Global Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain Market By Type (Public, Private, Hybrid), By Providers (Application providers, Middleware providers, Infrastructure providers), By Application (Risk and Compliance Management, Governance, Smart Contracts, Payment and Settlement, Product Traceability), Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2024-2033
- Published date: July 2024
- Report ID: 124280
- Number of Pages: 233
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
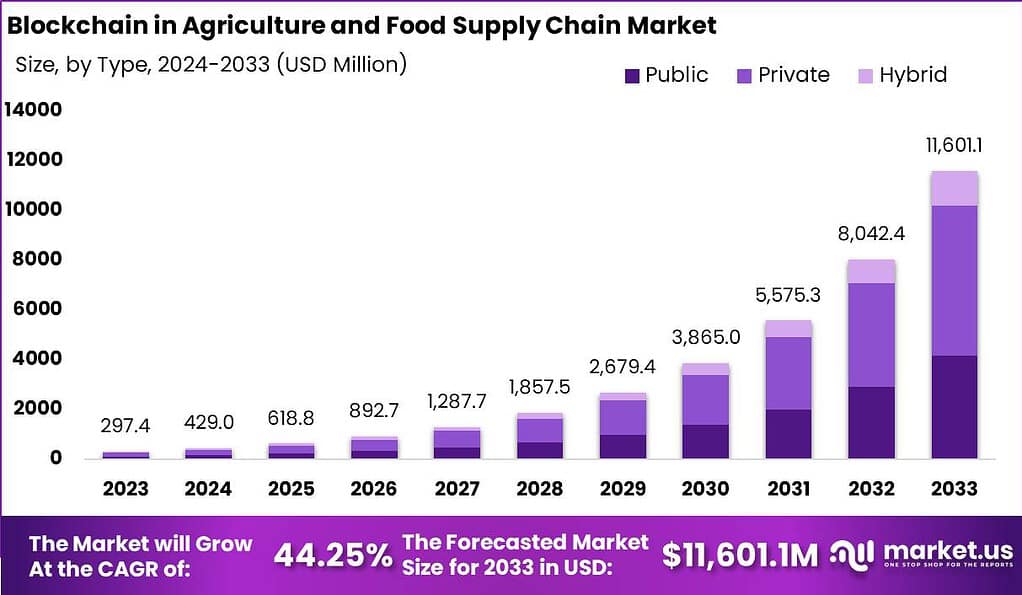
The Global Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain Market size is expected to be worth around USD 11,601.1 Million by 2033, from USD 297.4 Million in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 44.25% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
The Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain Market is poised for significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for transparency and traceability in food sourcing and distribution. Blockchain technology offers a robust solution for enhancing supply chain efficiency by providing a secure, immutable ledger for recording transactions. This ensures the integrity of data across the entire agricultural supply chain, from farm to table.
One of the primary growth factors in this market is the growing consumer awareness of food safety. Consumers are increasingly demanding information about the origin and handling of their food products, which blockchain technology can provide. Additionally, blockchain facilitates improved coordination between various stakeholders in the supply chain, such as farmers, processors, distributors, and retailers, leading to increased efficiency and reduced operational costs.
However, the adoption of blockchain faces several challenges. The high cost of implementing blockchain technology and the need for technical expertise to manage and maintain the blockchain system are significant hurdles. Additionally, there is a reluctance among some stakeholders to adopt new technologies, coupled with a lack of understanding of blockchain’s benefits.
Despite these challenges, the market holds promising opportunities for stakeholders. Companies can leverage blockchain to enhance product quality, ensure compliance with regulatory standards, and foster trust among consumers. Moreover, integrating blockchain with other technologies like IoT and AI can further revolutionize the agricultural and food supply chain, paving the way for a more sustainable and secure food system.
For instance, In May 2023, the Karnataka government introduced a blockchain-based seed traceability system across the state to enhance seed transportability. This initiative aimed to ensure the authenticity of seeds, increase transparency in seed distribution, and reduce incidents of seed theft.
