Global Biosimilars Market By Product Type (Monoclonal Antibodies, Recombinant Hormones, Anti-inflammatory Agents, and Other Product Types), Applications (Blood Disorders, Growth Hormonal Deficiency), By Region And Key Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends And Forecast 2023-2032
- Published date: Aug 2025
- Report ID: 96405
- Number of Pages: 302
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
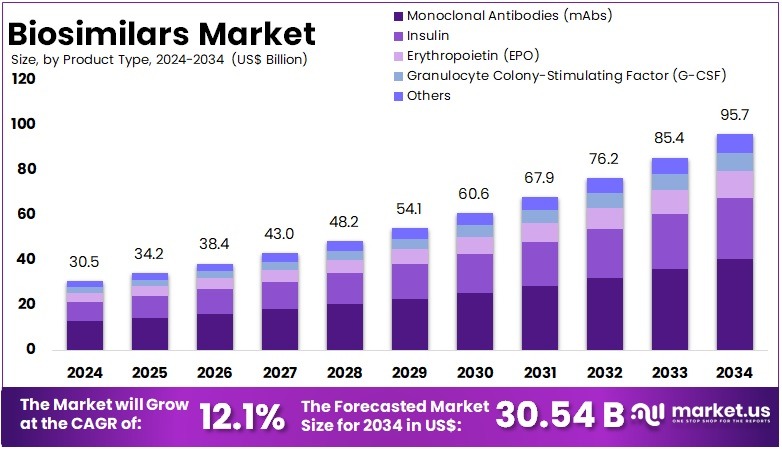
The Biosimilars Market size is expected to be worth around US$ 95.7 billion by 2034 from US$ 30.54 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 12.1% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
Biosimilars represent a promising category of products that offer patients and healthcare providers more affordable treatment alternatives. As of now, there have been 71 approvals and 55 launches in the U.S. biosimilar market. With the continued maturation of this market, its pipeline is expanding. This reference guide serves as a valuable resource to better understand the current product landscape and the potential future of this emerging market.
The biosimilars market refers to the segment of biotechnology focused on the development, manufacturing, and commercialization of biosimilars, which are highly similar to existing reference biologic drugs but are not identical. Biosimilars are developed once the patent protections of original biologics expire, offering a more cost-effective alternative while maintaining similar safety and efficacy profiles. This market has seen rapid growth due to the rising demand for affordable biologic therapies and the increasing pressure on healthcare systems to reduce spending.
A key example of biosimilars in the market is Zarxio (filgrastim), a biosimilar to Amgen’s Neupogen, approved by the U.S. FDA. Zarxio is used to treat neutropenia caused by chemotherapy and is a significant player in the hematology sector. Another prominent example is Herzuma, a biosimilar to Roche’s Herceptin, used in the treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer, which gained approval in both Europe and the U.S. Inflectra, a biosimilar to Remicade, also stands out in the autoimmune disease treatment area.
Key Takeaways
- In 2024, the market for Biosimilars generated a revenue of US$ 30.54 billion, with a CAGR of 12.1%, and is expected to reach US$ 95.7 billion by the year 2034.
- The product type segment is divided into Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs), Insulin, Erythropoietin (EPO), Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor (G-CSF), and Others with Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs) taking the lead in 2023 with a market share of 42.1%.
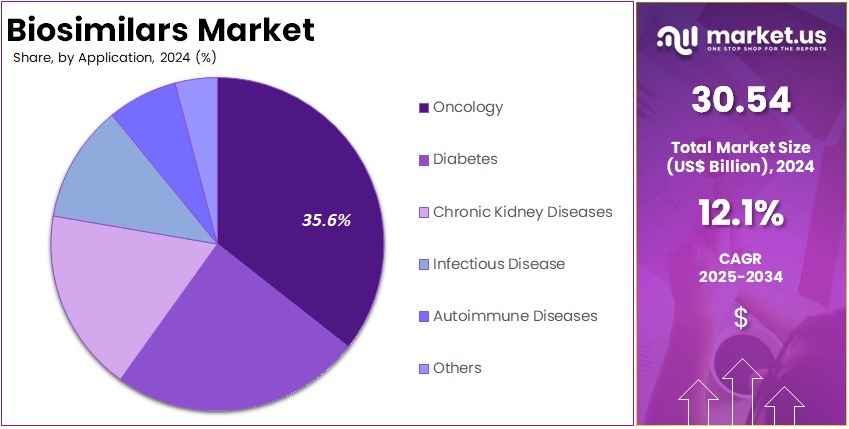
- By Application, the market is bifurcated into Oncology, Diabetes, Chronic Kidney Diseases, Infectious Disease, Autoimmune Diseases, and Others, with Oncology leading the market with 35.6% of market share.
