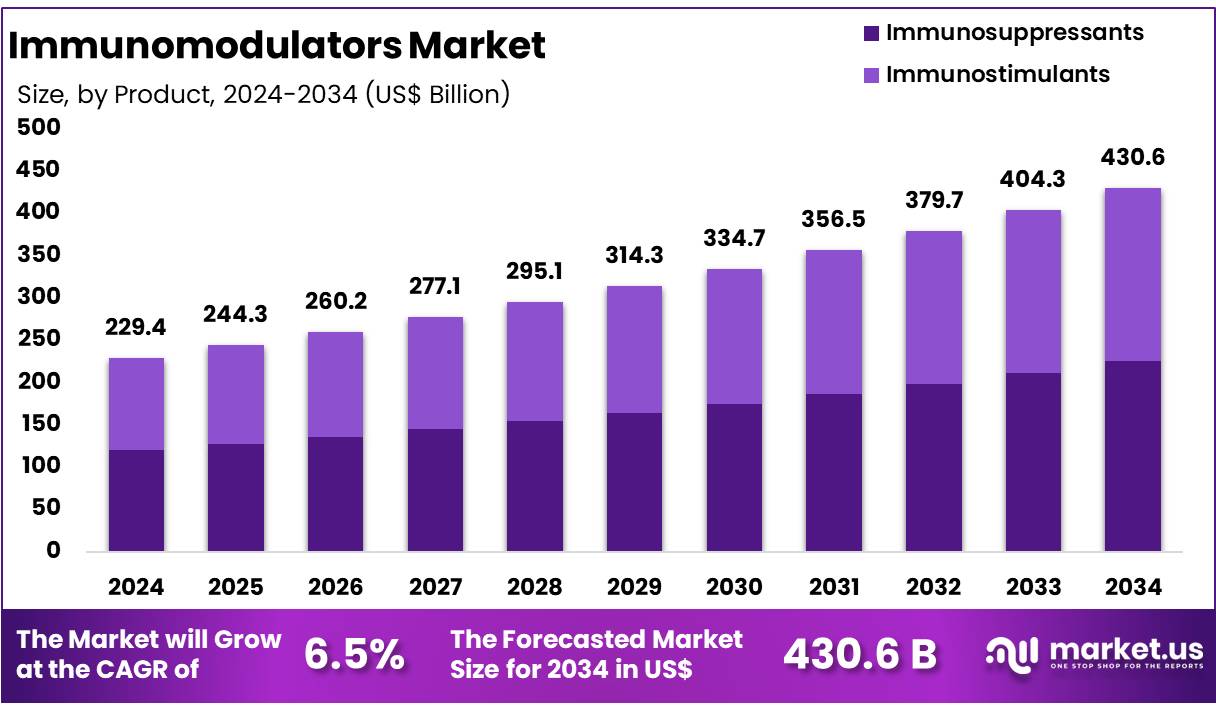
Global Immunomodulators Market size is forecasted to be valued at US$ 430.6 Billion by 2034 from US$ 229.4 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 6.5% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North America led the market, achieving over 39.0% share with a revenue of US$ 89.5 Billion.
The immunomodulators market is experiencing significant growth, driven by advancements in biotechnology, increasing prevalence of autoimmune diseases, and the rising demand for personalized medicine. Immunomodulators, which include both immunosuppressants and immunostimulants, play a crucial role in managing various conditions such as autoimmune disorders, cancers, and transplant rejection.
The immunosuppressant segment has been particularly dominant, accounting for a significant portion of the market share due to its widespread use in organ transplantation and autoimmune disease management. The market is also being driven by increasing prevalence rates of autoimmune diseases globally. Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and psoriasis are seeing a steady rise, particularly in aging populations across developed markets. This growing patient population, combined with an increasing focus on treating chronic conditions with long-term therapies, continues to fuel the demand for immunomodulatory drugs.
The market’s expansion is further supported by the increasing adoption of biologic therapies and the development of novel drug delivery systems. Biologics, such as monoclonal antibodies (mABs) and cytokines, have revolutionized the treatment landscape by offering targeted therapies with improved efficacy and reduced side effects. For example, in March 2025, INOVIO reported positive interim findings from a Phase 1 trial of DMAbs for COVID-19.
