Global Human Milk Fortifier Market Size, Share Report By Product Type (Powder, Liquid), By End User (Neonatal Intensive Care Units (NICUs), Hospitals and Clinics, Home Care Settings, Research Institutions, Others), By Distribution Channel (Hospital Supply Chains, Direct Sales, Online Retail, Pharmacies, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: July 2025
- Report ID: 154133
- Number of Pages: 202
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
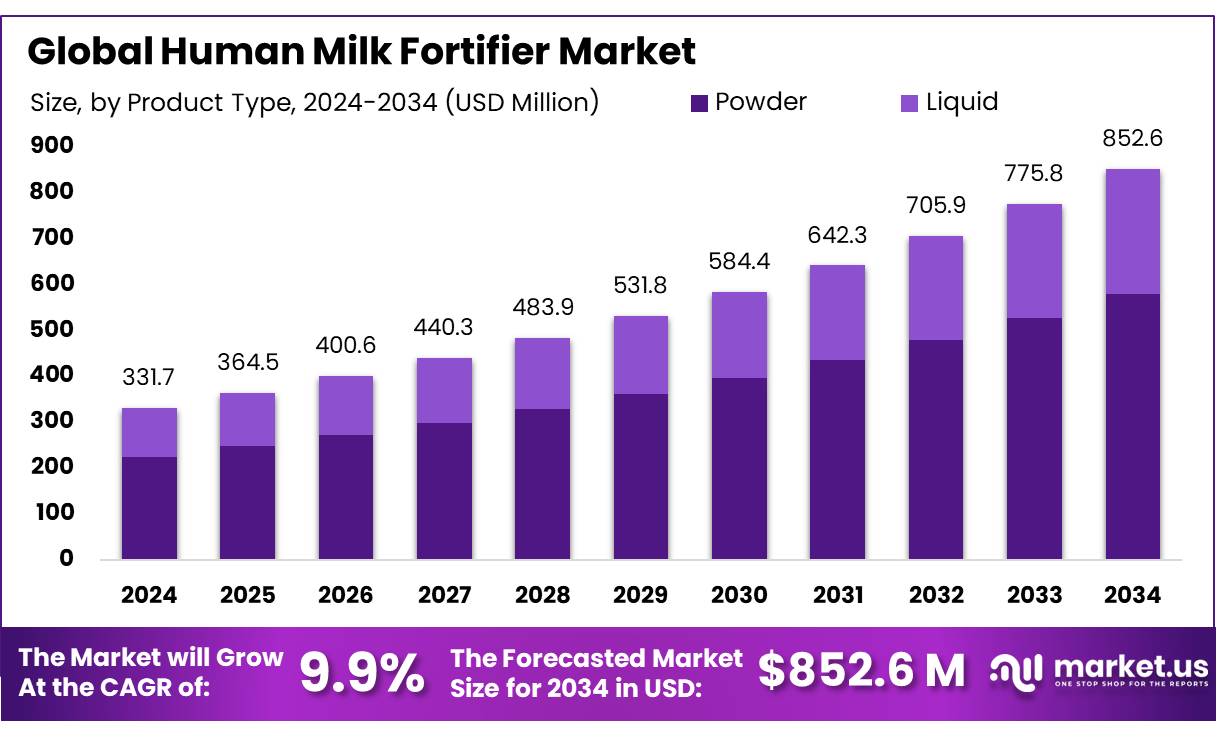
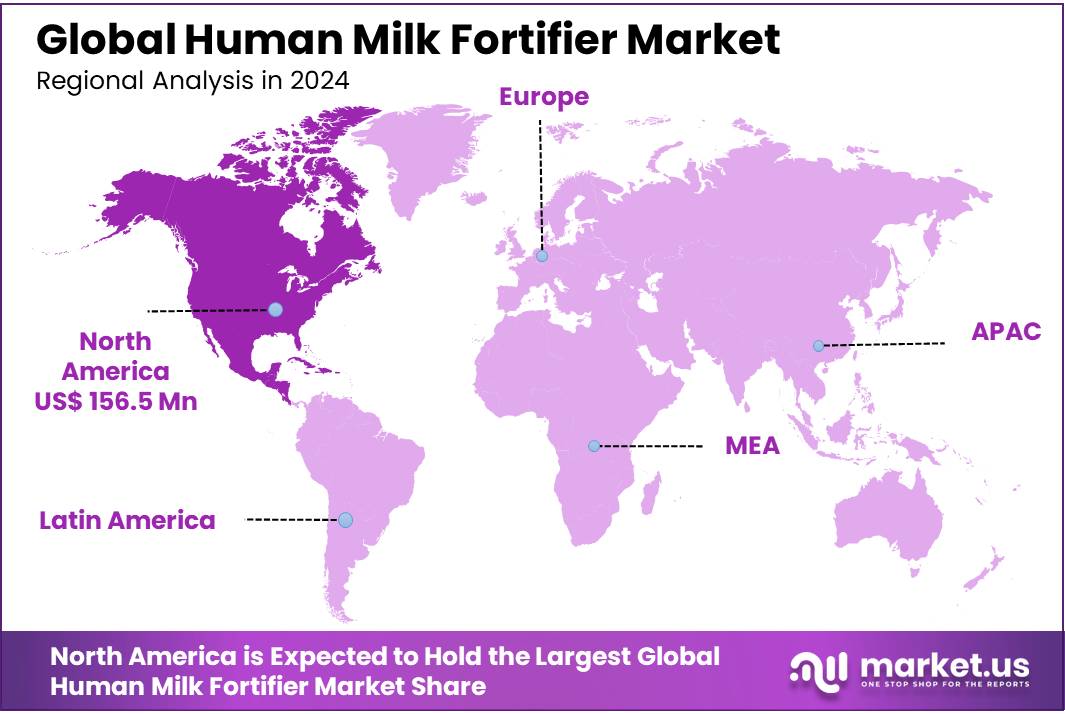
The Global Human Milk Fortifier Market size is expected to be worth around USD 852.6 Million by 2034, from USD 331.7 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 9.9% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 47.2% share, holding USD 156.5 Million in revenue.
Human Milk Fortifier (HMF) concentrates are nutritional supplements added to mother’s own milk or donor human milk to address the high nutrient requirements of preterm or very low birth‑weight neonates. Unlike standard breast milk, these concentrates enrich protein, calcium, phosphorus, vitamins, and other micronutrients, thereby supporting improved growth metrics such as weight gain of approximately 2.82 g/kg/day and length gains of around 0.21 cm/week in very preterm infants. While widely adopted in advanced healthcare systems, their adoption in countries like India remains limited, and usage often constrained by concerns over cost, feed intolerance, and operational logistics.
