Global COVID-19 Saliva Sampling Test Potential Market By Mode (Centralized Testing and Decentralized Testing), By Technology (Fluorescence-labeled Antigen/Antibodies Testing, RT-PCR and CRISPR-CAS9), By Location (Corporate Campus Environments, Travel Stations, Sports Arenas, Entertainment Venues and Universities & Colleges), Region and Companies – Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Dec 2025
- Report ID: 171322
- Number of Pages: 381
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
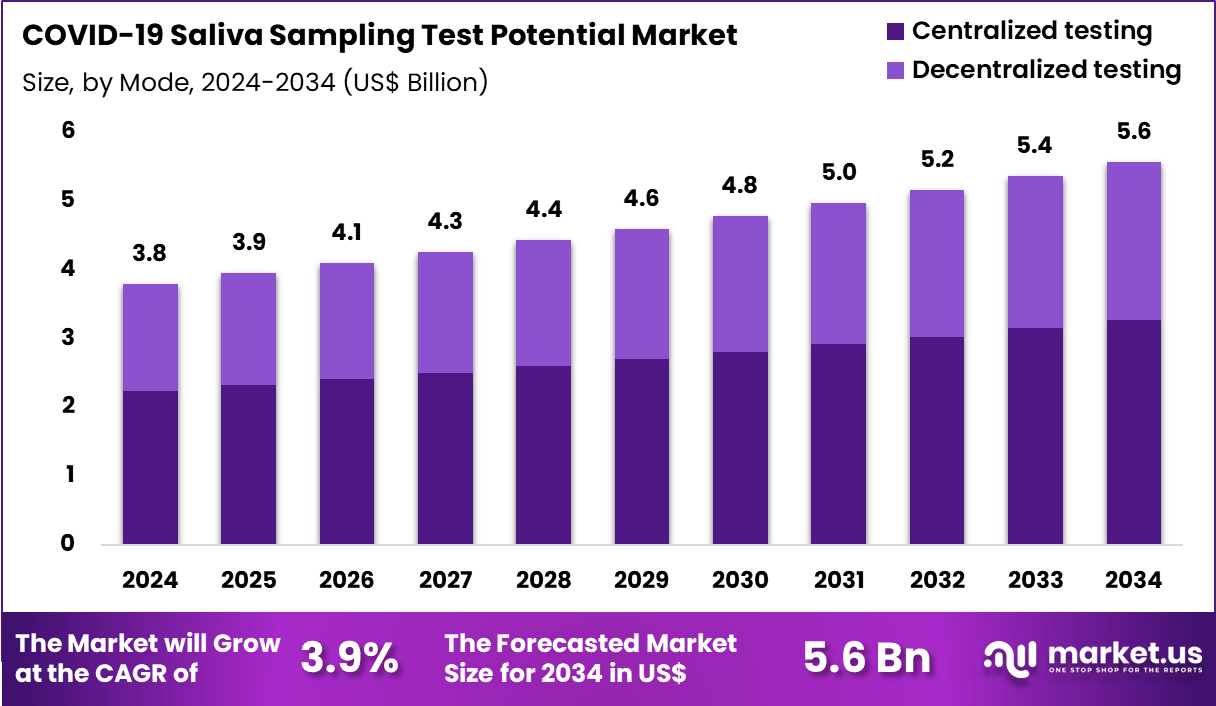
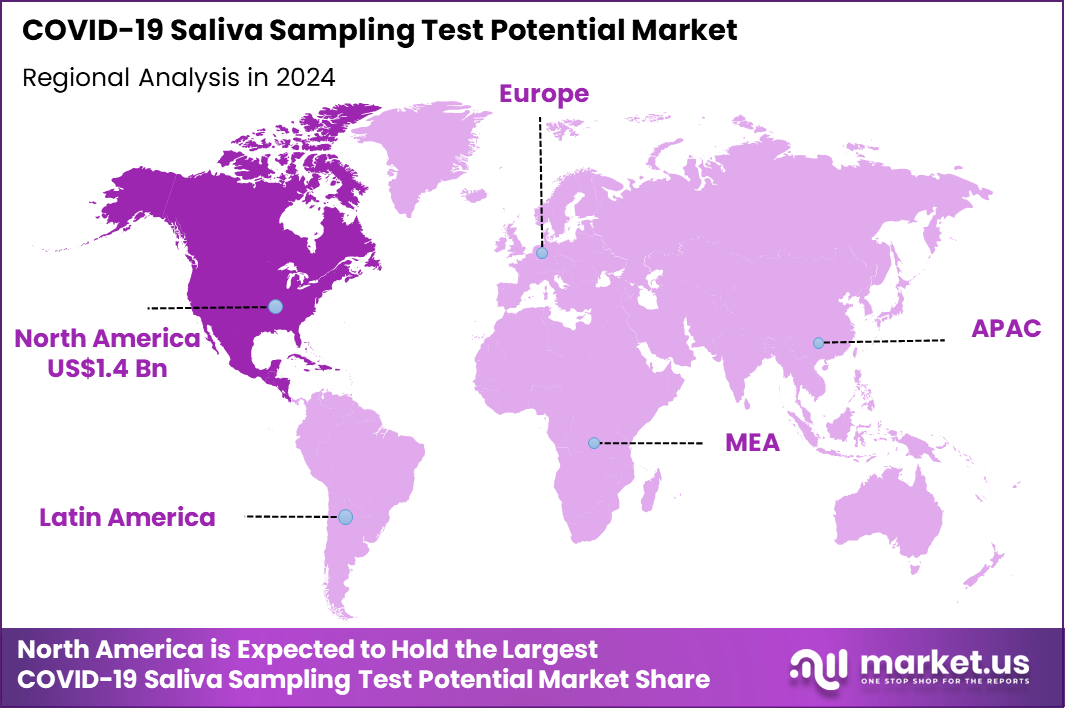
The Global COVID-19 Saliva Sampling Test Potential Market size is expected to be worth around US$ 5.6 Billion by 2034 from US$ 3.8 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 3.9% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North America led the market, achieving over 37.5% share with a revenue of US$ 1.4 Billion.
Increasing demand for non-invasive diagnostics propels the COVID-19 Saliva Sampling Test Potential market, as healthcare providers prioritize patient comfort and operational efficiency in mass screening scenarios. Diagnostic firms innovate with user-friendly collection kits that capture viral RNA from saliva without specialized training, reducing swab-related discomfort and supply dependencies.
These tests enable workplace surveillance for employee health assurance, school reopenings through asymptomatic student pooling, travel checkpoint verifications for rapid clearance, and community outbreak containment via drive-through stations. Public-private partnerships accelerate validation and deployment, creating opportunities for scalable, at-home formats that integrate with telehealth for result counseling.
In April 2023, BARDA partnered with Aptitude Medical Systems to expedite molecular diagnostics using saliva samples, affirming their clinical viability and broadening access to reliable testing beyond conventional healthcare venues. This collaboration underscores saliva’s role in democratizing diagnostics and fuels market expansion through enhanced equity in access.
