Global Food Texture Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Type (Cellulose Derivatives, Gums, Pectin, Gelatin, Starch, Inulin, Dextrin, Others), By Source (Natural, Synthetic), By Functionality (Thickening, Gelling, Emulsifying, Stabilizing, Others), By Form (Dry, Liquid), By Application (Bakery And Confectionery Products, Dairy And Frozen Foods, Meat And Poultry Products, Beverages, Snacks And Savory, Sauces And Dressings, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Dec 2025
- Report ID: 170039
- Number of Pages: 284
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
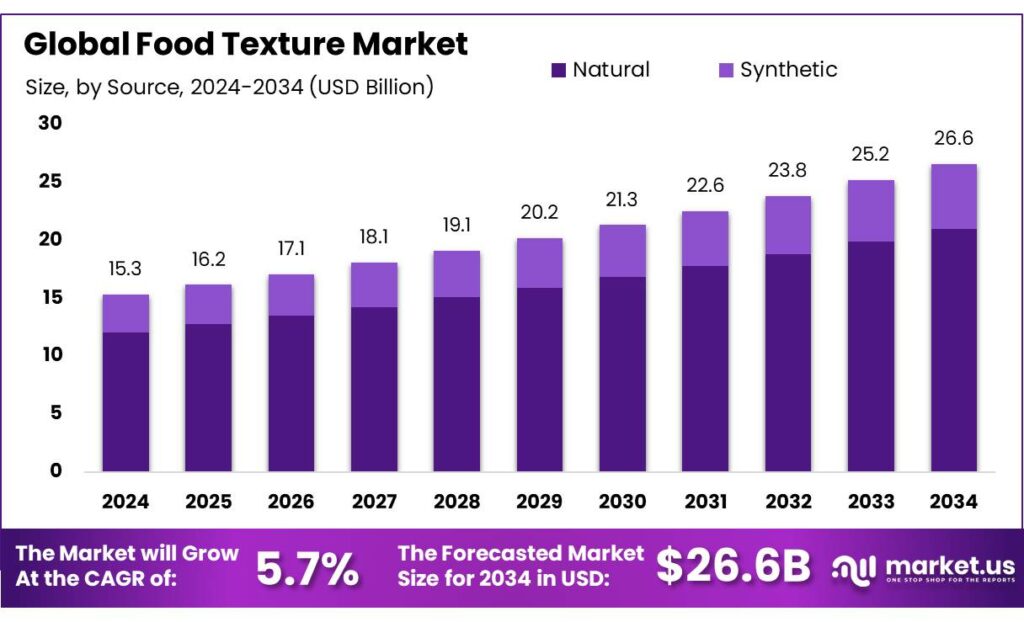
The Global Food Texture Market size is expected to be worth around USD 26.6 Billion by 2034, from USD 15.3 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 5.7% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North American held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.8% share, holding USD 6.7 Billion revenue.
Food texture is now treated as a strategic design variable in the global food industry rather than a secondary sensory attribute. As trade in agricultural and processed foods has expanded—FAO notes that the value of global agricultural exports in 2023 was 1.7 times higher than in 2010, while agriculture’s share of merchandise trade rose from 7% to 8%—manufacturers are increasingly using texture systems to differentiate products, localize formulations and manage shelf-life across long supply chains.
- Industrial demand for texture solutions is tightly linked to the shift toward processed and ultra-processed foods. A joint UNCTAD–WHO analysis reports that processed foods account for about 48% of total food imports in developed economies versus roughly 35% in developing ones. FAO further estimates that ultra-processed foods represent 7% of globally traded calories and about 12% of food import volumes in high-income countries as of 2021. In parallel, a Lancet analysis finds that ultra-processed foods already constitute roughly 50% of household food intake in many high-income countries.
At the same time, the public-health context is reshaping how industry approaches texture. UNICEF reports that 188 million children and adolescents are now living with obesity, as global childhood obesity prevalence has risen from about 3% to 9.4% since 2000, while underweight rates have fallen from 13% to 9.2%. This imbalance, driven partly by ultra-processed, energy-dense foods, is pushing regulators and brands to reformulate for lower salt, sugar and saturated fat while preserving indulgent texture, creating strong demand for advanced texturizing systems.