- Furthermore, concerning the Distribution Channel segment, the market is segregated into Hospital Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies, Online Pharmacies, and Others. The Hospital Pharmacies stands out as the dominant segment, holding the largest revenue share of 44.9% in the Biosimilars market.
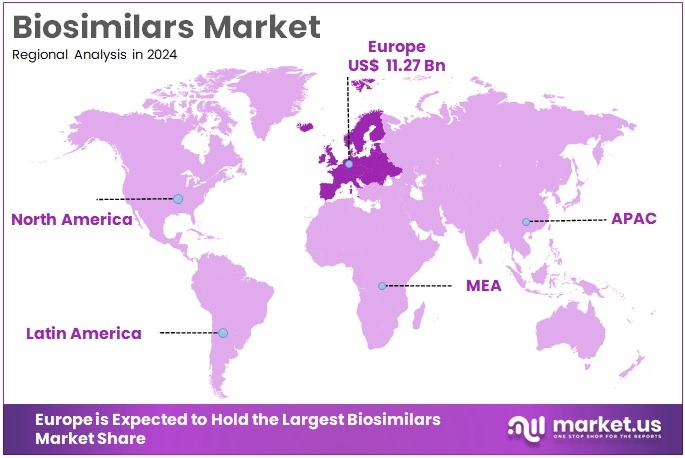
- Europe led the market by securing a market share of 36.9% in 2023.
Product Type Analysis
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) dominated the biosimilars market with 42.1% market share due to their widespread use in the treatment of various diseases, including cancer, autoimmune diseases, and infectious diseases. These lab-made molecules are designed to target specific proteins or cells in the body. Their strong therapeutic effects have made them a key option in modern treatment. Biosimilars such as Herzuma for HER2-positive breast cancer and Inflectra for rheumatoid arthritis show how effective mAbs can be across various conditions.
The popularity of mAbs in the biosimilars space is also linked to the high cost of original biologics. Many of these branded drugs are expensive and place a financial burden on healthcare systems. As a result, the growing availability of biosimilar versions offers a more affordable solution without reducing the quality of treatment. This shift is especially important as several leading biologics lose patent protection, opening the door for biosimilar competition.
In October 2024, Teva Pharmaceuticals International GmbH and mAbxience announced a new global licensing deal. This agreement focuses on developing a biosimilar for anti-PD-1 oncology treatment. It marks the second collaboration between the companies, following an earlier partnership in April 2024. Such alliances show the growing momentum in biosimilar development. They also reflect how pharmaceutical firms are investing in affordable options to meet rising global demand for effective therapies.
Application Analysis
Oncology is the dominant application segment in the biosimilars market accounting for 35.6% market share due to the high prevalence of cancer globally and the increasing number of biologic treatments used for oncology indications. Biologic therapies like monoclonal antibodies and immunotherapies are widely used in treating cancers such as breast cancer, colorectal cancer, and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. These treatments play a crucial role in cancer care. The rising demand for such therapies has led to increased interest in biosimilars that can offer similar results at a lower cost.
Biosimilar drugs like Zarxio and Herzuma have become more common in oncology. They provide cost-effective alternatives to original biologics. As the price of cancer treatments continues to rise, healthcare providers and patients are turning to biosimilars. These products help reduce the financial burden without compromising treatment quality. The affordability and growing trust in biosimilars have supported their adoption in cancer care across many regions.
Regulatory authorities like the FDA and EMA have also encouraged this trend. They are speeding up approvals for oncology biosimilars. This move has further boosted the market. A notable example is the FDA approval of Jobevne in April 2025. Jobevne, developed by Biocon Biologics Ltd, is a biosimilar of Bevacizumab. It is used intravenously to treat various cancers and is modeled after Avastin®. Such approvals highlight the growing role of biosimilars in oncology.
Distribution Channel Analysis
Hospital pharmacies lead the distribution channel segment in the biosimilars market with 44.9% market share. Hospitals are major healthcare providers where the bulk of biologic treatments, including biosimilars, are administered to patients. Biosimilars used for complex conditions such as cancer, autoimmune diseases, and chronic conditions are often prescribed within hospital settings due to the need for specialized care and monitoring.
Hospitals also play a central role in facilitating the use of high-cost biologics, which makes biosimilars a more attractive and cost-effective alternative for healthcare systems. As hospital pharmacies are equipped to handle complex biologic therapies, they are the most common distribution point for biosimilars.