Growing integration of multiplex molecular platforms accelerates the COVID-19 Saliva Sampling Test Potential market, as laboratories consolidate workflows to detect SARS-CoV-2 alongside influenza and RSV from single specimens. Biotechnology companies refine RT-PCR and CRISPR-based kits that process saliva with minimal preprocessing, delivering results in under two hours for timely interventions.
Applications encompass emergency department triage for febrile presentations, nursing home resident monitoring to safeguard vulnerable groups, athletic event participant screening for safe competition resumption, and pharmaceutical trial enrollment for precise cohort stratification. Technological refinements open avenues for point-of-care analyzers that minimize lab bottlenecks during surge periods.
Diagnostic developers increasingly collaborate with digital health firms to enable app-linked result sharing and automated exposure notifications. This convergence drives efficiency and positions saliva testing as a versatile tool in seasonal respiratory management.
Rising adoption of decentralized testing models invigorates the COVID-19 Saliva Sampling Test Potential market, as organizations deploy self-collection kits to empower individuals and reduce facility overcrowding. Innovators engineer stable, ambient-transportable reagents that maintain RNA integrity for mail-in processing, supporting remote diagnostics.
These solutions facilitate corporate wellness programs for ongoing employee health checks, university dormitory surveillance for cluster detection, entertainment venue entry protocols for crowd safety, and factory shift rotations to prevent production halts. Emerging opportunities include AI-enhanced result interpretation that flags variants and predicts transmission risks.
Research consortia actively validate saliva’s sensitivity against nasopharyngeal standards, paving the way for regulatory endorsements in non-clinical settings. This self-reliant paradigm transforms saliva testing into a cornerstone of resilient public health infrastructure.
