Global Kraft Lignin Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Form (Powder, Liquid, Granules), By Source (Softwood, Hardwood, Hybrid), By Application (Adhesives, Carbon Fiber Production, Animal Feed, Bioresins, Soil Conditioning, Others), By End Use (Construction, Agriculture, Food Beverage, Pharmaceutical, Personal Care, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends, and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: July 2025
- Report ID: 153906
- Number of Pages: 251
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
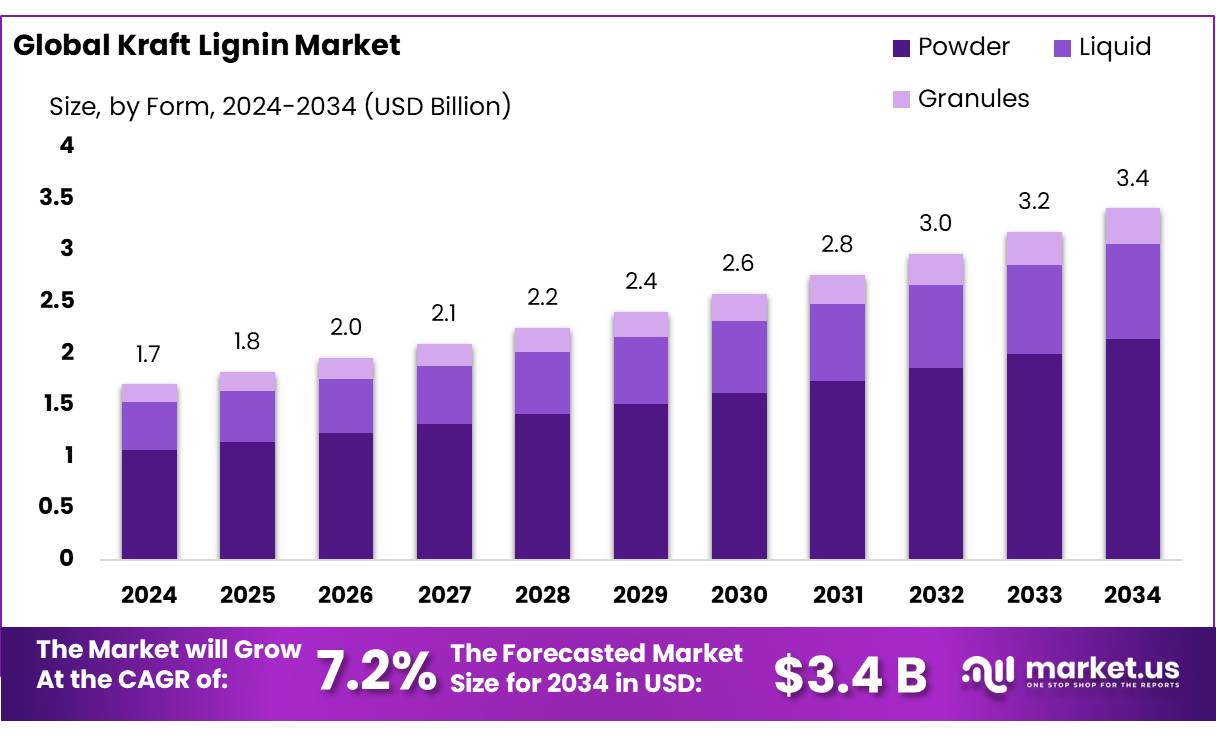
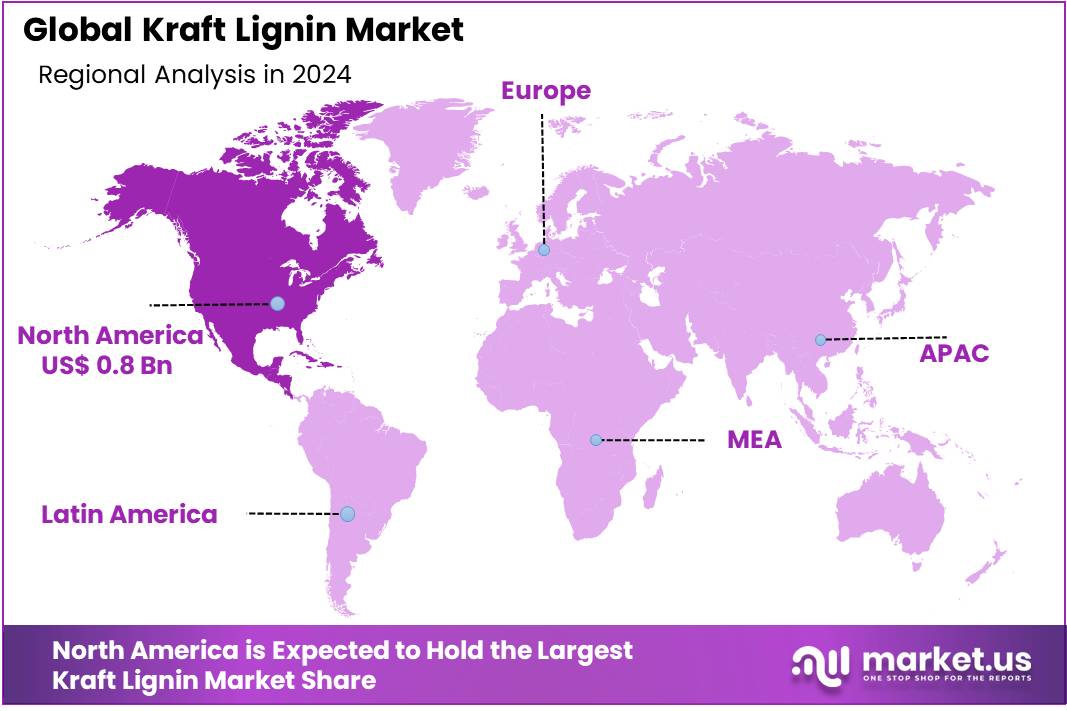
The Global Kraft Lignin Market size is expected to be worth around USD 3.4 Billion by 2034, from USD 1.7 Bn in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 7.2% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 48.2% share, holding USD 0.8 Billion revenue.
Kraft lignin, a high-purity biopolymer derived from the kraft pulping process, is emerging as a pivotal component in the global transition towards sustainable materials. In 2023, the global production capacity for kraft lignin reached approximately 112 kt per year. This surge reflects a growing recognition of lignin’s potential in various industrial applications, including bio-based adhesives, carbon fibers, and phenolic resins.
Industrial-scale production of kraft lignin is exemplified by facilities like Stora Enso’s Sunila mill in Finland, which produces 50,000 metric tons of lignin annually. Similarly, Södra’s new facility in Sweden, slated to commence operations in 2027, is expected to have the largest capacity for kraft lignin production in the world. These developments underscore the significant potential of kraft lignin as a valuable industrial resource.
In India, the government is actively promoting the utilization of lignin through initiatives like the ‘Make in India’ program. For instance, Praj Industries has developed a lignin-based bio-bitumen, which has been successfully used in road construction projects, replacing up to 15% of traditional bitumen. Additionally, the government has allowed the mixing of lignin up to 35% in petroleum-based bitumen, aiming to reduce dependence on imported bitumen and enhance sustainability.
Key Takeaways