Key Takeaways
- The Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain Market size is expected to be worth around USD 11,601.1 Million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 25% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
- In 2023, the Private segment held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 52% share.
- In 2023, the Application Providers segment held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 40% share.
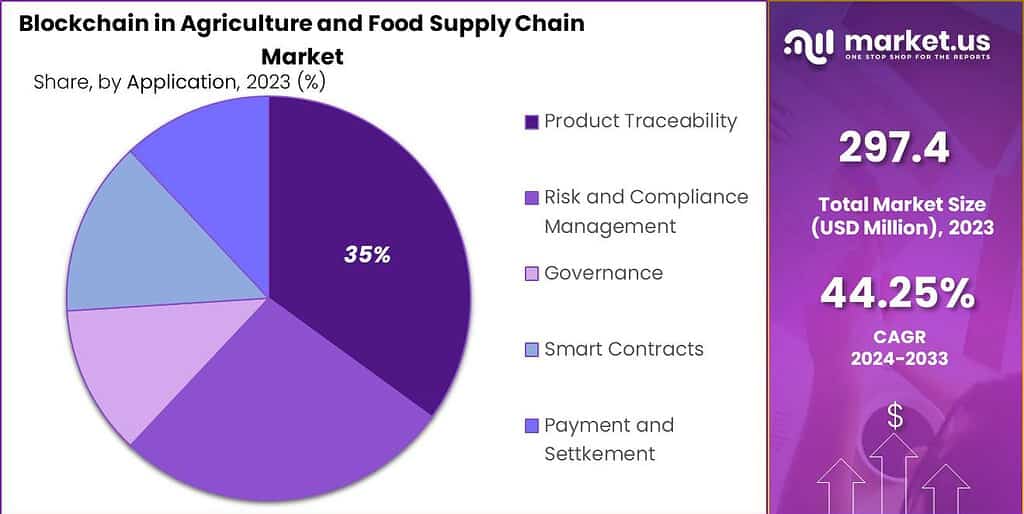
- In 2023, the Product Traceability segment held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 35% share.
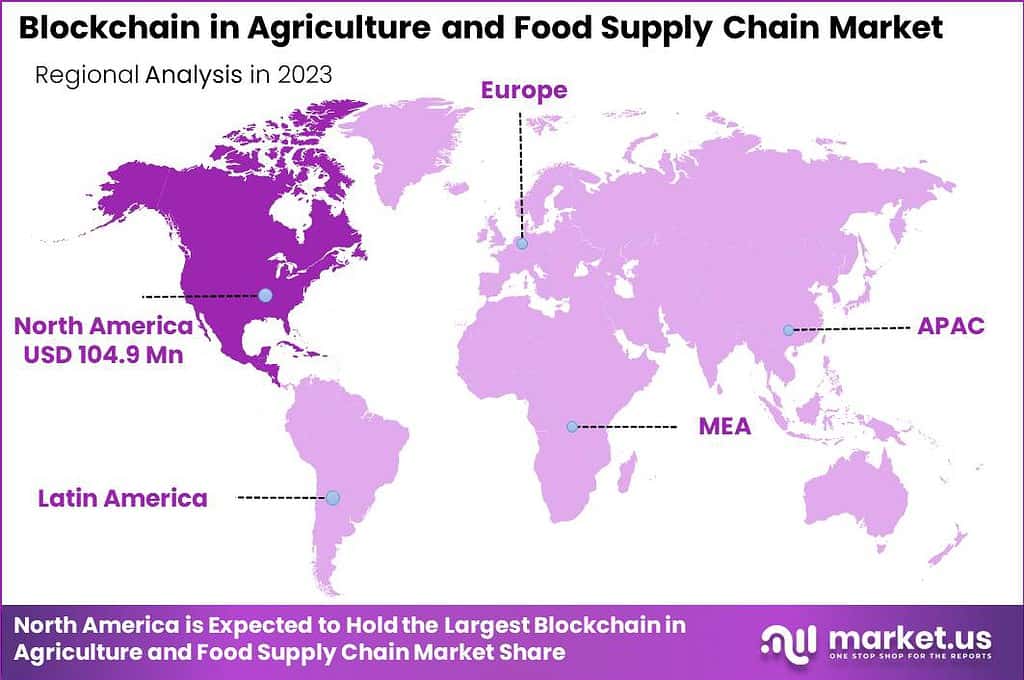
- In 2023, North America held a dominant market position in the blockchain in the agriculture and food supply chain sector, capturing more than a 35% share.