- Several major government initiatives explicitly support this reformulation agenda. In the United States, FDA’s voluntary sodium-reduction guidance covers 163 food categories and aims to cut average sodium intake from about 3,400 mg/day to 3,000 mg/day over 2.5 years, with new Phase II targets proposed in 2024. In India, FSSAI’s “Eat Right Movement”, launched on 10 July 2018, saw at least 15 large food firms pledge to reformulate products to reduce salt, sugar and fat and commit to “freedom from trans-fats by 2022”.
Consumer insight work from industry further supports investment in texture. Cargill’s proprietary research presented at SupplySide West shows that only 9% of surveyed consumers identified as vegan or vegetarian in 2022, down from 14% in 2021, while about 29% reported actively avoiding animal-based dairy versus 42% a year earlier.
Key Takeaways
- Food Texture Market size is expected to be worth around USD 26.6 Billion by 2034, from USD 15.3 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 5.7%.
- Starch held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 23.8% share.
- Natural held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 79.2% share.
- Thickening held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 34.7% share.
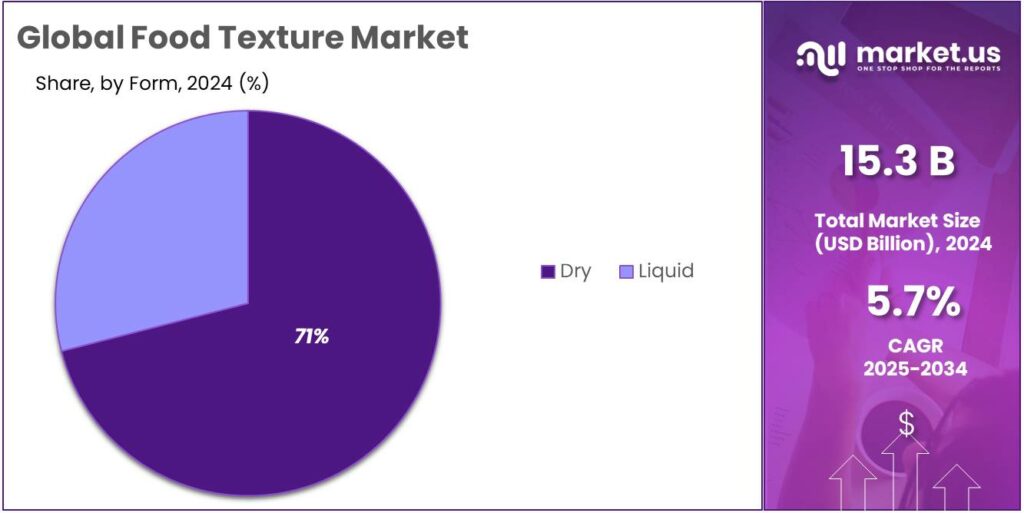
- Dry held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 71.3% share.
- Bakery & Confectionery Products held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 27.9% share.
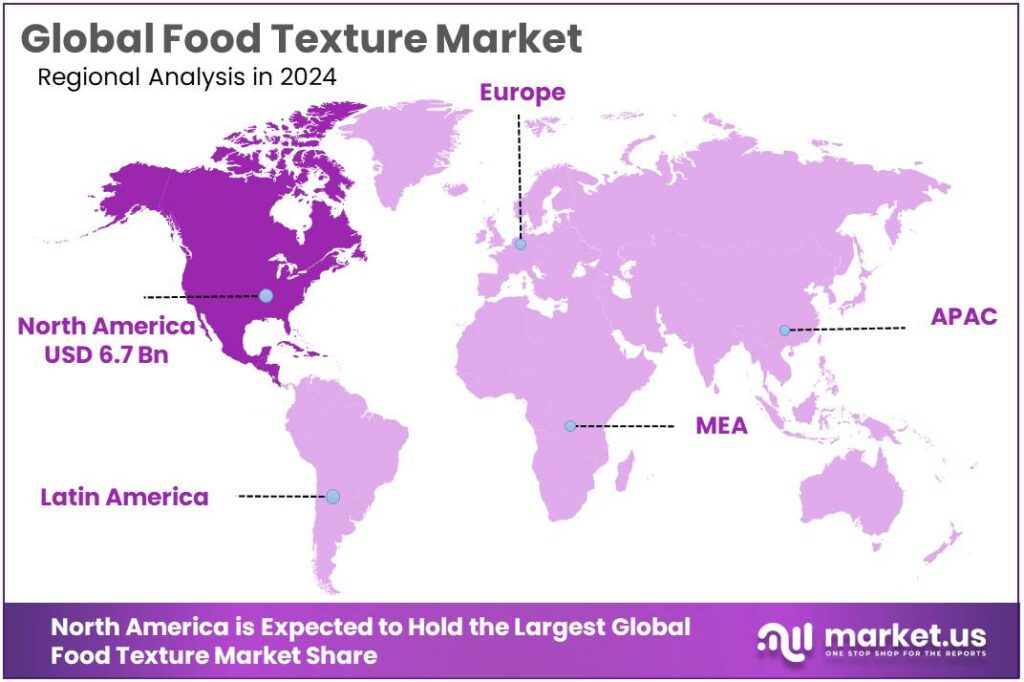
- North America held a dominant regional position in the food texture market, capturing 43.8% of global value and generating roughly USD 6.7 billion.