Key Takeaways
- In 2024, the market generated a revenue of US$ 3.8 Billion, with a CAGR of 3.9%, and is expected to reach US$ 5.6 Billion by the year 2034.
- The mode segment is divided into centralized testing and decentralized testing, with centralized testing taking the lead in 2024with a market share of 58.7%.
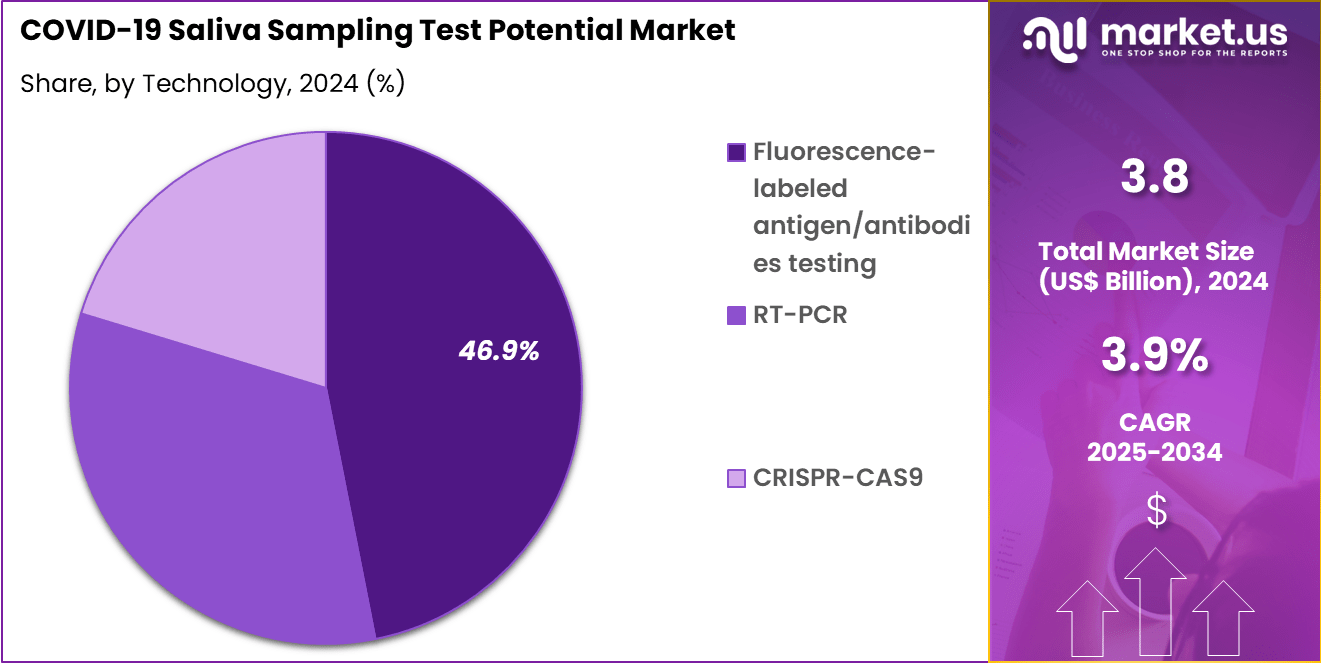
- Considering technology, the market is divided into fluorescence-labeled antigen/antibodies testing, RT-PCR and CRISPR-CAS9. Among these, fluorescence-labeled antigen/antibodies testing held a significant share of 46.9%.
- Furthermore, concerning the location segment, the market is segregated into corporate campus environments, travel stations, sports arenas, entertainment venues and universities & colleges. The corporate campus environments sector stands out as the dominant player, holding the largest revenue share of 39.4% in the market.
- North America led the market by securing a market share of 37.5% in 2024.
Mode Analysis
Centralized testing, holding 58.7%, is expected to dominate due to its high operational efficiency and ability to process large sample volumes with strong accuracy requirements. Centralized laboratories rely on advanced automation and standardized equipment, ensuring reliable quality control. Growing demand for mass-scale screening during outbreaks, especially in densely populated regions, strengthens the need for centralized workflows.
Government-supported testing programs rely heavily on centralized facilities for reporting and surveillance. High throughput and reduced cost per test make centralized testing a practical choice for routine monitoring and clinical decision-making. Increasing investments in laboratory infrastructure worldwide are projected to accelerate this adoption further.