- The Kraft Lignin Market is expected to grow from USD 1.7 billion in 2024 to approximately USD 3.4 billion by 2034, registering a CAGR of 7.2%.
- Powder form held the dominant position, capturing more than 62.8% of the total market share.
- Softwood was the leading source, accounting for over 57.1% of the market share.
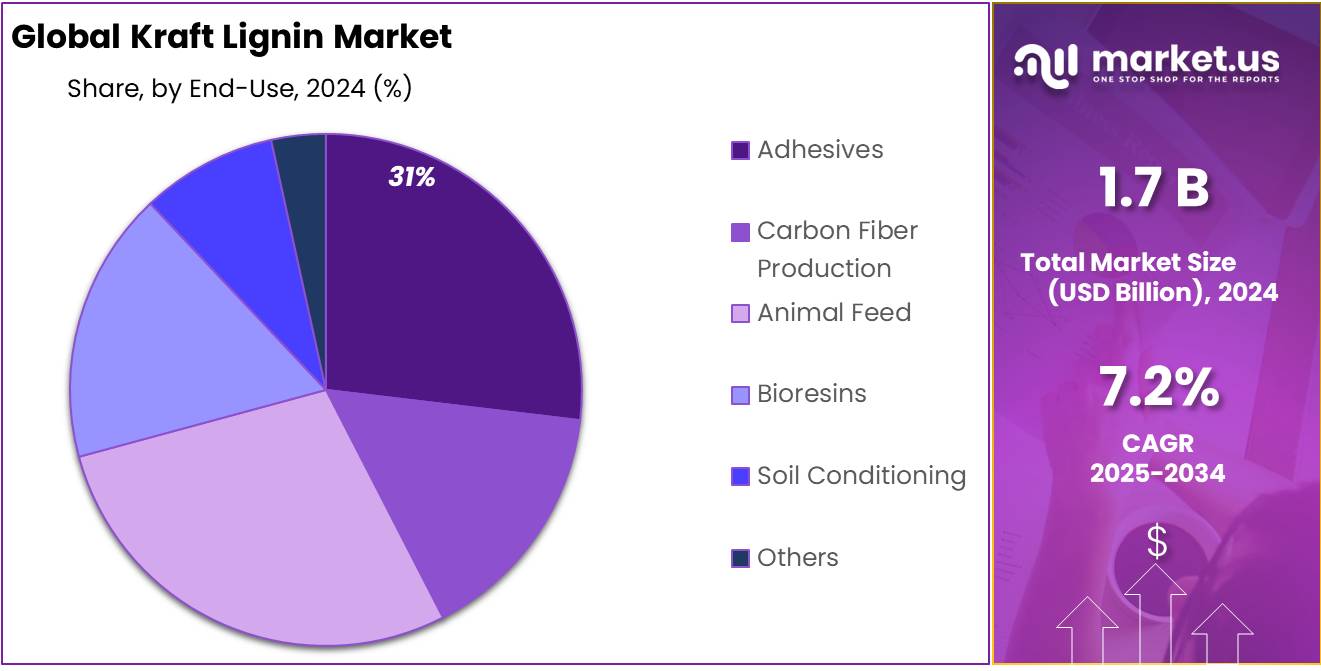
- Adhesives emerged as the top application, holding more than 31.3% of the global market.
- The Construction sector led the market, with a dominant share of over 34.6%.
- North America accounted for approximately 48.2% of the global Kraft Lignin Market, with a regional value estimated at USD 0.8 billion in 2024.
By Form Analysis
Powder Form Leads with 62.8% Market Share in 2024 Due to Easy Handling and Versatility
In 2024, Powder held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 62.8% share in the Kraft Lignin market by form. The powdered form is widely preferred across multiple industries due to its ease of storage, convenient transportation, and high solubility in processing applications. Its stable nature under various environmental conditions makes it suitable for use in adhesives, coatings, and dispersants, particularly within the construction, agricultural, and chemical sectors.
The ability of powder lignin to blend efficiently with other dry materials further adds to its industrial appeal. As industries focus more on sustainable and cost-effective raw materials, powdered kraft lignin continues to meet operational needs without compromising on performance. In 2025, the demand for powdered form is expected to witness steady growth, driven by increasing adoption in eco-friendly product formulations and ongoing research into lignin-based biopolymers.
By Source Analysis
Softwood Leads with 57.1% Share Owing to High Lignin Content and Industrial Suitability
In 2024, Softwood held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 57.1% share in the Kraft Lignin market by source. This dominance is mainly due to the higher lignin content present in softwood species compared to hardwoods, making extraction more efficient and yields more consistent.