Clinical evidence solidifies growth in usage of HMF concentrates. A WHO‑review of ten trials involving 635 preterm infants found fortified human milk significantly increased weight gain by an average of 1.81 g/kg/day, even in low- and middle-income country trials and particularly in very preterm infants. Growth in length and head circumference also showed statistically significant improvements. These robust clinical benefits underscore the nutritional imperative for fortifier adoption.
Although HMF is not yet widely mainstreamed through direct government fortification programs, broader fortification policies offer relevant context. In India, for example, the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare regulates fortification standards and promotes nutrient addition through its Food Fortification Regulations (Fortification of Foods) 2018, encouraging inclusion of fortified foods in public distributions and awareness campaigns.
The National Dairy Development Board (NDDB) launched milk fortification with vitamin D in 2017, and as of 2020, FSSAI issued draft mandates to fortify packaged toned, double‑toned, skimmed or standardized milk with vitamin A and D, reaching over 121 million people per day via packaged fortified milk across India. These initiatives reflect government recognition of early‑life micronutrient needs—establishing a regulatory precedent that may extend to fortified breast‑milk supplements like HMF in future neonatal guidelines,
Governments expanding donor milk banking through financial support, standardized protocols, and public‑private partnerships can expand supply. Innovations in point‑of‑care osmotic concentration devices offer potential to concentrate mother’s milk without relying on external fortifier powders, enhancing nutrient density by over 30 % at typical NICU temperatures—suggestive of scalable future pathways.