Technology Analysis
Fluorescence-labeled antigen/antibodies testing, holding 46.9%, is anticipated to remain dominant due to faster turnaround times and simplified testing protocols. These assays detect viral proteins or immune responses directly from saliva samples, making them suitable for rapid screening. Their ability to provide near-immediate results supports timely isolation and intervention strategies.
The affordability and portability of fluorescence-based kits encourage widespread adoption across healthcare networks and workplace screening programs. Continuous improvements in sensitivity strengthen their reliability in identifying infectious individuals. These advancements are expected to fuel ongoing market expansion for fluorescence-based saliva testing.
Location Analysis
Corporate campus environments, holding 39.4%, are projected to dominate due to the rise of workplace health safety initiatives. Large corporate offices adopt saliva-based surveillance to maintain uninterrupted operations and employee well-being. Non-invasive collection increases compliance, making frequent testing manageable.
The shift toward hybrid and on-site working strengthens demand for practical and fast testing options. Partnerships between corporations and diagnostic providers promote integrated on-site testing programs. As organizations emphasize early detection and infection prevention, corporate campuses are likely to remain the leading testing location segment in this market.
Key Market Segments
By Mode
- Centralized Testing
- Decentralized Testing
By Technology
- Fluorescence-labeled Antigen/Antibodies Testing
- RT-PCR
- CRISPR-Cas9
By Location
- Corporate Campus Environments
- Travel Stations
- Sports Arenas
- Entertainment Venues
- Universities & Colleges
Drivers
Non-invasiveness of saliva collection is driving the market
The non-invasive nature of saliva sampling for COVID-19 testing eliminates the discomfort associated with nasopharyngeal or oropharyngeal swabs, thereby encouraging higher participation rates among diverse populations. This method requires no specialized equipment beyond simple collection tubes, reducing the need for trained healthcare personnel and enabling self-collection in various settings.
Consequently, it facilitates broader testing access, particularly in community and remote areas where invasive procedures may deter individuals. During the endemic phase of the COVID-19 pandemic, this advantage has accelerated adoption by minimizing procedural barriers and enhancing user compliance. Saliva collection also lowers the risk of aerosol generation compared to swab-based methods, aligning with infection control protocols in healthcare facilities.
As a result, public health initiatives have increasingly incorporated saliva tests to achieve higher screening volumes without compromising safety. The simplicity of the process supports repeated testing, which is essential for ongoing surveillance and early detection efforts.
Furthermore, it promotes equity by accommodating populations averse to invasive diagnostics, such as children and the elderly. By streamlining logistics, non-invasiveness contributes to cost efficiencies in large-scale testing programs. Overall, this driver has propelled the potential of saliva-based COVID-19 tests toward sustained market integration.
Restraints
Variability in sensitivity across SARS-CoV-2 variants is restraining the market
The diagnostic sensitivity of saliva-based RT-PCR assays for COVID-19 exhibits notable variability depending on the dominant SARS-CoV-2 variant, which undermines confidence in consistent performance. Studies from 2020 to 2022 indicate an overall saliva sensitivity of 61.7% when benchmarked against nasopharyngeal swabs as the reference standard. For pre-Delta variants, sensitivity stood at 58.5%, reflecting challenges in viral detection from saliva specimens.
In contrast, Delta variant infections achieved a higher sensitivity of 79.6%, yet this elevation did not persist across subsequent strains. Omicron variant sensitivity dropped to 61.5%, comparable to earlier variants and highlighting persistent limitations in asymptomatic cases. This fluctuation arises from differences in viral shedding patterns in the oral cavity, influenced by variant-specific tropism.
Symptomatic individuals showed markedly higher detection rates, with odds 3.45 times greater than in asymptomatic ones, complicating universal application. High nasopharyngeal viral loads correlated with 4.0-fold increased odds of saliva positivity, but mismatches still occurred frequently. Such inconsistencies necessitate confirmatory testing, increasing operational burdens and costs for end-users. Ultimately, this restraint tempers the reliability of saliva tests, limiting their standalone use in high-stakes diagnostic scenarios.
