Global Printed Battery Market Size, Share Report By Voltage Range (Below 1.5 V, Between 1.5 V to 3 V, Above 3V), By Components (Anode, Cathode, Electrolyte, Collectors), By Product Type (Rechargeable, Non-Rechargeable), By Application (Consumer Electronics, Energy Harvesting, Medical Devices, Smart Packaging, Smart Cards, Wearable Technology, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Aug 2025
- Report ID: 154556
- Number of Pages: 370
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
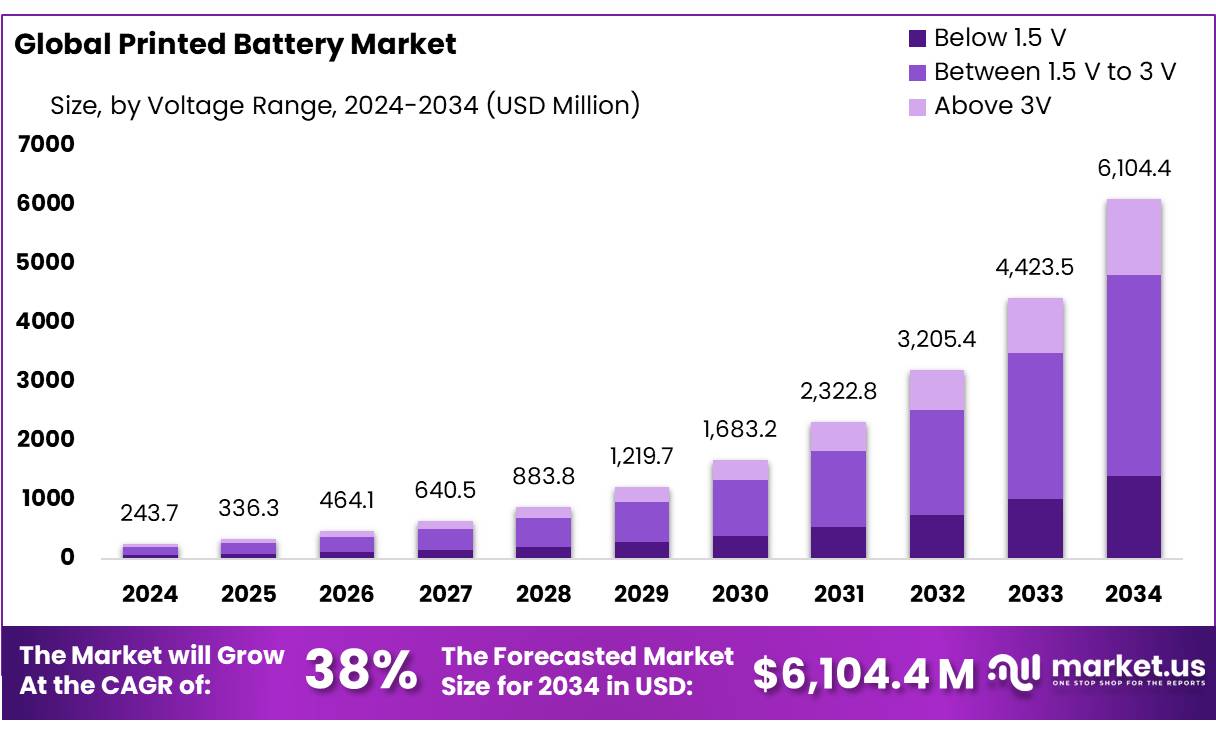
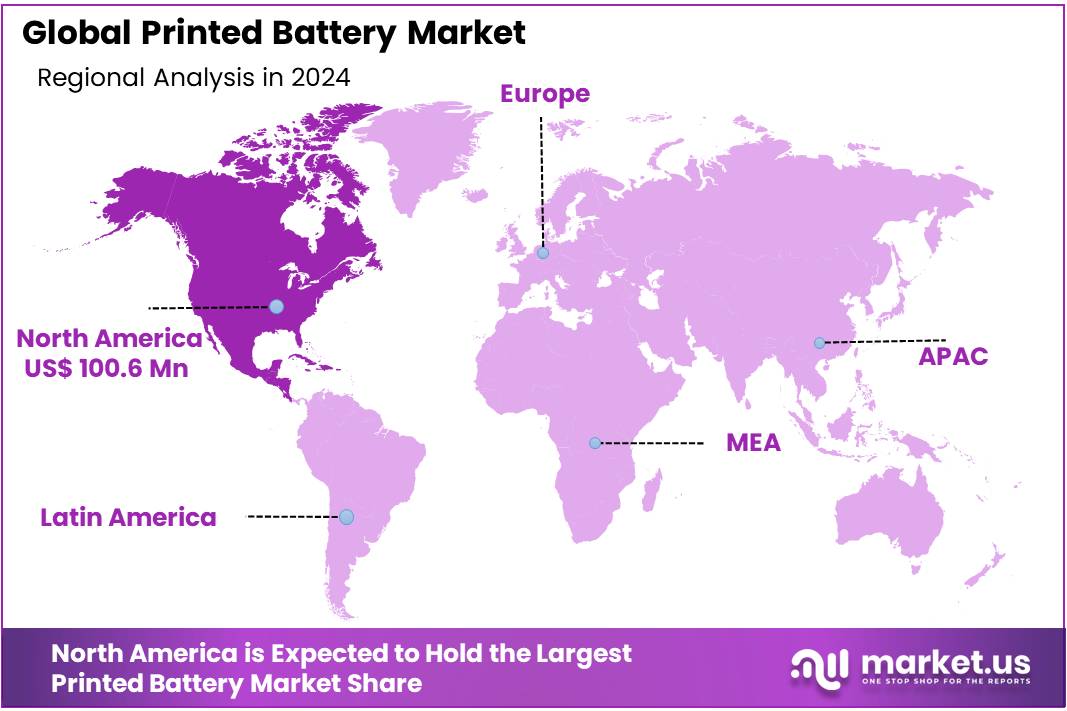
The Global Printed Battery Market size is expected to be worth around USD 6104.4 Million by 2034, from USD 243.7 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 38% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North American held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 41.3% share, holding USD 100.6 Million in revenue.
Printed battery technology represents a transformative advancement in energy storage, characterized by its lightweight, flexible, and miniaturized design. These batteries are fabricated using printing techniques such as screen printing and inkjet printing, enabling the integration of energy storage solutions directly into substrates like paper, plastic, and textiles. This innovation is particularly advantageous for applications in wearable electronics, medical devices, smart packaging, and Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, where compact and conformable power sources are essential.