The results showed that all participants (24/24) who reached week 72 retained significant DMAb levels, demonstrating sustained in vivo antibody production. None developed anti-drug antibodies, which are often seen with other gene-based systems like adeno-associated virus vectors. Mild, temporary injection site reactions were the most common side effect.
This trial is being conducted in collaboration with The Wistar Institute, INOVIO, AstraZeneca, and the University of Pennsylvania’s Perelman School of Medicine. Additionally, advancements in drug delivery technologies, including subcutaneous and oral formulations, have enhanced patient compliance and accessibility to treatments.
Moreover, the shift towards personalized medicine is reshaping the immunomodulator landscape. Advances in genomic profiling and biomarkers are enabling healthcare providers to tailor treatments to individual patients, improving outcomes and reducing adverse effects. This trend has particularly been noticeable in oncology, where immunotherapies are now being used in combination with traditional treatments to enhance efficacy.
Key Takeaways
- In 2024, the market for Immunofluorescence assay generated a revenue of US$ 229.4 Billion, with a CAGR of 6.5%, and is expected to reach US$ 430.6 Billion by the year 2034.
- Among the product segment, immunosuppressants dominated the market with 52.3% share in 2024.
- Oral route of administration held 52.1% share in 2024 and captured the dominant position.
- Cancer segment is the maximum revenue generating application holding 44.7% share in 2024.
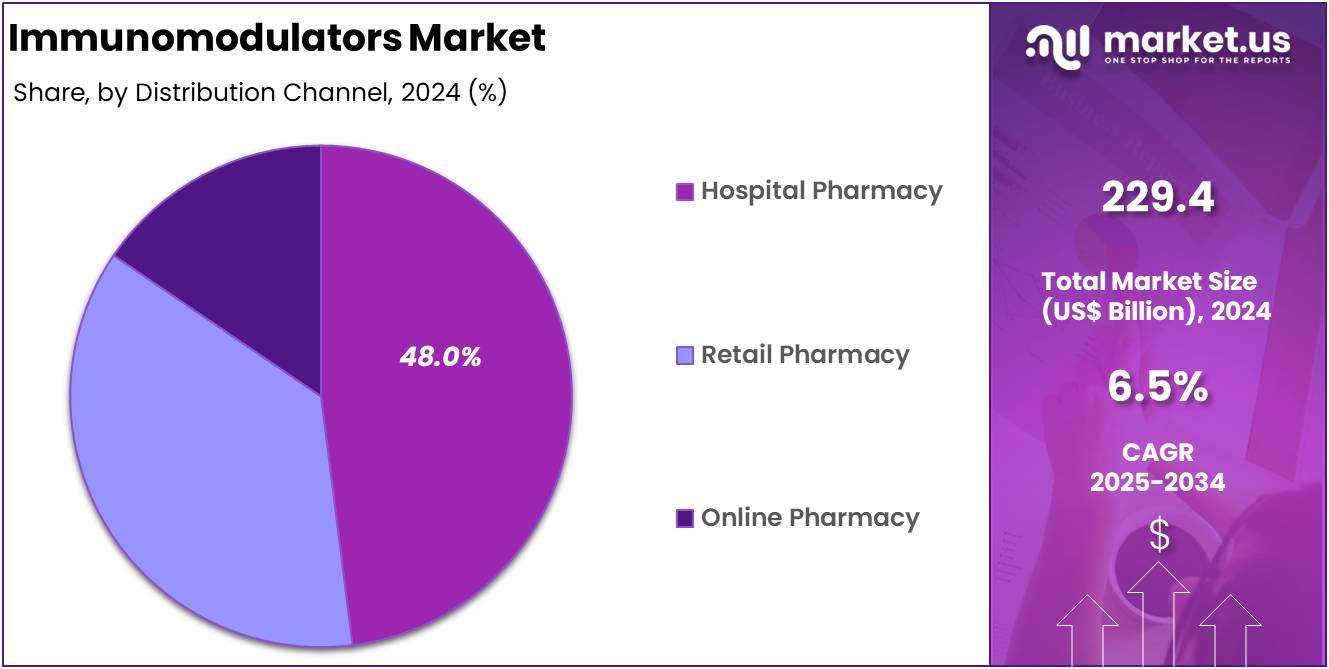
- Among the distribution channel segment, hospital pharmacy was the largest segment accounting for 48.0% in 2024.