Additionally, hospitals tend to have direct purchasing relationships with manufacturers, ensuring a steady supply of biosimilars. This segment is expected to grow as more biosimilars are approved and integrated into hospital formularies, enabling wider adoption of affordable biologic treatments.
Key Market Segments
By Product Type
- Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs)
- Insulin
- Erythropoietin (EPO)
- Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor (G-CSF)
- Others
By Application
- Oncology
- Diabetes
- Chronic Kidney Diseases
- Infectious Disease
- Autoimmune Diseases
- Others
By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies
- Others
Drivers
Increasing Cost-Effectiveness
The primary driver for the growth of the biosimilars market is the increasing demand for cost-effective biologic treatments. Traditional biologic therapies are expensive, often limiting patient access, especially in developing countries. Biosimilars, being lower-cost alternatives, are expected to help reduce healthcare expenditures significantly. For instance, in 2023, savings generated from the use of biosimilar medicines amounted to US$12.4 billion.
Since their market introduction in 2015, biosimilars have contributed a total of US$36 billion in savings. These products continue to demonstrate their safety and effectiveness, showing no significant differences in clinical outcomes. Additionally, according to a report from the European Commission, biosimilars have the potential to save up to €11 billion annually in the EU by 2020. As patent expirations for several high-cost biologics occur, the market for biosimilars is expanding rapidly.
Governments and healthcare systems worldwide are actively encouraging the adoption of biosimilars to reduce drug spending. For instance, the U.S. FDA has approved several biosimilars in recent years, reflecting the growing acceptance of these drugs. The ability to provide biologic treatments at a fraction of the cost has led to widespread healthcare adoption, making biosimilars a key player in improving global health outcomes.
Restraints
Regulatory Hurdles
A significant restraint in the biosimilars market is the complex and time-consuming regulatory approval process. Biosimilars must undergo rigorous testing to prove their similarity to the original biologic, which involves clinical trials and comparability studies. The regulatory requirements vary by region, adding another layer of complexity for companies.
The U.S. FDA and European Medicines Agency (EMA) have established biosimilar pathways, but the process can still be costly and lengthy, delaying market entry. The approval of these products can enhance patient access to care by increasing the availability of medication options and potentially reducing costs.
For instance, the approval of biosimilars in some regions requires extensive head-to-head trials against reference biologics, raising costs for manufacturers. Moreover, the uncertainty surrounding the regulatory landscape, including potential changes in rules and guidelines, often results in hesitation for companies to invest in biosimilar development. This complexity and the cost of complying with various regulatory standards can inhibit the speed at which biosimilars are introduced to the market.
Opportunities
Expanding Market in Emerging Economies
An emerging opportunity for the biosimilars market lies in the growing healthcare infrastructure in emerging economies, including India, China, and Latin America. These regions are witnessing an increase in the prevalence of chronic diseases, such as diabetes, cancer, and autoimmune disorders, which have traditionally been treated with high-cost biologics. As these markets develop, there is an urgent need for affordable healthcare solutions, creating a significant opportunity for biosimilars.
Governments in these countries are increasingly supporting biosimilars through policy reforms and by encouraging the use of lower-cost medicines to ease the burden on public healthcare systems. For example, India has approved several biosimilars, and companies such as Biocon and Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories are already expanding their presence in these regions. With rising healthcare spending and growing patient access, the biosimilars market is expected to experience substantial growth in emerging economies, further bolstering the global market.
In March 2025, the Board of Directors of the African Development Bank (AfDB) approved a US$ 17.5 million (EUR 15 million) senior corporate loan to Minapharm Pharmaceuticals S.A.E. (Minapharm), a leading biopharmaceutical company in Egypt. This investment will support Minapharm’s expansion and renovation program, significantly enhancing the development and production of affordable biosimilars for oncology and autoimmune diseases. This initiative aims to address critical healthcare needs across Africa and the Middle East.
Impact of Macroeconomic / Geopolitical Factors
Macroeconomic and geopolitical factors have a significant impact on the biosimilars market, influencing both the production and distribution of biosimilars globally. One of the most notable macroeconomic factors is the increasing pressure on healthcare budgets, especially in developed countries. With healthcare expenditures rising, governments are seeking more affordable solutions to expensive biologic drugs. This has created a favorable environment for the growth of the biosimilars market, as these therapies offer a cost-effective alternative to expensive originator biologics.