Industries favor softwood-derived kraft lignin for its stronger structural properties and better performance in applications such as resins, binders, and dispersants. The robust fiber structure of softwood also contributes to improved processing in pulping and chemical conversion processes. In 2025, the demand for softwood-based kraft lignin is expected to remain strong, especially in sectors focused on bio-based materials, where consistent quality and reliable supply are crucial for large-scale formulations.
By Application Analysis
Adhesives Dominate with 31.3% Share for Their Expanding Role in Bio-Based Formulations
In 2024, Adhesives held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 31.3% share in the Kraft Lignin market by application. The growing shift toward sustainable and eco-friendly raw materials has significantly increased the use of kraft lignin in adhesive formulations. Its natural bonding properties make it a suitable alternative to synthetic resins, especially in wood adhesives and construction applications.
Lignin-based adhesives offer lower toxicity, better biodegradability, and cost benefits, making them a preferred choice for manufacturers looking to reduce reliance on petroleum-derived inputs. In 2025, demand for kraft lignin in adhesives is projected to grow steadily, driven by green building standards and rising interest in renewable chemical ingredients across the packaging, furniture, and automotive sectors.
By End Use Analysis
Construction Leads with 34.6% Share Due to Rising Use in Eco-Friendly Building Materials
In 2024, Construction held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 34.6% share in the Kraft Lignin market by end use. The sector’s strong uptake is largely driven by the increasing demand for sustainable building materials and cost-effective additives. Kraft lignin is widely used in concrete admixtures, plasterboard binders, and insulation materials due to its water-reducing, dispersing, and binding properties.
Its ability to enhance the strength and durability of construction materials while reducing the environmental footprint makes it a preferred choice for green building initiatives. In 2025, the construction industry is expected to continue relying on kraft lignin, supported by regulations favoring low-emission materials and growing awareness around circular economy practices in infrastructure development.