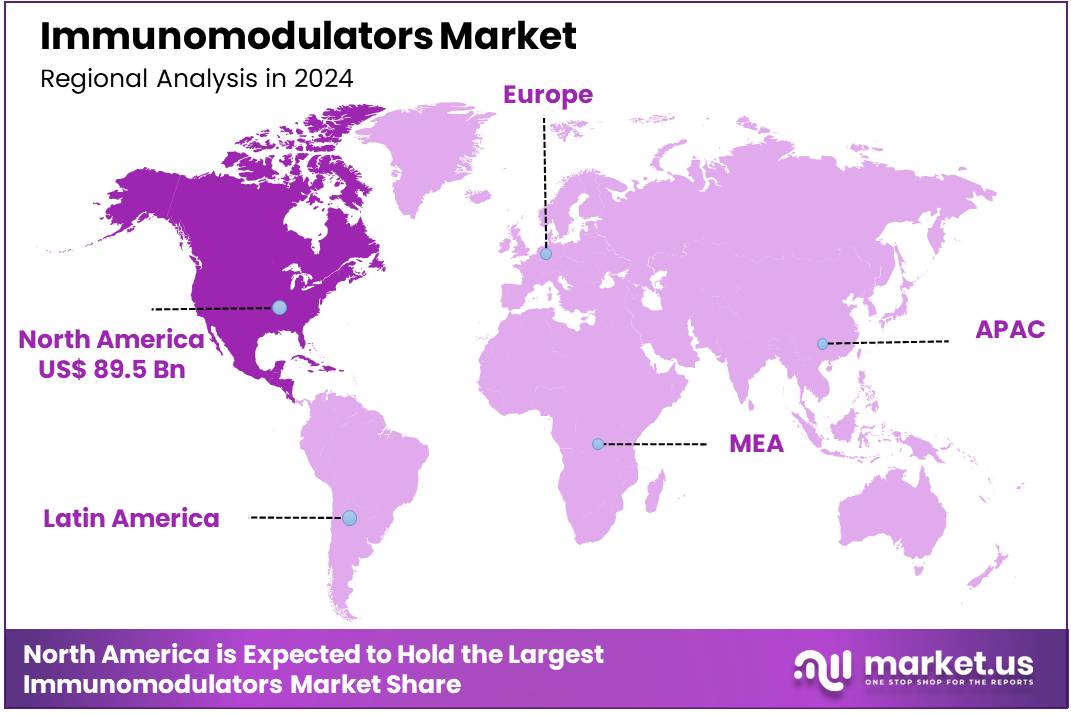
- North America held the largest share of 39.0% in 2024 in the global market.
Product Analysis
The immunosuppressants segment remains the dominant segment within the global immunomodulators market with 52.3% share in 2024, driven by their critical role in managing autoimmune diseases and preventing organ transplant rejection. Rejection occurs in 10 to 15 patients out of every 100 within the first year after a kidney transplant. Preliminary data from the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN) shows that more organ transplants were performed in the U.S. in 2024 than ever before, with 48,149 transplants, a 3.3% increase from 2023 and a 23.3% rise over the past five years.
Immunosuppressants encompass various drug classes, including corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors (e.g., cyclosporine and tacrolimus), monoclonal antibodies, mTOR inhibitors, and antiproliferative agents. These therapies are essential in treating conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis, and are pivotal in organ transplantation protocols.
For instance, calcineurin inhibitors like tacrolimus and cyclosporine are widely used to prevent acute transplant rejection and immediate graft loss. The increasing prevalence of autoimmune disorders and the rising number of organ transplantations globally are significant factors contributing to the sustained demand for immunosuppressive therapies. In 2024, 85 FDA-approved protein kinase antagonists target roughly two dozen enzymes, with four of these drugs being approved in 2024, and a fifth in 2025.
While immunostimulants are gaining traction, particularly in oncology and infectious disease treatments, immunosuppressants continue to lead the market due to their established efficacy and essential role in managing chronic immune-related conditions.