Government initiatives have provided tangible support to related battery and advanced materials sectors. For example, in India the government’s Production‑Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for advanced chemistry cells (ACCs) allocates USD 434.4 million to support domestic EV battery manufacturing, with plans to expand EV adoption from 2 percent of total vehicle sales toward 30 percent by 2030.
Government initiatives play a pivotal role in fostering the development of the printed battery industry in India. The Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for Advanced Chemistry Cells (ACC) is a notable example, aiming to bolster domestic manufacturing capabilities and reduce dependency on imports. Under this scheme, companies like Reliance Industries and Amara Raja have committed to establishing gigafactories for battery production, with a combined capacity of 10 GWh.
These efforts align with India’s broader objective to enhance its position in the global battery manufacturing sector and support the transition to electric mobility and renewable energy solutions. For instance, the PLI scheme for Advanced Chemistry Cells (ACC) has allocated ₹18,000 crore (approximately $2.5 billion) to encourage the establishment of battery manufacturing units in India.
Additionally, the Ministry of Heavy Industries has allocated 40 GWh of a targeted 50 GWh capacity under the Production‑Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for Advanced Chemistry Cell manufacturing, in order to enhance self‑reliance in cell production domestically. In November 2023, India launched an INR 80 billion (USD ≈960 million) incentive program to support establishment of next‑generation battery plants with combined output of 20 GWh, tied to performance-linked benefits over five years.