Opportunities
Scalability for large-scale surveillance is creating growth opportunities
The inherent scalability of saliva-based COVID-19 testing enables efficient processing of vast sample volumes, positioning it as a cornerstone for population-level surveillance programs. From April 2020 to December 2023, initiatives like the Arizona surveillance effort analyzed approximately 1.4 million saliva samples, identifying 94,330 infections with a 6.6% positivity rate. This capacity supports real-time outbreak detection through rapid turnaround times, averaging 12 days from collection to genomic sequencing data.
Saliva’s stability at ambient temperatures for up to 72 hours post-collection reduces logistical constraints, facilitating deployment in resource-limited environments. With 95% sensitivity and 99.2% specificity relative to nasopharyngeal swabs in paired validations, it offers robust accuracy for monitoring endemic transmission.
Integration with whole-genome sequencing on 69,595 positive samples yielded 54,040 high-quality genomes, enhancing variant tracking capabilities. Low invalid rates of 0.8% underscore the method’s reliability in high-throughput settings. Beyond detection, this scalability extends to multiplexing for co-infections, broadening applicability in public health networks.
As testing evolves toward integrated respiratory pathogen panels, saliva’s ease of self-collection amplifies opportunities for proactive epidemic management. In essence, these attributes foster expansion into routine surveillance frameworks, driving long-term market potential.
Impact of Macroeconomic / Geopolitical Factors
Macroeconomic forces boost the COVID-19 saliva sampling test potential market as healthcare investments climb and public health strategies evolve to track variants through non-invasive, at-home options that simplify surveillance and early detection. Developers swiftly advance user-friendly kits with rapid results, seizing opportunities in ongoing monitoring and integration with broader respiratory diagnostics to meet persistent global needs.
Lingering inflation and uneven economic recovery, however, strain public and private budgets, prompting health agencies to curtail routine testing programs and consumers to favor essential over optional screenings. Geopolitical strains, from U.S.-China trade barriers to supply interruptions in conflict zones, choke off access to specialized collection swabs and processing enzymes, breeding delays and cost spikes for international distributors.
Current U.S. tariffs, including a broad 10 percent levy on imports alongside targeted duties up to 145% on Chinese diagnostic components, inflate procurement expenses for saliva test materials and challenge affordability for American clinics and households. These policies provoke overseas countermeasures that snag U.S. kit shipments abroad and erode collaborative variant research efforts. Even so, the tariffs fuel aggressive reshoring of production lines and spur federal incentives for local innovation, crafting a tougher, more agile domestic ecosystem primed for reliable supply and expanded market leadership.
Latest Trends
Issuance of EUAs for at-home saliva tests is a recent trend
In 2024, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration issued several Emergency Use Authorizations for at-home saliva-based COVID-19 tests, signaling a shift toward decentralized diagnostics. For instance, on July 1, 2024, SalivaDirect received authorization for its real-time RT-PCR kit supporting home collection and pooling. This trend continued with the April 1, 2024, approval of the SalivaNow SARS-CoV-2 Assay by Lighthouse Lab Services, emphasizing single-target detection for accessibility.
By March 26, 2024, Nanobiosym’s Nano Test for COVID-19 was authorized, incorporating home collection for multiple targets. These developments reflect a broader emphasis on over-the-counter options, culminating in February 2025 authorizations for Aptitude Medical Systems’ Metrix COVID-19 and COVID/Flu Tests using loop-mediated isothermal amplification.
At least nine distinct saliva-related products, including collection devices, received EUAs in 2024-2025, enhancing consumer-led testing. This progression addresses barriers to clinic-based sampling, promoting self-testing in households. It aligns with ongoing needs for rapid, non-invasive tools amid variant circulation. Consequently, at-home saliva tests are gaining traction for personal and community monitoring. This 2024-2025 trend underscores regulatory momentum toward empowering users with convenient, FDA-vetted solutions.
Regional Analysis
North America is leading the COVID-19 Saliva Sampling Test Potential Market
North America accounted for 37.5% of the overall market in 2024, and the region witnessed considerable growth as public-health agencies, schools, and workplaces continued to use saliva-based testing as part of long-term SARS-CoV-2 surveillance efforts. Demand increased for non-invasive testing that supports frequent screening, especially in settings with high interaction levels such as universities and long-term care facilities.
Diagnostic laboratories adopted saliva-based RT-qPCR and isothermal amplification platforms because they reduce exposure risk for healthcare workers and eliminate the need for trained swab collectors. Research throughout 2023 and 2024 reinforced the accuracy of saliva testing, further supporting adoption. The CDC reported more than 1.1 million COVID-19 hospitalizations in the United States in 2023, highlighting the continued need for efficient testing in endemic conditions (CDC, 2023).