Type Analysis
In 2023, the Private segment held a dominant position in the Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain Market, capturing more than a 52% share. This leadership can be attributed to several factors that align with the unique needs of the agriculture sector.
Private blockchains offer enhanced security and privacy, critical in managing sensitive data related to food production and distribution. These systems allow only authorized participants to access the information, ensuring that data integrity is maintained and the risk of unauthorized tampering is minimized.
Private blockchains are particularly appealing in the agricultural sector where businesses often need to protect proprietary information while still benefiting from the efficiencies of blockchain technology. For instance, a company could use a private blockchain to track organic produce from the farm to the consumer, ensuring that all handling and processing meet strict organic standards without revealing sensitive operational details to competitors.
Additionally, the ability to set permissions at various levels enables businesses to manage who can view or alter the blockchain, providing a tailored approach that public or hybrid blockchains might not offer. The leading position of the private segment also stems from its scalability and speed, which are often superior to those of public blockchains.
In the agriculture and food supply chain, where timing and efficiency are crucial, private blockchains provide a fast, scalable solution that can handle large volumes of transactions without bogging down. This makes it particularly suitable for large agribusinesses and food producers who require robust, reliable technology to manage complex, global supply chains. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, the private segment is expected to maintain its dominance, driven by its ability to meet the specific, demanding needs of the agricultural sector.
Provider Analysis
In 2023, the Application Providers segment held a dominant market position in the Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain Market, capturing more than a 40% share. This segment’s prominence is largely due to its direct role in enhancing the functionality and user experience of blockchain technology within the agriculture sector.
Application providers develop specific blockchain-based solutions that address the practical needs of farmers, distributors, and retailers, such as tracking produce origin, ensuring compliance with health standards, and facilitating real-time data access across the supply chain. The success of the Application Providers segment is also driven by their ability to innovate and tailor solutions that integrate seamlessly with existing agricultural operations.
These applications not only help in tracking and verifying the authenticity of agricultural products but also simplify transactions and documentation, thereby reducing administrative burdens and increasing efficiency. For instance, blockchain applications can automate payments and contracts between farmers and buyers, ensuring transparency and trust without the need for intermediary verification.
Moreover, the demand for blockchain applications in agriculture is spurred by the growing consumer demand for transparency regarding the food they consume. Application providers play a crucial role in meeting this demand by offering solutions that provide clear, immutable records of food products from farm to table. As the agricultural sector continues to evolve with a greater focus on sustainability and ethical practices, the role of application providers is expected to expand, further solidifying their leadership in the market.
Application Analysis
In 2023, the Product Traceability segment held a dominant market position in the Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain Market, capturing more than a 35% share. This segment leads due to the critical need for transparency and authenticity in the food supply chain.
Blockchain technology enables detailed tracking of agricultural products from their origin to the end consumer, ensuring that all information regarding handling, processing, and shipping is accurate and immutable. This capability is essential for confirming product authenticity, particularly in markets sensitive to organic and non-GMO labels, where provenance is highly valued.
The significance of the Product Traceability segment is also heightened by the regulatory pressures and consumer demands for safe and reliable food products. Blockchain applications in this segment help comply with safety standards and regulatory requirements by providing a clear, auditable trail of product movements and handling processes. This reduces the risk of food fraud and improves response times during food recall events, enhancing consumer trust and safety.
Moreover, as global supply chains become more complex, the need for efficient traceability systems becomes more pronounced. Blockchain technology in product traceability not only boosts operational efficiency by reducing the need for manual tracking and verification but also facilitates greater cooperation and data sharing among stakeholders. This integrated approach is particularly advantageous in managing the challenges posed by global food supply chains, further driving the growth and predominance of the Product Traceability segment in the market.