Key Takeaways
- The global printed battery market is projected to reach approximately USD 6,104.4 million by 2034, rising from USD 243.7 million in 2024, with a strong CAGR of 38% during the forecast period.
- The Between 1.5 V to 3 V category dominated in 2024, accounting for over 56.8% of the total market share, owing to its suitability for compact electronic applications.
- The Anode segment led the market in 2024, capturing more than 34.2% of the global share, due to its essential role in battery efficiency and performance.
- Non-Rechargeable printed batteries held a commanding position in 2024, with a market share exceeding 65.9%, driven by demand for low-cost, disposable power sources.
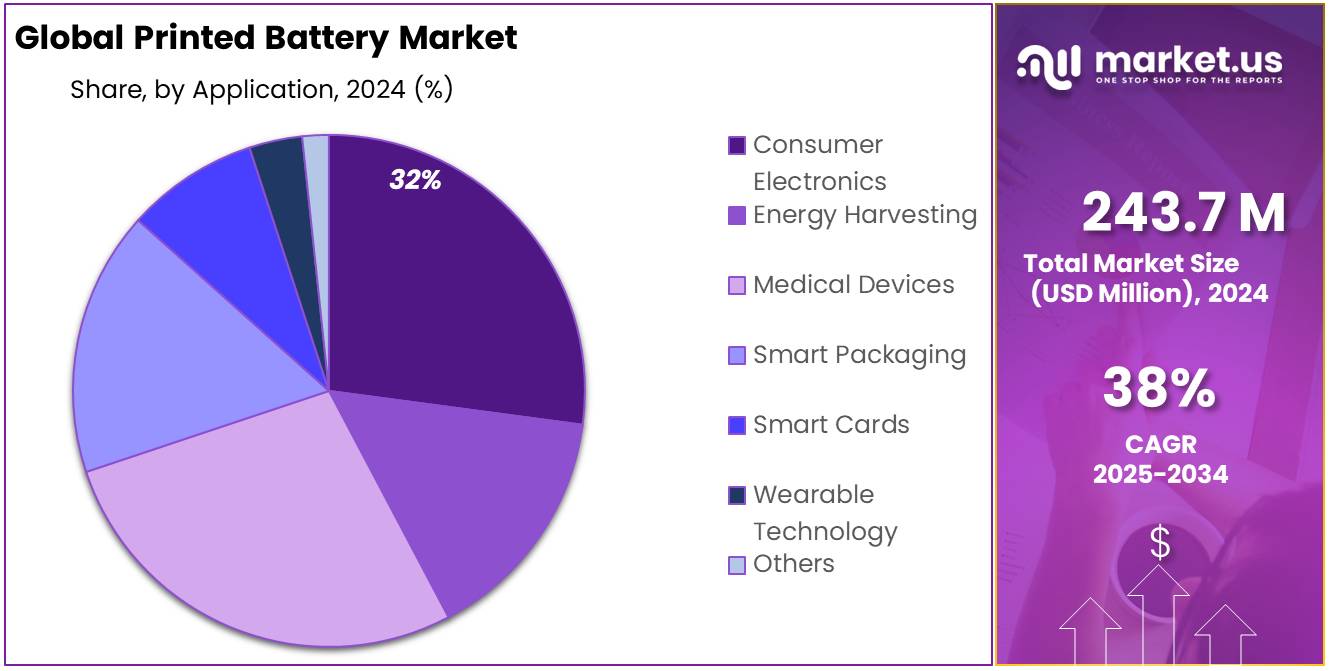
- Consumer Electronics emerged as the top application area, securing over 32.4% share in 2024, supported by increasing use in wearables, medical devices, and smart gadgets.
- North America led the global printed battery market in 2024, holding a 41.3% share, valued at approximately USD 100.6 million, driven by advanced manufacturing, R&D activities, and adoption across IoT and healthcare sectors.
By Voltage Range Analysis
Between 1.5 V to 3 V dominates with 56.8% due to its compatibility with compact electronics.
In 2024, Between 1.5 V to 3 V held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 56.8% share in the global printed battery market by voltage range. This segment’s strong presence is mainly supported by its widespread application in compact and low-power electronic devices, such as smart cards, medical patches, wearable sensors, and RFID tags.