Key Market Segments
By Form
- Powder
- Liquid
- Granules
By Source
- Softwood
- Hardwood
- Hybrid
By Application
- Adhesives
- Carbon Fiber Production
- Animal Feed
- Bioresins
- Soil Conditioning
- Others
By End Use
- Construction
- Agriculture
- Food Beverage
- Pharmaceutical
- Personal Care
- Others
Emerging Trends
Emerging Trends in Kraft Lignin for Sustainable Food Packaging
One notable trend is the development of lignin-based bioplastics. For instance, in March 2024, UPM-Kymmene advanced the development of lignin-based bioplastics, including filing a patent for a new material designed for agricultural applications like biodegradable pots, pipes, and mulch films. This innovation aligns with the growing consumer preference for eco-friendly and compostable packaging options.
Additionally, the European Union’s Circular Economy Action Plan aims for all packaging to be 100% recyclable and compostable by 2030, encouraging the development of bio-based alternatives to traditional plastics. Such regulatory frameworks are fostering the adoption of lignin-based materials in food packaging.
In India, the government’s initiatives to promote the use of biofuels and bio-based materials further bolster the potential for lignin in packaging applications. Policies encouraging the utilization of agricultural residues and biomass for biofuel production indirectly support the development of lignin-based materials, as these residues are rich sources of lignin.
Drivers
Government Initiatives Driving the Adoption of Kraft Lignin in Food Packaging
The increasing global emphasis on sustainability has led to significant governmental support for the adoption of eco-friendly materials, including kraft lignin, in various industries. Kraft lignin, a byproduct of the paper and pulp industry, is gaining attention for its potential applications in food packaging, offering a renewable alternative to conventional petroleum-based materials.
In the United States, the Department of Energy’s Bioenergy Technologies Office (BETO) has been actively promoting the development and commercialization of lignin-based products. Through initiatives like the Request for Information (RFI) on Cellulosic Sugar and Lignin Production Capabilities, BETO has sought to identify suppliers capable of producing lignin for use in biofuels and bioproducts. This effort underscores the government’s commitment to advancing lignin utilization in sustainable applications.
Similarly, the European Union’s Bioeconomy Strategy encourages the use of biological resources, including lignin, to promote sustainable growth. This strategy supports the development of bio-based industries and the adoption of lignin-derived products, aligning with the EU’s broader goals of reducing reliance on fossil fuels and enhancing environmental sustainability.
In India, the government has implemented policies to promote the use of biofuels and bio-based materials. For instance, the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas has allowed the use of biofuels made from agricultural residues, such as stubble, in aviation fuel. This policy not only addresses environmental concerns but also supports the utilization of lignin-rich agricultural residues in biofuel production, indirectly fostering the development of lignin-based materials for various applications, including food packaging.
Restraints
Challenges in Commercializing Kraft Lignin for Food Packaging
Despite the promising potential of kraft lignin as a sustainable alternative for food packaging, several challenges hinder its widespread adoption. One of the primary obstacles is the complex and variable chemical structure of lignin, which varies depending on the plant source and extraction process. This heterogeneity leads to inconsistent properties, making it difficult to standardize lignin-based materials for commercial use.
Additionally, lignin’s low reactivity and solubility pose significant challenges in processing and integration into packaging materials. These issues necessitate extensive chemical modifications to enhance its compatibility with other biopolymers, which can be costly and time-consuming.
Another significant barrier is the lack of established regulatory frameworks for lignin-based food packaging. In many regions, food safety regulations do not yet accommodate materials derived from lignin, leading to uncertainties regarding their approval for use in direct contact with food products. This regulatory gap creates hesitancy among manufacturers and consumers alike, slowing the adoption of lignin-based packaging solutions.
Furthermore, the scalability of lignin extraction and processing remains a concern. While lignin is abundantly produced as a byproduct in the paper and pulp industry, the infrastructure to efficiently extract and process it into high-quality materials suitable for food packaging is still under development. The absence of large-scale facilities and standardized processes limits the availability and affordability of lignin-based packaging options.
Opportunity
Growth Opportunities for Kraft Lignin in Food Packaging
A significant growth opportunity for kraft lignin lies in its application as a sustainable material in food packaging. With over 50 million tons of lignin produced annually as a byproduct of the pulp and paper industry, a substantial portion of this biomass is currently underutilized. Traditionally, approximately 98% to 99% of industrial lignin is incinerated for energy recovery, while only about 1% to 2% is converted into value-added products like lignosulfonates. This presents a considerable opportunity to redirect lignin towards more sustainable applications, such as food packaging materials.