Key Market Segments
By Type
- Public
- Private
- Hybrid
By Providers
- Application providers
- Middleware providers
- Infrastructure providers
By Application
- Risk and Compliance Management
- Governance
- Smart Contracts
- Payment and Settlement
- Product Traceability
Driver
Enhanced Traceability and Transparency
Enhanced traceability and transparency are pivotal drivers for the adoption of blockchain technology in the agriculture and food supply chain market. Blockchain provides an immutable, decentralized ledger that records every transaction and movement of goods from farm to table. This capability addresses critical issues such as food safety, fraud, and contamination by ensuring that every stakeholder in the supply chain can access reliable, tamper-proof information about product origins and handling processes.
With blockchain, each step of the supply chain is documented and time-stamped, creating a permanent record that is easily accessible and verifiable. This level of transparency helps in quickly identifying and isolating contaminated products, thereby mitigating the risks of widespread foodborne illnesses. In the event of a recall, companies can trace back through the supply chain to pinpoint the source of the problem with precision, ensuring swift and effective responses.
Furthermore, consumers are increasingly demanding transparency regarding the origin and quality of their food. Blockchain enables consumers to verify the authenticity of claims related to organic farming, fair trade practices, and sustainable sourcing. This builds consumer trust and loyalty, as they can be assured of the quality and safety of the food they consume.
Restraint
High Implementation Costs
High implementation costs pose a significant restraint for the adoption of blockchain technology in the agriculture and food supply chain market. Developing and deploying blockchain solutions require substantial financial investment, which can be prohibitive, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). These costs include not only the initial setup expenses for blockchain infrastructure but also the expenses associated with software development, hardware procurement, and network integration.
Moreover, blockchain technology often necessitates hiring specialized personnel with expertise in blockchain development, cybersecurity, and data management. This requirement further escalates operational costs, as these professionals command high salaries due to their specialized skills. In addition to staffing, continuous maintenance, system upgrades, and security enhancements add to the ongoing financial burden.
The complexity of blockchain technology can also lead to increased costs associated with training existing staff to understand and effectively use the new system. This training is essential to ensure that employees can manage blockchain applications and leverage their full potential, but it requires time and resources that many companies may find challenging to allocate.
Opportunity
Integration with IoT and Advanced Analytics
The integration of blockchain technology with the Internet of Things (IoT) and advanced analytics presents a significant opportunity for the agriculture and food supply chain market. This synergy can revolutionize how data is collected, recorded, and utilized across the entire supply chain, enhancing efficiency, transparency, and decision-making capabilities.
IoT devices, such as sensors and RFID tags, can collect real-time data on various parameters, including soil moisture levels, temperature, humidity, and the location of products during transportation. When this data is integrated with blockchain, it is securely recorded on an immutable ledger, ensuring its accuracy and reliability. This real-time, tamper-proof data enhances traceability, allowing stakeholders to monitor the condition and movement of agricultural products at every stage of the supply chain.
Advanced analytics further amplify the benefits of this integration by providing tools to analyze and interpret the vast amounts of data collected. Predictive analytics can forecast supply chain disruptions, optimize routes, and manage inventory levels more efficiently. For instance, data on weather patterns and soil conditions can be analyzed to predict crop yields, enabling farmers to make more informed decisions about planting and harvesting. Similarly, retailers can use analytics to track consumer demand trends and manage stock levels more effectively.
Challenge
Technological Complexity and Standardization
Technological complexities and inadequate standardization present a significant challenge to the adoption of blockchain in the agriculture and food supply chain market. by its nature, Blockchain technology tends to include intricate processes that need specialized knowledge for development, implementation, and maintenance.
Many stakeholders, especially in developing regions, may lack the technical expertise needed to effectively deploy and manage blockchain solutions. This expertise gap can lead to implementation delays, increased costs, and potential failures in integrating blockchain into existing systems. The complexity of blockchain technology also means that users must understand not only the basics of blockchain but also how it interacts with other technologies such as IoT devices and advanced analytics tools.