By Type Analysis
Starch dominates with 23.8% as the go-to natural thickener across food applications.
In 2024, Starch held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 23.8% share. This position was driven by its wide use as a texturizer, stabilizer and cost-effective bulking agent across sauces, soups, bakery, snacks and ready-to-eat meals. Preference for clean-label ingredients and simpler formulations has increased starch adoption, while ongoing product innovation—such as modified and pre-gelatinized grades—has expanded functional performance in chilled, frozen and high-shear processes.
Supply-chain stability and competitive pricing supported procurement decisions during 2024, and substitution away from synthetic thickeners was observed in several segments. From a regional perspective, demand was led by established food manufacturing hubs where process optimization and shelf-life extension were priorities. Into 2025, the starch segment was expected to remain prominent as manufacturers continued to prioritise natural texture solutions, cost control and regulatory acceptance, with incremental growth supported by new applications in plant-based and convenience food categories.
By Source Analysis
Natural dominates with 79.2% as clean-label ingredients remain the preferred choice.
In 2024, Natural held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 79.2% share. This strong lead was supported by rising consumer interest in clean-label, minimally processed and plant-derived ingredients across bakery, dairy, beverages and convenience foods. Natural texturizers such as starches, gums, pectins and fibers were widely adopted because they offer reliable thickening, stabilization and mouthfeel enhancement without synthetic additives.
Food manufacturers increased their use of natural sources in 2024 to meet regulatory expectations and strengthen product transparency, especially in premium and health-oriented categories. Supply availability from agricultural raw materials ensured stable procurement, while cost efficiency further encouraged large-scale adoption. Moving into 2025, the natural segment is expected to retain its lead, driven by continued reformulation efforts, demand for sustainable ingredient sourcing, and expansion of plant-based and clean-label product lines.
By Functionality Analysis
Thickening leads with 34.7% as demand rises for stable, uniform food textures.
In 2024, Thickening held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 34.7% share. This leadership was supported by its essential role in improving viscosity, mouthfeel and product stability across sauces, soups, dressings, dairy products, bakery fillings and ready meals. The need for consistent texture in large-scale food production encouraged the use of thickeners derived from starches, gums and plant fibers, all of which offered reliable performance under heat, shear and freezing conditions.
Manufacturers in 2024 increased their reliance on thickening agents as they worked to enhance sensory appeal while meeting clean-label requirements. Demand was further reinforced by the expansion of convenience foods and premium formulations where uniformity and shelf stability were prioritized. Going into 2025, the thickening segment is expected to maintain strong traction as companies continue reformulating products to improve texture, reduce waste and ensure stable performance across diverse processing environments.
By Form Analysis
Dry form dominates with 71.3% as it offers better stability and easier handling for manufacturers.
In 2024, Dry held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 71.3% share. The segment benefited from strong preference among food processors for powdered and granulated texturizers because they provide longer shelf life, simpler storage, and easier incorporation into large-scale production lines. Dry ingredients such as starches, gums, pectins, and fibers were widely used to achieve thickening, gelling, stabilizing, and emulsifying functions without the handling challenges associated with liquid forms.