These devices typically require a stable and moderate voltage range to function efficiently without compromising on form factor or energy efficiency. The 1.5 V to 3 V range offers an ideal balance of power and size, which aligns with the design needs of emerging flexible and miniaturized electronics. As a result, manufacturers prefer this voltage range to ensure optimal performance in applications where space and weight constraints are critical.
By Components Analysis
Anode dominates with 34.2% due to its critical role in printed battery performance and efficiency.
In 2024, Anode held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 34.2% share in the global printed battery market by component. The anode plays a central role in determining the overall capacity, charge rate, and lifecycle of printed batteries. Its ability to store and release ions efficiently makes it a vital element in maintaining consistent energy output, especially for applications in flexible electronics, medical devices, and smart packaging.
The rise in demand for high-performance, lightweight, and thin battery formats has led to a growing focus on advanced anode materials such as printed zinc, carbon-based inks, and hybrid composites. These materials offer improved conductivity, faster charge times, and enhanced mechanical flexibility, which are crucial for printed battery designs.
By Product Type Analysis
Non-Rechargeable dominates with 65.9% due to its low cost and wide use in disposable devices.
In 2024, Non-Rechargeable held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 65.9% share in the global printed battery market by product type. This strong share is primarily attributed to the growing use of disposable electronic devices where long-term power storage is not required. Products such as medical diagnostic patches, RFID tags, smart labels, and promotional electronics rely heavily on single-use power sources that are compact, cost-effective, and easy to integrate.
Non-rechargeable printed batteries are ideal for such applications because they can be mass-produced at low cost and require minimal charging infrastructure. Their simplified design also allows for thinner profiles and better flexibility, which aligns with the current trend toward lightweight and flexible electronics.
By Application Analysis
Consumer Electronics dominates with 32.4% due to growing demand for compact, flexible power sources.
In 2024, Consumer Electronics held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 32.4% share in the global printed battery market by application. This segment’s leadership is largely driven by the rising demand for lightweight, flexible, and portable power solutions in devices such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, hearing aids, wireless earbuds, and electronic patches.
Printed batteries offer an ideal fit for these compact gadgets, where traditional bulky batteries cannot be used without compromising the design or comfort. The shift toward thinner devices and wearables has made printed battery technology a preferred option, offering a balance of energy efficiency, thin profile, and design flexibility.
Key Market Segments
By Voltage Range
- Below 1.5 V
- Between 1.5 V to 3 V
- Above 3V
By Components
- Anode
- Cathode
- Electrolyte
- Collectors
By Product Type
- Rechargeable
- Non-Rechargeable
By Application
- Consumer Electronics
- Energy Harvesting
- Medical Devices
- Smart Packaging
- Smart Cards
- Wearable Technology
- Others
Emerging Trends
Integration of E-Waste Recycling in Battery Manufacturing
A significant and emerging trend in India’s battery manufacturing sector is the integration of electronic waste (e-waste) recycling into the production of lithium-ion batteries. This approach not only addresses the critical issue of raw material scarcity but also aligns with the nation’s sustainability goals by promoting a circular economy.
One notable example is Boson Cell, a startup based in Sriperumbudur, Tamil Nadu. Founded by Guru Punghavan, Boson Cell specializes in refining critical minerals—such as lithium, cobalt, nickel, and graphite—from e-waste and converting them into battery-grade chemicals. Their facility, with an initial capacity of 0.8 GWh, currently supplies approximately 30% of their material needs, significantly reducing reliance on imports, particularly from China.
This innovative approach has garnered attention from both the private and public sectors. The Indian government, recognizing the importance of sustainable practices, has been actively supporting initiatives like Boson Cell’s. Under the ‘Mission LiFE’ (Lifestyle for Environment) program, the government has transferred cost-effective lithium-ion battery recycling technology to startups and recycling industries, facilitating the development of indigenous capabilities in battery recycling.