This necessity for a broad skill set can be a substantial barrier to adoption, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that may not have the resources to hire or train specialized personnel. Furthermore, the absence of standardized protocols and regulations for blockchain applications in the food supply chain adds another layer of difficulty. Different blockchain platforms may use varying standards, making it challenging to achieve interoperability between systems.
This fragmentation can result in inefficiencies, as companies might need to invest additional time and resources to ensure their blockchain solutions can communicate with those of their partners and regulatory bodies. Standardization is crucial for fostering trust and ensuring seamless data exchange across the supply chain. Without it, the benefits of blockchain, such as enhanced traceability and transparency, may not be fully realized. The lack of clear regulatory guidelines also creates uncertainty, which can deter investment and slow the pace of innovation.
Growth Factors
- Increasing Demand for Transparency: Consumers and regulatory bodies demand greater transparency in food sourcing and production processes, driving the adoption of blockchain to provide immutable and accessible records.
- Enhanced Food Safety and Traceability: Blockchain’s ability to track and trace products from farm to table improves food safety by quickly identifying and isolating contaminated products, thus preventing widespread foodborne illnesses.
- Growing Consumer Awareness: Increasing consumer awareness and demand for sustainably sourced and ethically produced food products boosts the adoption of blockchain to verify and showcase these practices.
- Regulatory Compliance: Stringent food safety regulations and standards require reliable and transparent systems for compliance, which blockchain technology efficiently provides.
- Reduction in Food Fraud: Blockchain helps combat food fraud by providing a tamper-proof record of product history, ensuring the authenticity and quality of food products.
- Integration with IoT: The combination of blockchain with IoT devices enhances real-time data collection and monitoring, improving supply chain efficiency and product quality.
Latest Trends
- Traceability and Transparency: Blockchain enhances traceability by providing an immutable record of every transaction or event in the supply chain. This transparency is crucial for verifying the origin, quality, and safety of food products, which is increasingly demanded by consumers.
- Supply Chain Efficiency: Blockchain streamlines supply chain processes by reducing paperwork, minimizing errors, and speeding up transactions. Smart contracts automate payments, agreements, and compliance, fostering trust and efficiency among stakeholders.
- Authentication and Certification: Blockchain helps verify organic, fair trade, or other certifications by securely recording the entire certification process. This reduces fraud and ensures that claims about sustainability or ethical practices are backed by verifiable data.
- Consumer Engagement and Trust: Consumers are increasingly interested in knowing the journey of their food from farm to table. Blockchain provides a platform for brands to communicate directly with consumers, building trust through transparent and verified information.
- Integration with IoT and AI: Blockchain technology is being integrated with Internet of Things (IoT) devices and Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems to enhance data collection, analysis, and decision-making capabilities across the supply chain.
Regional Analysis
In 2023, North America held a dominant market position in the Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain Market, capturing more than a 35% share with revenue amounting to USD 104.9 million. This leadership is largely driven by the region’s advanced technological infrastructure and the strong presence of major blockchain technology providers.
North America has been at the forefront of adopting innovative technologies aimed at enhancing agricultural productivity and sustainability, which includes the integration of blockchain to ensure transparency and efficiency in the food supply chain. The prominence of North America in this market is further supported by the region’s stringent food safety regulations, which necessitate rigorous traceability and compliance measures.
Blockchain technology is particularly effective in meeting these requirements, offering a reliable and secure method to track food products throughout the supply chain. This capability not only helps in adhering to regulatory standards but also boosts consumer confidence in food products.
Additionally, the significant investment in research and development activities related to blockchain technology within the agricultural sector contributes to the growth and leadership of North America in this market. With a high concentration of startups and established companies focusing on developing blockchain solutions tailored to agriculture, the region continues to innovate and drive adoption, setting a robust path for future growth and development in the Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain Market.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherlands
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
These key players illustrate the diverse approaches and technologies being applied to integrate blockchain into agriculture and food supply chains, addressing challenges related to traceability, transparency, and consumer trust. As the market continues to evolve, collaborations and innovations among these companies are expected to drive further advancements in the industry.