Their compatibility with automated dosing systems enabled better process control and reduced product variability in 2024. Cost efficiency and broader formulation flexibility also supported the segment’s leadership, particularly in bakery mixes, beverages, snacks, and ready-to-eat foods. As manufacturers prioritize clean-label reformulations and stable supply chains, the dry form is expected to maintain strong demand into 2025 due to its reliability, scalability, and efficient logistics.
By Application Analysis
Bakery & Confectionery leads with 27.9% as texture and shelf-life needs drive ingredient choice.
In 2024, Bakery & Confectionery Products held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 27.9% share. This leadership was driven by the constant need for consistent crumb structure, improved sliceability, moisture retention and extended shelf life in bread, cakes, fillings and confectionery items. Manufacturers increased the use of texturizers, emulsifiers and stabilizers to meet consumer demand for soft mouthfeel and clean-label formulations, while processing efficiencies in large bakeries favoured ingredients that perform reliably under high shear and baking conditions.
Procurement decisions in 2024 were influenced by the dual priorities of cost control and product quality, prompting wide adoption of multifunctional systems that reduce formulation complexity. Attention to clean labeling and plant-based trends also encouraged reformulation efforts within the segment. Looking into 2025, the Bakery & Confectionery segment is expected to remain a key demand driver for food texture ingredients as product developers continue to balance sensory performance, shelf stability and ingredient transparency.
Key Market Segments
By Type
- Cellulose Derivatives
- Gums
- Pectin
- Gelatin
- Starch
- Inulin
- Dextrin
- Others
By Source
- Natural
- Synthetic
By Functionality
- Thickening
- Gelling
- Emulsifying
- Stabilizing
- Others
By Form
- Dry
- Liquid
By Application
- Bakery & Confectionery Products
- Dairy & Frozen Foods
- Meat & Poultry Products
- Beverages
- Snacks & Savory
- Sauces & Dressings
- Others
Emerging Trends
Soft, Joyful Textures in a Health-Conscious Food World
One of the clearest new trends in food texture is the move toward softer, smoother, “comforting” textures in products that also promise better health. As obesity and diet-related diseases rise, people are trying to cut sugar, fat and salt, but they don’t want to feel like they are being punished at mealtimes. The World Health Organization estimates that in 2022 around 2.5 billion adults were overweight and about 890 million were living with obesity, roughly 43% of the world’s adults. This pressure is pushing food companies to design textures that feel gentle, indulgent and emotionally reassuring, even in “light” or reformulated recipes.
Children and teenagers are part of the same story. UNICEF’s 2025 Child Nutrition Report shows that, for the first time, obesity among 5–19-year-olds (9.4%) has slightly overtaken underweight (9.2%), affecting about 188 million school-age children and adolescents worldwide. Parents are therefore hunting for snacks and drinks that still feel fun and comforting in the mouth, but carry less sugar and fat. This is a big reason why texture work has shifted away from extremely hard, sticky or “extreme” experiences towards softer bites, airy foams and creamy gels that can be delivered with more fibre and protein.
This trend goes well beyond candy. Plant-based meat and dairy alternatives also live or die on texture. Work from the Good Food Institute, using industry and public data, estimates that meeting ambitious global targets would require around 39 million tonnes of alternative meat demand by 2030, assuming price parity with conventional meat. To reach those volumes, plant-based burgers, yogurts and cheeses must not only taste good but also deliver the spring, bite, creaminess and melt that people associate with animal products. Many developers now start projects with a “texture brief” first and then build flavour and nutrition around it.
Drivers
Health-Focused Processed Foods Reformulation Drives Food Texture Demand
A big force behind the food-texture sector today is the global push to make processed foods healthier without losing pleasure in every bite. Across many high-income countries, ultra-processed foods already supply about 42–58% of daily calorie intake, according to a 2024 umbrella review in The BMJ. When so much of the diet comes from packaged products, manufacturers know that creamy, crispy or chewy textures are what keep people loyal, even as recipes change.
- At the same time, governments and health agencies are sounding the alarm on diet-related disease. UNICEF’s 2025 Child Nutrition Report shows that obesity has, for the first time, overtaken underweight among school-age children and adolescents. Around 188 million young people – roughly 1 in 10 worldwide – are now living with obesity, up from about 3% in 2000 to 9.4% in recent estimates. This data tells food companies that “business as usual” with salt, sugar and fat is no longer acceptable.