Route of Administration Analysis
In 2024, the oral route of administration was the dominant mode in the immunomodulators market holding 52.1% share, particularly for immunosuppressants, due to its convenience, patient compliance, and cost-effectiveness. Oral formulations are widely used in the management of autoimmune diseases and organ transplantations. For instance, drugs like methotrexate, azathioprine, and 6-mercaptopurine are commonly prescribed in oral forms to treat conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis.
These medications are effective in suppressing the immune system to prevent organ rejection and control inflammation in autoimmune disorders. The preference for oral administration is also evident in the treatment of multiple sclerosis. In a study by Novartis, Fingolimod (Gilenya), an oral sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulator, was shown to reduce relapse rates in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis by approximately 54% over two years. This oral medication offers a convenient alternative to injectable therapies, improving patient adherence to treatment regimens.
Application Analysis
In 2024, the cancer segment led the market with a share of 44.7%, highlighting the increasing reliance on immunomodulatory therapies in cancer care. These therapies, which include immune checkpoint inhibitors, monoclonal antibodies, and oncolytic viruses, work by enhancing the body’s immune response to target and eliminate cancer cells.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors, such as pembrolizumab (Keytruda) and nivolumab (Opdivo), have revolutionized the treatment of various cancers, including melanoma, non-small cell lung cancer, and colorectal cancer. These drugs function by blocking proteins like PD-1 and PD-L1, which tumors exploit to evade immune detection. Additionally, oncolytic viruses like talimogene laherparepvec (Imlygic) directly infect and destroy cancer cells while stimulating an immune response against the tumor.
The market’s expansion is further fueled by ongoing research and development, with companies exploring novel combinations and next-generation therapies to improve efficacy and reduce side effects. For instance, in May 2025, the FDA approved the combination of nivolumab (Opdivo) and ipilimumab (Yervoy) for the initial treatment of patients with advanced colorectal cancer whose tumors are classified as MSI-H or dMMR. These advancements underscore the pivotal role of immunomodulators in modern oncology, offering hope for more effective and personalized cancer treatments.
End-User Analysis
In 2024, hospital pharmacy segment accounted for 48.0% share of the market, driven by the necessity for professional administration and monitoring of immunomodulatory treatments. These therapies, including mABs and biologics, often require intravenous administration and close supervision due to potential adverse effects and the need for precise dosing. Hospital pharmacies are equipped with the infrastructure to manage these requirements, ensuring patient safety and optimal therapeutic outcomes.
Furthermore, hospital pharmacies benefit from established relationships with healthcare providers, facilitating coordinated care and streamlined access to medications. This integration enhances the efficiency of treatment regimens and supports the management of chronic conditions and complex diseases. As the demand for immunomodulatory therapies continues to rise, particularly in oncology and autoimmune disorders, the hospital pharmacy sector is poised to maintain its leading position in the distribution of these critical medications.
Key Market Segments
By Product
- Immunosuppressants
- Corticosteroids
- Calcineurin Inhibitors
- mTOR Inhibitors
- Antimetabolites
- Monoclonal Antibodies
- Others
- Immunostimulants
- Cytokines & Interleukins
- Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
- Vaccine Adjuvants
- Others
By Route of Administration
- Parenteral
- Oral
- Topical
By Application
- Cancer
- Autoimmune Disorders
- Lupus
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Psoriasis
- Others
- Respiratory Diseases
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Others
By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacy
- Retail Pharmacy
- Online Pharmacy
Drivers
Rising Prevalence of Target Diseases
The rising prevalence of target diseases, such as autoimmune disorders and cancer, is a major driver fueling the growth of the immunomodulators market. Autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis, have become increasingly prevalent globally. For example, the number of people diagnosed with autoimmune diseases continues to rise as diagnostic techniques improve and as the aging population grows.
According to 2024 data from the CDC, 1 in 5 adults in the U.S. has arthritis, and by 2040, it is projected that 78 million U.S. adults will be affected. Factors like genetics, environmental influences, and hormonal changes, particularly among women, have contributed to this surge. Additionally, autoimmune disorders often require long-term management, increasing the need for effective immunomodulatory treatments to control immune system activity and prevent organ damage.