On the other hand, geopolitical factors, including trade policies, tariffs, and international relations, also affect the biosimilars market. For instance, tariffs imposed on biologic drugs or their raw materials can increase production costs, potentially raising the prices of biosimilars and limiting their cost-saving benefits. Trade wars, particularly between the U.S. and China, have disrupted global supply chains for active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), which are critical for the production of biologics and biosimilars. This creates instability in the supply chain, leading to potential delays in biosimilar production and distribution.
Moreover, the varying regulatory environments across regions can also be influenced by geopolitical tensions. For example, stringent approval processes or delays in approvals from regulatory bodies in different countries can slow the market penetration of biosimilars. Conversely, the collaboration between countries or regions through international agreements or alliances can expedite the development and approval processes for biosimilars, enhancing market access.
Latest Trends
Growing Adoption of Biosimilars in Oncology
The growing adoption of biosimilars in oncology is a significant trend in the global biosimilars market. Oncology drugs are among the most expensive, with biologic therapies like monoclonal antibodies leading the charge in treatment costs. Biosimilars offer a cost-effective alternative to these branded biologic drugs, making cancer treatments more accessible to a broader patient population. With increasing pressure on healthcare systems to manage rising costs, biosimilars are seen as an essential strategy for reducing expenditures in oncology care.
Several biosimilars are already available for key oncology treatments. For example, Zirabev (bevacizumab-bvzr) is a biosimilar to Avastin, a widely used treatment for cancers like colorectal, lung, and kidney cancers. Mvasi (bevacizumab-awwb) is another biosimilar to Avastin, launched by Amgen and Allergan. Similarly, Truxima (rituximab-abbs), a biosimilar to Rituxan, has been gaining traction in treating cancers like non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
The adoption of biosimilars is expected to increase as more regulatory approvals are granted, and oncologists gain more confidence in the safety and efficacy of these therapies. With their lower price point, biosimilars are becoming critical in expanding patient access to life-saving treatments, improving healthcare equity, and driving competition in the oncology drug market. The trend is projected to accelerate further with the continued expiration of patents for major oncology biologics.
Regional Analysis
Europe is leading the Biosimilars Market
Europe leads the global biosimilars market with a dominant share of 36.9% in 2024. This leadership is supported by strong regulatory systems, economic policies, and advanced healthcare infrastructure. The region continues to encourage biosimilar development and use. A key driver is the European Medicines Agency (EMA), which plays a central role in biosimilar approvals. As of June 2025, the EMA has recommended 144 biosimilars for approval across various therapeutic classes. These include human growth hormones, insulin, and monoclonal antibodies used widely in chronic conditions.
Biosimilars have had a major economic impact across Europe. As of July 2024, biosimilar competition has saved healthcare systems a total of €56 billion. This reduction in spending has also led to greater patient access. Treatment volumes now exceed 6.9 billion patient treatment days. These savings are made possible by structured pricing policies, national tenders, and financial incentives. Such measures help lower costs while maintaining quality. Europe’s focus on affordability has helped it become a leader in expanding access to biologic therapies.
Country-specific policies further support biosimilar adoption. France has introduced a mandatory 40% discount on the price of originator biologics. Italy applies a 20% discount through both national and regional tendering processes. Germany uses hospital-level negotiations, which are influenced by internal reference pricing systems. In the United Kingdom, the National Health Service (NHS) drives biosimilar competition through centralized tenders. These national strategies provide a strong push for market penetration, ensuring high biosimilar uptake at the local level.
Europe’s success in the biosimilars market is rooted in regulatory foresight and financial strategy. Regulatory agencies like the EMA streamline the approval process. National policies ensure affordability and patient access. The integration of tenders and discounts supports a sustainable biosimilars ecosystem. As a result, Europe stands as a benchmark for other global regions. The region’s approach offers valuable insights into reducing healthcare costs while improving treatment availability. This positions Europe as a model for countries seeking to strengthen their biologics markets.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherland
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Key players in the Biosimilars market includes Amgen Inc., Sandoz (a Novartis division), Celltrion Healthcare, Samsung Bioepis, Mylan (now part of Viatris), Pfizer Inc., Biocon, AbbVie (Allergan), Eli Lilly and Company, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, Amgen Inc., Boehringer Ingelheim, Bayer AG, Stelis Biopharma, Zydus Cadila, Intas Pharmaceuticals, Fujifilm Diosynth Biotechnologies, and Other key players.
Amgen Inc. is a global biopharmaceutical leader, known for its innovation in biologic therapies. The company has expanded into the biosimilars market with the launch of its biosimilar products such as Amjevita (adalimumab) and Kanjinti (trastuzumab), which offer cost-effective alternatives to blockbuster biologics, providing patients with improved access to treatment.