Regulators are responding with specific numeric targets that directly reshape how texture systems are used. In the United States, the FDA’s voluntary sodium-reduction goals aim to bring average intake down from about 3,400 mg/day to 3,000 mg/day in Phase I, with a longer-term Phase II draft target of roughly 2,750 mg/day for the population. Cutting that much sodium from soups, sauces, snacks or ready meals is technically hard. Firms lean on hydrocolloids, starches and flavour-modulating texture systems to maintain body, crunch and mouthfeel when salt is removed.
Restraints
Rising Additive Skepticism and Tight Rules Slow Food Texture Expansion
One big brake on the food-texture business is the growing mistrust of “chemicals” in food, especially the emulsifiers, stabilisers and gums that actually create texture. At the same time, health concerns linked to ultra-processed foods keep regulators under pressure. The World Health Organization estimates that in 2022 about 2.5 billion adults were overweight and 890 million were living with obesity – roughly 43% of adults worldwide. As public debate increasingly blames packaged foods and additives, any ingredient that “sounds chemical” becomes harder to defend on a label, even when it is safe.
Ultra-processed foods already supply a very large share of calories in rich countries. A 2024 analysis in The BMJ reports that ultra-processed foods contribute between 42% and 58% of total dietary energy intake across high-income countries. These products rely heavily on texturising systems to deliver crunch, creaminess and chew. Because the same body of research links high ultra-processed intake with obesity and chronic disease, texture ingredients—rightly or wrongly—are often bundled into the public’s suspicion, making brands reluctant to use complex stabiliser blends.
Regulation reflects this tension. The Codex Alimentarius General Standard for Food Additives defines a “maximum use level” for each additive as the highest concentration, usually expressed in mg/kg of food, that is both functionally effective and considered safe. National authorities then convert this into detailed rules. The UK Food Standards Agency notes that there are currently 325 additives defined and authorised in Great Britain, most of them only allowed in specific foods and under strict quantitative limits. For texture suppliers, this means any new molecule or higher usage level requires lengthy risk assessment and legal change, which slows down innovation and adds regulatory cost.
Global efforts to cut food loss and waste also create subtle constraints. FAO estimates that around 14% of food produced is lost between harvest and retail and a further 17% is wasted at retail and consumer level – together worth about US$400 billion each year. Governments and NGOs now push for solutions that reduce waste without simply “adding more chemicals”, favouring better storage, logistics and packaging. This can make highly functional synthetic texturisers politically sensitive, even when they could extend shelf-life and reduce spoilage.
Opportunity
Clean-Label Texture Systems for Healthier Plant-Based Foods
One of the biggest growth openings in food texture is helping plant-based and “better-for-you” foods feel as good as the products they aim to replace. Health data keeps pushing this shift. The World Health Organization estimates that in 2022 about 2.5 billion adults were overweight and over 890 million were living with obesity – around 43% of all adults. This is forcing governments, retailers and brands to look for foods that are lighter in calories, salt and fat, but still deeply satisfying in the mouth.
At the same time, global crop output keeps rising, supporting a wider palette of plant ingredients that can be turned into texturizers. FAO reports that primary crop production reached about 9.9 billion tonnes in 2023, up 27% since 2010. Cereals, pulses and oilseeds provide starches, proteins and fibres that can be processed into clean-label gums, gels and fat mimetics. Texture companies that can transform this raw plant abundance into simple, familiar-sounding ingredients have a strong runway ahead.
Youth nutrition trends add more urgency. UNICEF’s 2025 child nutrition report shows that, for the first time, obesity among 5–19-year-olds (9.4%) has slightly surpassed underweight (9.2%), affecting about 188 million school-age children and adolescents worldwide. Families are looking for snacks, dairy drinks and ready meals that feel like treats but are nutritionally safer. That’s exactly where advanced food texture comes in: creating soft, airy, crunchy or creamy sensations using plant proteins and fibres instead of extra sugar and fat.