Similarly, the incidence of cancer has been on the rise due to various factors such as aging populations, lifestyle choices, and improved early detection methods. In many regions, cancer cases are expected to increase significantly in the coming decades. For instance, in 2022, it was estimated that 20 million new cancer cases were diagnosed globally, with projections indicating a rise to 32.6 million by 2045.
As the number of cancer patients rises, the demand for therapies that can enhance immune responses against tumors is increasing. Immunomodulators, including immune checkpoint inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies, are now integral to cancer treatment, offering patients more targeted and effective options.
This growing patient population create a continuous need for novel and efficient immunomodulatory therapies. As the prevalence of these diseases continues to rise, the demand for immunomodulators is expected to expand, driving significant growth in the market. The increasing need for personalized and targeted treatments ensures that immunomodulators will remain a critical component in managing these challenging health conditions.
Restraints
High Cost of Therapy
The high cost of immunomodulatory therapies presents a significant restraint in their widespread adoption and accessibility. For example, the estimated lifetime cost per patient for PD1/PD-L1 inhibitors in advanced NSCLC ranges from US$37,600 to US$75,100. With fixed dosing, total costs could reach US$14,087 million, while weight-based dosing could result in costs of US$9,080 million.
In comparison, initial treatment with azathioprine had the lowest cost and utility, amounting to $35,337 and 0.63 QALYs, whereas combination therapy, although the most expensive at $57,638, offered the greatest health benefits with 0.67 QALYs. These escalating costs place a considerable financial burden on patients, even those with insurance coverage, leading to concerns about affordability and access to necessary treatments.
Cancer immunotherapies, particularly immune checkpoint inhibitors and CAR T-cell therapies, are among the most expensive treatments. For instance, the cost of CAR T-cell therapies can exceed $1 million per patient, encompassing expenses for cell extraction, genetic modification, and administration. These high costs are primarily attributed to the complex manufacturing processes and the need for specialized medical facilities and personnel. Such expenses often result in limited access to these therapies, especially in low- and middle-income countries, where healthcare budgets are constrained.
Opportunities
Expansion of Immunomodulatory Therapies for Rare Diseases
The expansion of immunomodulatory therapies for rare diseases presents a significant opportunity in the medical field, addressing unmet needs for conditions affecting small patient populations. Despite the challenges posed by the rarity of these diseases, advancements in immunotherapy are offering new hope.
For instance, the development of gene therapies for rare genetic disorders. For instance, elivaldogene autotemcel (Skysona) is an autologous gene therapy approved for treating cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy (CALD), a rare neurodegenerative disease. This therapy involves modifying a patient’s own hematopoietic stem cells to express a functional copy of the ABCD1 gene, aiming to halt or reverse disease progression. Similarly, Strimvelis, another gene therapy, treats severe combined immunodeficiency due to adenosine deaminase deficiency (ADA-SCID) by introducing a functional ADA gene into the patient’s stem cells.
In addition to gene therapies, immunomodulatory approaches are being explored for autoimmune diseases. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy, primarily used in oncology, has shown potential in treating autoimmune conditions such as lupus, scleroderma, and idiopathic inflammatory myositis. A study published in the New England Journal of Medicine demonstrated that CAR-T therapy led to disease improvement in all patients with these autoimmune diseases, with lupus patients experiencing no relapses during a two-year follow-up period. This suggests that CAR-T therapy could serve as a promising treatment option for certain autoimmune diseases.
Furthermore, advancements in antibody therapies are providing targeted treatments for rare diseases. For example, canakinumab is an interleukin-1β inhibitor approved for treating various rare autoinflammatory diseases, including cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes and familial Mediterranean fever. By targeting specific components of the immune system, canakinumab helps reduce inflammation and manage symptoms in affected individuals.
These developments underscore the growing potential of immunomodulatory therapies in treating rare diseases. While challenges such as high treatment costs and limited patient populations remain, ongoing research and clinical trials are paving the way for more accessible and effective therapies. As the understanding of these diseases deepens and treatment options expand, patients with rare conditions are experiencing improved outcomes and quality of life.