Key Takeaways
- Human Milk Fortifier Market size is expected to be worth around USD 852.6 Million by 2034, from USD 331.7 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 9.9%.
- Powder held a dominant market position in the Human Milk Fortifier Market, capturing more than a 67.9% share.
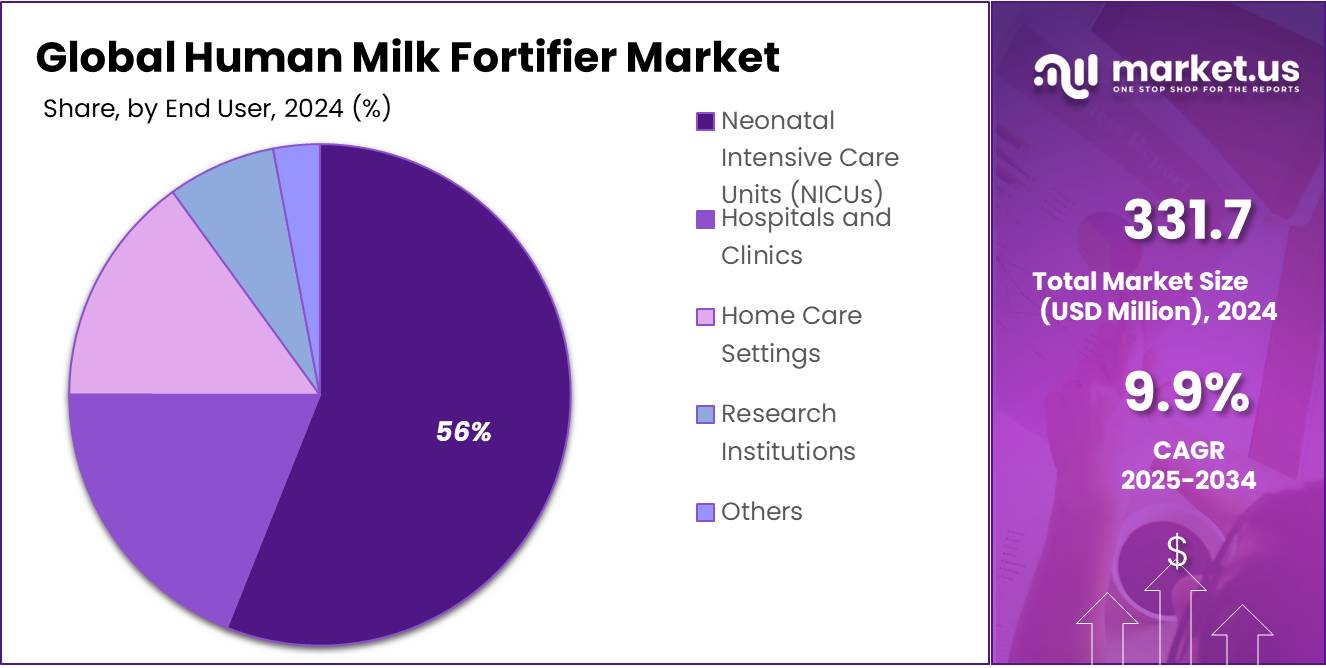
- Neonatal Intensive Care Units (NICUs) held a dominant market position in the Human Milk Fortifier Market, capturing more than a 56.1% share.
- Hospital Supply Chains held a dominant market position in the Human Milk Fortifier Market, capturing more than a 38.4% share.
- North America emerged as the leading region in the global Human Milk Fortifier Market, accounting for a substantial 47.2% share, which translated to a market value of approximately USD 156.5 million.
By Product Type Analysis
Powder Form Leads with 67.9% Market Share in 2024 Due to Easy Storage and Use
In 2024, Powder held a dominant market position in the Human Milk Fortifier Market, capturing more than a 67.9% share. This strong performance can be attributed to its longer shelf life, convenient handling, and compatibility with hospital feeding protocols. Powdered human milk fortifiers are widely preferred in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of storage.