Sandoz, a division of Novartis, is a pioneer in the biosimilars market, with a broad portfolio of biosimilar products such as Zarxio (filgrastim) and Erelzi (etanercept). The company leverages its extensive experience in generic pharmaceuticals to provide affordable, high-quality biosimilars, significantly improving patient access to life-saving therapies globally.
Celltrion Healthcare is a leading player in the biosimilars market, known for its robust biosimilar offerings like Remsima (infliximab) and Truxima (rituximab). The company focuses on providing affordable alternatives to high-cost biologics, supporting global healthcare systems in making biologic treatments more accessible and cost-effective for patients worldwide.
Top Key Players in the Biosimilars Market
- Amgen Inc.
- Sandoz (a Novartis division)
- Celltrion Healthcare
- Samsung Bioepis
- Mylan (now part of Viatris)
- Pfizer Inc.
- Biocon
- AbbVie (Allergan)
- Eli Lilly and Company
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
- Reddy’s Laboratories
- Amgen Inc.
- Boehringer Ingelheim
- Bayer AG
- Stelis Biopharma
- Zydus Cadila
- Intas Pharmaceuticals
- Fujifilm Diosynth Biotechnologies
- Other Prominent Players
Recent Developments
- In July 2025: Harrow, a leading North American eyecare pharmaceutical company, announced that it has entered into a definitive agreement with Samsung Bioepis Co. Ltd. to secure the exclusive U.S. commercial rights to Samsung Bioepis’ ophthalmology biosimilar portfolio. This includes BYOOVIZ (ranibizumab-nuna), an FDA-approved biosimilar referencing LUCENTIS (ranibizumab), and OPUVIZ (aflibercept-yszy), an FDA-approved biosimilar referencing EYLEA (aflibercept) — two of the most commonly used anti-VEGF therapies for retinal diseases.
- In July 2025: Fresenius announced that its operating company, Fresenius Kabi, has introduced two new biosimilars in the United States: Conexxence® (denosumab-bnht) and Bomyntra® (denosumab-bnht). These denosumab biosimilars have been approved by the FDA for all indications of the reference products, Prolia® (denosumab) and Xgeva® (denosumab), respectively.
- In June 2025: Celltrion UK has officially opened its new UK headquarters at the Charter Building in Uxbridge, UK, further solidifying the company’s commitment to long-term growth and partnerships in the UK market. This move marks the latest phase of Celltrion’s strategic vision for the UK, underscoring its dedication to being a trusted healthcare partner, contributing to the UK economy, and playing a pivotal role in the global biosimilars market.
- In April 2025: Organon, a global healthcare company with significant expertise in biosimilars, announced that it has acquired the regulatory and commercial rights in the U.S. for TOFIDENCE™ from Biogen Inc., a biosimilar to ACTEMRA for intravenous infusion. TOFIDENCE, the first approved tocilizumab biosimilar in the U.S. market, was launched in May 2024. It is indicated for certain patients to treat moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis, giant cell arteritis, polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis, systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis, and COVID-19.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) US$ 30.54 billion Forecast Revenue (2034) US$ 95.7 billion CAGR (2025-2034) 12.1% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, COVID-19 Impact, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Product Type (Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs), Insulin, Erythropoietin (EPO), Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) and Others), By Application (Oncology, Diabetes, Chronic Kidney Diseases, Infectious Disease, Autoimmune Diseases and Others), By Distribution Channel (Hospital Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies, Online Pharmacies, and Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Amgen Inc., Sandoz (a Novartis division), Celltrion Healthcare, Samsung Bioepis, Mylan (now part of Viatris), Pfizer Inc., Biocon, AbbVie (Allergan), Eli Lilly and Company, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, Amgen Inc., Boehringer Ingelheim, Bayer AG, Stelis Biopharma, Zydus Cadila, Intas Pharmaceuticals, Fujifilm Diosynth Biotechnologies, and Other key players Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Novartis
- Amgen Inc.
- Pfizer Inc.
- Viatris Inc.
- Eli Lilly
- Synthon Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
- LG Life Sciences
- Celltrion
- Biocon Biologics Ltd.
- Coherus Biosciences, Inc.
- Bio-Thera Solutions
- Intas Pharmaceuticals Ltd.
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
- Samsung Bioepis Co.
- Hospira
- Merck Serono
- Biogen Idec Inc.
- Genentech