The European Union’s Circular Economy Action Plan and the European Strategy for Plastics in a Circular Economy are pivotal in promoting the use of renewable resources like lignin in packaging. These policies aim to ensure that all plastic packaging placed on the EU market is reusable or recyclable by 2030, encouraging the development of bio-based alternatives to traditional plastics.
Research indicates that lignin-based materials exhibit promising properties for food packaging, including antioxidant, antibacterial, and UV barrier capabilities. For instance, studies have shown that incorporating lignin into biodegradable polymer films can enhance their mechanical strength and provide additional protection against food spoilage . Furthermore, lignin’s natural origin and biodegradability align with the growing consumer demand for environmentally friendly packaging solutions.
Regional Insights
North America Leads with 48.2% Share (USD 0.8 Billion) as the Dominant Region
In 2024, North America accounted for approximately 48.2% of the global Kraft lignin market, representing a regional market value of around USD 0.8 billion. This leadership position is a reflection of strong industrial uptake of kraft lignin across varied applications such as construction chemicals, adhesives, agriculture, and carbon materials.
The North American region’s dominance is underpinned by environmental regulations and sustainability mandates that favor bio-based and circular economy materials. Both the United States and Canada have invested in research and infrastructure that support biorefinery development and lignin valorization. As a result, kraft lignin consumption in North America is driven by demand from sectors seeking low-carbon, renewable feedstocks
By 2025, North America is expected to retain its leading position, with steady growth aligned with rising demand for eco-friendly resins, dispersants, and agricultural additives. The regional market’s share of nearly half of the global kraft lignin market highlights ongoing momentum in innovation, regulatory incentives, and strong feedstock supply chains.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Domtar Corporation, headquartered in Montreal and Fort Mill, operates a large pulp and paper network across North America. Its Plymouth mill uses the LignoBoost process to produce BioChoice™ kraft lignin at up to 75 tonnes/day capacity. Domtar supplies kraft lignin to buyers such as UPM Biochemicals, supporting development of renewable phenolic resins and engineered biopolymers.
Rayonier Advanced Materials (RYAM) manufactures high-purity cellulose and kraft lignin co-products at its Fernandina Beach, Florida mill, in collaboration with Borregaard LignoTech. Its fiber-based materials support development of sustainable engineered polymers and lignin derivatives. While high-purity cellulose operations were suspended at Temiscaming, lignin value chains continue to be a strategic focus as part of its sustainable materials platform.
Nippon Paper Industries of Japan is the only lignin manufacturer in the country and offers branded lignin products—such as SAN X, VANILLEX, and PEARLLEX—with dispersing, binding, and chelating functions. These are deployed in concrete admixtures, binding agents, and chemical applications. Its chemical business efficiently utilizes wood-derived constituents, contributing to a diversified portfolio of cellulose and lignin-based specialties.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Borregaard Lignotech
- Domtar Corporation
- NIPPON PAPER INDUSTRIES CO. LTD
- Rayonier Advanced Materials
- Resolute forest products
- Stora Enso
- Suzano
- UPM Biochemicals
- West Fraser
- WestRock Company
- Weyerhaeuser Company
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024, Borregaard LignoTech remained the leading kraft lignin producer globally, supporting approximately 40 % of world production capacity through its network of plants across Norway, the US, Brazil, Germany, and the UK.
In 2024, Rayonier Advanced Materials operated a high‑yield pulp mill in Temiscaming, Canada, with an annual capacity of about 290,000 MT, of which approximately 65,000 MT was used internally to produce high‑purity cellulose and kraft lignin co‑products.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 1.7 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 3.4 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 7.2% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Form (Powder, Liquid, Granules), By Source (Softwood, Hardwood, Hybrid), By Application (Adhesives, Carbon Fiber Production, Animal Feed, Bioresins, Soil Conditioning, Others), By End Use (Construction, Agriculture, Food Beverage, Pharmaceutical, Personal Care, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Borregaard Lignotech, Domtar Corporation, NIPPON PAPER INDUSTRIES CO. LTD, Rayonier Advanced Materials, Resolute forest products, Stora Enso, Suzano, UPM Biochemicals, West Fraser, WestRock Company, Weyerhaeuser Company Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Borregaard Lignotech
- Domtar Corporation
- NIPPON PAPER INDUSTRIES CO. LTD
- Rayonier Advanced Materials
- Resolute forest products
- Stora Enso
- Suzano
- UPM Biochemicals
- West Fraser
- WestRock Company
- Weyerhaeuser Company