They allow flexible dosage adjustments based on infant weight and medical condition, which supports customized nutrition strategies for preterm and low birth weight infants. The powder format is also more economical to produce and distribute, making it highly suitable for large-scale institutional use. Looking ahead to 2025, this segment is expected to maintain its leading position, supported by its widespread acceptance in clinical settings and continued preference among healthcare providers for its practicality and efficiency.
By End User Analysis
NICUs Lead Human Milk Fortifier Market with 56.1% Share in 2024 Due to High Preterm Infant Demand
In 2024, Neonatal Intensive Care Units (NICUs) held a dominant market position in the Human Milk Fortifier Market, capturing more than a 56.1% share. This leadership is mainly driven by the increasing number of preterm births and the need for specialized nutrition in hospital care settings. NICUs rely heavily on human milk fortifiers to meet the critical dietary needs of premature and low birth weight infants who require enhanced nutritional support for proper growth and development.
The clinical focus on exclusive human milk diets in NICUs has further strengthened demand for fortifiers. Hospitals are equipped with feeding protocols that integrate fortifiers as standard care, making them the largest end-user of these products. Looking into 2025, NICUs are expected to retain this leading share as healthcare systems continue to improve neonatal survival rates and focus on nutritional interventions to reduce complications related to premature birth.
By Distribution Channel Analysis
Hospital Supply Chains Dominate with 38.4% Share in 2024 Due to Institutional Buying Power
In 2024, Hospital Supply Chains held a dominant market position in the Human Milk Fortifier Market, capturing more than a 38.4% share. This leadership is largely attributed to the centralized purchasing systems and standardized supply protocols followed by hospitals, especially those with Neonatal Intensive Care Units (NICUs). Hospitals procure human milk fortifiers in bulk through established supply chains to ensure uninterrupted availability for neonatal care.
These institutional channels are trusted for maintaining product quality, regulatory compliance, and timely delivery. Additionally, hospital supply systems are designed to support clinical use, making them the most efficient and widely adopted distribution channel. By 2025, this segment is expected to continue its dominance, driven by rising hospital births, growing NICU admissions, and strengthened healthcare infrastructure in both developed and developing regions.
Key Market Segments
By Product Type
- Powder
- Liquid
By End User
- Neonatal Intensive Care Units (NICUs)
- Hospitals and Clinics
- Home Care Settings
- Research Institutions
- Others
By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Supply Chains
- Direct Sales
- Online Retail
- Pharmacies
- Others
Emerging Trends
FDA Approval of Human Milk‑Based Fortifier for Term Infants
A heart‑warming development in human milk fortifier (HMF) is the FDA’s recent approval in early 2025 of the first human milk‑based fortifier specifically for full‑term infants. Branded as Surgifort, this clear milestone marks a shift: HMF is no longer limited to premature babies. It’s now a nutritional option for term infants recovering from serious conditions like gastroschisis surgery, where the extra protein and calories support healing in the weeks after birth
Although gastroschisis affects under 2,400 babies each year in the U.S., these infants have intense nutrient needs post-surgery. Surgifort offers a compassionate, targeted solution—blending greater nutrition with the safety of human milk. That approval signals broader possibilities for babies who are medically fragile but born at term
On a larger scale, this change reflects evolving global policy. While no mandate mandates universal term‑baby fortification, guidelines from trusted bodies like Health Canada and FDA now define clearer standards for testing and safety of fortifiers even in new use cases like term infants. This may encourage other national authorities to follow. It opens regulatory pathways for products tailored to specific clinical needs—nurturing growth in ways that feel intentional and caring.
When a baby has to recover, whether premature or term, they often need more fuel to bounce back. The FDA’s green light reminds us that care can evolve gently, thoughtfully, and scientifically. For industry, that translates to smarter products. For clinicians, it means more tailored support. And for families, it’s hope: extra nourishment when their little one needs it most.
Drivers
Rising Preterm Births and Global Nutritional Need
Every year, approximately 13.4 million babies are born preterm (before 37 weeks gestation), accounting for almost 10 % of all live births worldwide. The World Health Organization reports that these early arrivals face significant health risks, with preterm birth being the leading cause of death among children under five, resulting in around 900,000 deaths in 2019. This continued rise in preterm births—especially in low‑ and middle‑income countries—creates immense pressure on healthcare systems to meet complex nutritional needs right from day one.