Furthermore, the Department of Science and Technology (DST) is backing 32 projects focused on battery storage, underscoring the government’s commitment to advancing research and development in energy storage technologies.
Drivers
Government Incentives and Policies
One of the most significant driving forces behind the growth of printed battery technologies in India is the robust support provided by the government through various initiatives and policies. Recognizing the critical role of energy storage in the transition to a sustainable and self-reliant energy ecosystem, the Indian government has introduced several measures to promote the development and manufacturing of advanced battery technologies, including printed batteries.
A notable example is the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme, which offers financial incentives to manufacturers based on their incremental sales. This scheme has been instrumental in attracting investments and encouraging companies to establish manufacturing units within the country. For instance, JSW Group, Amara Raja, and Reliance Industries have submitted bids to set up battery manufacturing facilities in India, aiming to produce advanced chemistry cells with a combined capacity of 10 GWh. These projects are supported by the government’s PLI scheme, which has an allocated budget of ₹36.20 billion (approximately $434.41 million) to boost local battery production.
In addition to these financial incentives, the government has been actively working on enhancing the infrastructure necessary for the growth of the electric vehicle (EV) ecosystem, which directly influences the demand for advanced battery technologies. For example, the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME) scheme provides subsidies for the purchase of electric vehicles and the establishment of charging infrastructure. This initiative aims to reduce the cost of EVs and make them more accessible to consumers, thereby driving the demand for batteries.
Collectively, these government initiatives are creating a conducive environment for the growth of the printed battery sector in India. By providing financial incentives, reducing import duties on critical materials, and supporting infrastructure development, the government is fostering an ecosystem that encourages innovation and investment in advanced battery technologies. This support not only accelerates the adoption of sustainable energy solutions but also positions India as a competitive player in the global battery manufacturing landscape.
Restraints
Raw Material Dependency and Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
A significant challenge hindering the growth of printed battery technologies in India is the nation’s heavy reliance on imported raw materials, particularly critical minerals like lithium, cobalt, nickel, and graphite. Currently, India imports over 80% of its lithium-ion battery cells, predominantly from China, leaving the domestic market vulnerable to supply chain disruptions and price volatility.
The global demand for these minerals is escalating due to the rapid adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy storage solutions. This surge in demand has intensified competition among countries to secure access to these essential resources.
- For instance, China dominates the processing of critical minerals, controlling over 50% of lithium processing, 75% of cobalt, and more than 90% of graphite refining. Such concentration of supply poses geopolitical risks, especially for nations like India that are striving to establish a self-reliant battery manufacturing ecosystem.
In response to these challenges, the Indian government has initiated several measures to enhance domestic sourcing of critical minerals. Under the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for Advanced Chemistry Cells (ACC), the government has allocated ₹18,100 crore (approximately $2.5 billion) to incentivize the establishment of battery manufacturing capacities. The aim is to install 50 GWh of domestic battery manufacturing capacity by 2026. Additionally, Coal India is exploring lithium reserves in Argentina and Chile to diversify supply sources and reduce dependence on imports.
Despite these efforts, the path to achieving material security is fraught with challenges. The exploration and development of domestic mining operations for critical minerals are time-consuming processes, often taking several years from discovery to production. For example, India’s need for lithium carbonate for batteries is projected at 56,000 metric tons annually by 2030, necessitating significant investments in exploration and processing infrastructure.
Opportunity
Expansion of Battery Manufacturing Capacity
India is witnessing a significant surge in investments aimed at bolstering its battery manufacturing capabilities, presenting a substantial growth opportunity for the sector. The government’s strategic initiatives, coupled with private sector investments, are paving the way for India to become a global hub for battery production.
This initiative aims to set up a 50 GWh battery manufacturing capacity by 2026, with an additional 34 GWh planned for grid-scale storage. As of 2024, companies like Reliance Industries, Rajesh Exports, and Ola Electric have been selected under the PLI scheme to receive incentives for cell manufacturing, with operations expected to commence by 2024.