Consumers embraced convenient home-collection kits, while public policies encouraged accessible screening to prevent outbreaks. Together, these factors contributed to the strong expansion of saliva-based testing in North America during 2024.
The Asia Pacific region is expected to experience the highest CAGR during the forecast period
Asia Pacific is expected to experience notable growth during the forecast period as healthcare systems strengthen viral-surveillance infrastructure amid ongoing variant circulation. Countries with large populations increasingly prefer self-collection saliva methods to reduce strain on clinical staff and allow faster scaling of testing programs.
Governments are incorporating saliva-based screening into school health programs, community monitoring, and travel-safety measures. Higher awareness of asymptomatic transmission encourages individuals to test more frequently before gatherings or work. Diagnostic manufacturers in the region are expanding availability of saliva-compatible molecular assays, supporting broader access across urban and semi-urban markets.
The World Health Organization reported continued COVID-19 case activity across Asia Pacific in 2023, emphasizing the relevance of ongoing testing within community health strategies. These advancements position the region for sustained adoption of saliva-based diagnostics over the coming years.
Key Regions and Countries
North America
- US
- Canada
Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherland
- Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Key diagnostics manufacturers concentrate on saliva-based sampling portfolios that simplify self-collection, reduce reliance on swabs, and appeal to employers, public-health agencies, and travel programs that seek scalable screening. Management teams allocate capital to expand automated RT-PCR and molecular workflows that handle high sample volumes from mail-in, workplace, and community-testing channels while keeping turnaround times competitive.
Commercial leaders negotiate framework agreements with governments, universities, and large enterprises to secure recurring testing volumes and to position saliva collection as a default option in surveillance strategies. R&D groups refine stabilization chemistries that protect viral RNA in transport, extend ambient-temperature stability, and lower logistics complexity for decentralized programs across major regions.
Marketing and medical-affairs units run evidence-based campaigns that highlight comfort, accuracy, and cost advantages of saliva sampling, which helps shift clinician and consumer preference away from more invasive methods.
OraSure Technologies, through its DNA Genotek subsidiary, develops saliva collection devices that testing laboratories integrate into authorized COVID-19 assays, operates as a global specialist in non-invasive diagnostic and sample-collection solutions from its Bethlehem, Pennsylvania base, and leverages its manufacturing footprint and infectious-disease portfolio to deepen penetration in saliva-based screening markets.
Top Key Players
- Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.
- QIAGEN N.V.
- Roche Diagnostics
- Abbott Laboratories
- Hologic, Inc.
- Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.
- Takara Bio, Inc.
- GeneProof
Recent Developments
- In October 2024, a study featured in The Lancet Digital Health detailed progress on a compact saliva-based oral cancer test that incorporates artificial intelligence. The system can provide results in about 15 minutes, showcasing how digital diagnostics paired with saliva sampling are advancing well beyond their early use in COVID-19 testing.
- On November 16, 2024, Abbott Laboratories secured FDA Emergency Use Authorization for a rapid multiplex molecular test that can identify COVID-19, RSV, and Influenza A/B from a single nasal swab. This move reflects competitive pressure in the rapid diagnostics field, where developers of saliva-based solutions must offer similar levels of convenience and multi-pathogen coverage.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) US$ 3.8 Billion Forecast Revenue (2034) US$ 5.6 Billion CAGR (2025-2034) 3.9 Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, COVID-19 Impact, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Mode (Centralized Testing and Decentralized Testing), By Technology (Fluorescence-labeled Antigen/Antibodies Testing, RT-PCR and CRISPR-CAS9), By Location (Corporate Campus Environments, Travel Stations, Sports Arenas, Entertainment Venues and Universities & Colleges) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., QIAGEN N.V., Roche Diagnostics, Abbott Laboratories, Hologic, Inc., Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Takara Bio, Inc., GeneProof Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  COVID-19 Saliva Sampling Test Potential MarketPublished date: Dec 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
COVID-19 Saliva Sampling Test Potential MarketPublished date: Dec 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.
- QIAGEN N.V.
- Roche Diagnostics
- Abbott Laboratories
- Hologic, Inc.
- Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.
- Takara Bio, Inc.
- GeneProof