Impact of Macroeconomic / Geopolitical Factors
Macroeconomic and geopolitical factors significantly influence the immunomodulators market, affecting both supply chains and demand dynamics. Economic downturns can lead to reduced healthcare budgets, impacting the affordability and accessibility of immunomodulatory treatments. For instance, during periods of inflation, pharmaceutical companies may face increased production costs, which can be passed on to consumers, making treatments less accessible. Additionally, economic uncertainty can lead to delays in research and development investments, slowing the introduction of new therapies.
Geopolitical tensions and trade policies also play a crucial role in shaping the immunomodulators market. Export restrictions and sanctions can disrupt the global supply chain, leading to shortages of essential raw materials and finished products. Such disruptions can delay the availability of treatments in certain regions, affecting patient care. Moreover, political instability in key manufacturing countries can lead to uncertainties in production and distribution, further impacting the market.
The limited access to mAbs in Africa is significantly influenced by macroeconomic and geopolitical factors, despite the continent’s substantial disease burden. Africa accounts for approximately 20% of the global population but represents only about 1% of global mAb sales. This disparity is largely due to high production costs, inadequate infrastructure, and limited local manufacturing capabilities, which hinder the affordability and availability of mAb-based therapies.
Additionally, geopolitical factors such as trade restrictions and intellectual property barriers further complicate access. For instance, the high cost of mAb development and production, coupled with limited local manufacturing capacity, makes these therapies unaffordable for many African countries.
Latest Trends
Rise of Biologic Immunomodulators
The rise of biologic immunomodulators marks a transformative shift in the treatment of various diseases, particularly autoimmune disorders and cancers. Unlike traditional small-molecule drugs, biologics are derived from living organisms and include monoclonal antibodies, recombinant proteins, and gene therapies. These therapies offer targeted mechanisms of action, enhancing their efficacy and safety profiles.
In oncology, biologics have revolutionized treatment paradigms. Monoclonal antibodies such as trastuzumab (Herceptin) and rituximab (Rituxan) have significantly improved outcomes for breast cancer and lymphoma patients, respectively. Additionally, immune checkpoint inhibitors like pembrolizumab (Keytruda) have shown promise in treating various cancers by enhancing the body’s immune response against tumor cells. In autoimmune diseases, biologics have provided new avenues for treatment.
For instance, adalimumab (Humira) and etanercept (Enbrel) are widely used to manage rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory conditions, offering patients relief from chronic symptoms and improved quality of life. These therapies work by targeting specific components of the immune system involved in the inflammatory process. For instance, in February 2024, AbbVie Inc. and OSE Immunotherapeutics SA formed a strategic partnership to develop OSE-230, a monoclonal antibody targeting chronic and severe inflammation, which is currently in pre-clinical development.
The development of biologics has been propelled by advancements in biotechnology and a deeper understanding of immunology. As research continues, the pipeline for new biologic therapies remains robust, with numerous candidates undergoing clinical trials. This ongoing innovation promises to expand treatment options and improve outcomes for patients worldwide.
Regional Analysis
North America is leading the Immunomodulators Market
North America held a dominant position in the global immunomodulators market, accounting for 39.0% market share in 2024. This leadership is primarily attributed to the high prevalence of autoimmune diseases and cancers, which drive the demand for immunomodulatory therapies. According to the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), about 8% of the U.S. population has an autoimmune disease.
The American Cancer Society projects over 2 million new cancer cases in the U.S. in 2025, with more than 618,000 deaths from the disease. The region’s robust healthcare infrastructure, substantial healthcare expenditure, and advanced research and development initiatives further bolster its market position. However, the high cost of immunomodulatory therapies remains a significant barrier, potentially limiting access for certain patient populations.
The Asia Pacific region is expected to experience the highest CAGR during the forecast period
Asia Pacific is experiencing the fastest growth in the immunomodulators market from 2025 to 2034. This rapid expansion is driven by factors such as the increasing incidence of autoimmune diseases and cancers, rising healthcare awareness, and government initiatives to improve healthcare access. For example, GLOBOCAN predicts that cancer cases in India will rise to 2.08 million by 2040, representing a 57.5% increase compared to 2020.