Regional Insights
North America dominates with 43.8% share and approximately USD 6.7 billion in 2024
In 2024, North America held a dominant regional position in the food texture market, capturing 43.8% of global value and generating roughly USD 6.7 billion in revenues; this dominance was supported by a concentrated food-manufacturing base, advanced processing capabilities, and widespread adoption of texture systems across bakery, dairy, convenience and meat-alternative segments.
The region’s leadership was driven by strong investment in product reformulation for clean-label and plant-based offerings, where demand for natural thickeners, stabilizers and texturizers accelerated procurement cycles; processors in the United States and Canada accounted for a significant portion of industrial volumes, while rising export flows amplified regional production intensity.
Supply-chain maturity and proximity to raw-material sources reduced lead times and enabled rapid scale-up for new functional grades, which in turn encouraged greater use of dry powdered systems and multifunctional blends. Regulatory clarity on ingredient labelling and food safety standards supported faster adoption of certified natural sources, and procurement tended to favour suppliers able to provide traceability and technical application support.
In 2024, large-scale bakeries, industrial savoury processors and beverage formulators represented the bulk of demand, with smaller but fast-growing contributions from plant-based and ready-meal manufacturers. Looking into 2025, North America is expected to retain its leading position in absolute value terms as reformulation and convenience-food expansion continue to underpin texture ingredient consumption; market participants are likely to prioritise solutions that deliver consistent performance, scalability and demonstrable supply-chain transparency.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Ajinomoto Co., Inc. — Ajinomoto’s food-ingredient and functional-ingredient business supports texture and savoury systems used in food processing. In 2024 the group reported USD 9.93 billion in revenue and maintained a global workforce of ~110,000; these resources underpinned application support for starches, hydrocolloids and enzymatic systems used in bakery and savoury formulations.
Ashland — Ashland provides specialty food-grade binders, texturizers and processing aids for bakery and confectionery applications. In fiscal 2024 the company recorded USD 2.11 billion in net sales and reported ~USD 169 million in net income for the year, supporting continued R&D in application-centric additives for texture improvement.
International Flavors & Fragrances (IFF) — IFF supplies hydrocolloids, proteins and flavour-functional systems used to tune mouthfeel and texture. The company reported USD 2.44 billion in reported sales for full-year 2024; restructuring and impairment actions in 2024 affected near-term profitability but left core ingredient capabilities intact for food-texture projects.
Cargill — Cargill is a major supplier of starches, texturizers and processing solutions for global food industries. Fiscal 2024 revenues were approximately USD 160 billion, with a workforce above 160,000; this scale supports wide raw-material sourcing, custom starch grades and technical services for large food processors and ingredient formulators.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Ajinomoto Co. Inc.
- ADM
- Ashland
- IFF
- Cargill
- Avebe
- CP kelco
- kerry group
- DSM
- Ingredion
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024, Ajinomoto reported consolidated sales of ¥1.53 trillion (≈ USD 10.6 billion) and a business profit of ¥147.6 billion, supported by a global workforce of ~34,860 employees; these numeric indicators demonstrate capacity to supply functional ingredients and application support to food manufacturers.
In 2024, Ajinomoto reported consolidated sales of ¥1.53 trillion (≈ USD 10.6 billion) and a business profit of ¥147.6 billion, supported by a global workforce of ~34,860 employees; these numeric indicators demonstrate capacity to supply functional ingredients and application support to food manufacturers.
In 2024, Cargill reported USD 160.0 billion in annual revenues and employed ~160,000 people, figures that demonstrate the company’s scale to supply starches, syrups and other texture-building ingredients to global food manufacturers.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 15.3 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 26.6 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 5.7% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Type (Cellulose Derivatives, Gums, Pectin, Gelatin, Starch, Inulin, Dextrin, Others), By Source (Natural, Synthetic), By Functionality (Thickening, Gelling, Emulsifying, Stabilizing, Others), By Form (Dry, Liquid), By Application (Bakery And Confectionery Products, Dairy And Frozen Foods, Meat And Poultry Products, Beverages, Snacks And Savory, Sauces And Dressings, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Ajinomoto Co. Inc., ADM, Ashland, IFF, Cargill, Avebe, CP kelco, kerry group, DSM, Ingredion Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Ajinomoto Co. Inc.
- ADM
- Ashland
- IFF
- Cargill
- Avebe
- CP kelco
- kerry group
- DSM
- Ingredion