Human milk provides unmatched benefits. But for preterm and very low birth‑weight infants, additional enrichment is essential. Studies of fortified human milk show babies gain on average 1.81 g/kg/day more weight, and in very low birth‑weight infants this increases to 2.82 g/kg/day, compared to infants fed unfortified milk. Similarly, length gain improves by about 0.12 to 0.21 cm/week, and head circumference by 0.08 to 0.11 cm/week. These are not small numbers—they translate directly into healthier growth, stronger immunity, and reduced risk of complications like sepsis and necrotizing enterocolitis.
Governments and global health bodies recognize this urgent need. The WHO has issued clear nutrition support recommendations for very low birth‑weight infants, including multi‑nutrient fortification of human milk to reduce mortality and improve outcomes. Initiatives to improve access to safe donor human milk and fortifier supplements are being rolled out, particularly in regions where preterm birth accounts for over 60 % of cases—namely South Asia and sub‑Saharan Africa.
Restraints
High Cost and Limited Evidence for Human Milk Fortifier
One of the most significant challenges holding back wider adoption of human milk fortifier (HMF) concentrates is the high cost combined with limited assurance of clinical effectiveness. Although these products promise meaningful benefits, the evidence supporting their use is still mixed and of very low certainty, leaving both clinicians and policymakers cautious. Researchers reviewing very low birth weight infants (≤ 1,250 g) found that while HMF may reduce the incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) and retinopathy of prematurity (ROP), the total quality of evidence remains low to very low. That means outcomes like feeding intolerance, bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), and neurodevelopment show inconsistent or minimal improvements.
Further complicating acceptance is the high price tag attached to human milk–based fortifiers. A comparison analysis from 2019–2020 found that while human milk fortifier programs cost about €41,005 in total to implement, they generated hospital revenue gains of €39,854, translating to approximately €5,958 net benefit per patient, compared to negligible returns for bovine-based alternatives. Although this indicates potential cost offsets, it also shows how tight margins are, and how upfront costs may deter hospitals with limited NICU budgets.
Government bodies and health systems are aware of these hurdles. In the United States, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Surgeon General have highlighted economic and regulatory barriers, including inconsistent reimbursement for donor milk and fortifier use under Medicaid programs. They have advocated for policy reforms to improve affordability and access, especially for high-risk infants. Yet, these proposals remain largely unimplemented or vary widely across states.
Beyond economic concerns, there is unease among healthcare workers about variability in milk composition. Fortifiers often assume a standard nutrient profile in human milk, but in reality, breast milk varies widely between mothers and over time. This inconsistency can challenge “standard” perfunctory dosing and risks under- or over-fortification, which might impact digestion or nutrient balance. Targeted fortification systems are promising but demand equipment and training that most NICUs do not yet have.
Opportunity
Expansion of Human Milk Banking Supports Wider HMF Use
A powerful opportunity for the growth of human milk fortifier (HMF) concentrates lies in the steady expansion of national human milk banking systems, which ensures safe donor milk becomes available for preterm and vulnerable infants. As more governments support milk banks, there’s real potential that more babies will benefit from fortified feed when mother’s own milk is insufficient.
For example, India’s government-backed “National Guidelines on Lactation Management Centres in Public Health Facilities” promote the establishment of lactation support centres integrated with milk banks. These centres strengthen breastfeeding education, kangaroo mother care, and ensure safe donor human milk is available when needed. Reflecting this push, the number of human milk banks in India has grown from around 50 in 2019 to over 90 by 2021, largely due to increased institutional support. That doubling in just two years underscores how policy can drive real change.
Globally, over 700 human milk banks now operate, according to WHO estimates, spreading across at least 33 countries guided by programs like the International Milk Banking Initiative (IMBI). Each milk bank provides donor human milk that often needs fortification to meet the high protein, energy, and mineral demands of preterm infants. As these banks scale up, demand for HMF concentrates naturally increases, creating both a humanitarian and industrial opportunity.