Countries like India and China are investing heavily in biotechnology and pharmaceutical research, aiming to enhance local production capabilities and reduce dependency on imports. For instance, in January 2025, China’s National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) approved Sarclisa, an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody, in combination with pomalidomide and dexamethasone for treating multiple myeloma in patients who have received at least one prior therapy, including lenalidomide and a proteasome inhibitor.
Despite these advancements, challenges such as regulatory hurdles, affordability, and infrastructure limitations persist, potentially impacting the equitable distribution of immunomodulatory treatments across the region.
Key Regions and Countries
North America
- US
- Canada
Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherland
- Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
The global immunomodulators market is highly competitive, with several major players shaping its landscape through continuous innovation and strategic expansions. F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. leads with a robust portfolio of monoclonal antibodies and biologic therapies, particularly in oncology and autoimmune disorders. Amgen Inc. is another key player, known for its contributions to immunology, particularly in oncology and autoimmune diseases, through groundbreaking treatments.
AbbVie Inc. has made a significant impact with its immunology drugs like Skyrizi and Rinvoq, both of which have shown impressive sales growth. Novartis AG continues to strengthen its position by focusing on innovative therapies and biosimilars.
Bristol-Myers Squibb Company stands out in the immuno-oncology sector, driven by its advancements in immune checkpoint inhibitors. Merck & Co., Inc. maintains a strong presence in the immuno-oncology space with its therapies. Additionally, companies such as Biogen Inc., Pfizer Inc., and Johnson & Johnson contribute to the diverse range of immunomodulatory therapies, fueling the market’s growth and competition.
Top Key Players
- Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd
- Amgen Inc.
- Novartis AG
- Abbott
- Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.
- Eli Lilly and Company
- Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- Biogen
- Pfizer Inc.
- Biogen Inc.
- AstraZeneca plc
- Gilead Sciences Inc.
- AbbVie Inc.
- Astellas Pharma Inc.
- Horizon Therapeutics
Recent Developments
- In May 2025, the Subject Expert Committee (SEC) under the CDSCO approved a protocol amendment for the Iptacopan (LNP023) study by Novartis Healthcare, aimed at evaluating long-term efficacy and safety in patients with C3 glomerulopathy or idiopathic immune-complex-membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis.
- In April 2025, Repertoire Immune Medicines announced a partnership with Roche’s Genentech division to develop treatments for an unspecified autoimmune disease, with Genentech providing $35 million upfront.
- In September 2024, Eli Lilly partnered with Egypt-based EVA Pharma to improve access to Eli Lilly’s baricitinib (Olumiant) across African nations.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) US$ 229.4 Billion Forecast Revenue (2034) US$ 430.6 Billion CAGR (2025-2034) 6.5% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, COVID-19 Impact, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Product (Immunosuppressants- Corticosteroids, Calcineurin Inhibitors, mTOR Inhibitors, Antimetabolites, Monoclonal Antibodies, Others, Immunostimulants- Cytokines & Interleukins, Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors, Vaccine Adjuvants, Others), By Route of Administration (Parenteral, Oral, Topical), By Application (Cancer, Autoimmune Disorders- Lupus, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Multiple Sclerosis, Psoriasis, Others, Respiratory Diseases, Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Others), By Distribution Channel (Hospital Pharmacy, Retail Pharmacy, Online Pharmacy) Regional Analysis North America-US, Canada, Mexico;Europe-Germany, UK, France, Italy, Russia, Spain, Rest of Europe;APAC-China, Japan, South Korea, India, Rest of Asia-Pacific;South America-Brazil, Argentina, Rest of South America;MEA-GCC, South Africa, Israel, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Amgen Inc., Novartis AG, Abbott, Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc., Eli Lilly and Company, Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Merck & Co., Inc., Biogen, Pfizer Inc., Biogen Inc., AstraZeneca plc, Gilead Sciences Inc., AbbVie Inc., Astellas Pharma Inc., Horizon Therapeutics. Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd
- Amgen Inc.
- Novartis AG
- Abbott
- Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.
- Eli Lilly and Company
- Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- Biogen
- Pfizer Inc.
- Biogen Inc.
- AstraZeneca plc
- Gilead Sciences Inc.
- AbbVie Inc.
- Astellas Pharma Inc.
- Horizon Therapeutics