Top Key Players in the Market
- IBM
- Microsoft
- TE-Food International GmbH
- Ambrosus
- ACR-NET
- SAP SE
- OriginTrail
- Provenance
- Chainvine
- Roipe.io
- Others
Recent Developments
- May 2023: Microsoft launched an updated version of its Azure Blockchain Service, enhancing its capabilities for managing consortium blockchain networks. The update includes tools for easier integration and governance of blockchain applications, particularly in food supply chain tracking.
- April 2023: IBM announced a collaboration with Nestlé to expand the use of blockchain for tracing the supply chain of its Zoégas coffee brand. This expansion aims to enhance transparency and allow consumers to trace their coffee back to its source using QR codes.
- March 2023: TE-FOOD launched a new blockchain-based traceability solution tailored for fresh produce. This solution helps ensure the quality and safety of fresh produce from farm to table by providing detailed tracking information throughout the supply chain.
- January 2023: Ambrosus introduced AMB-NET, a software solution that utilizes IoT sensors to provide real-time data on food quality and traceability. This launch aims to enhance transparency and reduce food fraud in the supply chain.
- June 2023: OriginTrail announced a partnership with BSI, the business improvement company, to enhance the traceability and quality assurance of food products using blockchain technology. This partnership aims to provide end-to-end visibility across the food supply chain.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2023) USD 297.4 Mn Forecast Revenue (2032) USD 11,601.1 Mn CAGR (2023-2032) 44.25% Base Year for Estimation 2023 Historic Period 2016-2022 Forecast Period 2023-2032 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, COVID-19 Impact, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Type (Public, Private, Hybrid), By Providers (Application providers, Middleware providers, Infrastructure providers), By Application (Risk and Compliance Management, Governance, Smart Contracts, Payment and Settlement, Product Traceability) Regional Analysis North America – The U.S. & Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands & Rest of Europe; APAC- China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam & Rest of APAC; Latin America- Brazil, Mexico & Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa- South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE & Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape IBM, Microsoft, TE-Food International GmbH, Ambrosus, ACR-NET, SAP SE, OriginTrail, Provenance, Chainvine, Roipe.io, Others Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is blockchain technology in the context of agriculture and food supply chains?Blockchain technology in agriculture and food supply chains involves using a decentralized, digital ledger to record and verify transactions across various stages of the supply chain, from farm to fork. This ensures transparency, traceability, and security of data.
How big is Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain Market?The Global Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain Market size is expected to be worth around USD 11,601.1 Million by 2033, from USD 297.4 Million in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 44.25% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
What are the key factors driving the growth of the Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain Market?The growth is driven by the need for enhanced traceability and transparency, increasing food safety concerns, the demand for efficient supply chain management, and the reduction of food fraud and wastage.
What are the current trends and advancements in the Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain Market?Current trends include the integration of IoT with blockchain for real-time monitoring, the use of smart contracts for automated transactions, advancements in blockchain-based platforms for supply chain visibility, and increased adoption by major food and agriculture companies.
What are the major challenges and opportunities in the Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain Market?Challenges include high implementation costs, scalability issues, and the need for industry-wide standards. Opportunities lie in improving food safety, increasing consumer trust, enhancing supply chain efficiency, and enabling sustainable agricultural practices.
Who are the leading players in the Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain Market?Leading players include IBM, Microsoft, TE-Food International GmbH, Ambrosus, ACR-NET, SAP SE, OriginTrail, Provenance, Chainvine, Roipe.io, Others
 Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain MarketPublished date: July 2024add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Blockchain in Agriculture and Food Supply Chain MarketPublished date: July 2024add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- IBM
- Microsoft
- TE-Food International GmbH
- Ambrosus
- ACR-NET
- SAP SE
- OriginTrail
- Provenance
- Chainvine
- Roipe.io
- Others