Regional Insights
North America Commands 47.2% Share in Human Milk Fortifier Market, Valued at USD 156.5 Million in 2024
In 2024, North America emerged as the leading region in the global Human Milk Fortifier Market, accounting for a substantial 47.2% share, which translated to a market value of approximately USD 156.5 million. This dominant position can be attributed to the region’s highly developed healthcare infrastructure, widespread access to neonatal intensive care units (NICUs), and strong clinical emphasis on preterm infant nutrition. The United States, in particular, has shown consistent demand for human milk fortifiers, driven by high rates of hospital births and an advanced medical care system that prioritizes early-life nutrition.
Government-backed programs such as the Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) program play a critical role in promoting the use of human milk fortifiers when medically necessary, especially for low-income families. Additionally, increased awareness among healthcare professionals about the benefits of human milk–based diets for premature infants has led to a growing preference for fortifiers in NICU feeding protocols. The presence of key pediatric hospitals and a growing number of preterm births—about 1 in 10 babies in the U.S. is born prematurely according to the CDC—further strengthens demand in the region.
North America is expected to maintain its leadership in the market. This will be supported by ongoing investments in neonatal care, favorable reimbursement policies, and continued clinical research that highlights the long-term benefits of fortified human milk in reducing complications and improving outcomes for low birth weight infants.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Abbott plays a leading role in the human milk fortifier market with its Similac® brand, offering both powdered and liquid forms of fortifiers tailored for premature infants. The company’s focus remains on evidence-backed nutrition solutions, with distribution across hospitals and NICUs globally. In 2024, Abbott strengthened its clinical partnerships and ensured consistent hospital supply in North America and Europe, maintaining a strong presence through trusted product lines and compliance with neonatal nutrition standards.
Mead Johnson, a subsidiary of Reckitt, continues to be a major contributor to the human milk fortifier market, especially through its Enfamil brand. The company offers concentrated liquid fortifiers widely used in NICUs across the U.S. and other advanced healthcare systems. In 2024, it emphasized product safety, clinical efficacy, and compatibility with human milk-based feeding strategies. Mead Johnson’s wide hospital network and focus on preterm nutrition have enabled it to sustain strong institutional demand.
NeoLacta Lifesciences Pvt Ltd, based in India, is a pioneer in offering 100% human milk–derived fortifiers, setting it apart from bovine-based alternatives. The company has a strong focus on neonatal nutrition and operates one of Asia’s first human milk processing facilities. In 2024, NeoLacta expanded its presence in emerging markets and partnered with several hospitals for clinical use. Its product line aligns with exclusive human milk diet protocols, especially in preterm and critically ill neonates.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Abbott
- MeadJohnson
- NeoLacta Lifesciences Pvt Ltd
- Nestle SA
- Prolacta Bioscience Inc
- NeoKare Nutrition Ltd
- Danone SA
- Neolac Inc
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024, Nestlé SA stood among the key providers in the global human milk fortifier market alongside Abbott and Mead Johnson, with an estimated presence in the overall industry (global market value ~USD 393.7million in 2024).
In 2024, Mead Johnson (Reckitt) continued to be a focal provider in the human milk fortifier liquid segment, which recorded a total market value of USD 150 million that year.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 331.7 Mn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 852.6 Mn CAGR (2025-2034) 9.9% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Product Type (Powder, Liquid), By End User (Neonatal Intensive Care Units (NICUs), Hospitals and Clinics, Home Care Settings, Research Institutions, Others), By Distribution Channel (Hospital Supply Chains, Direct Sales, Online Retail, Pharmacies, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Abbott, MeadJohnson, NeoLacta Lifesciences Pvt Ltd, Nestle SA, Prolacta Bioscience Inc, NeoKare Nutrition Ltd, Danone SA, Neolac Inc Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Human Milk Fortifier MarketPublished date: July 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Human Milk Fortifier MarketPublished date: July 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Abbott
- MeadJohnson
- NeoLacta Lifesciences Pvt Ltd
- Nestle SA
- Prolacta Bioscience Inc
- NeoKare Nutrition Ltd
- Danone SA
- Neolac Inc