Private sector investments are also contributing significantly to this growth. Reliance Industries is constructing a battery gigafactory in Jamnagar with an annual capacity of 30 GWh, focusing initially on assembling Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) for utility-scale, residential, commercial, and mobility markets. Similarly, JSW Group has announced plans to establish a battery manufacturing facility with a capacity of 50 GWh by 2028-2030, starting with a 10 GWh capacity target by 2026.
These developments are in line with India’s broader goal to become the world’s third-largest automotive market by 2026, with a significant demand for lithium-ion batteries. The government’s target of 30% of new vehicle sales to be electric by 2030 and the need for 34 GWh of battery storage to add 450 GW of renewables by 2030 further underscore the importance of expanding battery manufacturing capacity.
Regional Insights
In 2024, North America emerged as the leading region in the global printed battery market, capturing a dominant market share of 41.3%, which accounted for approximately USD 100.6 million in revenue. This leadership can be attributed to the strong presence of advanced electronics manufacturing, high consumer demand for wearable devices, and rapid adoption of smart packaging and RFID applications across retail and healthcare sectors.
The United States, in particular, remains at the forefront of technological innovation, supported by active collaborations between research institutions, battery manufacturers, and electronics companies. Additionally, government-backed programs and funding initiatives for printed electronics and energy storage technologies have further propelled the growth of the printed battery market in the region.
North America’s printed battery development is also influenced by the region’s significant investment in the Internet of Things (IoT) infrastructure. With a growing number of connected devices requiring compact and flexible power sources, printed batteries have become a key enabler of IoT integration in applications such as asset tracking, remote sensors, and wireless health monitors. Furthermore, rising awareness around sustainable and recyclable energy solutions is pushing industries to adopt printed batteries due to their low environmental footprint and minimal use of toxic materials.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Samsung SDI is a leading South Korean company known for its advanced battery solutions. The company produces high-performance batteries for various applications, including electric vehicles, energy storage systems, and consumer electronics. Samsung SDI’s expertise in lithium-ion and printed batteries has positioned it as a key player in the global market. The company emphasizes innovation, efficiency, and sustainability in its battery technology, continually advancing its production capabilities to meet the growing demand for green energy solutions.
Xymox Technologies Inc is a US-based company that focuses on developing innovative battery technologies, including printed batteries. The company is recognized for its expertise in creating low-cost, flexible, and efficient printed batteries for IoT devices, wearables, and other small-scale applications. Xymox’s printed battery solutions offer a combination of high energy density, lightweight design, and environmental benefits. Their technology is geared toward providing reliable power sources for a wide range of emerging tech applications in a growing connected world.
Enfucell Oy is a Finnish company specializing in the development and production of printed battery technologies. The company focuses on manufacturing flexible, lightweight, and environmentally-friendly batteries for applications in the Internet of Things (IoT), wearables, and smart packaging. Enfucell’s technology enables cost-efficient and scalable production, with a strong commitment to sustainability. Their printed batteries offer energy solutions with reduced environmental impact, catering to industries looking for innovative power sources for low-energy devices.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Enfucell Oy
- Samsung SDI Co., Ltd
- Xymox Technologis Inc
Recent Industry Developments
For Samsung SDI, full‑year reported group sales totaled approximately USD 17.24 billion in 2023, with net income of USD 1.50 billion and operating income of USD 1.25 billion in the same year.
Xymox Technologies Inc., Wisconsin, and operating as part of the RAFI Group, the company employs approximately 51 staff and achieved a peak estimated revenue of USD 9.7 million in 2024
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 243.7 Mn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 6104.4 Mn CAGR (2025-2034) 38% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Voltage Range (Below 1.5 V, Between 1.5 V to 3 V, Above 3V), By Components (Anode, Cathode, Electrolyte, Collectors), By Product Type (Rechargeable, Non-Rechargeable), By Application (Consumer Electronics, Energy Harvesting, Medical Devices, Smart Packaging, Smart Cards, Wearable Technology, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Enfucell Oy, Samsung SDI Co., Ltd, Xymox Technologis Inc Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Enfucell Oy
- Samsung SDI Co., Ltd
- Xymox Technologis Inc










